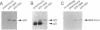Abstract
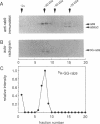
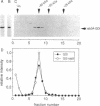
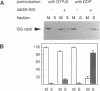
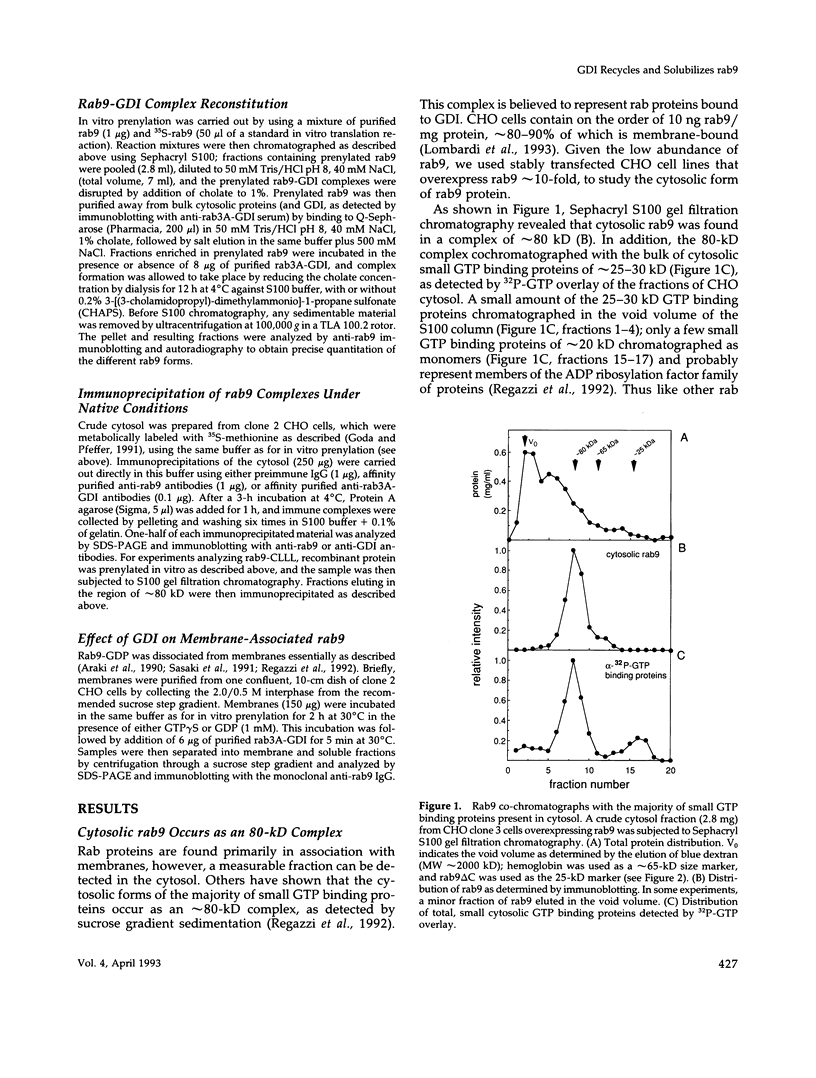
Rab proteins are thought to function in the processes by which transport vesicles identify and/or fuse with their respective target membranes. The bulk of these proteins are membrane associated, but a measurable fraction can be found in the cytosol. The cytosolic forms of rab3A, rab11, and Sec4 occur as equimolar complexes with a class of proteins termed "GDIs," or "GDP dissociation inhibitors." We show here that the cytosolic form of rab9, a protein required for transport between late endosomes and the trans Golgi network, also occurs as a complex with a GDI-like protein, with an apparent mass of approximately 80 kD. Complex formation could be reconstituted in vitro using recombinant rab9 protein, cytosol, ATP, and geranylgeranyl diphosphate, and was shown to require an intact rab9 carboxy terminus, as well as rab9 geranylgeranylation. Monoprenylation was sufficient for complex formation because a mutant rab9 protein bearing the carboxy terminal sequence, CLLL, was prenylated in vitro by geranylgeranyl transferase I and was efficiently incorporated into 80-kD complexes. Purified, prenylated rab9 could also assemble into 80-kD complexes by addition of purified, rab3A GDI. Finally, rab3A-GDI had the capacity to solubilize rab9GDP, but not rab9GTP, from cytoplasmic membranes. These findings support the proposal that GDI proteins serve to recycle rab proteins from their target membranes after completion of a rab protein-mediated, catalytic cycle. Thus GDI proteins have the potential to regulate the availability of specific intracellular transport factors.
