Abstract
The structure of the title compound (common name: amodiaquinium dichloride dihydrate), C20H24ClN3O2 +·2Cl−·2H2O, was previously determined from powder diffraction data [Llinàs et al. (2006 ▶). Acta Cryst. E62, o4196-o4199]. It has now been refined from diffractometer data to a significantly higher precision. The dihedral angle between the quinoline and benzene rings is 54.57 (6)°. The central amino N atom interacts more strongly with the quinoline ring than with the benzene ring, as indicated by the shorter C—N bond length [1.341 (2) Å compared to 1.431 (2) Å]. In the crystal, molecules are packed into a three-dimensional network/supramolecular structure through hydrogen bonds between the amodiaquinium cations, chloride anions and water molecules.
Related literature
Amodiaquine, as a dihydrochloride salt, is often used as a synthetic antimalarial drug against chloroquine-sensitive and chloroquine-resistant strains of Plasmodium falciparum, see: Olliaro & Taylor (2003 ▶). For related structures, see: Llinàs et al. (2006 ▶); Yennawar & Viswamitra (1991 ▶); Semeniuk et al. (2008 ▶).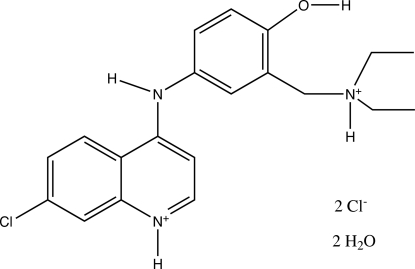
Experimental
Crystal data
C20H24ClN3O2+·2Cl−·2H2O
M r = 464.80
Monoclinic,
a = 7.7622 (1) Å
b = 26.8709 (4) Å
c = 10.7085 (2) Å
β = 92.784 (1)°
V = 2230.91 (6) Å3
Z = 4
Cu Kα radiation
μ = 3.94 mm−1
T = 100 K
0.56 × 0.14 × 0.12 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART 6000 CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 1997 ▶) T min = 0.312, T max = 0.623
31612 measured reflections
3917 independent reflections
3699 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.088
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.038
wR(F 2) = 0.100
S = 1.10
3917 reflections
287 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.40 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.32 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 1997 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 1997 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶) and DIAMOND (Brandenburg, 2010 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: PLATON.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810031806/lx2163sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810031806/lx2163Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1N⋯Cl2 | 0.89 (2) | 2.32 (2) | 3.1913 (16) | 166.8 (19) |
| N2—H2N⋯O2Wi | 0.83 (2) | 2.07 (2) | 2.880 (2) | 167 (2) |
| N3—H3N⋯Cl3 | 0.85 (2) | 2.26 (2) | 3.0771 (14) | 161 (2) |
| O1—H1O⋯Cl2ii | 0.84 | 2.22 | 3.0640 (12) | 177 |
| O1W—H1WA⋯Cl3iii | 0.88 (3) | 2.30 (3) | 3.1778 (16) | 175 (3) |
| O1W—H1WB⋯Cl3i | 0.80 (3) | 2.42 (3) | 3.2100 (16) | 171 (3) |
| O2W—H2WA⋯O1W | 0.83 (3) | 1.95 (3) | 2.775 (2) | 174 (2) |
| O2W—H2WB⋯Cl2ii | 0.83 (3) | 2.33 (3) | 3.1585 (15) | 173 (3) |
Symmetry codes: (i) 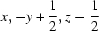 ; (ii)
; (ii) 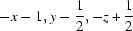 ; (iii)
; (iii) 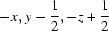 .
.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
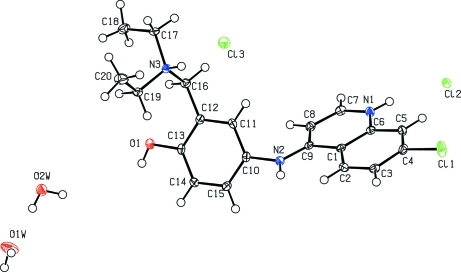
Amodiaquine, 4-[7-chloro-4-quinolinyl)amino]-2-[(diethylamino)methyl]phenol, is as dihydrochloride salt, often used as synthetic antimalarial drug against chloroquine-sensitive and chloroquine-resistant strains of Plasmodium falciparum (Olliaro & Taylor, 2003). The single-crystal structure of the monohydrate form has been reported by Yennawar & Viswamitra (1991) and by Semeniuk et al. (2008). The room temperature structure of the dihydrate form based on powder diffraction at 1.79 Å resolution has been reported by Llinàs et al. (2006). Here we report the crystal structure of the title compound (I) at 100 K and a resolution of 0.84 Å (Fig. 1).
