Abstract
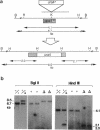
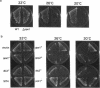
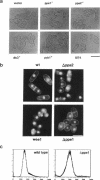
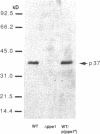
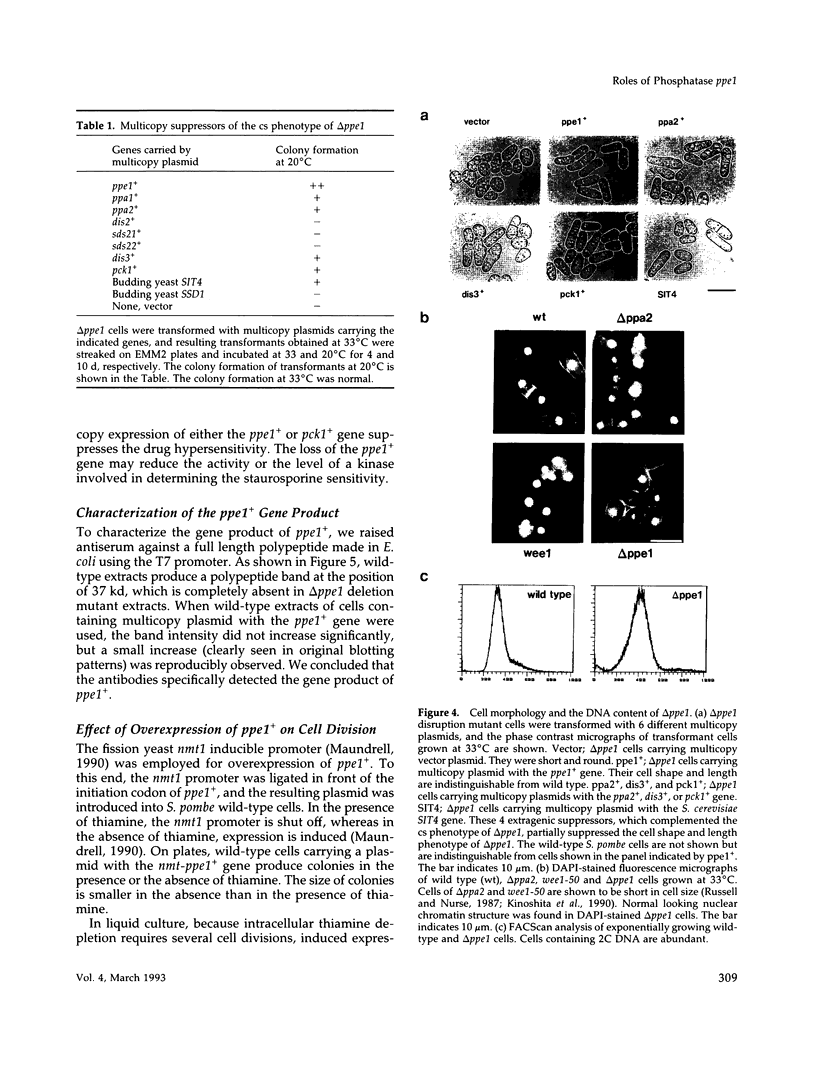
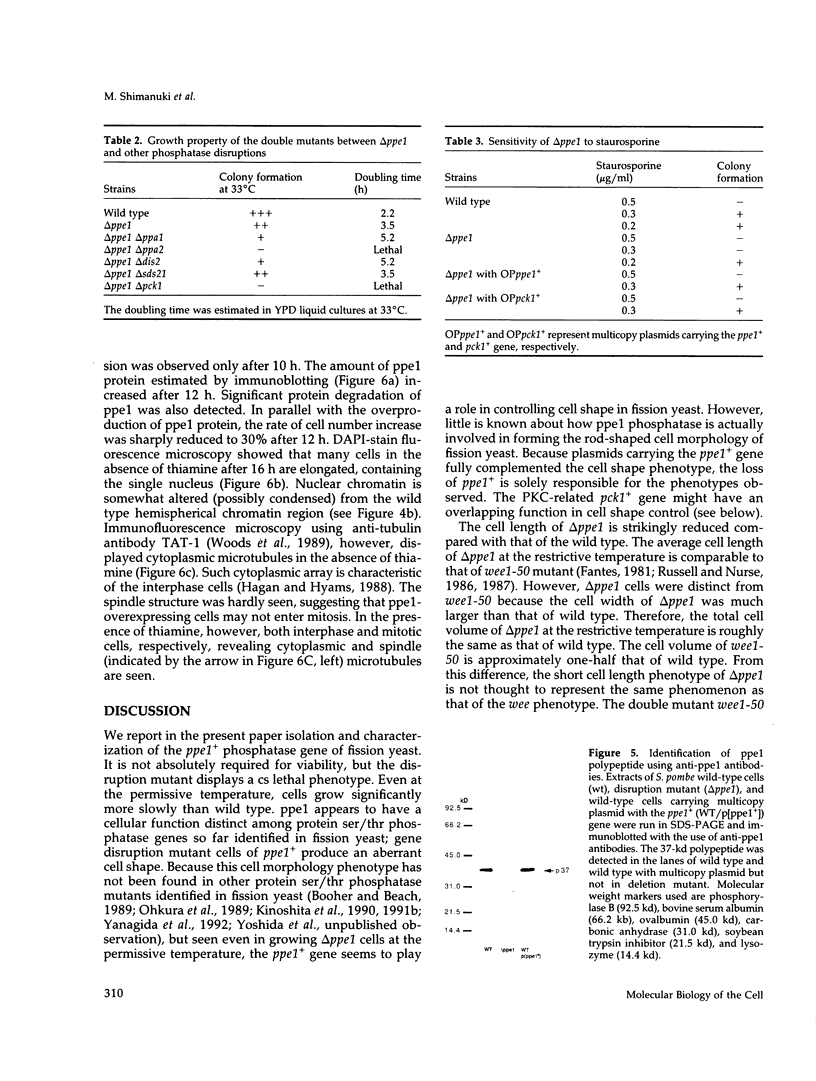
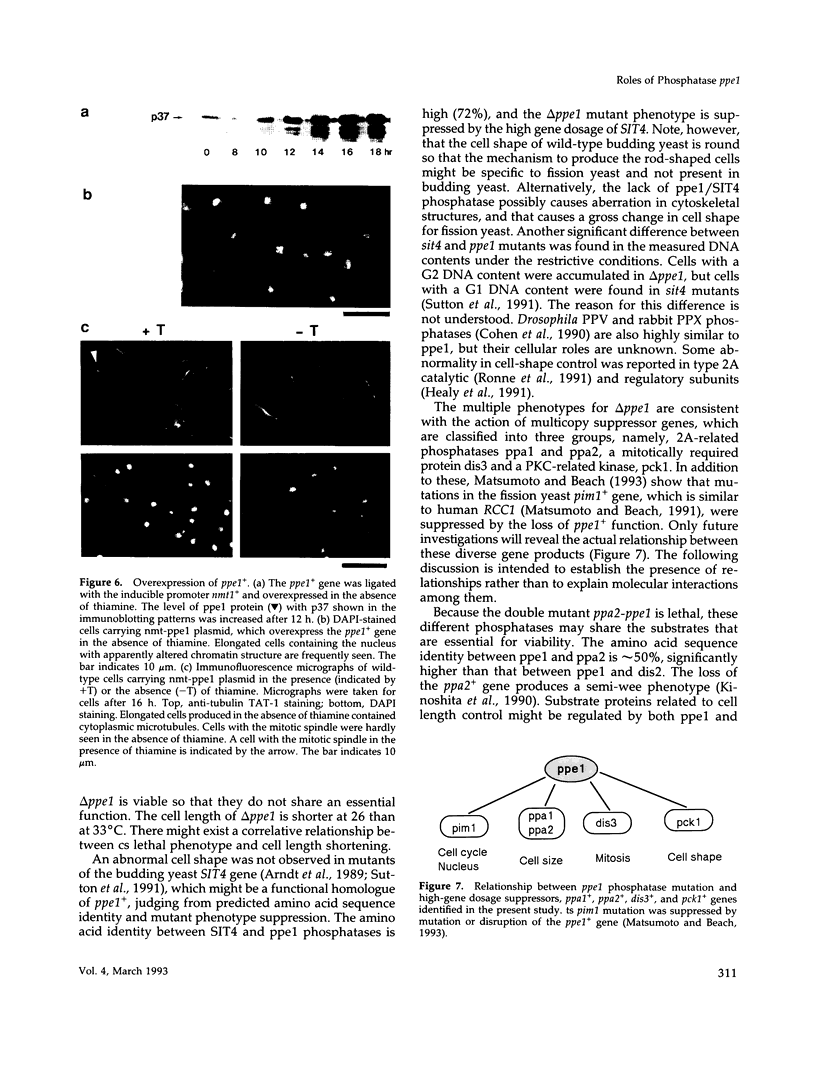
We isolated a fission yeast putative protein serine/threonine phosphatase gene designated ppe1+ by hybridization. The predicted amino acid sequence is similar to those of the fission yeast ppa2 (53% identity) and dis2 (39%) phosphatases, and highly similar to those of the budding yeast SIT4 (72%), Drosophila PPV (68%) and rabbit PPX (61%) phosphatases. Antibodies against ppe1 protein identified a 37-kd polypeptide in fission yeast. A gene disruption (designated delta ppe1) caused cold-sensitive lethality and short, pear-shaped cells. These phenotypes were fully suppressed by a plasmid carrying ppe1+. Three classes of multicopy suppressor genes for delta ppe1 were identified as follows: 1) ppa1+ and ppa2+ encoding type 2A-like phosphatases, 2) mitotically essential dis3+ similar to the budding yeast SSD1/SRK1, a suppressor for sit4, and 3) pck1+ coding for a protein kinase C-like kinase. Consistently, the budding yeast SIT4 gene was also a multicopy suppressor for delta ppe1. Phosphatase ppe1 may play a role in cell morphogenesis and mitosis by either regulating or being regulated by these multicopy suppressor gene products. Consistent with this hypothesis, double mutants ppe1-ppa2 and ppe1-pck1 are lethal at the permissive temperature.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arndt K. T., Styles C. A., Fink G. R. A suppressor of a HIS4 transcriptional defect encodes a protein with homology to the catalytic subunit of protein phosphatases. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):527–537. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90576-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axton J. M., Dombrádi V., Cohen P. T., Glover D. M. One of the protein phosphatase 1 isoenzymes in Drosophila is essential for mitosis. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):33–46. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90286-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booher R., Beach D. Involvement of a type 1 protein phosphatase encoded by bws1+ in fission yeast mitotic control. Cell. 1989 Jun 16;57(6):1009–1016. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90339-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. T., Brewis N. D., Hughes V., Mann D. J. Protein serine/threonine phosphatases; an expanding family. FEBS Lett. 1990 Aug 1;268(2):355–359. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81285-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The structure and regulation of protein phosphatases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:453–508. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.002321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cyert M. S., Kunisawa R., Kaim D., Thorner J. Yeast has homologs (CNA1 and CNA2 gene products) of mammalian calcineurin, a calmodulin-regulated phosphoprotein phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7376–7380. