Abstract
In the title compound, C17H14ClF2NO2, the aminoacryloyloxy group makes dihedral angles of 47.55 (11)° with the 4-chlorophenyl group and 8.74 (12)° with the difluorophenyl group; the dihedral angle between the rings is 52.32 (11)°. The structure of the title compound reveals a Z configuration with respect to the C=C double bond in the aminoacrylate fragment. A bifurcated intramolecular N—H⋯(O,F) hydrogen bond occurs. In the crystal, molecules are linked into chains by C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds.
Related literature
For background to Schiff bases, see: You & Zhu, 2006 ▶. For applications of enamines, see: Xiao et al. (2007 ▶, 2008a
▶,b
▶,c
▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C17H14ClF2NO2
M r = 337.74
Monoclinic,

a = 16.276 (3) Å
b = 7.5030 (15) Å
c = 13.812 (3) Å
β = 111.11 (3)°
V = 1573.5 (5) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.27 mm−1
T = 298 K
0.30 × 0.10 × 0.10 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: ψ scan (North et al., 1968 ▶) T min = 0.923, T max = 0.973
2957 measured reflections
2824 independent reflections
1566 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.027
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.065
wR(F 2) = 0.170
S = 0.99
2824 reflections
213 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.26 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.29 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 2007 ▶); cell refinement: SMART; data reduction: SAINT (Bruker, 2007 ▶); program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810043801/bq2244sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810043801/bq2244Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H18⋯F1 | 0.83 (3) | 2.29 (3) | 2.674 (3) | 108 (3) |
| N1—H18⋯O1 | 0.83 (3) | 2.07 (3) | 2.675 (4) | 129 (3) |
| C6—H6⋯O1i | 0.93 | 2.51 | 3.321 (4) | 146 |
Symmetry code: (i)  .
.
Acknowledgments
This work was financed by the Scientific Research Fund of Hunan Provincial Education Department (Project No. 09B083) and by a grant from Jishou University for talent introduction (project No. JSDXKYZZ0801).
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
A 2-aryl-3-arylaminoacrylate contains characteristic N—C═C bond and is therefore identified as enamine. It is well known that Schiff base harbors an N═C—C bond, which indicates that an enamine is the tautomeric isomer of the correspond Schiff base. Enamines, like Schiff bases (You & Zhu, 2006), show good antimicrobial activities (Xiao et al., 2007; Xiao et al., 2008a), especially against bacterium. On the other hand, an enamine is the key intermediate for anticancer agents, 3-arylquinolone (Xiao et al., 2008b) and 3-arylquinoline (Xiao et al., 2008c). In a continuation of our work on the structural characterization of enamine derivatives, we report herein the crystal structure of the title compound, (I).
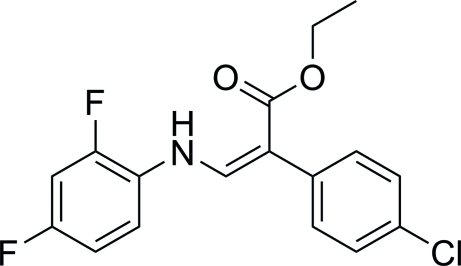
The bond length of C13—N1 (1.344 (4) Å) is shorter than standard C—N single bond (1.48 Å) but longer than C—N double bond (1.28 Å), indicating that the p orbital of N1 is conjugated with the π molecular orbital of C13—C14 double bond. For the same reason, C1—N1 (1.394 (4) Å) is single bond with some double-bond character. The stereochemistry of the double bond in aminoacrylate moiety was assigned as (E)-configuration based on X-ray crystallography (Fig. 1) of the title compound.
Aminoacryloyloxy moiety, O2—C15—O1—C14—C13, forms a plane with the mean deviation of 0.0249 Å, which makes a dihedral angle of 47.55 (11) ° with the 4-chlorophenyl group and 8.74 (12) ° with the difluorophenyl group. The molecules are linked through intermolecular C—H···O hydrogen bonds, forming an infinite one-dimensional ribbons (Table 1, Fig. 2).