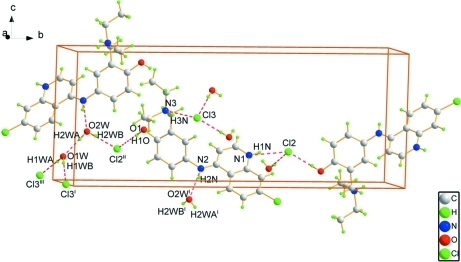
Two N atoms (N1 and N3) are protonated indicating that the dihydrochloride salt of amodiaquine is present. The shape of the molecule is mainly dominated by three torsion angles: C8–C9–N2–C19 (τ1 = -7.7 (3)°), C9–N2–C10–C11 (τ2 = -52.8 (2)°) and C11–C12–C16–N3 (τ3 = -85.85 (18)°). It was suggested by Yennawar & Viswamitra (1991) that the C–N bonds linking both aromatic rings have double-bond character. However, we observe a large difference between both bonds C9–N2 (1.341 (2) Å) and N2–C10 (1.431 (2) Å), indicating that N2 interacts more with the quinoline than with the benzene unit. It is also clear from inspection of τ1 and τ2 that the overlap of the lone pair of the sp2-hybridized N2 with the quinoline unit is favoured, and this despite the short H2N···H2 contact distance (2.08 Å). The dihedral angle between the quinoline and benzene units is 54.57 (6)°. An intramolecular close contact between H16A and O1 (2.396 Å) is observed by Llinàs et al. (2006). The r.m.s. deviation when fitting the amodiaquinium units obtained by single-crystal and powder diffraction (Llinàs et al., 2006) is 0.0739 Å. The hydrogen bonds in the crystal packing (Table 1, Fig. 2) are similar to those described by Llinàs et al. (2006).
Experimental
Amodiaquinium dichloride dihydrate was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Belgium). Colourless crystals were obtained at room temperature by slow evaporation from a DMSO solution of (I).
Refinement
H atoms of the NH groups and of both waters were located in a difference map. The other H atoms were positioned with idealized geometry using a riding model with C–H = 0.95-0.99 Å. All H atoms were refined with isotropic displacement parameters (set to 1.2 or 1.5 times the Ueq of the parent atom).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound with the atom numbering scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level. H atoms are presented as a small spheres of arbitrary radius.
Fig. 2.
N–H···Cl, N–H···O, O–H···Cl, and O–H···O hydrogen bonds (dotted lines) in the crystal structure of the title compound. [Symmetry codes : (i) x , - y + 1/2, z - 1/2; (ii) -x - 1, y - 1/2, - z + 1/2; (iii) - x , y -1/2, - z + 1/2.]
