Abstract
In the title compound, C18H10Cl2O4, the chromen-2-one ring system is almost planar [maximum deviation = 0.028 (1) Å] and is inclined at an angle of 16.35 (4)° with respect to the benzene ring. The C=C bond has an E configuration. The molecular conformation is stabilized by an almost symmetric intramolecular O⋯H⋯O hydrogen bond and a C—H⋯O interaction, both of which form S(6) ring motifs. In the crystal structure, molecules are linked into sheets lying parallel to (100) via intermolecular C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds. The crystal packing is further consolidated by π–π stacking interactions [centroid-to-centroid separation = 3.6615 (6) Å].
Related literature
For general background to and the biological activity of chalcones, see: Claisen et al. (1881 ▶); Siddiqui et al. (2008 ▶); Harborne & Mabry (1982 ▶); Bandgar et al. (2010 ▶). For related structures, see: Arshad et al. (2010 ▶); Asad et al. (2010 ▶). For bond-length data, see: Allen et al. (1987 ▶). For hydrogen-bond motifs, see: Bernstein et al. (1995 ▶). For the stability of the temperature controller used for the data collection, see: Cosier & Glazer (1986 ▶).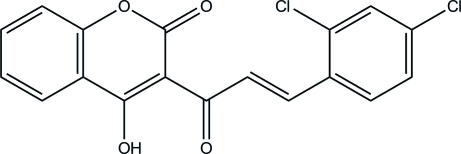
Experimental
Crystal data
C18H10Cl2O4
M r = 361.16
Monoclinic,
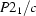
a = 4.5233 (2) Å
b = 21.2099 (9) Å
c = 15.6304 (7) Å
β = 91.607 (1)°
V = 1498.97 (11) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.45 mm−1
T = 100 K
0.35 × 0.15 × 0.09 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART APEXII DUO CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2009 ▶) T min = 0.857, T max = 0.959
25117 measured reflections
6698 independent reflections
5270 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.033
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.036
wR(F 2) = 0.101
S = 1.05
6698 reflections
222 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.54 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.34 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2009 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2009 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXTL; molecular graphics: SHELXTL; software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810043837/hb5700sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810043837/hb5700Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O3—H1O⋯O4 | 1.27 (2) | 1.17 (2) | 2.3947 (11) | 156 (2) |
| C11—H11A⋯O2 | 0.93 | 2.29 | 2.8704 (12) | 120 |
| C4—H4A⋯O4i | 0.93 | 2.45 | 3.2514 (13) | 144 |
| C17—H17A⋯O1ii | 0.93 | 2.54 | 3.3966 (13) | 154 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 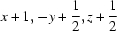 ; (ii)
; (ii) 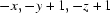 .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Universiti Sains Malaysia (USM) for providing the necessary research facilities and RU research funding under grant No. 1001/PKIMIA/811134. HKF and CKQ thank USM for Research University Grant No. 1001/PFIZIK/811160. MA thanks USM for the award of a postdoctoral fellowship. CKQ thanks USM for the award of a USM fellowship.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Chalcones are generally prepared from aldehydes and methyl ketones under basic conditions by applying the Claisen–Schmidt condensation (Claisen et al., 1881; Siddiqui et al., 2008). A large number of chalcones and their derivatives are found in natural and synthetic products and are also biogenetically precursors of known flavonoids, isoflavonoids (Harborne & Mabry, 1982) which exhibited a potential variety of biological activities (Bandgar et al., 2010).
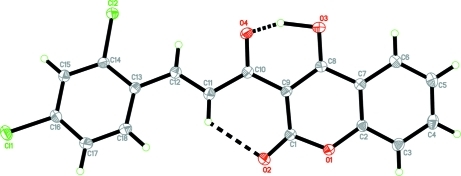
In the title molecule, (I), (Fig. 1), the chromen-2-one (O1/C1–C9) ring system is nearly planar (maximum deviation = 0.028 (1) Å for atom C1) and is inclined at an angle of 16.35 (4) ° with the phenyl ring (C13–C18). The C11═C12 bond has an E configuration. The molecule is stabilized by intramolecular O3—H1O···O4 and C11—H11A···O2 hydrogen bonds, which form S(6) ring motifs (Bernstein et al., 1995). Bond lengths (Allen et al., 1987) and angles are within normal ranges and comparable with the related structures (Arshad et al., 2010; Asad et al., 2010).