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Da Cruz e Silva E. F., Hughes V., McDonald P., Stark M. J., Cohen P. T. Protein phosphatase 2Bw and protein phosphatase Z are Saccharomyces cerevisiae enzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jun 13;1089(2):269–272. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(91)90023-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doonan J. H., Morris N. R. The bimG gene of Aspergillus nidulans, required for completion of anaphase, encodes a homolog of mammalian phosphoprotein phosphatase 1. Cell. 1989 Jun 16;57(6):987–996. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90337-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantes P. A. Isolation of cell size mutants of a fission yeast by a new selective method: characterization of mutants and implications for division control mechanisms. J Bacteriol. 1981 May;146(2):746–754. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.2.746-754.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagan I. M., Hyams J. S. The use of cell division cycle mutants to investigate the control of microtubule distribution in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. J Cell Sci. 1988 Mar;89(Pt 3):343–357. doi: 10.1242/jcs.89.3.343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Healy A. M., Zolnierowicz S., Stapleton A. E., Goebl M., DePaoli-Roach A. A., Pringle J. R. CDC55, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene involved in cellular morphogenesis: identification, characterization, and homology to the B subunit of mammalian type 2A protein phosphatase. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;11(11):5767–5780. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.11.5767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano T., Hiraoka Y., Yanagida M. A temperature-sensitive mutation of the Schizosaccharomyces pombe gene nuc2+ that encodes a nuclear scaffold-like protein blocks spindle elongation in mitotic anaphase. J Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;106(4):1171–1183. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.4.1171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T. A thousand and one protein kinases. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):823–829. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90509-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita N., Goebl M., Yanagida M. The fission yeast dis3+ gene encodes a 110-kDa essential protein implicated in mitotic control. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;11(12):5839–5847. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.12.5839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita N., Ohkura H., Yanagida M. Distinct, essential roles of type 1 and 2A protein phosphatases in the control of the fission yeast cell division cycle. Cell. 1990 Oct 19;63(2):405–415. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90173-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y., Ishii S., Tokai M., Tsutsumi H., Ohki O., Akada R., Tanaka K., Tsuchiya E., Fukui S., Miyakawa T. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae genes (CMP1 and CMP2) encoding calmodulin-binding proteins homologous to the catalytic subunit of mammalian protein phosphatase 2B. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 May;227(1):52–59. doi: 10.1007/BF00260706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto T., Beach D. Interaction of the pim1/spi1 mitotic checkpoint with a protein phosphatase. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Mar;4(3):337–345. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.3.337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto T., Beach D. Premature initiation of mitosis in yeast lacking RCC1 or an interacting GTPase. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):347–360. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90624-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maundrell K. nmt1 of fission yeast. A highly transcribed gene completely repressed by thiamine. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 5;265(19):10857–10864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurse P., Thuriaux P., Nasmyth K. Genetic control of the cell division cycle in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Jul 23;146(2):167–178. doi: 10.1007/BF00268085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkura H., Adachi Y., Kinoshita N., Niwa O., Toda T., Yanagida M. Cold-sensitive and caffeine-supersensitive mutants of the Schizosaccharomyces pombe dis genes implicated in sister chromatid separation during mitosis. EMBO J. 1988 May;7(5):1465–1473. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02964.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkura H., Kinoshita N., Miyatani S., Toda T., Yanagida M. The fission yeast dis2+ gene required for chromosome disjoining encodes one of two putative type 1 protein phosphatases. Cell. 1989 Jun 16;57(6):997–1007. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90338-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkura H., Yanagida M. S. pombe gene sds22+ essential for a midmitotic transition encodes a leucine-rich repeat protein that positively modulates protein phosphatase-1. Cell. 1991 Jan 11;64(1):149–157. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90216-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtsubo M., Kai R., Furuno N., Sekiguchi T., Sekiguchi M., Hayashida H., Kuma K., Miyata T., Fukushige S., Murotsu T. Isolation and characterization of the active cDNA of the human cell cycle gene (RCC1) involved in the regulation of onset of chromosome condensation. Genes Dev. 1987 Aug;1(6):585–593. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.6.585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posas F., Casamayor A., Morral N., Ariño J. Molecular cloning and analysis of a yeast protein phosphatase with an unusual amino-terminal region. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 15;267(17):11734–11740. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronne H., Carlberg M., Hu G. Z., Nehlin J. O. Protein phosphatase 2A in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: effects on cell growth and bud morphogenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):4876–4884. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.4876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. J. One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:202–211. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P., Nurse P. Negative regulation of mitosis by wee1+, a gene encoding a protein kinase homolog. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):559–567. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90458-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P., Nurse P. cdc25+ functions as an inducer in the mitotic control of fission yeast. Cell. 1986 Apr 11;45(1):145–153. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90546-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sneddon A. A., Cohen P. T., Stark M. J. Saccharomyces cerevisiae protein phosphatase 2A performs an essential cellular function and is encoded by two genes. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4339–4346. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07883.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone E. M., Yamano H., Kinoshita N., Yanagida M. Mitotic regulation of protein phosphatases by the fission yeast sds22 protein. Curr Biol. 1993 Jan;3(1):13–26. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(93)90140-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton A., Immanuel D., Arndt K. T. The SIT4 protein phosphatase functions in late G1 for progression into S phase. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):2133–2148. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.2133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda T., Shimanuki M., Yanagida M. Fission yeast genes that confer resistance to staurosporine encode an AP-1-like transcription factor and a protein kinase related to the mammalian ERK1/MAP2 and budding yeast FUS3 and KSS1 kinases. Genes Dev. 1991 Jan;5(1):60–73. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.1.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda T., Yamamoto M., Yanagida M. Sequential alterations in the nuclear chromatin region during mitosis of the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe: video fluorescence microscopy of synchronously growing wild-type and cold-sensitive cdc mutants by using a DNA-binding fluorescent probe. J Cell Sci. 1981 Dec;52:271–287. doi: 10.1242/jcs.52.1.271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R. B., Tatchell K. SRA5 encodes the low-Km cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):505–510. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods A., Sherwin T., Sasse R., MacRae T. H., Baines A. J., Gull K. Definition of individual components within the cytoskeleton of Trypanosoma brucei by a library of monoclonal antibodies. J Cell Sci. 1989 Jul;93(Pt 3):491–500. doi: 10.1242/jcs.93.3.491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagida M., Kinoshita N., Stone E. M., Yamano H. Protein phosphatases and cell division cycle control. Ciba Found Symp. 1992;170:130–146. doi: 10.1002/9780470514320.ch9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]