Crystal data
| C20H24ClN3O2+·2Cl−·2H2O | F(000) = 976 |
| Mr = 464.80 | Dx = 1.384 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54178 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 6662 reflections |
| a = 7.7622 (1) Å | θ = 3.3–70.5° |
| b = 26.8709 (4) Å | µ = 3.94 mm−1 |
| c = 10.7085 (2) Å | T = 100 K |
| β = 92.784 (1)° | Prism, colourless |
| V = 2230.91 (6) Å3 | 0.56 × 0.14 × 0.12 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART 6000 CCD diffractometer | 3917 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 3699 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| crossed Göbel mirrors | Rint = 0.088 |
| Detector resolution: 0.92 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 66.6°, θmin = 3.3° |
| ω and φ scans | h = −8→9 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 1997) | k = −31→31 |
| Tmin = 0.312, Tmax = 0.623 | l = −12→12 |
| 31612 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.038 | Hydrogen site location: difference Fourier map |
| wR(F2) = 0.100 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.10 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0443P)2 + 1.0601P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3917 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 287 parameters | Δρmax = 0.40 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.32 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | −0.2951 (2) | 0.51757 (6) | 0.06525 (16) | 0.0118 (3) | |
| C2 | −0.2063 (2) | 0.52058 (6) | −0.04673 (16) | 0.0131 (4) | |
| H2 | −0.1539 | 0.4915 | −0.0782 | 0.016* | |
| C3 | −0.1939 (2) | 0.56445 (7) | −0.11087 (16) | 0.0140 (4) | |
| H3 | −0.1362 | 0.5658 | −0.1870 | 0.017* | |
| C4 | −0.2681 (2) | 0.60736 (7) | −0.06187 (17) | 0.0147 (4) | |
| C5 | −0.3573 (2) | 0.60667 (6) | 0.04469 (17) | 0.0141 (4) | |
| H5 | −0.4080 | 0.6362 | 0.0753 | 0.017* | |
| C6 | −0.3724 (2) | 0.56123 (6) | 0.10810 (16) | 0.0118 (3) | |
| C7 | −0.4831 (2) | 0.51792 (7) | 0.27924 (16) | 0.0141 (4) | |
| H7 | −0.5498 | 0.5183 | 0.3513 | 0.017* | |
| C8 | −0.4081 (2) | 0.47445 (6) | 0.24440 (16) | 0.0138 (4) | |
| H8 | −0.4226 | 0.4453 | 0.2928 | 0.017* | |
| C9 | −0.3097 (2) | 0.47234 (6) | 0.13779 (16) | 0.0118 (3) | |
| C10 | −0.2219 (2) | 0.38571 (6) | 0.17370 (16) | 0.0127 (4) | |
| C11 | −0.1590 (2) | 0.38657 (6) | 0.29763 (16) | 0.0125 (4) | |
| H11 | −0.1216 | 0.4171 | 0.3343 | 0.015* | |
| C12 | −0.1502 (2) | 0.34316 (6) | 0.36829 (16) | 0.0115 (3) | |
| C13 | −0.2084 (2) | 0.29835 (6) | 0.31382 (17) | 0.0121 (3) | |
| C14 | −0.2641 (2) | 0.29733 (6) | 0.18823 (17) | 0.0139 (4) | |
| H14 | −0.2977 | 0.2667 | 0.1501 | 0.017* | |
| C15 | −0.2709 (2) | 0.34090 (7) | 0.11850 (17) | 0.0140 (4) | |
| H15 | −0.3091 | 0.3400 | 0.0329 | 0.017* | |
| C16 | −0.0831 (2) | 0.34431 (6) | 0.50266 (16) | 0.0133 (4) | |
| H16A | −0.1354 | 0.3166 | 0.5485 | 0.016* | |
| H16B | −0.1191 | 0.3759 | 0.5414 | 0.016* | |