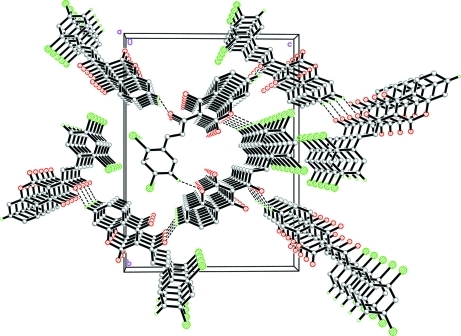
In the crystal packing (Fig. 2), the molecules are linked into two-dimensional sheets parallel to (100) via intermolecular C4—H4A···O4 and C17—H17A···O1 hydrogen bonds (Table 1). Short intermolecular distances [3.6615 (6) Å] between symmetry-related O1/C1/C2/C7–C9 (centroid Cg1) and C2–C7 (centroid Cg2) rings [symmetry code: -1+x, y, z] indicate the existence of π–π stacking interactions.
Experimental
To a stirred solution of 3-acetyl-4-hydroxycoumarin (0.98 mmol, 200 mg) in ethyl alcohol (10 ml), 2,4-dichlorobenzaldehyde (0.98 mmol, 171 mg) was added in the presence of one drop of piperidine. The mixture was refluxed on water bath for 14 h. After cooling at room temperature, a yellow solid was obtained, filtered, washed with ethanol–water, dried and recrystallized from chloroform as shining yellow needles of (I) in 70% yield.
Refinement
H1O was located in a difference Fourier map and allowed to refined freely. The remaining H atoms were positioned geometrically and refined using a riding model with C—H = 0.93 Å and Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C). The highest residual electron density peak is located at 0.64 Å from C12 and the deepest hole is located at 1.13 Å from Cl2.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound showing 50% probability displacement ellipsoids for non-H atoms. Intramolecular interactions are shown in dashed lines.
Fig. 2.
The crystal structure of the title compound, viewed along the a axis. H atoms not involved in hydrogen bonds (dashed lines) have been omitted for clarity.
Crystal data
| C18H10Cl2O4 | F(000) = 736 |
| Mr = 361.16 | Dx = 1.600 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 9100 reflections |
| a = 4.5233 (2) Å | θ = 2.3–35.1° |
| b = 21.2099 (9) Å | µ = 0.45 mm−1 |
| c = 15.6304 (7) Å | T = 100 K |
| β = 91.607 (1)° | Needle, yellow |
| V = 1498.97 (11) Å3 | 0.35 × 0.15 × 0.09 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEXII DUO CCD diffractometer | 6698 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 5270 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.033 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 35.3°, θmin = 1.6° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2009) | h = −7→7 |
| Tmin = 0.857, Tmax = 0.959 | k = −27→34 |
