Abstract
In the title compound, C21H33N4S3 3+·3I−, three secondary amines are protonated, while the central amine remains unprotonated. One thiophene is disordered with an occupancy ratio of 0.868 (6)/0.132 (6). Each protonated amine is involved in N—H⋯I hydrogen-bonding interactions with the iodide anions.
Related literature
For general background to anion hosts, see: Bianchi et al. (1997 ▶); Kang et al. (2005 ▶); Hossain (2008 ▶); For related structures, see: Bazzicalupi et al. (2009 ▶); Hossain et al. (2002 ▶, 2004 ▶); Burgess et al. (1991 ▶); Saeed et al. (2010 ▶).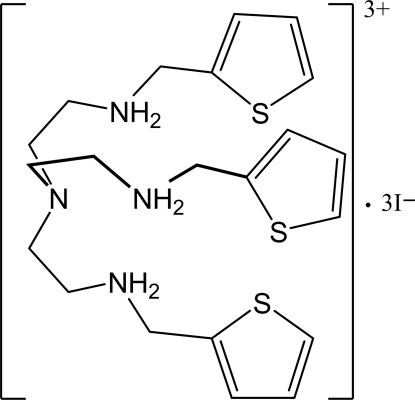
Experimental
Crystal data
C21H33N4S3 3+·3I−
M r = 818.42
Orthorhombic,
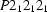
a = 10.5433 (5) Å
b = 11.4203 (6) Å
c = 24.5107 (15) Å
V = 2951.3 (3) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 3.41 mm−1
T = 90 K
0.20 × 0.17 × 0.15 mm
Data collection
Nonius KappaCCD diffractometer with Oxford Cryostream
Absorption correction: multi-scan (HKL SCALEPACK; Otwinowski & Minor, 1997 ▶) T min = 0.549, T max = 0.629
90447 measured reflections
10653 independent reflections
9446 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.069
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.038
wR(F 2) = 0.093
S = 1.04
10653 reflections
277 parameters
30 restraints
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 2.96 e Å−3
Δρmin = −2.18 e Å−3
Absolute structure: Flack (1983 ▶), 4708 Friedel pairs
Flack parameter: 0.02 (2)
Data collection: COLLECT (Nonius, 2000 ▶); cell refinement: DENZO and SCALEPACK (Otwinowski & Minor, 1997 ▶); data reduction: DENZO and SCALEPACK; program(s) used to solve structure: SIR97 (Altomare et al., 1999 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP–3 (Farrugia, 1997 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810039462/rk2235sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810039462/rk2235Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2—H21N⋯I1i | 0.92 | 2.79 | 3.557 (4) | 142 |
| N2—H22N⋯I2 | 0.92 | 2.67 | 3.543 (4) | 160 |
| N3—H31N⋯I1 | 0.92 | 2.78 | 3.547 (3) | 142 |
| N3—H32N⋯I3 | 0.92 | 2.59 | 3.460 (3) | 158 |
| N4—H41N⋯I1 | 0.92 | 2.73 | 3.553 (4) | 150 |
| N4—H42N⋯I2ii | 0.92 | 2.57 | 3.479 (4) | 172 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 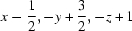 ; (ii)
; (ii) 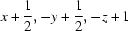 .
.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health, Division of National Center for Research Resources, under grant No. G12RR013459. This material is based upon work supported by the National Science Foundation under CHE–0821357. Purchase of the diffractometer was made possible by grant No. LEQSF (1999–2000)–ENH–TR–13, administered by the Louisiana Board of Regents.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Anions play a key role in many chemical and biological processes. In particular, structural characterization of an anion complex is important in achieving selective hosts for anions (Hossain, 2008, Saeed et al., 2010). Among the numerous systems, trigonal receptors are of interest because of their synthetic simplicity and capability for anion binding though hydrogen bonding interactions. Tris(aminoethyl)–amine is an excellent building block for synthesizing fuctionalized tripodal hosts for anion binding (Burgess et al., 1991; Hossain et al., 2004; Bazzicalupi, et al., 2009). These molecules have been shown to bind a variety of anion including nitrate, phosphate and sulfate (Bianchi et al., 1997; Kang et al., 2005). Herein, we report the molecular structure of the title compound in which three iodides are held by hydrogen bonding with protonated secondary amines.