Experimental
Equimolar quantities (6 mmol) of ethyl 2-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-oxopropanoate (1.36 g) and 2,4-difluorobenzenamine (0.77 g) in absolute alcohol (18 ml) were heated at 344–354 K for 2 h. The excess solvent was removed under reduced pressure. The residue was purified by a flash chromatography with EtOAc–petrolum ether (1:6, v/v) to afford two fractions. The second fraction gave a E-isomer, and the first fraction, after partial solvent evaporated, furnished colorless blocks of (I) suitable for single-crystal structure determination.
Refinement
The H atom bonded to N1 was located in a difference Fourier map. All other H atoms were placed in geometrically idealized positions and constrained to ride on their parent atoms with C—H = 0.93, 0.96 and 0.97 Å for the aromatic, CH3 and CH2 type H atoms, respectively. Uiso = 1.2Ueq(parent atoms) were assigned for aromatic and CH2 type H-atoms and 1.5Ueq(parent atoms) for CH3 type H-atoms.
Figures
Fig. 1.
Molecular structure of the title compound, showing the atom-numbering scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 30% probability level.
Fig. 2.
An infinite two-dimensional ribbon is formed through intermolecular C—H···O hydrogen bonds.
Crystal data
| C17H14ClF2NO2 | F(000) = 696 |
| Mr = 337.74 | Dx = 1.426 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 1318 reflections |
| a = 16.276 (3) Å | θ = 1.8–24.7° |
| b = 7.5030 (15) Å | µ = 0.27 mm−1 |
| c = 13.812 (3) Å | T = 298 K |
| β = 111.11 (3)° | Block, colourless |
| V = 1573.5 (5) Å3 | 0.30 × 0.10 × 0.10 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART CCD area-detector diffractometer | 2824 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1566 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.027 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 25.3°, θmin = 1.3° |
| Absorption correction: ψ scan (North et al., 1968) | h = −19→18 |
| Tmin = 0.923, Tmax = 0.973 | k = −9→0 |
| 2957 measured reflections | l = 0→16 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.065 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.170 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 0.99 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0804P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2824 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 213 parameters | Δρmax = 0.26 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.29 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R-factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 1.0185 (2) | 0.7793 (5) | 0.9700 (2) | 0.0447 (9) | |
| C2 | 1.1023 (2) | 0.7723 (5) | 1.0451 (2) | 0.0473 (9) | |
| C3 | 1.1764 (2) | 0.8338 (5) | 1.0316 (3) | 0.0575 (10) | |
| H3 | 1.2316 | 0.8267 | 1.0841 | 0.069* | |
| C4 | 1.1653 (2) | 0.9062 (6) | 0.9370 (3) | 0.0591 (10) | |
| C5 | 1.0852 (3) | 0.9180 (5) | 0.8598 (3) | 0.0614 (11) | |
| H5 | 1.0799 | 0.9696 | 0.7966 | 0.074* | |
| C6 | 1.0122 (2) | 0.8536 (5) | 0.8756 (3) | 0.0561 (10) | |
| H6 | 0.9575 | 0.8598 | 0.8222 | 0.067* | |
| C7 | 0.7054 (2) | 0.6470 (5) | 0.8669 (2) | 0.0418 (8) | |