| 25117 measured reflections | l = −25→22 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.036 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.101 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.05 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0509P)2 + 0.2749P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 6698 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 222 parameters | Δρmax = 0.54 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.34 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Experimental. The crystal was placed in the cold stream of an Oxford Cyrosystems Cobra open-flow nitrogen cryostat (Cosier & Glazer, 1986) operating at 100.0 (1) K. |
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2sigma(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cl1 | −0.68600 (6) | 0.640460 (12) | 0.153533 (17) | 0.02236 (7) | |
| Cl2 | −0.07973 (6) | 0.434153 (13) | 0.069793 (16) | 0.02180 (7) | |
| O1 | 0.69790 (16) | 0.35450 (4) | 0.57063 (5) | 0.01808 (14) | |
| O2 | 0.37593 (19) | 0.41872 (4) | 0.51001 (5) | 0.02516 (17) | |
| O3 | 0.96509 (16) | 0.28446 (4) | 0.34161 (5) | 0.01797 (14) | |
| O4 | 0.63677 (16) | 0.35486 (4) | 0.26596 (5) | 0.01701 (14) | |
| C1 | 0.5646 (2) | 0.37989 (5) | 0.49758 (6) | 0.01664 (17) | |
| C2 | 0.9014 (2) | 0.30666 (5) | 0.56843 (6) | 0.01535 (17) | |
| C3 | 1.0072 (2) | 0.28411 (5) | 0.64694 (7) | 0.01883 (18) | |
| H3A | 0.9402 | 0.3009 | 0.6978 | 0.023* | |
| C4 | 1.2149 (2) | 0.23600 (5) | 0.64775 (7) | 0.02067 (19) | |
| H4A | 1.2889 | 0.2207 | 0.6998 | 0.025* | |
| C5 | 1.3149 (2) | 0.21011 (5) | 0.57151 (7) | 0.02046 (19) | |
| H5A | 1.4544 | 0.1779 | 0.5731 | 0.025* | |
| C6 | 1.2059 (2) | 0.23256 (5) | 0.49397 (7) | 0.01786 (18) | |
| H6A | 1.2708 | 0.2153 | 0.4431 | 0.021* | |
| C7 | 0.9967 (2) | 0.28162 (5) | 0.49195 (6) | 0.01467 (16) | |
| C8 | 0.87645 (19) | 0.30746 (4) | 0.41294 (6) | 0.01417 (16) | |
| C9 | 0.6643 (2) | 0.35648 (4) | 0.41544 (6) | 0.01407 (16) | |
| C10 | 0.54393 (19) | 0.37953 (5) | 0.33533 (6) | 0.01447 (16) | |
| C11 | 0.3233 (2) | 0.42963 (5) | 0.32717 (6) | 0.01642 (17) | |
| H11A | 0.2750 | 0.4541 | 0.3742 | 0.020* | |
| C12 | 0.1915 (2) | 0.43961 (5) | 0.25011 (6) | 0.01545 (17) | |
| H12A | 0.2476 | 0.4133 | 0.2058 | 0.019* | |
| C13 | −0.0299 (2) | 0.48736 (5) | 0.22909 (6) | 0.01444 (16) | |
| C14 | −0.1625 (2) | 0.49008 (5) | 0.14673 (6) | 0.01522 (16) | |
| C15 | −0.3651 (2) | 0.53657 (5) | 0.12291 (6) | 0.01714 (17) | |
| H15A | −0.4475 | 0.5379 | 0.0677 | 0.021* | |
| C16 | −0.4410 (2) | 0.58096 (5) | 0.18364 (7) | 0.01636 (17) | |
| C17 | −0.3254 (2) | 0.57894 (5) | 0.26670 (7) | 0.01765 (17) | |
| H17A | −0.3843 | 0.6082 | 0.3072 | 0.021* | |
| C18 | −0.1210 (2) | 0.53266 (5) | 0.28840 (6) | 0.01714 (17) | |
| H18A | −0.0415 | 0.5315 | 0.3439 | 0.021* | |
| H1O | 0.812 (5) | 0.3171 (11) | 0.2882 (15) | 0.077 (7)* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl1 | 0.02114 (11) | 0.01919 (12) | 0.02702 (13) | 0.00611 (8) | 0.00565 (9) | 0.00516 (9) |