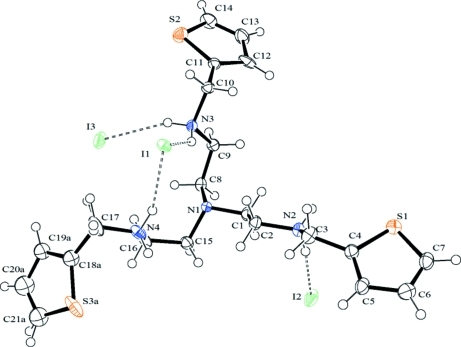
Single crystal analysis of the title compound reveals that the molecule crystallizes in its orthorhombic space group forming a cavity. The tren unit is triply charged, where all three secondary N atoms are protonated. The central amine is not protonated. The three arms form a cavity, and one thiophene unit is disordered. In the complex, the protonated amines are involved in hydrogen bonding interactions with iodide anions having N···I distances 3.460 (3) to 3.553 (4)Å (Fig. 1 and Table 1). One iodide (I1) accepts two hydrogen bonds from two protonated amines (N3 and N4), while each of the other two iodides accepts one hydrogen bond from N2 and N3. Therefore, one secondary nitrogen (N3) donates two hydrogen bonds to two iodides (I1 and I3). The N···I distances are comparable with those observed in an iodide complex of an azacryptand (3.476 (4)Å and 3.632 (4)Å) reported earlier (Hossain et al., 2002).
The disorder of the thiophene ring containing S3 involves two conformations, differing by rotation about two different bonds. One is a twofold rotation about C17—C18, which swaps S3 and C19. Refinement of this type of model resulted in elongated ellipsoids in the plane of the ring for all atoms of the thiophene, as well as unacceptable residual densities. This was interpreted as a second conformational difference involving a difference in rotation about the N4—C17 bond, amounting to a torsional difference of 11.7°.
Experimental
To a solution of 2–thiophene aldehyde (4.60 g, 41 mmol) in diethylether (50 ml) was added tris(2–aminoethyl)amine (2.00 g, 13.7 mmol) in ethanol (50 ml). The mixture was stirred overnight at room temperature, and the solvent was evaporated. After diluting with methanol (100 ml), NaBH4 (2.00 g) was added to convert the imine into the corresponding amine. The reaction mixture was stirred for 24 hrs at room temperature. After evaporation of the solvent, the residue was partitioned in water/CH2Cl2 (50/50 ml). The organic layers were collected and dried with MgSO4 to give an oily product. Yield 4.38 g (74%). 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3, TMS): δ 2.58 (t, 6H, NCH2), 2.69 ((t, 6H, NCH2CH2), 3.95 (s, 6H, ArCH2)), 6.89 (b, 3H, ArH), 6.93 (b, ArH), 7.18 (b, ArH). MS (ESI): m/z (+) 435 (M + H)+. The iodide salt was prepared from the reaction of the free amine (0.20 g, 0.47 mmol) with HI in ethanol. The white precipitate was obtained after evaporation of the solvent. The salt was redissolved in water and ethanol (1:2 v/v, 1 ml) and crystals suitable for X–ray analysis were grown from slow evaporation of the solvent at room temperature.
Refinement
H atoms based on C were placed in idealized positions with C—H distances 0.95Å–0.99Å, N—H distances 0.92Å, and thereafter treated as riding. Uiso for H was assigned as 1.2 times Ueq of the attached atom. The largest residual density peak was 0.81Å from I2, and the deepest hole was 0.59Å from I2. The disorder in the thiophene ring containing S3 was modeled with two orientations having populations 0.868 (6) and 0.132 (6), their geometries being restrained to be the same as that of the thiophene containing S1. This required 30 restraints. Full anisotropic refinement was not successful for the disordered region, and it was necessary to treat nine atoms as isotropic, with a common displacement parameter for the five atoms of the minor contributor thiophene ring. The absolute structure was determined by refinement of the Flack (1983) parameter, based on 4708 Friedel pairs. Six low–angle reflections were given zero weight in the refinement.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The structure of the title compound with the atom numbering scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level. H atoms are presented as small spheres of arbitrary radius. Only major fragment is drawn. The several H bonds are drawn by dashed lines.