| C8 | 0.6325 (2) | 0.7235 (5) | 0.8805 (3) | 0.0534 (10) | |
| H8 | 0.6377 | 0.7669 | 0.9456 | 0.064* | |
| C9 | 0.5528 (2) | 0.7365 (5) | 0.7997 (3) | 0.0568 (10) | |
| H9 | 0.5046 | 0.7872 | 0.8103 | 0.068* | |
| C10 | 0.5451 (2) | 0.6741 (5) | 0.7036 (3) | 0.0538 (10) | |
| C11 | 0.6148 (2) | 0.5949 (5) | 0.6881 (3) | 0.0567 (10) | |
| H11 | 0.6087 | 0.5507 | 0.6229 | 0.068* | |
| C12 | 0.6946 (2) | 0.5807 (5) | 0.7697 (2) | 0.0474 (9) | |
| H12 | 0.7418 | 0.5255 | 0.7590 | 0.057* | |
| C13 | 0.8638 (2) | 0.7024 (5) | 0.9292 (2) | 0.0463 (9) | |
| H13 | 0.8524 | 0.7370 | 0.8610 | 0.056* | |
| C14 | 0.7936 (2) | 0.6482 (5) | 0.9515 (2) | 0.0423 (8) | |
| C15 | 0.8066 (2) | 0.5946 (5) | 1.0578 (2) | 0.0480 (9) | |
| C16 | 0.7412 (2) | 0.4743 (6) | 1.1713 (2) | 0.0622 (11) | |
| H16A | 0.7579 | 0.5751 | 1.2184 | 0.075* | |
| H16B | 0.7856 | 0.3821 | 1.1972 | 0.075* | |
| C17 | 0.6536 (2) | 0.4057 (6) | 1.1638 (3) | 0.0708 (12) | |
| H17A | 0.6094 | 0.4936 | 1.1312 | 0.106* | |
| H17B | 0.6540 | 0.3807 | 1.2321 | 0.106* | |
| H17C | 0.6408 | 0.2985 | 1.1231 | 0.106* | |
| Cl1 | 0.44479 (7) | 0.69755 (18) | 0.60035 (8) | 0.0887 (5) | |
| F1 | 1.10991 (12) | 0.7013 (3) | 1.13887 (14) | 0.0654 (7) | |
| F2 | 1.23767 (15) | 0.9700 (4) | 0.92091 (18) | 0.0856 (8) | |
| N1 | 0.94818 (18) | 0.7123 (4) | 0.9939 (2) | 0.0483 (8) | |
| O1 | 0.87698 (16) | 0.6036 (4) | 1.13063 (17) | 0.0660 (8) | |
| O2 | 0.73408 (15) | 0.5283 (3) | 1.06790 (16) | 0.0521 (7) | |
| H18 | 0.961 (2) | 0.673 (4) | 1.054 (3) | 0.050 (11)* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0458 (19) | 0.047 (2) | 0.0377 (18) | 0.0000 (17) | 0.0109 (15) | −0.0070 (17) |
| C2 | 0.047 (2) | 0.056 (2) | 0.0355 (18) | 0.0045 (18) | 0.0104 (15) | −0.0033 (17) |
| C3 | 0.041 (2) | 0.077 (3) | 0.049 (2) | −0.006 (2) | 0.0093 (16) | −0.010 (2) |
| C4 | 0.052 (2) | 0.070 (3) | 0.062 (2) | −0.007 (2) | 0.028 (2) | −0.011 (2) |
| C5 | 0.070 (3) | 0.073 (3) | 0.044 (2) | −0.002 (2) | 0.024 (2) | 0.001 (2) |
| C6 | 0.049 (2) | 0.073 (3) | 0.0389 (19) | −0.004 (2) | 0.0072 (16) | −0.0010 (19) |
| C7 | 0.0405 (18) | 0.043 (2) | 0.0397 (18) | −0.0037 (16) | 0.0115 (14) | 0.0044 (16) |
| C8 | 0.047 (2) | 0.063 (2) | 0.045 (2) | 0.0019 (19) | 0.0100 (16) | −0.0049 (19) |
| C9 | 0.043 (2) | 0.062 (3) | 0.061 (2) | 0.0066 (19) | 0.0144 (18) | 0.005 (2) |
| C10 | 0.045 (2) | 0.055 (2) | 0.046 (2) | −0.0034 (19) | −0.0015 (16) | 0.0091 (18) |
| C11 | 0.058 (2) | 0.065 (3) | 0.0392 (19) | −0.005 (2) | 0.0082 (17) | −0.0021 (19) |
| C12 | 0.0463 (19) | 0.054 (2) | 0.0399 (18) | 0.0003 (18) | 0.0130 (15) | −0.0008 (17) |
| C13 | 0.047 (2) | 0.053 (2) | 0.0334 (17) | 0.0049 (18) | 0.0082 (15) | 0.0008 (16) |
| C14 | 0.0426 (19) | 0.048 (2) | 0.0317 (17) | 0.0011 (17) | 0.0079 (14) | −0.0009 (15) |
| C15 | 0.047 (2) | 0.052 (2) | 0.0404 (19) | −0.0026 (18) | 0.0103 (16) | −0.0019 (17) |
| C16 | 0.069 (3) | 0.077 (3) | 0.0365 (19) | −0.007 (2) | 0.0138 (18) | 0.001 (2) |
| C17 | 0.075 (3) | 0.081 (3) | 0.058 (2) | −0.013 (3) | 0.026 (2) | 0.000 (2) |
