Abstract
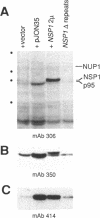
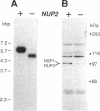
We have isolated a new gene, NUP2, that encodes a constituent of the yeast-nuclear pore complex (NPC). The NUP2 protein sequence shares a central repetitive domain with NSP1 and NUP1, the two previously characterized yeast nucleoporins. Like NUP1 and NSP1, NUP2 localizes to discrete spots in the nuclear envelope, as determined by indirect immunofluorescence. Although the sequence similarity among these three nucleoporins suggests that they have a similar role in the nuclear pore complex, NUP2, in contrast to NSP1 and NUP1, is not required for growth. Some combinations of mutant alleles of NUP1, NSP1, and NUP2 display "synthetic lethal" relationships that provide evidence for functional interaction between these NPC components. This genetic evidence of overlapping function suggests that the nucleoporins act in concert, perhaps participating in the same step of the recognition or transit of macromolecules through the NPC.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam S. A., Gerace L. Cytosolic proteins that specifically bind nuclear location signals are receptors for nuclear import. Cell. 1991 Sep 6;66(5):837–847. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90431-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adam S. A., Lobl T. J., Mitchell M. A., Gerace L. Identification of specific binding proteins for a nuclear location sequence. Nature. 1989 Jan 19;337(6204):276–279. doi: 10.1038/337276a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akey C. W., Goldfarb D. S. Protein import through the nuclear pore complex is a multistep process. J Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;109(3):971–982. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.3.971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aris J. P., Blobel G. Yeast nuclear envelope proteins cross react with an antibody against mammalian pore complex proteins. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;108(6):2059–2067. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.6.2059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., LaCroute F., Fink G. R. A positive selection for mutants lacking orotidine-5'-phosphate decarboxylase activity in yeast: 5-fluoro-orotic acid resistance. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;197(2):345–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00330984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson M., Botstein D. Two differentially regulated mRNAs with different 5' ends encode secreted with intracellular forms of yeast invertase. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):145–154. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90384-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clary D. O., Griff I. C., Rothman J. E. SNAPs, a family of NSF attachment proteins involved in intracellular membrane fusion in animals and yeast. Cell. 1990 May 18;61(4):709–721. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90482-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabauvalle M. C., Schulz B., Scheer U., Peters R. Inhibition of nuclear accumulation of karyophilic proteins in living cells by microinjection of the lectin wheat germ agglutinin. Exp Cell Res. 1988 Jan;174(1):291–296. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(88)90163-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis L. I., Blobel G. Identification and characterization of a nuclear pore complex protein. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):699–709. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90784-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis L. I., Blobel G. Nuclear pore complex contains a family of glycoproteins that includes p62: glycosylation through a previously unidentified cellular pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7552–7556. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis L. I. Control of nucleocytoplasmic transport. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;4(3):424–429. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90007-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis L. I., Fink G. R. The NUP1 gene encodes an essential component of the yeast nuclear pore complex. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):965–978. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90062-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg D., Weiss R. M., Terwilliger T. C. The hydrophobic moment detects periodicity in protein hydrophobicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):140–144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay D. R., Forbes D. J. Reconstitution of biochemically altered nuclear pores: transport can be eliminated and restored. Cell. 1990 Jan 12;60(1):17–29. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90712-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay D. R., Meier E., Bradley P., Horecka J., Forbes D. J. A complex of nuclear pore proteins required for pore function. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;114(1):169–183. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.1.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay D. R., Newmeyer D. D., Price T. M., Forbes D. J. Inhibition of in vitro nuclear transport by a lectin that binds to nuclear pores. J Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;104(2):189–200. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.2.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer U., Darzynkiewicz E., Tahara S. M., Dathan N. A., Lührmann R., Mattaj I. W. Diversity in the signals required for nuclear accumulation of U snRNPs and variety in the pathways of nuclear transport. J Cell Biol. 1991 May;113(4):705–714. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.4.705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs R. MacPattern: protein pattern searching on the Apple Macintosh. Comput Appl Biosci. 1991 Jan;7(1):105–106. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/7.1.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Bustos J. F., Wagner P., Hall M. N. Nuclear import substrates compete for a limited number of binding sites. Evidence for different classes of yeast nuclear import receptors. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 25;266(33):22303–22306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Bustos J., Heitman J., Hall M. N. Nuclear protein localization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Mar 7;1071(1):83–101. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(91)90013-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauber J., Stucka R., Krieg R., Feldmann H. Analysis of yeast chromosomal regions carrying members of the glutamate tRNA gene family: various transposable elements are associated with them. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 25;16(22):10623–10634. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.22.10623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopper A. K., Traglia H. M., Dunst R. W. The yeast RNA1 gene product necessary for RNA processing is located in the cytosol and apparently excluded from the nucleus. J Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;111(2):309–321. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huffaker T. C., Hoyt M. A., Botstein D. Genetic analysis of the yeast cytoskeleton. Annu Rev Genet. 1987;21:259–284. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.21.120187.001355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurt E. C. A novel nucleoskeletal-like protein located at the nuclear periphery is required for the life cycle of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4323–4334. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03331.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurt E. C. Targeting of a cytosolic protein to the nuclear periphery. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 2):2829–2837. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.2829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchison H. T., Hartwell L. H., McLaughlin C. S. Temperature-sensitive yeast mutant defective in ribonucleic acid production. J Bacteriol. 1969 Sep;99(3):807–814. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.3.807-814.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser C. A., Schekman R. Distinct sets of SEC genes govern transport vesicle formation and fusion early in the secretory pathway. Cell. 1990 May 18;61(4):723–733. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90483-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. C., Mélèse T. Identification and characterization of a nuclear localization sequence-binding protein in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8808–8812. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. C., Xue Z. X., Mélèse T. The NSR1 gene encodes a protein that specifically binds nuclear localization sequences and has two RNA recognition motifs. J Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;113(1):1–12. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaud N., Goldfarb D. S. Multiple pathways in nuclear transport: the import of U2 snRNP occurs by a novel kinetic pathway. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;112(2):215–223. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.2.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nehrbass U., Kern H., Mutvei A., Horstmann H., Marshallsay B., Hurt E. C. NSP1: a yeast nuclear envelope protein localized at the nuclear pores exerts its essential function by its carboxy-terminal domain. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):979–989. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90063-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newmeyer D. D., Forbes D. J. Nuclear import can be separated into distinct steps in vitro: nuclear pore binding and translocation. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):641–653. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90402-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newmeyer D. D., Lucocq J. M., Bürglin T. R., De Robertis E. M. Assembly in vitro of nuclei active in nuclear protein transport: ATP is required for nucleoplasmin accumulation. EMBO J. 1986 Mar;5(3):501–510. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04239.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newport J. W., Forbes D. J. The nucleus: structure, function, and dynamics. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:535–565. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.002535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieuwint R. T., Molenaar C. M., van Bommel J. H., van Raamsdonk-Duin M. M., Mager W. H., Planta R. J. The gene for yeast ribosomal protein S31 contains an intron in the leader sequence. Curr Genet. 1985;10(1):1–5. doi: 10.1007/BF00418486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohashi A., Gibson J., Gregor I., Schatz G. Import of proteins into mitochondria. The precursor of cytochrome c1 is processed in two steps, one of them heme-dependent. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):13042–13047. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park M. K., D'Onofrio M., Willingham M. C., Hanover J. A. A monoclonal antibody against a family of nuclear pore proteins (nucleoporins): O-linked N-acetylglucosamine is part of the immunodeterminant. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6462–6466. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichelt R., Holzenburg A., Buhle E. L., Jr, Jarnik M., Engel A., Aebi U. Correlation between structure and mass distribution of the nuclear pore complex and of distinct pore complex components. J Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;110(4):883–894. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.4.883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson H. E., Wittenberg C., Cross F., Reed S. I. An essential G1 function for cyclin-like proteins in yeast. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1127–1133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90768-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson W. D., Mills A. D., Dilworth S. M., Laskey R. A., Dingwall C. Nuclear protein migration involves two steps: rapid binding at the nuclear envelope followed by slower translocation through nuclear pores. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):655–664. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90403-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Hieter P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver P. A. How proteins enter the nucleus. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):489–497. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90233-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver P., Sadler I., Osborne M. A. Yeast proteins that recognize nuclear localization sequences. J Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;109(3):983–989. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.3.983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snow C. M., Senior A., Gerace L. Monoclonal antibodies identify a group of nuclear pore complex glycoproteins. J Cell Biol. 1987 May;104(5):1143–1156. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.5.1143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr C. M., D'Onofrio M., Park M. K., Hanover J. A. Primary sequence and heterologous expression of nuclear pore glycoprotein p62. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;110(6):1861–1871. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.6.1861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterne-Marr R., Blevitt J. M., Gerace L. O-linked glycoproteins of the nuclear pore complex interact with a cytosolic factor required for nuclear protein import. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;116(2):271–280. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.2.271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda T., Cameron S., Sass P., Zoller M., Wigler M. Three different genes in S. cerevisiae encode the catalytic subunits of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Cell. 1987 Jul 17;50(2):277–287. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90223-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson I. A., Niman H. L., Houghten R. A., Cherenson A. R., Connolly M. L., Lerner R. A. The structure of an antigenic determinant in a protein. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):767–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90412-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]