Crystal data
| C21H33N4S33+·3I− | F(000) = 1576 |
| Mr = 818.42 | Dx = 1.842 Mg m−3 |
| Orthorhombic, P212121 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: P 2ac 2ab | Cell parameters from 5918 reflections |
| a = 10.5433 (5) Å | θ = 2.5–32.6° |
| b = 11.4203 (6) Å | µ = 3.41 mm−1 |
| c = 24.5107 (15) Å | T = 90 K |
| V = 2951.3 (3) Å3 | Block, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.20 × 0.17 × 0.15 mm |
Data collection
| Nonius KappaCCD diffractometer with Oxford Cryostream | 10653 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine–focus sealed tube | 9446 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.069 |
| ω– and φ–scans | θmax = 32.6°, θmin = 2.6° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (HKL SCALEPACK; Otwinowski & Minor, 1997) | h = −15→15 |
| Tmin = 0.549, Tmax = 0.629 | k = −17→17 |
| 90447 measured reflections | l = −36→36 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.038 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.093 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0425P)2 + 8.7643P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.04 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.003 |
| 10653 reflections | Δρmax = 2.96 e Å−3 |
| 277 parameters | Δρmin = −2.18 e Å−3 |
| 30 restraints | Absolute structure: Flack (1983), 4708 Friedel pairs |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Flack parameter: 0.02 (2) |
Special details
| Geometry. All s.u.'s (except the s.u. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell s.u.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of s.u.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between s.u.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell s.u.'s is used for estimating s.u.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R–factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R–factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R–factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R–factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R–factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | Occ. (<1) | |
| I1 | 0.66009 (2) | 0.80566 (2) | 0.512489 (10) | 0.01937 (5) | |
| I2 | 0.28784 (4) | 0.15756 (3) | 0.526628 (15) | 0.03742 (9) | |
| I3 | 0.69376 (3) | 0.78787 (3) | 0.708662 (14) | 0.03409 (8) | |
| S2 | 0.31359 (12) | 1.01963 (11) | 0.68942 (5) | 0.0312 (2) | |
| N1 | 0.4937 (3) | 0.5219 (3) | 0.59749 (14) | 0.0169 (6) | |
| N2 | 0.3384 (4) | 0.4343 (3) | 0.46508 (14) | 0.0209 (6) | |
| H21N | 0.2630 | 0.4723 | 0.4718 | 0.025* | |
| H22N | 0.3266 | 0.3558 | 0.4717 | 0.025* | |
| N3 | 0.4390 (3) | 0.7677 (3) | 0.62014 (14) | 0.0179 (6) | |
| H31N | 0.4863 | 0.7388 | 0.5916 | 0.021* | |
| H32N | 0.4946 | 0.7922 | 0.6467 | 0.021* | |
| N4 | 0.7721 (4) | 0.5480 (4) | 0.57790 (16) | 0.0247 (7) | |
| H41N | 0.7136 | 0.6020 | 0.5660 | 0.030* | |
| H42N | 0.7851 | 0.4954 | 0.5500 | 0.030* | |
| C1 | 0.3954 (4) | 0.4734 (4) | 0.56157 (18) | 0.0210 (8) | |
