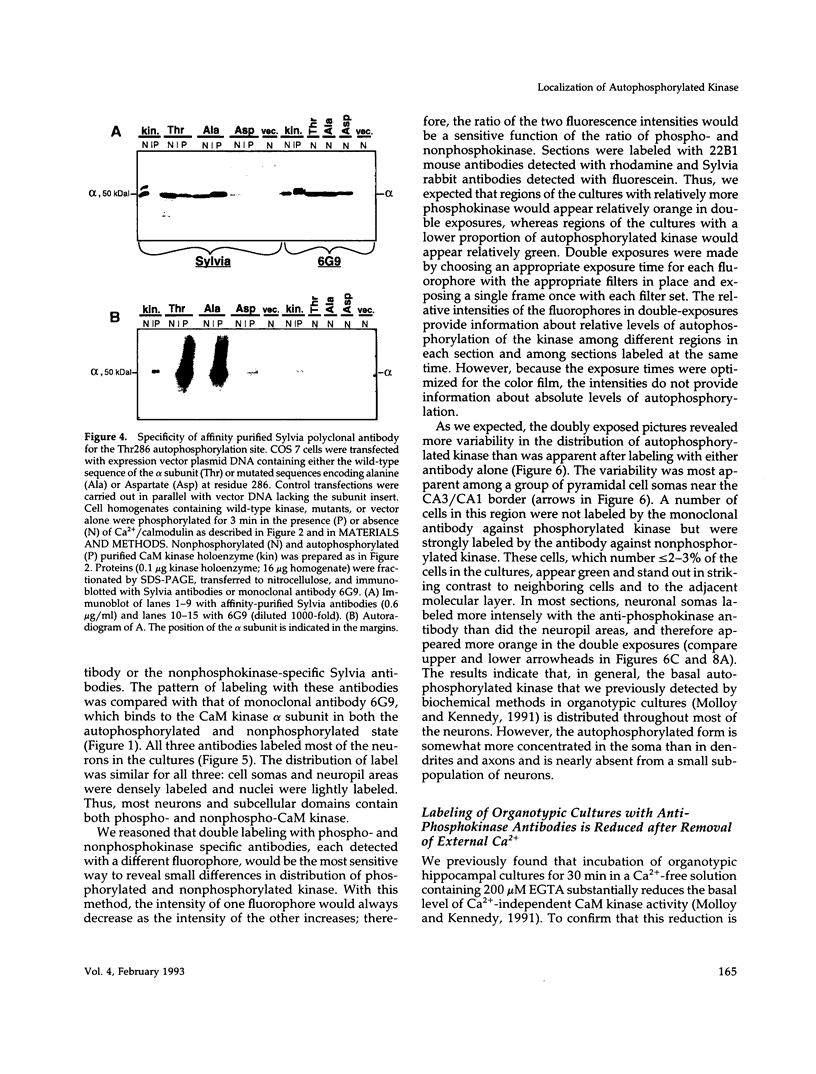
Abstract
We have visualized the distribution of autophosphorylated type II CaM kinase in neural tissue with the use of two complementary antibodies: a monoclonal antibody that binds to the alpha and beta subunits of the kinase only when they are autophosphorylated at threonine-286 (287 in beta) and affinity-purified rabbit antibodies that bind to both subunits only when they are not phosphorylated at these residues. We used these antibodies to double-label organotypic hippocampal cultures, detecting the mouse monoclonal antibody with rhodamine and the rabbit polyclonal antibodies with fluorescein. In double-exposed photographs, the ratios of intensities of the two fluorophores revealed the relative proportion of autophosphorylated and nonphosphorylated kinase in individual neurons throughout the cultures. We found that autophosphorylated and nonphosphorylated kinase are colocalized throughout most neurons rather than segregated within distinct cells or subcellular domains. However, the variations in intensity of the two fluorophores indicated that the proportion of autophosphorylated kinase is consistently higher in neuronal somas than in the neuropil. Incubation of the cultures in Ca2+ free medium dramatically reduced both the level of autophosphorylated kinase detected biochemically and the relative intensity of fluorescent staining with the phosphokinase specific monoclonal antibody. These results support the hypothesis that regulation of Ca(2+)-independent CaM kinase activity in vivo occurs by a dynamic equilibrium between autophosphorylation and dephosphorylation and that this equilibrium is maintained, at varying steady-state levels, in all parts of neurons.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arendt A., Palczewski K., Moore W. T., Caprioli R. M., McDowell J. H., Hargrave P. A. Synthesis of phosphopeptides containing O-phosphoserine or O-phosphothreonine. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1989 Jun;33(6):468–476. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1989.tb00225.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. K., Erondu N. E., Kennedy M. B. Purification and characterization of a calmodulin-dependent protein kinase that is highly concentrated in brain. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12735–12744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. K., Kennedy M. B. Deduced primary structure of the beta subunit of brain type II Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase determined by molecular cloning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):1794–1798. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.1794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Hwang P. M., Glatt C. E., Lowenstein C., Reed R. R., Snyder S. H. Cloned and expressed nitric oxide synthase structurally resembles cytochrome P-450 reductase. Nature. 1991 Jun 27;351(6329):714–718. doi: 10.1038/351714a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulleit R. F., Bennett M. K., Molloy S. S., Hurley J. B., Kennedy M. B. Conserved and variable regions in the subunits of brain type II Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase. Neuron. 1988 Mar;1(1):63–72. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90210-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassel D., Glaser L. Resistance to phosphatase of thiophosphorylated epidermal growth factor receptor in A431 membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2231–2235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho K. O., Wall J. B., Pugh P. C., Ito M., Mueller S. A., Kennedy M. B. The alpha subunit of type II Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase is highly conserved in Drosophila. Neuron. 1991 Sep;7(3):439–450. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90296-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colbran R. J., Schworer C. M., Hashimoto Y., Fong Y. L., Rich D. P., Smith M. K., Soderling T. R. Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. Biochem J. 1989 Mar 1;258(2):313–325. doi: 10.1042/bj2580313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Camilli P., Benfenati F., Valtorta F., Greengard P. The synapsins. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:433–460. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.002245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erondu N. E., Kennedy M. B. Regional distribution of type II Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase in rat brain. J Neurosci. 1985 Dec;5(12):3270–3277. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-12-03270.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukunaga K., Rich D. P., Soderling T. R. Generation of the Ca2(+)-independent form of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II in cerebellar granule cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21830–21836. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldenring J. R., Gonzalez B., McGuire J. S., Jr, DeLorenzo R. J. Purification and characterization of a calmodulin-dependent kinase from rat brain cytosol able to phosphorylate tubulin and microtubule-associated proteins. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12632–12640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gratecos D., Fischer E. H. Adenosine 5'-O(3-thiotriphosphate) in the control of phosphorylase activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Jun 18;58(4):960–967. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80237-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith L. C., Schulman H. The multifunctional Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase mediates Ca2+-dependent phosphorylation of tyrosine hydroxylase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9542–9549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gähwiler B. H. Slice cultures of cerebellar, hippocampal and hypothalamic tissue. Experientia. 1984 Mar 15;40(3):235–243. doi: 10.1007/BF01947561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson P. I., Kapiloff M. S., Lou L. L., Rosenfeld M. G., Schulman H. Expression of a multifunctional Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase and mutational analysis of its autoregulation. Neuron. 1989 Jul;3(1):59–70. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90115-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T. A thousand and one protein kinases. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):823–829. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90509-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferson A. B., Travis S. M., Schulman H. Activation of multifunctional Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase in GH3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 25;266(3):1484–1490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. B., Bennett M. K., Bulleit R. F., Erondu N. E., Jennings V. R., Miller S. G., Molloy S. S., Patton B. L., Schenker L. J. Structure and regulation of type II calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase in central nervous system neurons. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1990;55:101–110. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1990.055.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. B., Bennett M. K., Erondu N. E. Biochemical and immunochemical evidence that the "major postsynaptic density protein" is a subunit of a calmodulin-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7357–7361. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. B. Regulation of synaptic transmission in the central nervous system: long-term potentiation. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):777–787. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90601-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacombe J. M., Andriamanampisoa F., Pavia A. A. Solid-phase synthesis of peptides containing phosphoserine using phosphate tert.-butyl protecting group. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1990 Sep;36(3):275–280. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1990.tb00978.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee V. M., Otvos L., Jr, Carden M. J., Hollosi M., Dietzschold B., Lazzarini R. A. Identification of the major multiphosphorylation site in mammalian neurofilaments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1998–2002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lickteig R., Shenolikar S., Denner L., Kelly P. T. Regulation of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II by Ca2+/calmodulin-independent autophosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):19232–19239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C. R., Kapiloff M. S., Durgerian S., Tatemoto K., Russo A. F., Hanson P., Schulman H., Rosenfeld M. G. Molecular cloning of a brain-specific calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5962–5966. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisman J. E. A mechanism for memory storage insensitive to molecular turnover: a bistable autophosphorylating kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):3055–3057. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.3055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisman J. E., Goldring M. A. Feasibility of long-term storage of graded information by the Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase molecules of the postsynaptic density. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5320–5324. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., McGuinness T. L., Leonard C. S., Sugimori M., Greengard P. Intraterminal injection of synapsin I or calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II alters neurotransmitter release at the squid giant synapse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):3035–3039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.3035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopata M. A., Cleveland D. W., Sollner-Webb B. High level transient expression of a chloramphenicol acetyl transferase gene by DEAE-dextran mediated DNA transfection coupled with a dimethyl sulfoxide or glycerol shock treatment. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5707–5717. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luthman H., Magnusson G. High efficiency polyoma DNA transfection of chloroquine treated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1295–1308. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malinow R., Schulman H., Tsien R. W. Inhibition of postsynaptic PKC or CaMKII blocks induction but not expression of LTP. Science. 1989 Aug 25;245(4920):862–866. doi: 10.1126/science.2549638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T., Hanson P. I., Stryer L., Schulman H. Calmodulin trapping by calcium-calmodulin-dependent protein kinase. Science. 