| C17 | 0.1735 (2) | 0.34491 (6) | 0.65140 (16) | 0.0136 (4) | |
| H17A | 0.1177 | 0.3744 | 0.6876 | 0.016* | |
| H17B | 0.2995 | 0.3509 | 0.6553 | 0.016* | |
| C18 | 0.1364 (3) | 0.29984 (7) | 0.73055 (17) | 0.0206 (4) | |
| H18A | 0.0146 | 0.2906 | 0.7179 | 0.031* | |
| H18B | 0.1614 | 0.3077 | 0.8189 | 0.031* | |
| H18C | 0.2090 | 0.2720 | 0.7061 | 0.031* | |
| C19 | 0.1800 (2) | 0.29476 (7) | 0.45331 (16) | 0.0145 (4) | |
| H19A | 0.1337 | 0.2938 | 0.3655 | 0.017* | |
| H19B | 0.1390 | 0.2646 | 0.4960 | 0.017* | |
| C20 | 0.3754 (3) | 0.29404 (8) | 0.45504 (19) | 0.0242 (4) | |
| H20A | 0.4172 | 0.3254 | 0.4210 | 0.036* | |
| H20B | 0.4137 | 0.2662 | 0.4040 | 0.036* | |
| H20C | 0.4217 | 0.2900 | 0.5412 | 0.036* | |
| N1 | −0.4650 (2) | 0.56009 (6) | 0.21445 (14) | 0.0137 (3) | |
| H1N | −0.514 (3) | 0.5883 (9) | 0.237 (2) | 0.016* | |
| N2 | −0.2317 (2) | 0.43058 (5) | 0.10177 (14) | 0.0126 (3) | |
| H2N | −0.190 (3) | 0.4290 (8) | 0.032 (2) | 0.015* | |
| N3 | 0.1117 (2) | 0.33997 (5) | 0.51605 (14) | 0.0114 (3) | |
| H3N | 0.152 (3) | 0.3658 (9) | 0.482 (2) | 0.015 (5)* | |
| O1 | −0.20278 (17) | 0.25706 (4) | 0.38692 (12) | 0.0160 (3) | |
| H1O | −0.2483 | 0.2331 | 0.3472 | 0.024* | |
| O1W | −0.0091 (2) | 0.02817 (6) | 0.17421 (15) | 0.0321 (4) | |
| H1WA | −0.080 (4) | 0.0063 (12) | 0.139 (3) | 0.038* | |
| H1WB | 0.063 (4) | 0.0345 (11) | 0.126 (3) | 0.038* | |
| O2W | −0.08987 (19) | 0.09265 (5) | 0.36517 (13) | 0.0201 (3) | |
| H2WA | −0.073 (3) | 0.0731 (10) | 0.307 (3) | 0.024* | |
| H2WB | −0.157 (4) | 0.1146 (10) | 0.337 (2) | 0.024* | |
| Cl1 | −0.24427 (7) | 0.663720 (16) | −0.13878 (5) | 0.02505 (15) | |
| Cl2 | −0.63123 (6) | 0.667531 (14) | 0.24913 (4) | 0.01525 (13) | |
| Cl3 | 0.24523 (6) | 0.444735 (15) | 0.45660 (4) | 0.02012 (14) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0116 (8) | 0.0129 (8) | 0.0105 (8) | −0.0019 (7) | −0.0021 (7) | 0.0008 (6) |
| C2 | 0.0133 (8) | 0.0126 (8) | 0.0134 (8) | −0.0003 (7) | 0.0005 (7) | −0.0025 (6) |
| C3 | 0.0148 (9) | 0.0163 (8) | 0.0110 (8) | −0.0015 (7) | 0.0004 (7) | 0.0011 (7) |
| C4 | 0.0153 (9) | 0.0129 (8) | 0.0156 (8) | −0.0009 (7) | −0.0013 (7) | 0.0041 (7) |
| C5 | 0.0144 (9) | 0.0110 (8) | 0.0168 (8) | 0.0017 (7) | 0.0000 (7) | −0.0009 (7) |
| C6 | 0.0100 (8) | 0.0141 (8) | 0.0110 (8) | −0.0001 (6) | −0.0012 (7) | −0.0003 (6) |
| C7 | 0.0133 (8) | 0.0174 (9) | 0.0117 (8) | −0.0014 (7) | 0.0017 (7) | 0.0012 (7) |
| C8 | 0.0144 (8) | 0.0135 (8) | 0.0135 (8) | −0.0013 (7) | 0.0002 (7) | 0.0023 (6) |
| C9 | 0.0109 (8) | 0.0127 (8) | 0.0115 (8) | −0.0005 (6) | −0.0038 (7) | 0.0002 (6) |
| C10 | 0.0128 (8) | 0.0119 (8) | 0.0134 (8) | 0.0025 (7) | 0.0013 (7) | 0.0018 (6) |
| C11 | 0.0128 (8) | 0.0093 (8) | 0.0153 (8) | 0.0010 (6) | 0.0014 (7) | −0.0012 (6) |
| C12 | 0.0104 (8) | 0.0134 (8) | 0.0108 (8) | 0.0020 (6) | 0.0024 (7) | 0.0006 (6) |