| H1A | 0.3155 | 0.5180 | 0.5662 | 0.025* | |
| H1B | 0.3789 | 0.3907 | 0.5713 | 0.025* | |
| C2 | 0.4394 (4) | 0.4811 (4) | 0.50268 (17) | 0.0225 (8) | |
| H2A | 0.4580 | 0.5637 | 0.4933 | 0.027* | |
| H2B | 0.5183 | 0.4352 | 0.4980 | 0.027* | |
| C3 | 0.3761 (5) | 0.4522 (4) | 0.40606 (18) | 0.0273 (9) | |
| H3A | 0.3702 | 0.5367 | 0.3973 | 0.033* | |
| H3B | 0.4657 | 0.4283 | 0.4015 | 0.033* | |
| S1 | 0.13415 (11) | 0.40416 (11) | 0.36040 (5) | 0.0283 (2) | |
| C4 | 0.2957 (4) | 0.3848 (4) | 0.36614 (18) | 0.0251 (8) | |
| C5 | 0.3416 (5) | 0.3115 (4) | 0.32588 (17) | 0.0267 (8) | |
| H5 | 0.4283 | 0.2907 | 0.3217 | 0.032* | |
| C6 | 0.2417 (5) | 0.2710 (4) | 0.29130 (19) | 0.0315 (10) | |
| H6 | 0.2547 | 0.2187 | 0.2617 | 0.038* | |
| C7 | 0.1270 (5) | 0.3147 (4) | 0.30498 (19) | 0.0296 (9) | |
| H7 | 0.0509 | 0.2974 | 0.2858 | 0.036* | |
| C8 | 0.4383 (4) | 0.5616 (4) | 0.64961 (17) | 0.0205 (7) | |
| H8A | 0.5074 | 0.5772 | 0.6760 | 0.025* | |
| H8B | 0.3845 | 0.4985 | 0.6648 | 0.025* | |
| C9 | 0.3594 (4) | 0.6709 (4) | 0.64269 (16) | 0.0196 (7) | |
| H9A | 0.2878 | 0.6549 | 0.6177 | 0.024* | |
| H9B | 0.3240 | 0.6948 | 0.6784 | 0.024* | |
| C10 | 0.3644 (4) | 0.8723 (4) | 0.60019 (17) | 0.0202 (8) | |
| H10A | 0.4240 | 0.9363 | 0.5908 | 0.024* | |
| H10B | 0.3179 | 0.8505 | 0.5666 | 0.024* | |
| C11 | 0.2721 (4) | 0.9156 (4) | 0.64173 (17) | 0.0209 (8) | |
| C12 | 0.1429 (5) | 0.8797 (5) | 0.64632 (19) | 0.0309 (11) | |
| H12 | 0.1017 | 0.8239 | 0.6237 | 0.037* | |
| C13 | 0.0854 (5) | 0.9420 (5) | 0.6908 (2) | 0.0340 (11) | |
| H13 | −0.0005 | 0.9312 | 0.7013 | 0.041* | |
| C14 | 0.1650 (5) | 1.0182 (5) | 0.7170 (2) | 0.0336 (10) | |
| H14 | 0.1403 | 1.0651 | 0.7472 | 0.040* | |
| C15 | 0.5898 (4) | 0.4310 (4) | 0.6089 (2) | 0.0243 (8) | |
| H15A | 0.6016 | 0.3819 | 0.5760 | 0.029* | |
| H15B | 0.5590 | 0.3798 | 0.6387 | 0.029* | |
| C16 | 0.7168 (4) | 0.4837 (4) | 0.62527 (18) | 0.0235 (8) | |
| H16A | 0.7049 | 0.5382 | 0.6563 | 0.028* | |
| H16B | 0.7755 | 0.4208 | 0.6370 | 0.028* | |
| C17 | 0.8947 (4) | 0.6105 (5) | 0.5889 (2) | 0.0337 (11) | |
| H17A | 0.8785 | 0.6789 | 0.6127 | 0.040* | 0.868 (6) |
| H17B | 0.9304 | 0.6396 | 0.5541 | 0.040* | 0.868 (6) |
| H17C | 0.8735 | 0.6876 | 0.6050 | 0.040* | 0.132 (6) |
| H17D | 0.9355 | 0.6258 | 0.5532 | 0.040* | 0.132 (6) |
| S3A | 1.04963 (14) | 0.40627 (17) | 0.58903 (9) | 0.0441 (6) | 0.868 (6) |
| C18A | 0.9893 (7) | 0.5305 (6) | 0.6160 (3) | 0.0322 (13)* | 0.868 (6) |
| C19A | 1.0385 (6) | 0.5521 (6) | 0.6685 (3) | 0.0331 (12)* | 0.868 (6) |
| H19A | 1.0177 | 0.6178 | 0.6905 | 0.040* | 0.868 (6) |
| C20A | 1.1234 (8) | 0.4622 (7) | 0.6835 (3) | 0.0493 (18)* | 0.868 (6) |
| H20A | 1.1680 | 0.4617 | 0.7172 | 0.059* | 0.868 (6) |
| C21A | 1.1351 (8) | 0.3783 (7) | 0.6464 (3) | 0.0448 (17)* | 0.868 (6) |
| H21A | 1.1856 | 0.3103 | 0.6513 | 0.054* | 0.868 (6) |
| S3B | 1.0412 (10) | 0.6016 (10) | 0.6856 (4) | 0.033 (3)* | 0.132 (6) |
| C18B | 0.993 (4) | 0.554 (3) | 0.6254 (12) | 0.033 (3)* | 0.132 (6) |