| Cl2 | 0.02795 (12) | 0.02120 (13) | 0.01605 (11) | 0.00727 (9) | −0.00287 (8) | −0.00406 (9) |
| O1 | 0.0216 (3) | 0.0197 (4) | 0.0130 (3) | 0.0062 (3) | 0.0009 (2) | 0.0002 (3) |
| O2 | 0.0307 (4) | 0.0272 (4) | 0.0177 (4) | 0.0140 (3) | 0.0026 (3) | 0.0002 (3) |
| O3 | 0.0201 (3) | 0.0190 (3) | 0.0149 (3) | 0.0025 (3) | 0.0016 (2) | −0.0027 (3) |
| O4 | 0.0179 (3) | 0.0202 (4) | 0.0130 (3) | 0.0002 (2) | −0.0004 (2) | −0.0016 (3) |
| C1 | 0.0194 (4) | 0.0166 (4) | 0.0139 (4) | 0.0014 (3) | 0.0001 (3) | 0.0004 (3) |
| C2 | 0.0154 (4) | 0.0149 (4) | 0.0157 (4) | 0.0007 (3) | 0.0009 (3) | 0.0016 (3) |
| C3 | 0.0196 (4) | 0.0212 (5) | 0.0157 (4) | 0.0006 (3) | 0.0005 (3) | 0.0030 (4) |
| C4 | 0.0194 (4) | 0.0220 (5) | 0.0204 (5) | 0.0004 (4) | −0.0016 (3) | 0.0068 (4) |
| C5 | 0.0181 (4) | 0.0179 (5) | 0.0254 (5) | 0.0025 (3) | 0.0000 (3) | 0.0038 (4) |
| C6 | 0.0169 (4) | 0.0161 (4) | 0.0206 (4) | 0.0007 (3) | 0.0016 (3) | −0.0001 (4) |
| C7 | 0.0150 (4) | 0.0137 (4) | 0.0154 (4) | −0.0010 (3) | 0.0009 (3) | 0.0007 (3) |
| C8 | 0.0140 (4) | 0.0140 (4) | 0.0146 (4) | −0.0021 (3) | 0.0009 (3) | −0.0007 (3) |
| C9 | 0.0147 (4) | 0.0150 (4) | 0.0125 (4) | −0.0001 (3) | 0.0004 (3) | 0.0002 (3) |
| C10 | 0.0135 (4) | 0.0147 (4) | 0.0152 (4) | −0.0027 (3) | −0.0004 (3) | 0.0000 (3) |
| C11 | 0.0164 (4) | 0.0167 (4) | 0.0161 (4) | 0.0000 (3) | −0.0008 (3) | 0.0006 (3) |
| C12 | 0.0148 (4) | 0.0158 (4) | 0.0156 (4) | −0.0012 (3) | −0.0005 (3) | 0.0006 (3) |
| C13 | 0.0146 (4) | 0.0150 (4) | 0.0138 (4) | −0.0014 (3) | 0.0004 (3) | 0.0010 (3) |
| C14 | 0.0165 (4) | 0.0156 (4) | 0.0135 (4) | 0.0001 (3) | 0.0008 (3) | −0.0009 (3) |
| C15 | 0.0173 (4) | 0.0181 (5) | 0.0160 (4) | 0.0013 (3) | −0.0001 (3) | 0.0008 (3) |
| C16 | 0.0148 (4) | 0.0145 (4) | 0.0200 (4) | 0.0007 (3) | 0.0037 (3) | 0.0021 (3) |
| C17 | 0.0187 (4) | 0.0164 (4) | 0.0179 (4) | −0.0005 (3) | 0.0035 (3) | −0.0017 (3) |
| C18 | 0.0179 (4) | 0.0181 (4) | 0.0154 (4) | −0.0013 (3) | 0.0004 (3) | −0.0012 (3) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Cl1—C16 | 1.7358 (10) | C6—H6A | 0.9300 |
| Cl2—C14 | 1.7376 (10) | C7—C8 | 1.4436 (13) |
| O1—C2 | 1.3711 (12) | C8—C9 | 1.4162 (13) |
| O1—C1 | 1.3851 (12) | C9—C10 | 1.4371 (13) |
| O2—C1 | 1.2059 (12) | C10—C11 | 1.4610 (13) |
| O3—C8 | 1.2910 (11) | C11—C12 | 1.3457 (13) |
| O3—H1O | 1.27 (2) | C11—H11A | 0.9300 |
| O4—C10 | 1.2851 (12) | C12—C13 | 1.4554 (13) |
| O4—H1O | 1.17 (2) | C12—H12A | 0.9300 |
| C1—C9 | 1.4595 (13) | C13—C18 | 1.4050 (14) |
| C2—C7 | 1.3877 (14) | C13—C14 | 1.4061 (13) |
| C2—C3 | 1.3895 (14) | C14—C15 | 1.3896 (13) |