| C13 | 0.0098 (8) | 0.0106 (8) | 0.0159 (9) | 0.0018 (6) | 0.0015 (7) | 0.0030 (6) |
| C14 | 0.0154 (9) | 0.0106 (8) | 0.0154 (9) | −0.0005 (6) | −0.0014 (7) | −0.0011 (6) |
| C15 | 0.0145 (9) | 0.0152 (9) | 0.0120 (8) | 0.0023 (7) | −0.0018 (7) | 0.0001 (6) |
| C16 | 0.0127 (9) | 0.0154 (8) | 0.0119 (8) | 0.0008 (7) | 0.0014 (7) | −0.0010 (6) |
| C17 | 0.0160 (9) | 0.0158 (8) | 0.0087 (8) | −0.0004 (7) | −0.0016 (7) | −0.0013 (6) |
| C18 | 0.0265 (10) | 0.0228 (10) | 0.0123 (8) | −0.0023 (8) | −0.0021 (8) | 0.0032 (7) |
| C19 | 0.0168 (9) | 0.0153 (8) | 0.0113 (8) | 0.0019 (7) | −0.0004 (7) | −0.0029 (6) |
| C20 | 0.0173 (10) | 0.0341 (11) | 0.0210 (10) | 0.0059 (8) | −0.0007 (8) | −0.0101 (8) |
| N1 | 0.0149 (8) | 0.0124 (7) | 0.0140 (7) | 0.0027 (6) | 0.0025 (6) | −0.0007 (6) |
| N2 | 0.0169 (8) | 0.0113 (7) | 0.0098 (7) | 0.0003 (6) | 0.0021 (6) | 0.0013 (5) |
| N3 | 0.0137 (8) | 0.0113 (7) | 0.0093 (7) | −0.0015 (6) | 0.0004 (6) | 0.0019 (6) |
| O1 | 0.0223 (7) | 0.0093 (6) | 0.0163 (6) | −0.0028 (5) | −0.0011 (5) | 0.0030 (5) |
| O1W | 0.0378 (9) | 0.0334 (9) | 0.0259 (8) | −0.0084 (7) | 0.0113 (7) | −0.0119 (7) |
| O2W | 0.0264 (8) | 0.0181 (7) | 0.0161 (6) | 0.0032 (6) | 0.0033 (6) | 0.0022 (5) |
| Cl1 | 0.0353 (3) | 0.0141 (2) | 0.0266 (3) | 0.00221 (18) | 0.0109 (2) | 0.00951 (17) |
| Cl2 | 0.0173 (2) | 0.0126 (2) | 0.0157 (2) | 0.00398 (15) | −0.00045 (17) | −0.00229 (14) |
| Cl3 | 0.0266 (3) | 0.0168 (2) | 0.0171 (2) | −0.00626 (17) | 0.00212 (19) | 0.00298 (15) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| C1—C6 | 1.405 (2) | C14—H14 | 0.9500 |
| C1—C2 | 1.414 (3) | C15—H15 | 0.9500 |
| C1—C9 | 1.450 (2) | C16—N3 | 1.516 (2) |
| C2—C3 | 1.370 (3) | C16—H16A | 0.9900 |
| C2—H2 | 0.9500 | C16—H16B | 0.9900 |
| C3—C4 | 1.402 (3) | C17—N3 | 1.510 (2) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | C17—C18 | 1.514 (2) |
| C4—C5 | 1.364 (3) | C17—H17A | 0.9900 |
| C4—Cl1 | 1.7381 (17) | C17—H17B | 0.9900 |
| C5—C6 | 1.405 (2) | C18—H18A | 0.9800 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9500 | C18—H18B | 0.9800 |
| C6—N1 | 1.376 (2) | C18—H18C | 0.9800 |
| C7—N1 | 1.340 (2) | C19—N3 | 1.497 (2) |
| C7—C8 | 1.365 (3) | C19—C20 | 1.516 (3) |
| C7—H7 | 0.9500 | C19—H19A | 0.9900 |
| C8—C9 | 1.405 (3) | C19—H19B | 0.9900 |
| C8—H8 | 0.9500 | C20—H20A | 0.9800 |
| C9—N2 | 1.340 (2) | C20—H20B | 0.9800 |
| C10—C15 | 1.386 (3) | C20—H20C | 0.9800 |
| C10—C11 | 1.392 (3) | N1—H1N | 0.89 (2) |
| C10—N2 | 1.431 (2) | N2—H2N | 0.83 (3) |
| C11—C12 | 1.390 (2) | N3—H3N | 0.85 (3) |
| C11—H11 | 0.9500 | O1—H1O | 0.8400 |
| C12—C13 | 1.403 (2) | O1W—H1WA | 0.88 (3) |
| C12—C16 | 1.507 (2) | O1W—H1WB | 0.80 (3) |
| C13—O1 | 1.357 (2) | O2W—H2WA | 0.83 (3) |
| C13—C14 | 1.393 (3) | O2W—H2WB | 0.84 (3) |
| C14—C15 | 1.388 (3) | ||
| C6—C1—C2 | 117.57 (16) | C12—C16—N3 | 112.69 (14) |
| C6—C1—C9 | 118.64 (16) | C12—C16—H16A | 109.1 |