| C19B | 1.054 (4) | 0.447 (3) | 0.6152 (12) | 0.033 (3)* | 0.132 (6) |
| H19B | 1.0474 | 0.4043 | 0.5819 | 0.040* | 0.132 (6) |
| C20B | 1.128 (4) | 0.408 (2) | 0.6616 (14) | 0.033 (3)* | 0.132 (6) |
| H20B | 1.1692 | 0.3344 | 0.6640 | 0.040* | 0.132 (6) |
| C21B | 1.132 (3) | 0.489 (3) | 0.7001 (13) | 0.033 (3)* | 0.132 (6) |
| H21B | 1.1821 | 0.4833 | 0.7323 | 0.040* | 0.132 (6) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| I1 | 0.01816 (10) | 0.02106 (11) | 0.01888 (10) | 0.00339 (9) | 0.00220 (9) | 0.00444 (9) |
| I2 | 0.0504 (2) | 0.02224 (13) | 0.03961 (17) | −0.01073 (13) | −0.01876 (15) | 0.00445 (12) |
| I3 | 0.03868 (16) | 0.02779 (14) | 0.03580 (15) | −0.00952 (12) | −0.01948 (13) | 0.00415 (12) |
| S2 | 0.0324 (6) | 0.0314 (6) | 0.0298 (5) | 0.0004 (5) | 0.0018 (5) | −0.0100 (4) |
| N1 | 0.0152 (14) | 0.0155 (14) | 0.0200 (15) | 0.0018 (12) | −0.0020 (12) | −0.0027 (12) |
| N2 | 0.0193 (14) | 0.0213 (15) | 0.0221 (15) | −0.0023 (13) | −0.0029 (13) | −0.0018 (12) |
| N3 | 0.0152 (14) | 0.0196 (15) | 0.0189 (15) | −0.0007 (11) | −0.0005 (12) | −0.0024 (12) |
| N4 | 0.0216 (17) | 0.0277 (18) | 0.0248 (17) | 0.0067 (14) | 0.0015 (14) | 0.0108 (14) |
| C1 | 0.0190 (18) | 0.0216 (19) | 0.0223 (18) | −0.0027 (15) | −0.0032 (15) | 0.0002 (15) |
| C2 | 0.0193 (17) | 0.0244 (19) | 0.024 (2) | −0.0032 (15) | 0.0001 (14) | −0.0034 (15) |
| C3 | 0.034 (2) | 0.030 (2) | 0.0179 (18) | −0.0056 (18) | 0.0019 (17) | 0.0004 (16) |
| S1 | 0.0268 (6) | 0.0249 (5) | 0.0334 (6) | 0.0016 (4) | −0.0023 (4) | −0.0020 (4) |
| C4 | 0.0248 (19) | 0.0242 (19) | 0.026 (2) | −0.0003 (17) | −0.0041 (17) | 0.0008 (16) |
| C5 | 0.033 (2) | 0.026 (2) | 0.0215 (17) | −0.0029 (19) | −0.0073 (16) | 0.0021 (16) |
| C6 | 0.047 (3) | 0.028 (2) | 0.0199 (19) | 0.0038 (19) | −0.0049 (19) | 0.0035 (17) |
| C7 | 0.035 (2) | 0.027 (2) | 0.027 (2) | −0.0053 (18) | −0.0090 (17) | 0.0038 (17) |
| C8 | 0.0180 (17) | 0.0239 (19) | 0.0196 (18) | −0.0032 (14) | −0.0006 (14) | 0.0003 (15) |
| C9 | 0.0171 (17) | 0.0211 (18) | 0.0208 (17) | −0.0004 (13) | 0.0043 (13) | −0.0005 (14) |
| C10 | 0.023 (2) | 0.0185 (17) | 0.0191 (17) | 0.0024 (14) | 0.0001 (14) | −0.0026 (13) |
| C11 | 0.0221 (19) | 0.0207 (18) | 0.0200 (18) | 0.0051 (15) | −0.0031 (15) | −0.0042 (14) |
| C12 | 0.030 (2) | 0.040 (3) | 0.0221 (19) | 0.024 (2) | 0.0050 (17) | −0.0012 (18) |
| C13 | 0.025 (2) | 0.044 (3) | 0.034 (2) | 0.010 (2) | −0.0009 (19) | −0.008 (2) |
| C14 | 0.032 (2) | 0.042 (3) | 0.027 (2) | 0.012 (2) | 0.0066 (19) | −0.0079 (19) |
| C15 | 0.0193 (19) | 0.023 (2) | 0.030 (2) | 0.0009 (15) | 0.0007 (15) | 0.0011 (17) |
| C16 | 0.0158 (18) | 0.027 (2) | 0.027 (2) | 0.0045 (15) | 0.0024 (15) | 0.0129 (16) |
| C17 | 0.0174 (19) | 0.043 (3) | 0.041 (3) | 0.0009 (18) | −0.0022 (19) | 0.024 (2) |
| S3A | 0.0175 (6) | 0.0484 (11) | 0.0664 (13) | 0.0046 (6) | 0.0020 (7) | 0.0329 (9) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| S2—C14 | 1.706 (5) | C9—H9B | 0.9900 |