| Cl1 | 0.0566 (7) | 0.1127 (10) | 0.0672 (7) | 0.0014 (7) | −0.0135 (5) | 0.0174 (7) |
| F1 | 0.0531 (12) | 0.0978 (18) | 0.0363 (11) | −0.0016 (12) | 0.0051 (9) | 0.0110 (12) |
| F2 | 0.0689 (15) | 0.119 (2) | 0.0838 (17) | −0.0253 (15) | 0.0458 (13) | −0.0121 (16) |
| N1 | 0.0402 (17) | 0.063 (2) | 0.0353 (16) | −0.0006 (15) | 0.0063 (13) | 0.0050 (16) |
| O1 | 0.0500 (15) | 0.099 (2) | 0.0373 (14) | −0.0152 (15) | 0.0018 (12) | 0.0058 (14) |
| O2 | 0.0481 (14) | 0.0676 (17) | 0.0374 (12) | −0.0045 (13) | 0.0116 (10) | 0.0026 (12) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| C1—C2 | 1.385 (4) | C10—C11 | 1.364 (5) |
| C1—C6 | 1.387 (5) | C10—Cl1 | 1.747 (3) |
| C1—N1 | 1.394 (4) | C11—C12 | 1.384 (5) |
| C2—F1 | 1.365 (4) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| C2—C3 | 1.365 (5) | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| C3—C4 | 1.366 (5) | C13—N1 | 1.344 (4) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C13—C14 | 1.348 (5) |
| C4—C5 | 1.357 (5) | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| C4—F2 | 1.362 (4) | C14—C15 | 1.463 (4) |
| C5—C6 | 1.371 (5) | C15—O1 | 1.225 (4) |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | C15—O2 | 1.333 (4) |
| C6—H6 | 0.9300 | C16—O2 | 1.449 (4) |
| C7—C12 | 1.383 (4) | C16—C17 | 1.484 (5) |
| C7—C8 | 1.390 (5) | C16—H16A | 0.9700 |
| C7—C14 | 1.489 (4) | C16—H16B | 0.9700 |
| C8—C9 | 1.377 (4) | C17—H17A | 0.9600 |
| C8—H8 | 0.9300 | C17—H17B | 0.9600 |
| C9—C10 | 1.370 (5) | C17—H17C | 0.9600 |
| C9—H9 | 0.9300 | N1—H18 | 0.83 (3) |
| C2—C1—C6 | 116.0 (3) | C10—C11—H11 | 120.2 |
| C2—C1—N1 | 118.7 (3) | C12—C11—H11 | 120.2 |
| C6—C1—N1 | 125.3 (3) | C7—C12—C11 | 121.1 (3) |
| F1—C2—C3 | 118.6 (3) | C7—C12—H12 | 119.4 |
| F1—C2—C1 | 117.0 (3) | C11—C12—H12 | 119.4 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 124.4 (3) | N1—C13—C14 | 127.8 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 116.4 (3) | N1—C13—H13 | 116.1 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 121.8 | C14—C13—H13 | 116.1 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 121.8 | C13—C14—C15 | 119.0 (3) |
| C5—C4—F2 | 119.4 (4) | C13—C14—C7 | 118.7 (3) |
| C5—C4—C3 | 122.5 (4) | C15—C14—C7 | 122.4 (3) |
| F2—C4—C3 | 118.1 (4) | O1—C15—O2 | 122.4 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 119.6 (4) | O1—C15—C14 | 124.3 (3) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 120.2 | O2—C15—C14 | 113.2 (3) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 120.2 | O2—C16—C17 | 107.1 (3) |
| C5—C6—C1 | 121.1 (3) | O2—C16—H16A | 110.3 |
| C5—C6—H6 | 119.5 | C17—C16—H16A | 110.3 |
| C1—C6—H6 | 119.5 | O2—C16—H16B | 110.3 |
| C12—C7—C8 | 117.7 (3) | C17—C16—H16B | 110.3 |
| C12—C7—C14 | 120.8 (3) | H16A—C16—H16B | 108.6 |
| C8—C7—C14 | 121.3 (3) | C16—C17—H17A | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—C7 | 121.3 (3) | C16—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—H8 | 119.3 | H17A—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—H8 | 119.3 | C16—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C10—C9—C8 | 119.5 (4) | H17A—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C10—C9—H9 | 120.3 | H17B—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C8—C9—H9 | 120.3 | C13—N1—C1 | 126.4 (3) |