| C2—C1—C9 | 123.79 (16) | N3—C16—H16A | 109.1 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 121.54 (16) | C12—C16—H16B | 109.1 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 119.2 | N3—C16—H16B | 109.1 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 119.2 | H16A—C16—H16B | 107.8 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 118.68 (16) | N3—C17—C18 | 114.01 (14) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 120.7 | N3—C17—H17A | 108.8 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 120.7 | C18—C17—H17A | 108.8 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 122.46 (16) | N3—C17—H17B | 108.8 |
| C5—C4—Cl1 | 118.58 (14) | C18—C17—H17B | 108.8 |
| C3—C4—Cl1 | 118.96 (14) | H17A—C17—H17B | 107.6 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 118.29 (16) | C17—C18—H18A | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 120.9 | C17—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 120.9 | H18A—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| N1—C6—C1 | 120.02 (16) | C17—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| N1—C6—C5 | 118.59 (16) | H18A—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C1—C6—C5 | 121.40 (16) | H18B—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| N1—C7—C8 | 121.68 (16) | N3—C19—C20 | 112.36 (15) |
| N1—C7—H7 | 119.2 | N3—C19—H19A | 109.1 |
| C8—C7—H7 | 119.2 | C20—C19—H19A | 109.1 |
| C7—C8—C9 | 120.83 (16) | N3—C19—H19B | 109.1 |
| C7—C8—H8 | 119.6 | C20—C19—H19B | 109.1 |
| C9—C8—H8 | 119.6 | H19A—C19—H19B | 107.9 |
| N2—C9—C8 | 122.57 (16) | C19—C20—H20A | 109.5 |
| N2—C9—C1 | 119.97 (16) | C19—C20—H20B | 109.5 |
| C8—C9—C1 | 117.46 (16) | H20A—C20—H20B | 109.5 |
| C15—C10—C11 | 119.80 (16) | C19—C20—H20C | 109.5 |
| C15—C10—N2 | 119.74 (15) | H20A—C20—H20C | 109.5 |
| C11—C10—N2 | 120.43 (15) | H20B—C20—H20C | 109.5 |
| C12—C11—C10 | 120.72 (16) | C7—N1—C6 | 121.31 (15) |
| C12—C11—H11 | 119.6 | C7—N1—H1N | 121.8 (14) |
| C10—C11—H11 | 119.6 | C6—N1—H1N | 116.8 (14) |
| C11—C12—C13 | 119.18 (16) | C9—N2—C10 | 124.30 (16) |
| C11—C12—C16 | 120.54 (16) | C9—N2—H2N | 120.2 (15) |
| C13—C12—C16 | 120.26 (15) | C10—N2—H2N | 115.4 (15) |
| O1—C13—C14 | 122.72 (15) | C19—N3—C17 | 113.52 (13) |
| O1—C13—C12 | 117.46 (16) | C19—N3—C16 | 113.13 (14) |
| C14—C13—C12 | 119.79 (16) | C17—N3—C16 | 110.65 (14) |
| C15—C14—C13 | 120.30 (16) | C19—N3—H3N | 108.9 (15) |
| C15—C14—H14 | 119.8 | C17—N3—H3N | 103.8 (15) |
| C13—C14—H14 | 119.8 | C16—N3—H3N | 106.1 (15) |
| C10—C15—C14 | 120.05 (16) | C13—O1—H1O | 109.5 |
| C10—C15—H15 | 120.0 | H1WA—O1W—H1WB | 108 (3) |
| C14—C15—H15 | 120.0 | H2WA—O2W—H2WB | 107 (2) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | 0.7 (3) | C11—C12—C13—O1 | −177.99 (16) |
| C9—C1—C2—C3 | −178.97 (16) | C16—C12—C13—O1 | 0.6 (2) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 1.5 (3) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | 3.8 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −2.5 (3) | C16—C12—C13—C14 | −177.60 (16) |