| S2—C11 | 1.723 (4) | C10—C11 | 1.493 (6) |
| N1—C1 | 1.468 (5) | C10—H10A | 0.9900 |
| N1—C8 | 1.476 (5) | C10—H10B | 0.9900 |
| N1—C15 | 1.477 (6) | C11—C12 | 1.427 (7) |
| N2—C2 | 1.506 (5) | C12—C13 | 1.436 (7) |
| N2—C3 | 1.514 (6) | C12—H12 | 0.9500 |
| N2—H21N | 0.9200 | C13—C14 | 1.368 (8) |
| N2—H22N | 0.9200 | C13—H13 | 0.9500 |
| N3—C9 | 1.493 (5) | C14—H14 | 0.9500 |
| N3—C10 | 1.512 (5) | C15—C16 | 1.522 (6) |
| N3—H31N | 0.9200 | C15—H15A | 0.9900 |
| N3—H32N | 0.9200 | C15—H15B | 0.9900 |
| N4—C16 | 1.492 (5) | C16—H16A | 0.9900 |
| N4—C17 | 1.501 (6) | C16—H16B | 0.9900 |
| N4—H41N | 0.9200 | C17—C18A | 1.507 (8) |
| N4—H42N | 0.9200 | C17—C18B | 1.51 (2) |
| C1—C2 | 1.519 (6) | C17—H17A | 0.9900 |
| C1—H1A | 0.9900 | C17—H17B | 0.9900 |
| C1—H1B | 0.9900 | C17—H17C | 0.9900 |
| C2—H2A | 0.9900 | C17—H17D | 0.9900 |
| C2—H2B | 0.9900 | S3A—C18A | 1.690 (6) |
| C3—C4 | 1.506 (6) | S3A—C21A | 1.700 (7) |
| C3—H3A | 0.9900 | C18A—C19A | 1.409 (8) |
| C3—H3B | 0.9900 | C19A—C20A | 1.411 (9) |
| S1—C7 | 1.702 (5) | C19A—H19A | 0.9500 |
| S1—C4 | 1.724 (5) | C20A—C21A | 1.327 (10) |
| C4—C5 | 1.382 (6) | C20A—H20A | 0.9500 |
| C5—C6 | 1.429 (6) | C21A—H21A | 0.9500 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9500 | S3B—C21B | 1.641 (16) |
| C6—C7 | 1.350 (7) | S3B—C18B | 1.655 (16) |
| C6—H6 | 0.9500 | C18B—C19B | 1.406 (17) |
| C7—H7 | 0.9500 | C19B—C20B | 1.448 (17) |
| C8—C9 | 1.510 (6) | C19B—H19B | 0.9500 |
| C8—H8A | 0.9900 | C20B—C21B | 1.322 (17) |
| C8—H8B | 0.9900 | C20B—H20B | 0.9500 |
| C9—H9A | 0.9900 | C21B—H21B | 0.9500 |
| C14—S2—C11 | 91.7 (2) | H10A—C10—H10B | 107.9 |
| C1—N1—C8 | 110.8 (3) | C12—C11—C10 | 125.5 (4) |
| C1—N1—C15 | 109.5 (3) | C12—C11—S2 | 112.8 (3) |
| C8—N1—C15 | 108.9 (3) | C10—C11—S2 | 121.7 (3) |
| C2—N2—C3 | 110.6 (3) | C11—C12—C13 | 108.7 (5) |
| C2—N2—H21N | 109.5 | C11—C12—H12 | 125.7 |
| C3—N2—H21N | 109.5 | C13—C12—H12 | 125.7 |
| C2—N2—H22N | 109.5 | C14—C13—C12 | 114.3 (5) |
| C3—N2—H22N | 109.5 | C14—C13—H13 | 122.8 |
| H21N—N2—H22N | 108.1 | C12—C13—H13 | 122.8 |
| C9—N3—C10 | 114.3 (3) | C13—C14—S2 | 112.6 (4) |
| C9—N3—H31N | 108.7 | C13—C14—H14 | 123.7 |
| C10—N3—H31N | 108.7 | S2—C14—H14 | 123.7 |
| C9—N3—H32N | 108.7 | N1—C15—C16 | 112.1 (4) |
| C10—N3—H32N | 108.7 | N1—C15—H15A | 109.2 |
| H31N—N3—H32N | 107.6 | C16—C15—H15A | 109.2 |
| C16—N4—C17 | 115.5 (4) | N1—C15—H15B | 109.2 |
| C16—N4—H41N | 108.4 | C16—C15—H15B | 109.2 |
| C17—N4—H41N | 108.4 | H15A—C15—H15B | 107.9 |
| C16—N4—H42N | 108.4 | N4—C16—C15 | 109.5 (4) |
| C17—N4—H42N | 108.4 | N4—C16—H16A | 109.8 |
| H41N—N4—H42N | 107.5 | C15—C16—H16A | 109.8 |
| N1—C1—C2 | 109.4 (3) | N4—C16—H16B | 109.8 |
| N1—C1—H1A | 109.8 | C15—C16—H16B | 109.8 |
| C2—C1—H1A | 109.8 | H16A—C16—H16B | 108.2 |
| N1—C1—H1B | 109.8 | N4—C17—C18A | 111.1 (5) |
| C2—C1—H1B | 109.8 | N4—C17—C18B | 119.4 (19) |
| H1A—C1—H1B | 108.2 | N4—C17—H17A | 109.4 |
| N2—C2—C1 | 110.2 (3) | C18A—C17—H17A | 109.4 |
| N2—C2—H2A | 109.6 | C18B—C17—H17A | 96.2 |