1992 May 22;256(5060):1199–1202. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5060.1199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. G., Kennedy M. B. Distinct forebrain and cerebellar isozymes of type II Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase associate differently with the postsynaptic density fraction. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 25;260(15):9039–9046. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. G., Kennedy M. B. Regulation of brain type II Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase by autophosphorylation: a Ca2+-triggered molecular switch. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):861–870. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90008-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. G., Patton B. L., Kennedy M. B. Sequences of autophosphorylation sites in neuronal type II CaM kinase that control Ca2(+)-independent activity. Neuron. 1988 Sep;1(7):593–604. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90109-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molloy S. S., Kennedy M. B. Autophosphorylation of type II Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase in cultures of postnatal rat hippocampal slices. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4756–4760. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols R. A., Sihra T. S., Czernik A. J., Nairn A. C., Greengard P. Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II increases glutamate and noradrenaline release from synaptosomes. Nature. 1990 Feb 15;343(6259):647–651. doi: 10.1038/343647a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizawa K., Yano T., Shibata M., Ando S., Saga S., Takahashi T., Inagaki M. Specific localization of phosphointermediate filament protein in the constricted area of dividing cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 15;266(5):3074–3079. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ocorr K. A., Schulman H. Activation of multifunctional Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinase in intact hippocampal slices. Neuron. 1991 Jun;6(6):907–914. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90231-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patton B. L., Miller S. G., Kennedy M. B. Activation of type II calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase by Ca2+/calmodulin is inhibited by autophosphorylation of threonine within the calmodulin-binding domain. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 5;265(19):11204–11212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schworer C. M., Colbran R. J., Keefer J. R., Soderling T. R. Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. Identification of a regulatory autophosphorylation site adjacent to the inhibitory and calmodulin-binding domains. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 25;263(27):13486–13489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva A. J., Paylor R., Wehner J. M., Tonegawa S. Impaired spatial learning in alpha-calcium-calmodulin kinase II mutant mice. Science. 1992 Jul 10;257(5067):206–211. doi: 10.1126/science.1321493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva A. J., Stevens C. F., Tonegawa S., Wang Y. Deficient hippocampal long-term potentiation in alpha-calcium-calmodulin kinase II mutant mice. Science. 1992 Jul 10;257(5067):201–206. doi: 10.1126/science.1378648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skene J. H. Axonal growth-associated proteins. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1989;12:127–156. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.12.030189.001015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squire L. R., Zola-Morgan S. The medial temporal lobe memory system. Science. 1991 Sep 20;253(5026):1380–1386. doi: 10.1126/science.1896849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stähli C., Staehelin T., Miggiano V., Schmidt J., Häring P. High frequencies of antigen-specific hybridomas: dependence on immunization parameters and prediction by spleen cell analysis. J Immunol Methods. 1980;32(3):297–304. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90194-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiel G., Czernik A. J., Gorelick F., Nairn A. C., Greengard P. Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II: identification of threonine-286 as the autophosphorylation site in the alpha subunit associated with the generation of Ca2+-independent activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6337–6341. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waymire J. C., Johnston J. P., Hummer-Lickteig K., Lloyd A., Vigny A., Craviso G. L. Phosphorylation of bovine adrenal chromaffin cell tyrosine hydroxylase. Temporal correlation of acetylcholine's effect on site phosphorylation, enzyme activation, and catecholamine synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12439–12447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto H., Fukunaga K., Tanaka E., Miyamoto E. Ca2+- and calmodulin-dependent phosphorylation of microtubule-associated protein 2 and tau factor, and inhibition of microtubule assembly. J Neurochem. 1983 Oct;41(4):1119–1125. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb09060.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]