| C3—C4 | 1.3869 (15) | C15—C16 | 1.3870 (14) |
| C3—H3A | 0.9300 | C15—H15A | 0.9300 |
| C4—C5 | 1.3988 (16) | C16—C17 | 1.3867 (14) |
| C4—H4A | 0.9300 | C17—C18 | 1.3841 (14) |
| C5—C6 | 1.3804 (15) | C17—H17A | 0.9300 |
| C5—H5A | 0.9300 | C18—H18A | 0.9300 |
| C6—C7 | 1.4062 (13) | ||
| C2—O1—C1 | 122.95 (8) | C10—C9—C1 | 122.14 (8) |
| C8—O3—H1O | 100.6 (11) | O4—C10—C9 | 118.16 (9) |
| C10—O4—H1O | 105.2 (12) | O4—C10—C11 | 117.46 (8) |
| O2—C1—O1 | 115.24 (9) | C9—C10—C11 | 124.38 (9) |
| O2—C1—C9 | 127.70 (9) | C12—C11—C10 | 118.48 (9) |
| O1—C1—C9 | 117.06 (8) | C12—C11—H11A | 120.8 |
| O1—C2—C7 | 122.00 (8) | C10—C11—H11A | 120.8 |
| O1—C2—C3 | 116.57 (9) | C11—C12—C13 | 126.60 (9) |
| C7—C2—C3 | 121.43 (9) | C11—C12—H12A | 116.7 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 118.53 (10) | C13—C12—H12A | 116.7 |
| C4—C3—H3A | 120.7 | C18—C13—C14 | 116.78 (9) |
| C2—C3—H3A | 120.7 | C18—C13—C12 | 122.66 (8) |
| C3—C4—C5 | 121.09 (9) | C14—C13—C12 | 120.56 (9) |
| C3—C4—H4A | 119.5 | C15—C14—C13 | 122.39 (9) |
| C5—C4—H4A | 119.5 | C15—C14—Cl2 | 116.89 (7) |
| C6—C5—C4 | 119.76 (9) | C13—C14—Cl2 | 120.72 (7) |
| C6—C5—H5A | 120.1 | C16—C15—C14 | 118.18 (9) |
| C4—C5—H5A | 120.1 | C16—C15—H15A | 120.9 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 119.91 (9) | C14—C15—H15A | 120.9 |
| C5—C6—H6A | 120.0 | C17—C16—C15 | 121.71 (9) |
| C7—C6—H6A | 120.0 | C17—C16—Cl1 | 119.83 (8) |
| C2—C7—C6 | 119.27 (9) | C15—C16—Cl1 | 118.46 (8) |
| C2—C7—C8 | 118.22 (8) | C18—C17—C16 | 118.89 (9) |
| C6—C7—C8 | 122.51 (9) | C18—C17—H17A | 120.6 |
| O3—C8—C9 | 121.89 (9) | C16—C17—H17A | 120.6 |
| O3—C8—C7 | 118.46 (8) | C17—C18—C13 | 121.97 (9) |
| C9—C8—C7 | 119.64 (8) | C17—C18—H18A | 119.0 |
| C8—C9—C10 | 117.78 (8) | C13—C18—H18A | 119.0 |
| C8—C9—C1 | 120.01 (8) | ||
| C2—O1—C1—O2 | 175.23 (9) | O2—C1—C9—C10 | 1.19 (16) |
| C2—O1—C1—C9 | −4.08 (14) | O1—C1—C9—C10 | −179.59 (8) |
| C1—O1—C2—C7 | 2.35 (14) | C8—C9—C10—O4 | −0.56 (13) |
| C1—O1—C2—C3 | −177.35 (9) | C1—C9—C10—O4 | −177.65 (9) |
| O1—C2—C3—C4 | −179.58 (9) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | 179.82 (9) |
| C7—C2—C3—C4 | 0.72 (15) | C1—C9—C10—C11 | 2.74 (14) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.55 (16) | O4—C10—C11—C12 | 11.55 (13) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −0.03 (16) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | −168.83 (9) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | 0.47 (15) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | −179.31 (9) |
| O1—C2—C7—C6 | −179.98 (9) | C11—C12—C13—C18 | 4.13 (15) |
| C3—C2—C7—C6 | −0.30 (15) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | −176.17 (9) |