| C1—C2—H2A | 109.6 | N4—C17—H17B | 109.4 |
| N2—C2—H2B | 109.6 | C18A—C17—H17B | 109.4 |
| C1—C2—H2B | 109.6 | C18B—C17—H17B | 113.2 |
| H2A—C2—H2B | 108.1 | H17A—C17—H17B | 108.0 |
| C4—C3—N2 | 113.8 (4) | N4—C17—H17C | 107.5 |
| C4—C3—H3A | 108.8 | C18A—C17—H17C | 120.9 |
| N2—C3—H3A | 108.8 | C18B—C17—H17C | 107.5 |
| C4—C3—H3B | 108.8 | H17B—C17—H17C | 97.5 |
| N2—C3—H3B | 108.8 | N4—C17—H17D | 107.5 |
| H3A—C3—H3B | 107.7 | C18A—C17—H17D | 102.1 |
| C7—S1—C4 | 91.8 (2) | C18B—C17—H17D | 107.5 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 125.2 (4) | H17A—C17—H17D | 117.2 |
| C5—C4—S1 | 111.5 (3) | H17C—C17—H17D | 107.0 |
| C3—C4—S1 | 122.9 (4) | C18A—S3A—C21A | 91.9 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 111.2 (4) | C19A—C18A—C17 | 122.7 (6) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 124.4 | C19A—C18A—S3A | 111.4 (5) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 124.4 | C17—C18A—S3A | 125.8 (5) |
| C7—C6—C5 | 113.2 (4) | C18A—C19A—C20A | 110.2 (6) |
| C7—C6—H6 | 123.4 | C18A—C19A—H19A | 124.9 |
| C5—C6—H6 | 123.4 | C20A—C19A—H19A | 124.9 |
| C6—C7—S1 | 112.3 (4) | C21A—C20A—C19A | 113.9 (7) |
| C6—C7—H7 | 123.8 | C21A—C20A—H20A | 123.0 |
| S1—C7—H7 | 123.8 | C19A—C20A—H20A | 123.0 |
| N1—C8—C9 | 112.0 (3) | C20A—C21A—S3A | 112.5 (6) |
| N1—C8—H8A | 109.2 | C20A—C21A—H21A | 123.8 |
| C9—C8—H8A | 109.2 | S3A—C21A—H21A | 123.8 |
| N1—C8—H8B | 109.2 | C21B—S3B—C18B | 96.6 (11) |
| C9—C8—H8B | 109.2 | C19B—C18B—C17 | 125.6 (18) |
| H8A—C8—H8B | 107.9 | C19B—C18B—S3B | 107.7 (14) |
| N3—C9—C8 | 110.1 (3) | C17—C18B—S3B | 126.6 (17) |
| N3—C9—H9A | 109.6 | C18B—C19B—C20B | 111.8 (16) |
| C8—C9—H9A | 109.6 | C18B—C19B—H19B | 124.1 |
| N3—C9—H9B | 109.6 | C20B—C19B—H19B | 124.1 |
| C8—C9—H9B | 109.6 | C21B—C20B—C19B | 111.5 (17) |
| H9A—C9—H9B | 108.1 | C21B—C20B—H20B | 124.2 |
| C11—C10—N3 | 112.3 (3) | C19B—C20B—H20B | 124.2 |
| C11—C10—H10A | 109.1 | C20B—C21B—S3B | 111.9 (15) |
| N3—C10—H10A | 109.1 | C20B—C21B—H21B | 124.0 |
| C11—C10—H10B | 109.1 | S3B—C21B—H21B | 124.0 |
| N3—C10—H10B | 109.1 | ||
| C8—N1—C1—C2 | 156.4 (4) | C1—N1—C15—C16 | 156.8 (4) |
| C15—N1—C1—C2 | −83.5 (4) | C8—N1—C15—C16 | −82.0 (4) |
| C3—N2—C2—C1 | 174.6 (4) | C17—N4—C16—C15 | 176.8 (4) |
| N1—C1—C2—N2 | −178.7 (3) | N1—C15—C16—N4 | −66.4 (5) |
| C2—N2—C3—C4 | 167.0 (4) | C16—N4—C17—C18A | 50.2 (6) |
| N2—C3—C4—C5 | −128.0 (5) | C16—N4—C17—C18B | 38.5 (15) |
| N2—C3—C4—S1 | 60.0 (5) | N4—C17—C18A—C19A | −118.1 (7) |
| C7—S1—C4—C5 | 0.3 (4) | C18B—C17—C18A—C19A | 12 (9) |
| C7—S1—C4—C3 | 173.3 (4) | N4—C17—C18A—S3A | 61.9 (7) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −173.7 (4) | C18B—C17—C18A—S3A | −168 (10) |
| S1—C4—C5—C6 | −0.9 (5) | C21A—S3A—C18A—C19A | 2.0 (6) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | 1.1 (6) | C21A—S3A—C18A—C17 | −178.0 (7) |
| C5—C6—C7—S1 | −0.9 (6) | C17—C18A—C19A—C20A | 179.3 (7) |
| C4—S1—C7—C6 | 0.3 (4) | S3A—C18A—C19A—C20A | −0.7 (8) |
| C1—N1—C8—C9 | −71.3 (4) | C18A—C19A—C20A—C21A | −1.4 (10) |