| C2—C3—C4—Cl1 | 177.02 (14) | O1—C13—C14—C15 | 178.55 (16) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 1.1 (3) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | −3.4 (3) |
| Cl1—C4—C5—C6 | −178.43 (13) | C11—C10—C15—C14 | 2.8 (3) |
| C2—C1—C6—N1 | 178.00 (16) | N2—C10—C15—C14 | −179.04 (17) |
| C9—C1—C6—N1 | −2.3 (2) | C13—C14—C15—C10 | 0.1 (3) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | −2.1 (3) | C11—C12—C16—N3 | −85.8 (2) |
| C9—C1—C6—C5 | 177.54 (16) | C13—C12—C16—N3 | 95.62 (19) |
| C4—C5—C6—N1 | −178.85 (16) | C8—C7—N1—C6 | 1.3 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | 1.3 (3) | C1—C6—N1—C7 | 0.2 (3) |
| N1—C7—C8—C9 | −0.6 (3) | C5—C6—N1—C7 | −179.66 (16) |
| C7—C8—C9—N2 | 178.87 (17) | C8—C9—N2—C10 | −7.7 (3) |
| C7—C8—C9—C1 | −1.6 (3) | C1—C9—N2—C10 | 172.72 (15) |
| C6—C1—C9—N2 | −177.47 (16) | C15—C10—N2—C9 | 129.05 (19) |
| C2—C1—C9—N2 | 2.2 (3) | C11—C10—N2—C9 | −52.8 (3) |
| C6—C1—C9—C8 | 2.9 (2) | C20—C19—N3—C17 | −59.3 (2) |
| C2—C1—C9—C8 | −177.40 (17) | C20—C19—N3—C16 | 173.55 (15) |
| C15—C10—C11—C12 | −2.3 (3) | C18—C17—N3—C19 | −55.1 (2) |
| N2—C10—C11—C12 | 179.55 (16) | C18—C17—N3—C16 | 73.33 (19) |
| C10—C11—C12—C13 | −1.0 (3) | C12—C16—N3—C19 | −55.29 (19) |
| C10—C11—C12—C16 | −179.61 (16) | C12—C16—N3—C17 | 176.05 (14) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1N···Cl2 | 0.89 (2) | 2.32 (2) | 3.1913 (16) | 166.8 (19) |
| N2—H2N···O2Wi | 0.83 (2) | 2.07 (2) | 2.880 (2) | 167 (2) |
| N3—H3N···Cl3 | 0.85 (2) | 2.26 (2) | 3.0771 (14) | 161 (2) |
| O1—H1O···Cl2ii | 0.84 | 2.22 | 3.0640 (12) | 177 |
| O1W—H1WA···Cl3iii | 0.88 (3) | 2.30 (3) | 3.1778 (16) | 175 (3) |
| O1W—H1WB···Cl3i | 0.80 (3) | 2.42 (3) | 3.2100 (16) | 171 (3) |
| O2W—H2WA···O1W | 0.83 (3) | 1.95 (3) | 2.775 (2) | 174 (2) |
| O2W—H2WB···Cl2ii | 0.83 (3) | 2.33 (3) | 3.1585 (15) | 173 (3) |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, −y+1/2, z−1/2; (ii) −x−1, y−1/2, −z+1/2; (iii) −x, y−1/2, −z+1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: LX2163).
References
- Brandenburg, K. (2010). DIAMOND Crystal Impact GbR, Bonn, Germany.
- Bruker (1997). SMART, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Llinàs, A., Fábián, L., Burley, J. C., van de Streek, J. & Goodman, J. M. (2006). Acta Cryst. E62, o4196–o4199.
- Olliaro, P. L. & Taylor, W. R. J. (2003). J. Exp. Biol.206, 3753–3759. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Semeniuk, A., Niedospial, A., Kalinowska-Tluscik, J., Nitek, W. & Oleksyn, B. J. (2008). J. Mol. Struct.875, 32–41.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Yennawar, H. P. & Viswamitra, M. A. (1991). Curr. Sci.61, 39–43.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810031806/lx2163sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810031806/lx2163Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report