| O1—C2—C7—C8 | 0.23 (14) | C18—C13—C14—C15 | 2.61 (14) |
| C3—C2—C7—C8 | 179.92 (9) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | −177.10 (9) |
| C5—C6—C7—C2 | −0.31 (14) | C18—C13—C14—Cl2 | −176.94 (7) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | 179.47 (9) | C12—C13—C14—Cl2 | 3.35 (13) |
| C2—C7—C8—O3 | 179.79 (9) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | −1.12 (14) |
| C6—C7—C8—O3 | 0.01 (14) | Cl2—C14—C15—C16 | 178.44 (7) |
| C2—C7—C8—C9 | −0.80 (13) | C14—C15—C16—C17 | −1.44 (14) |
| C6—C7—C8—C9 | 179.43 (9) | C14—C15—C16—Cl1 | 178.24 (7) |
| O3—C8—C9—C10 | 1.20 (13) | C15—C16—C17—C18 | 2.35 (15) |
| C7—C8—C9—C10 | −178.19 (8) | Cl1—C16—C17—C18 | −177.32 (8) |
| O3—C8—C9—C1 | 178.35 (9) | C16—C17—C18—C13 | −0.73 (15) |
| C7—C8—C9—C1 | −1.04 (13) | C14—C13—C18—C17 | −1.66 (14) |
| O2—C1—C9—C8 | −175.83 (10) | C12—C13—C18—C17 | 178.05 (9) |
| O1—C1—C9—C8 | 3.39 (13) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O3—H1O···O4 | 1.27 (2) | 1.17 (2) | 2.3947 (11) | 156 (2) |
| C11—H11A···O2 | 0.93 | 2.29 | 2.8704 (12) | 120 |
| C4—H4A···O4i | 0.93 | 2.45 | 3.2514 (13) | 144 |
| C17—H17A···O1ii | 0.93 | 2.54 | 3.3966 (13) | 154 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x+1, −y+1/2, z+1/2; (ii) −x, −y+1, −z+1.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: HB5700).
References
- Allen, F. H., Kennard, O., Watson, D. G., Brammer, L., Orpen, A. G. & Taylor, R. (1987). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. S1–19.
- Arshad, A., Osman, H., Lam, C. K., Quah, C. K. & Fun, H.-K. (2010). Acta Cryst. E66, o1446–o1447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Asad, M., Oo, C.-W., Osman, H., Quah, C. K. & Fun, H.-K. (2010). Acta Cryst. E66, o2491–o2492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Bandgar, B. P., Gawande, S. S., Bodade, R. G., Totre, J. V. & Khobragade, C. N. (2010). Bioorg. Med. Chem.18, 1364–1370. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl.34, 1555–1573.
- Bruker (2009). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Claisen, L., Claparede, A. & Schmidt, J. G. (1881). Berichte, 14, 2460, 1459.
- Cosier, J. & Glazer, A. M. (1986). J. Appl. Cryst.19, 105–107.
- Harborne, J. B. & Mabry, T. J. (1982). The Flavonoids: Advances in Research, pp. 313–416. London: Chapman and Hall.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, Z. N., Asad, M. & Praveen, S. (2008). Med. Chem. Res.17, 318–325.
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810043837/hb5700sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810043837/hb5700Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report