Full text
PDF

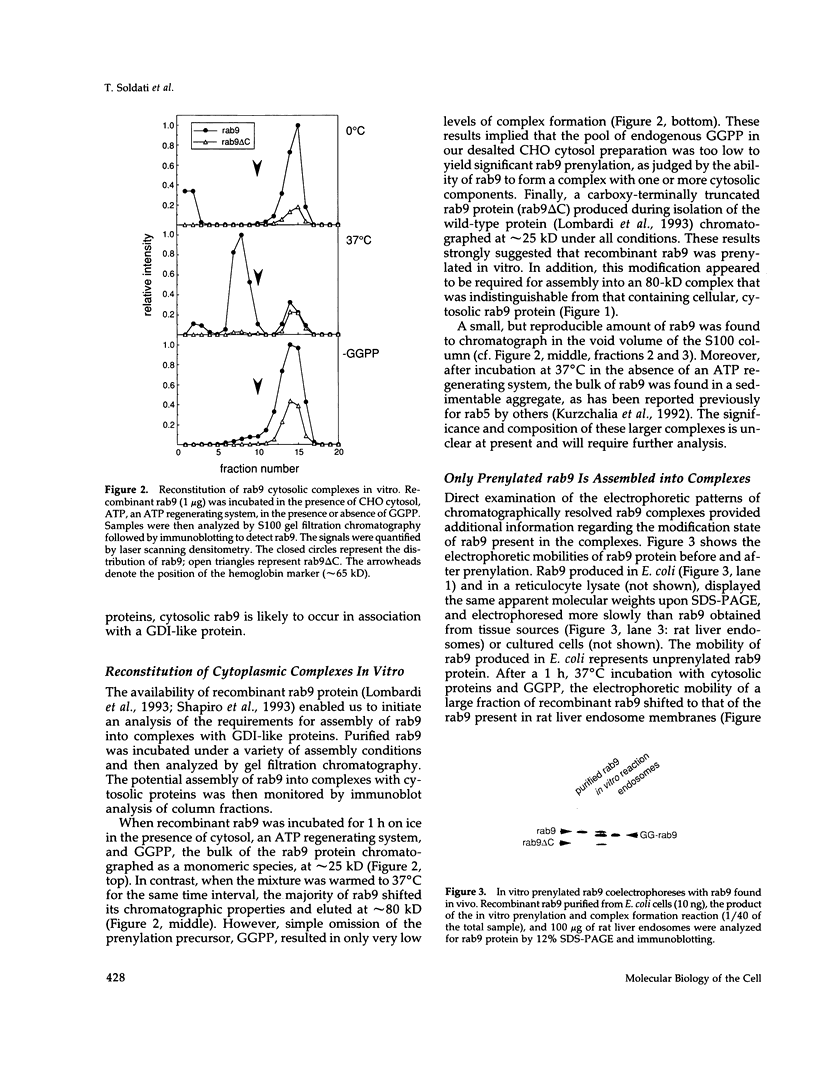
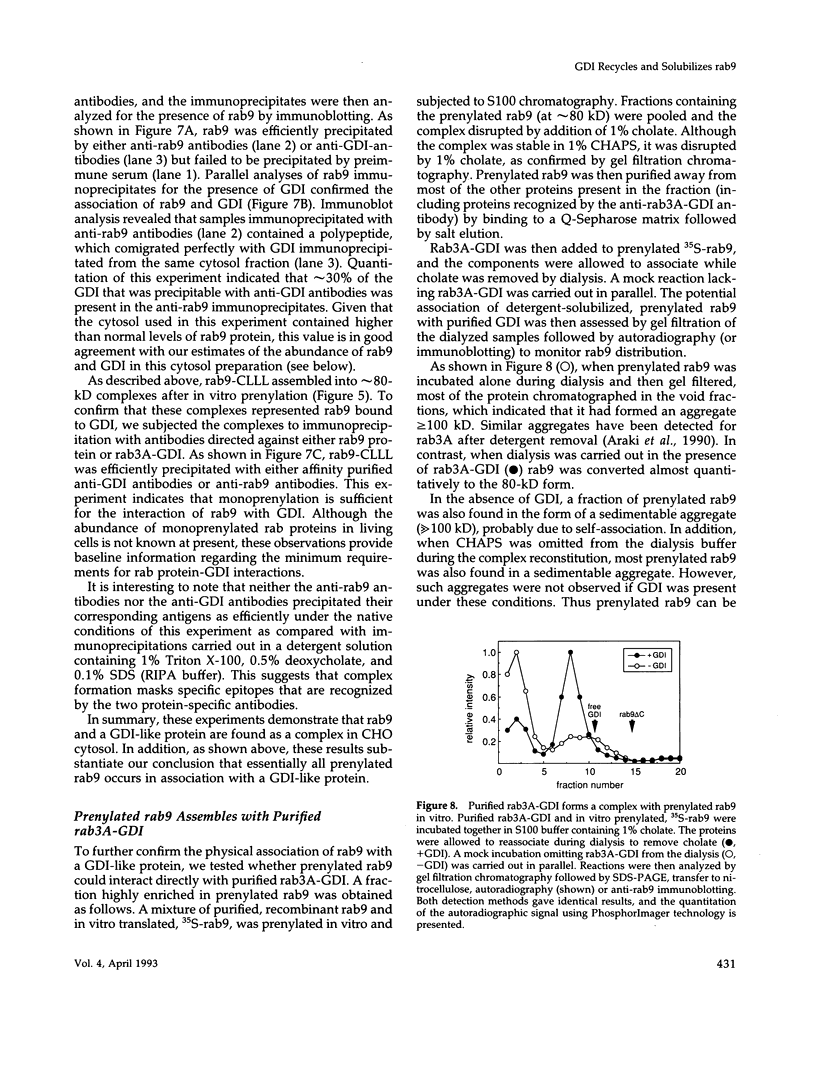
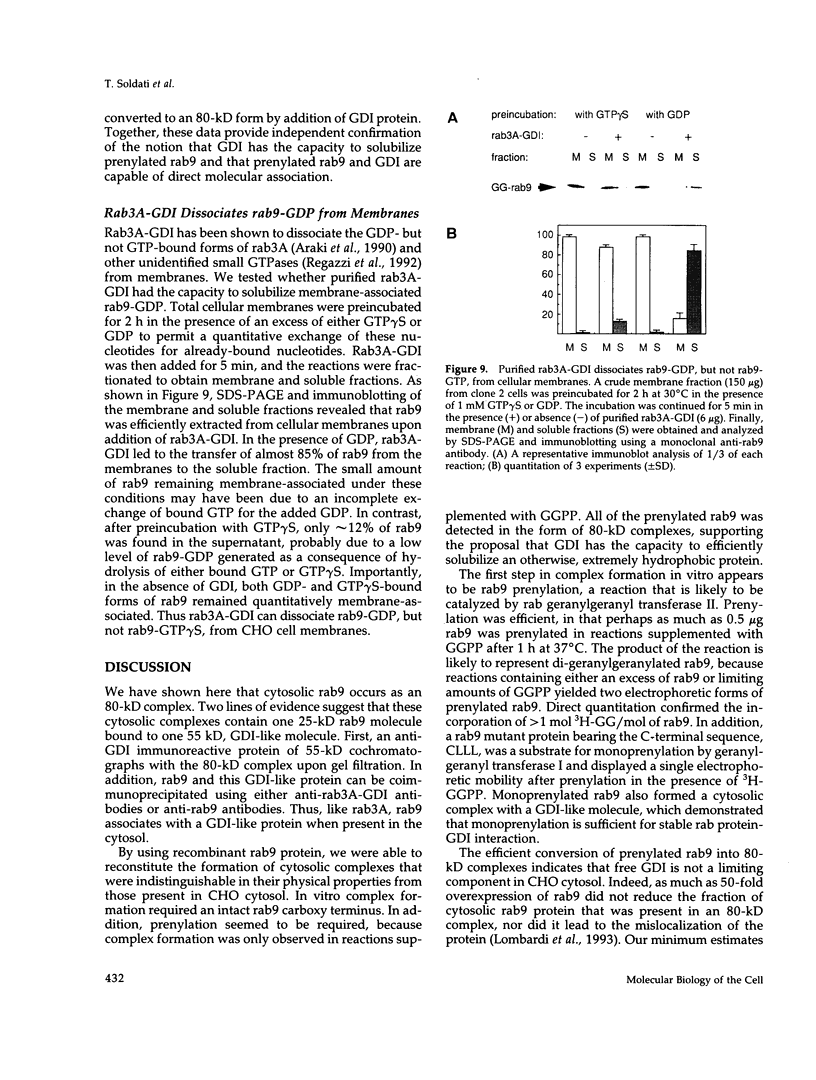


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Araki S., Kikuchi A., Hata Y., Isomura M., Takai Y. Regulation of reversible binding of smg p25A, a ras p21-like GTP-binding protein, to synaptic plasma membranes and vesicles by its specific regulatory protein, GDP dissociation inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):13007–13015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balch W. E., Dunphy W. G., Braell W. A., Rothman J. E. Reconstitution of the transport of protein between successive compartments of the Golgi measured by the coupled incorporation of N-acetylglucosamine. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(2 Pt 1):405–416. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90019-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
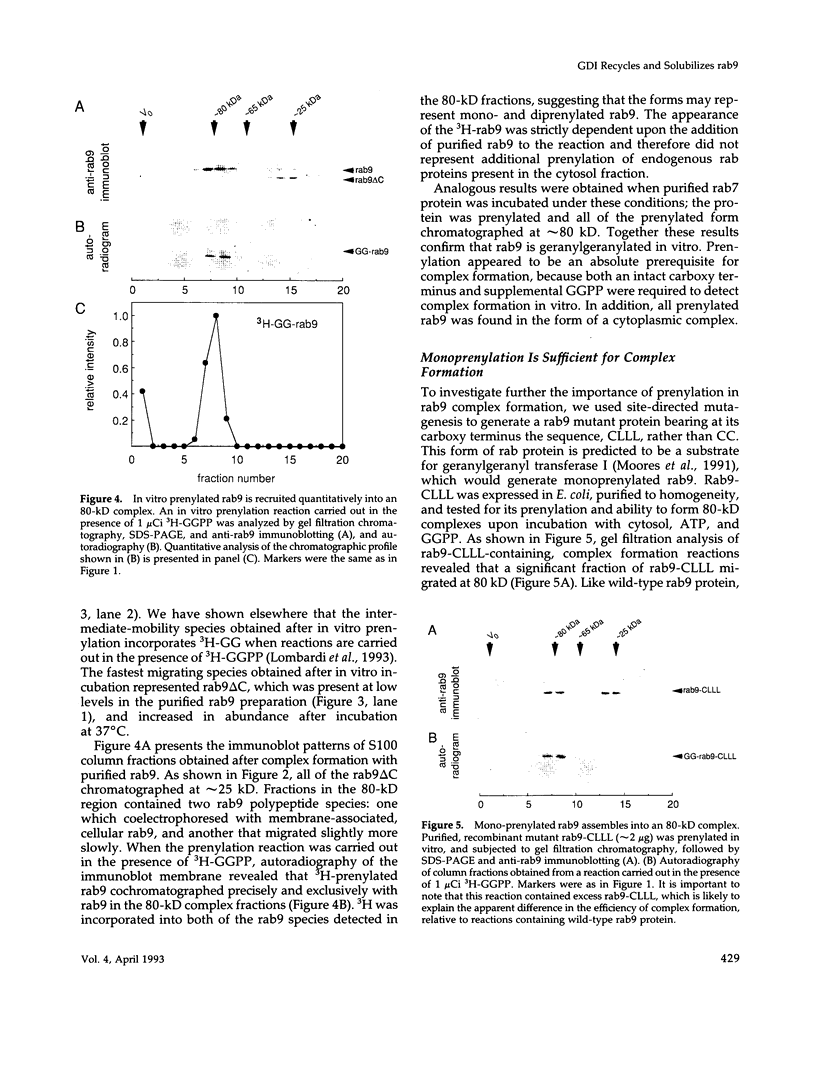
- Balch W. E. Small GTP-binding proteins in vesicular transport. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Dec;15(12):473–477. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90301-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: conserved structure and molecular mechanism. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):117–127. doi: 10.1038/349117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goda Y., Pfeffer S. R. Identification of a novel, N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive cytosolic factor required for vesicular transport from endosomes to the trans-Golgi network in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;112(5):823–831. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.5.823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goda Y., Pfeffer S. R. Selective recycling of the mannose 6-phosphate/IGF-II receptor to the trans Golgi network in vitro. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):309–320. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90054-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
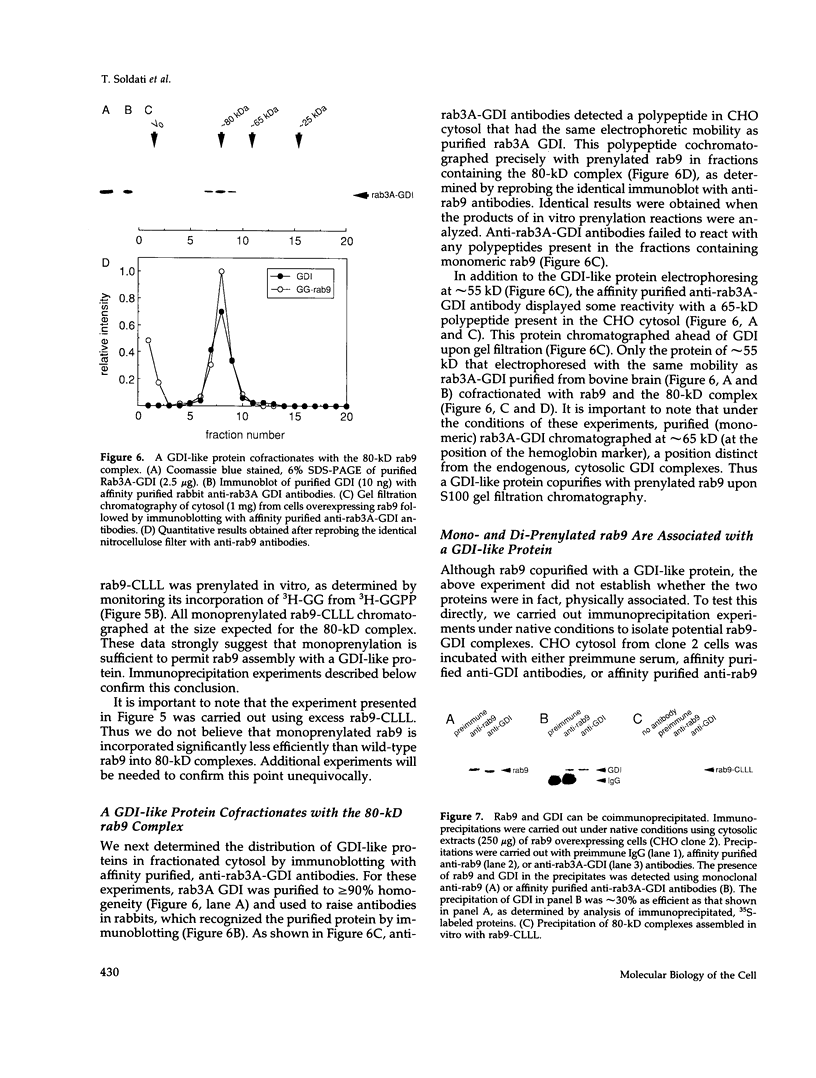
- Gorvel J. P., Chavrier P., Zerial M., Gruenberg J. rab5 controls early endosome fusion in vitro. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):915–925. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90316-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goud B., McCaffrey M. Small GTP-binding proteins and their role in transport. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;3(4):626–633. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90033-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall A. Ras-related GTPases and the cytoskeleton. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 May;3(5):475–479. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.5.475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurzchalia T. V., Gorvel J. P., Dupree P., Parton R., Kellner R., Houthaeve T., Gruenberg J., Simons K. Interactions of rab5 with cytosolic proteins. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 15;267(26):18419–18423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombardi D., Soldati T., Riederer M. A., Goda Y., Zerial M., Pfeffer S. R. Rab9 functions in transport between late endosomes and the trans Golgi network. EMBO J. 1993 Feb;12(2):677–682. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05701.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee T., Newman C. The role of lipid anchors for small G proteins in membrane trafficking. Trends Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;2(11):318–323. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(92)90172-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui Y., Kikuchi A., Araki S., Hata Y., Kondo J., Teranishi Y., Takai Y. Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel type of regulatory protein (GDI) for smg p25A, a ras p21-like GTP-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4116–4122. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moores S. L., Schaber M. D., Mosser S. D., Rands E., O'Hara M. B., Garsky V. M., Marshall M. S., Pompliano D. L., Gibbs J. B. Sequence dependence of protein isoprenylation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 5;266(22):14603–14610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick P., Field C., Schekman R. Identification of 23 complementation groups required for post-translational events in the yeast secretory pathway. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):205–215. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90128-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer S. R. GTP-binding proteins in intracellular transport. Trends Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;2(2):41–46. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(92)90161-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plutner H., Cox A. D., Pind S., Khosravi-Far R., Bourne J. R., Schwaninger R., Der C. J., Balch W. E. Rab1b regulates vesicular transport between the endoplasmic reticulum and successive Golgi compartments. J Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;115(1):31–43. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regazzi R., Kikuchi A., Takai Y., Wollheim C. B. The small GTP-binding proteins in the cytosol of insulin-secreting cells are complexed to GDP dissociation inhibitor proteins. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 5;267(25):17512–17519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rexach M. F., Schekman R. W. Distinct biochemical requirements for the budding, targeting, and fusion of ER-derived transport vesicles. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;114(2):219–229. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.2.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salminen A., Novick P. J. A ras-like protein is required for a post-Golgi event in yeast secretion. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):527–538. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90455-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki T., Kaibuchi K., Kabcenell A. K., Novick P. J., Takai Y. A mammalian inhibitory GDP/GTP exchange protein (GDP dissociation inhibitor) for smg p25A is active on the yeast SEC4 protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2909–2912. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki T., Kikuchi A., Araki S., Hata Y., Isomura M., Kuroda S., Takai Y. Purification and characterization from bovine brain cytosol of a protein that inhibits the dissociation of GDP from and the subsequent binding of GTP to smg p25A, a ras p21-like GTP-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 5;265(4):2333–2337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segev N. Mediation of the attachment or fusion step in vesicular transport by the GTP-binding Ypt1 protein. Science. 1991 Jun 14;252(5012):1553–1556. doi: 10.1126/science.1904626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serafini T., Orci L., Amherdt M., Brunner M., Kahn R. A., Rothman J. E. ADP-ribosylation factor is a subunit of the coat of Golgi-derived COP-coated vesicles: a novel role for a GTP-binding protein. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):239–253. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90176-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro A. D., Riederer M. A., Pfeffer S. R. Biochemical analysis of rab9, a ras-like GTPase involved in protein transport from late endosomes to the trans Golgi network. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 5;268(10):6925–6931. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda T., Takeyama Y., Ohmori T., Ohyanagi H., Saitoh Y., Takai Y. Purification and characterization from rat liver cytosol of a GDP dissociation inhibitor (GDI) for liver 24K G, a ras p21-like GTP-binding protein, with properties similar to those of smg p25A GDI. Biochemistry. 1991 Jan 29;30(4):909–917. doi: 10.1021/bi00218a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]