| C11—C10—C9 | 120.7 (3) | C13—N1—H18 | 118 (2) |
| C11—C10—Cl1 | 120.1 (3) | C1—N1—H18 | 116 (2) |
| C9—C10—Cl1 | 119.3 (3) | C15—O2—C16 | 116.6 (3) |
| C10—C11—C12 | 119.7 (3) | ||
| C6—C1—C2—F1 | 179.4 (3) | C8—C7—C12—C11 | 1.9 (5) |
| N1—C1—C2—F1 | −0.8 (5) | C14—C7—C12—C11 | −173.6 (3) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | 0.4 (6) | C10—C11—C12—C7 | −0.6 (6) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | −179.8 (4) | N1—C13—C14—C15 | 1.0 (6) |
| F1—C2—C3—C4 | −179.0 (3) | N1—C13—C14—C7 | −179.7 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.1 (6) | C12—C7—C14—C13 | 44.5 (5) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.3 (6) | C8—C7—C14—C13 | −130.9 (4) |
| C2—C3—C4—F2 | 179.6 (3) | C12—C7—C14—C15 | −136.2 (3) |
| F2—C4—C5—C6 | 179.8 (4) | C8—C7—C14—C15 | 48.4 (5) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −0.9 (6) | C13—C14—C15—O1 | 3.8 (6) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | 1.2 (6) | C7—C14—C15—O1 | −175.5 (4) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | −1.0 (5) | C13—C14—C15—O2 | −174.1 (3) |
| N1—C1—C6—C5 | 179.2 (4) | C7—C14—C15—O2 | 6.5 (5) |
| C12—C7—C8—C9 | −1.3 (6) | C14—C13—N1—C1 | −175.8 (4) |
| C14—C7—C8—C9 | 174.2 (3) | C2—C1—N1—C13 | −177.2 (3) |
| C7—C8—C9—C10 | −0.5 (6) | C6—C1—N1—C13 | 2.6 (6) |
| C8—C9—C10—C11 | 1.9 (6) | O1—C15—O2—C16 | 2.9 (5) |
| C8—C9—C10—Cl1 | −177.9 (3) | C14—C15—O2—C16 | −179.2 (3) |
| C9—C10—C11—C12 | −1.3 (6) | C17—C16—O2—C15 | 180.0 (3) |
| Cl1—C10—C11—C12 | 178.5 (3) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H18···F1 | 0.83 (3) | 2.29 (3) | 2.674 (3) | 108 (3) |
| N1—H18···O1 | 0.83 (3) | 2.07 (3) | 2.675 (4) | 129 (3) |
| C6—H6···O1i | 0.93 | 2.51 | 3.321 (4) | 146 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, −y+3/2, z−1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: BQ2244).
References
- Bruker (2007). SMART and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- North, A. C. T., Phillips, D. C. & Mathews, F. S. (1968). Acta Cryst. A24, 351–359.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Z.-P., Fang, R.-Q., Li, H.-Q., Xue, J.-Y., Zheng, Y. & Zhu, H.-L. (2008a). Eur. J. Med. Chem.43, 1828–1836. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Z.-P., Li, H.-Q., Shi, L., Lv, P.-C., Song, Z.-C. & Zhu, H.-L. (2008b). ChemMedChem, 3, 1077–1082. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Z.-P., Lv, P.-C., Xu, S.-P., Zhu, T.-T. & Zhu, H.-L. (2008c). ChemMedChem3, 1516–1519. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Z.-P., Xue, J.-Y., Tan, S.-H., Li, H.-Q. & Zhu, H. L. (2007). Bioorg. Med. Chem.15, 4212–4219. [DOI] [PubMed]
- You, Z.-L. & Zhu, H. L. (2006). Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem.632, 140–146.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810043801/bq2244sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810043801/bq2244Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




