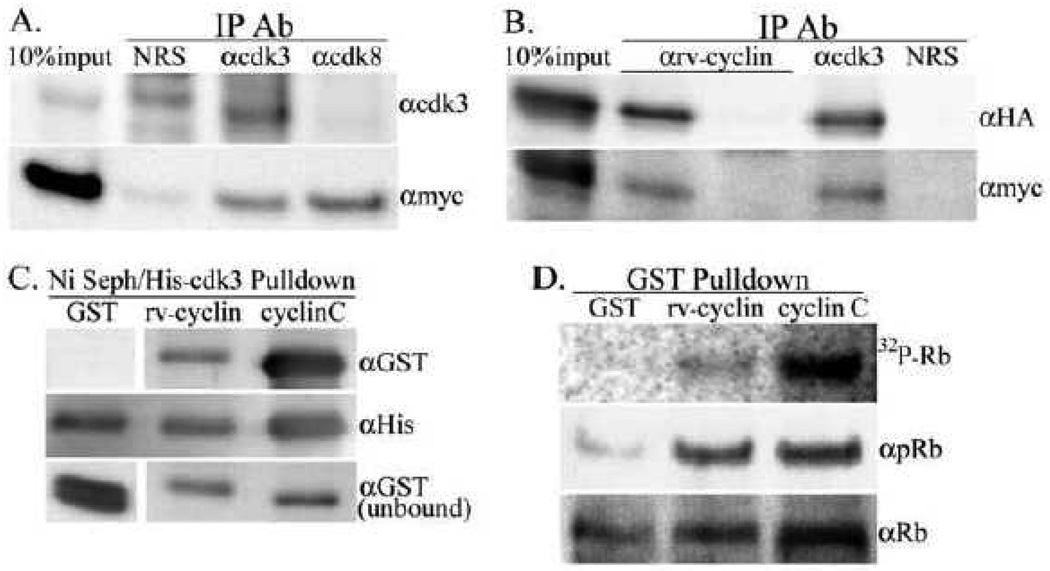
Fig. 5.
Interaction of rv-cyclin and cdk3. A. Nuclear extracts from induced HeLa Tet-Off myc-rv-cyclin cells after 72 hours serum starvation followed by 3 hrs of serum restoration were subject to co-IP with the indicated IP antibodies, normal rabbit serum (NRS), anti-cdk3 (αcdk3) and anti-cdk8 (αcdk8). The western blot was probed first with anti-myc Ab (αmyc) to detect precipitation of myc-tagged rv-cyclin followed by anti-cdk3 Ab (αcdk3) to detect precipitation of endogenous cdk3. B. Over-expressed, HA-tagged cdk3 was subject to co-IP with anti-rv-cyclin (αrv-cyclin) from nuclear extracts of HeLa cells with or without induced expression of myc-tagged rv-cyclin. Blots were probed first with anti-HA (αHA) to detect HA-cdk3 followed by anti-myc (αmyc) to confirm myc-rv-cyclin expression. Co-IPs with anti-cdk3 (αcdk3) and normal rabbit sera (NRS) were from extracts of rv-cyclin-induced cells. C. Ni Sepharose-His-cdk3 pulldown of soluble GST, GST-rv-cyclin (rv-cyclin) or GST-cyclin C (cyclinC) probed with anti-GST antibody (αGST). The blot was reprobed with anti-polyHis (αHis) to detect input His-cdk3. Total unbound GSTs from each reaction were run separately (bottom panels). GST-rv-cyclin and GST-cyclin C are of similar molecular weight (64 KDa vs. 60 KDa); the GST panels show signal for proteins at 27 KDa (GST). D. GST-pulldowns of over-expressed cdk3 were tested in kinase assays for phosphorylation of an Rb fusion protein (MBP-Rb-C, a.a. 379–928). The top panel shows the autoradiograph (32P-Rb) followed by antibodies for phosphorylated residues S807 and S811 of Rb (αpRb, middle panel) and for input MBP-Rb-C substrate (αRb, bottom panel).