| C15—N1—C8—C9 | 168.2 (3) | C19A—C20A—C21A—S3A | 3.0 (10) |
| C10—N3—C9—C8 | 167.4 (3) | C18A—S3A—C21A—C20A | −2.9 (7) |
| N1—C8—C9—N3 | −59.3 (4) | N4—C17—C18B—C19B | 62 (5) |
| C9—N3—C10—C11 | 51.0 (4) | C18A—C17—C18B—C19B | 7(6) |
| N3—C10—C11—C12 | −91.8 (5) | N4—C17—C18B—S3B | −114 (3) |
| N3—C10—C11—S2 | 89.5 (4) | C18A—C17—C18B—S3B | −169 (13) |
| C14—S2—C11—C12 | 0.6 (4) | C21B—S3B—C18B—C19B | −2(4) |
| C14—S2—C11—C10 | 179.4 (4) | C21B—S3B—C18B—C17 | 175 (4) |
| C10—C11—C12—C13 | −179.4 (4) | C17—C18B—C19B—C20B | −172 (4) |
| S2—C11—C12—C13 | −0.6 (5) | S3B—C18B—C19B—C20B | 5(5) |
| C11—C12—C13—C14 | 0.3 (6) | C18B—C19B—C20B—C21B | −7(6) |
| C12—C13—C14—S2 | 0.1 (6) | C19B—C20B—C21B—S3B | 5(5) |
| C11—S2—C14—C13 | −0.4 (4) | C18B—S3B—C21B—C20B | −2(4) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N2—H21N···I1i | 0.92 | 2.79 | 3.557 (4) | 142 |
| N2—H22N···I2 | 0.92 | 2.67 | 3.543 (4) | 160 |
| N3—H31N···I1 | 0.92 | 2.78 | 3.547 (3) | 142 |
| N3—H32N···I3 | 0.92 | 2.59 | 3.460 (3) | 158 |
| N4—H41N···I1 | 0.92 | 2.73 | 3.553 (4) | 150 |
| N4—H42N···I2ii | 0.92 | 2.57 | 3.479 (4) | 172 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x−1/2, −y+3/2, −z+1; (ii) x+1/2, −y+1/2, −z+1.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: RK2235).
References
- Altomare, A., Burla, M. C., Camalli, M., Cascarano, G. L., Giacovazzo, C., Guagliardi, A., Moliterni, A. G. G., Polidori, G. & Spagna, R. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst.32, 115–119.
- Bazzicalupi, C., Bencini, A., Bianchi, A., Danesi, A., Giorgi, C. & Valtancoli, B. (2009). Inorg. Chem.48, 2391–2398. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Bianchi, A., García-España, E. & Bowman-James, K. (1997). Supramolecular Chemistry of Anions. New York: Wiley–VCH.
- Burgess, J., Al-Alousy, A., Fawcett, J. & Russell, D. R. (1991). Acta Cryst. C47, 2506–2508.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst.30, 565.
- Flack, H. D. (1983). Acta Cryst. A39, 876–881.
- Hossain, M. A. (2008). Curr. Org. Chem.12, 1231–1256.
- Hossain, M. A., Lilinares, J. M., Powell, R. D. & Bowman-James, K. (2002). J. Supramol. Chem.2, 143–151.
- Hossain, M. A., Liljegren, J. A., Powell, R. D. & Bowman-James, K. (2004). Inorg. Chem.43, 3751–3755. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Kang, S. O., Hossain, M. A., Powell, D. & Bowman-James, K. (2005). Chem. Commun. pp. 328–330. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Nonius (2000). COLLECT. Nonius BV, Delft, The Netherlands.
- Otwinowski, Z. & Minor, W. (1997). Methods in Enzymology, Vol. 276, Macromolecular Crystallography, Part A, edited by C. W. Carter Jr & R. M. Sweet, pp. 307–326. New York: Academic Press.
- Saeed, M. A., Fronczek, F. R. & Hossain, M. A. (2010). Acta Cryst. E66, o656–o657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810039462/rk2235sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810039462/rk2235Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report