Abstract
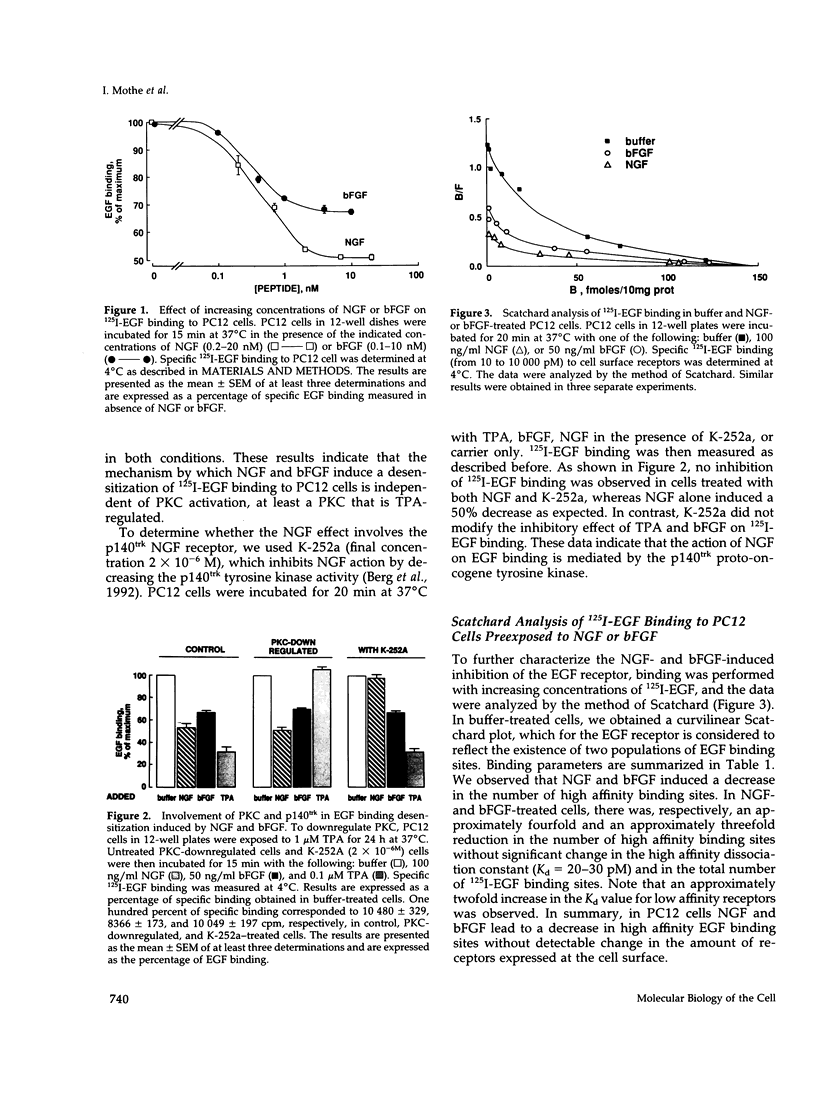
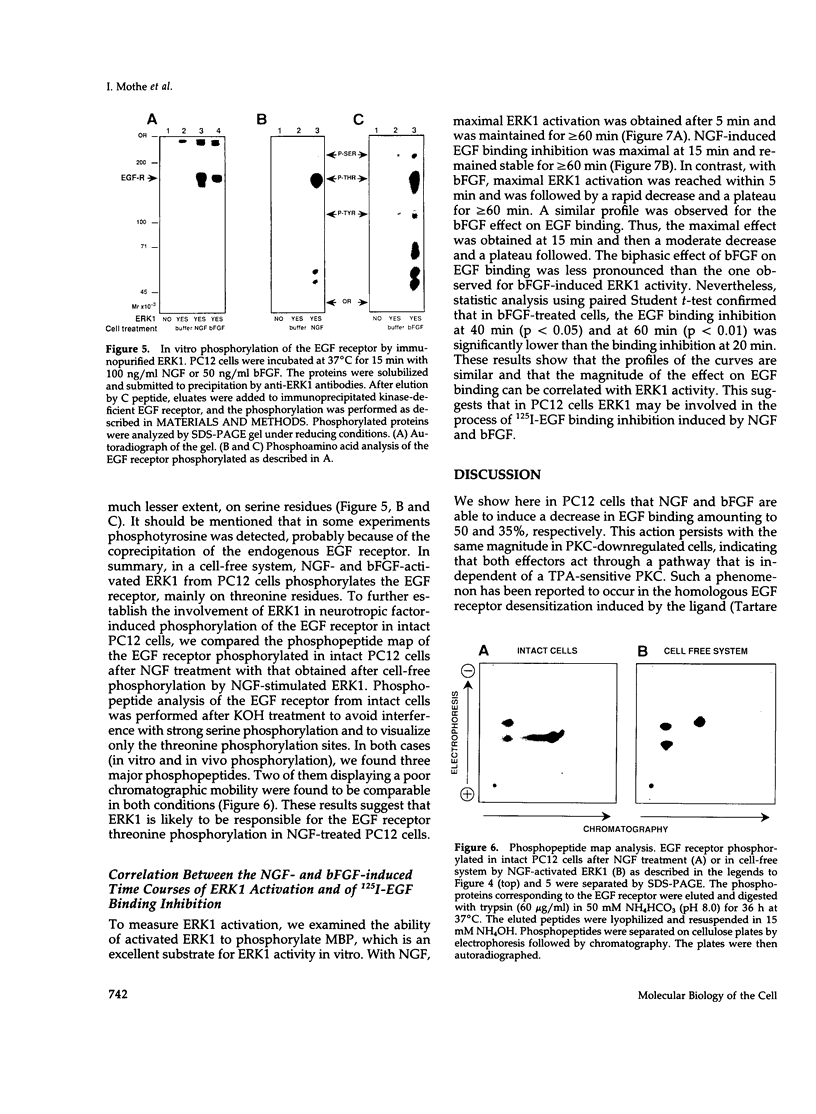
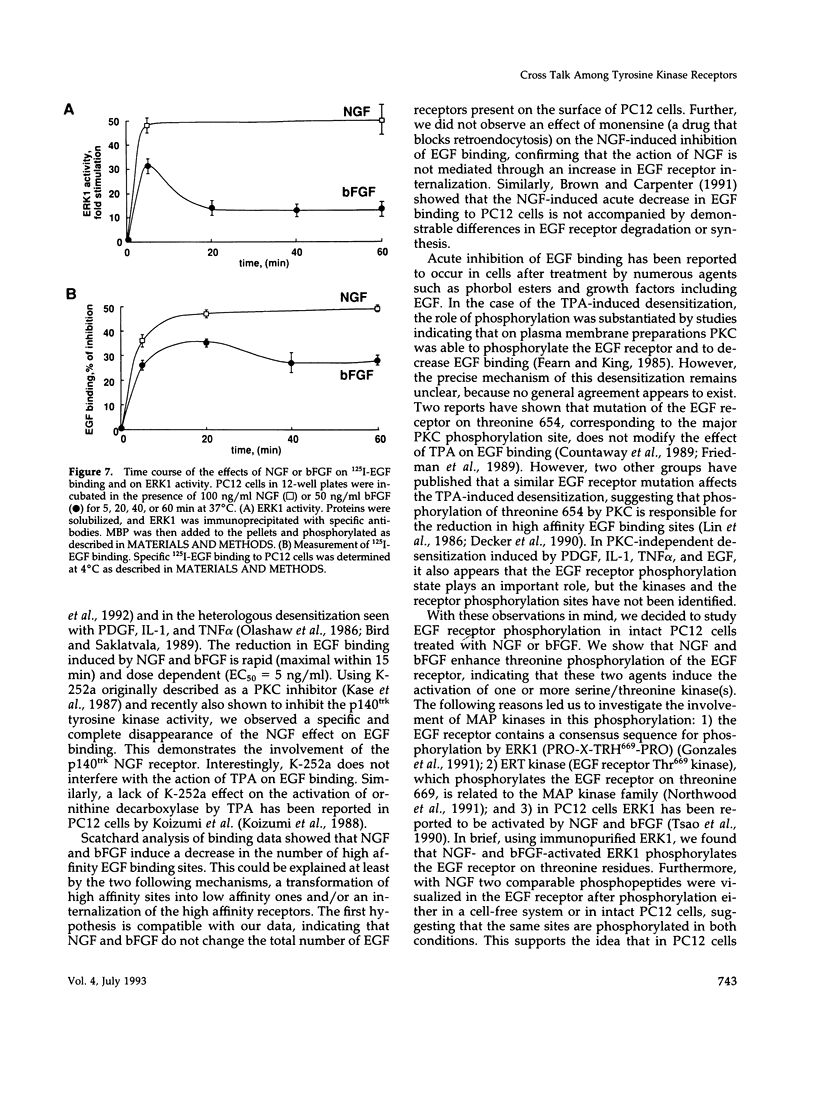
We have studied the effects of nerve growth factor (NGF) and basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) on epidermal growth factor (EGF) binding to PC12 cells. We show that NGF and bFGF rapidly induce a reduction in 125I-EGF binding to PC12 cells in a dose-dependent manner. This decrease amounts to 50% for NGF and 35% for bFGF. Both factors appear to act through a protein kinase C(PKC)-independent pathway, because their effect persists in PKC-downregulated PC12 cells. Scatchard analysis indicates that NGF and bFGF decrease the number of high affinity EGF binding sites. In addition to their effect on EGF binding, NGF and bFGF activate in intact PC12 cells one or several serine/threonine kinases leading to EGF receptor threonine phosphorylation. Using an in vitro phosphorylation system, we show that NGF- or bFGF-activated extracellular regulated kinase 1 (ERK1) is able to phosphorylate a kinase-deficient EGF receptor. Phosphoamino acid analysis indicates that this phosphorylation occurs mainly on threonine residues. Furthermore, two comparable phosphopeptides are observed in the EGF receptor, phosphorylated either in vivo after NGF treatment or in a cell-free system by NGF-activated ERK1. Finally, a good correlation was found between the time courses of ERK1 activation and 125I-EGF binding inhibition after NGF or bFGF treatment. In conclusion, in PC12 cells the NGF- and bFGF-stimulated ERK1 appears to be involved in the induction of the threonine phosphorylation of the EGF receptor and the decrease in the number of high affinity EGF binding sites.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballotti R., Lammers R., Scimeca J. C., Dull T., Schlessinger J., Ullrich A., Van Obberghen E. Intermolecular transphosphorylation between insulin receptors and EGF-insulin receptor chimerae. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3303–3309. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08491.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellot F., Moolenaar W., Kris R., Mirakhur B., Verlaan I., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J., Felder S. High-affinity epidermal growth factor binding is specifically reduced by a monoclonal antibody, and appears necessary for early responses. J Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;110(2):491–502. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.2.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg M. M., Sternberg D. W., Parada L. F., Chao M. V. K-252a inhibits nerve growth factor-induced trk proto-oncogene tyrosine phosphorylation and kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 5;267(1):13–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird T. A., Saklatvala J. Down-modulation of epidermal growth factor receptor affinity in fibroblasts treated with interleukin 1 or tumor necrosis factor is associated with phosphorylation at a site other than threonine 654. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):235–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird T. A., Saklatvala J. IL-1 and TNF transmodulate epidermal growth factor receptors by a protein kinase C-independent mechanism. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 1;142(1):126–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. B., Carpenter G. Acute regulation of the epidermal growth factor receptor in response to nerve growth factor. J Neurochem. 1991 Nov;57(5):1740–1749. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb06376.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess W. H., Maciag T. The heparin-binding (fibroblast) growth factor family of proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:575–606. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.003043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Sefton B. M., Hunter T. Detection and quantification of phosphotyrosine in proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1983;99:387–402. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)99075-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Countaway J. L., Gironès N., Davis R. J. Reconstitution of epidermal growth factor receptor transmodulation by platelet-derived growth factor in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13642–13647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Countaway J. L., McQuilkin P., Gironès N., Davis R. J. Multisite phosphorylation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Use of site-directed mutagenesis to examine the role of serine/threonine phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3407–3416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Countaway J. L., Nairn A. C., Davis R. J. Mechanism of desensitization of the epidermal growth factor receptor protein-tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):1129–1140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. J., Czech M. P. Stimulation of epidermal growth factor receptor threonine 654 phosphorylation by platelet-derived growth factor in protein kinase C-deficient human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6832–6841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. J., Czech M. P. Tumor-promoting phorbol diesters cause the phosphorylation of epidermal growth factor receptors in normal human fibroblasts at threonine-654. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):1974–1978. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. J. Independent mechanisms account for the regulation by protein kinase C of the epidermal growth factor receptor affinity and tyrosine-protein kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9462–9469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker S. J., Ellis C., Pawson T., Velu T. Effects of substitution of threonine 654 of the epidermal growth factor receptor on epidermal growth factor-mediated activation of phospholipase C. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):7009–7015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Defize L. H., Boonstra J., Meisenhelder J., Kruijer W., Tertoolen L. G., Tilly B. C., Hunter T., van Bergen en Henegouwen P. M., Moolenaar W. H., de Laat S. W. Signal transduction by epidermal growth factor occurs through the subclass of high affinity receptors. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):2495–2507. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.2495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearn J. C., King A. C. EGF receptor affinity is regulated by intracellular calcium and protein kinase C. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):991–1000. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90359-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
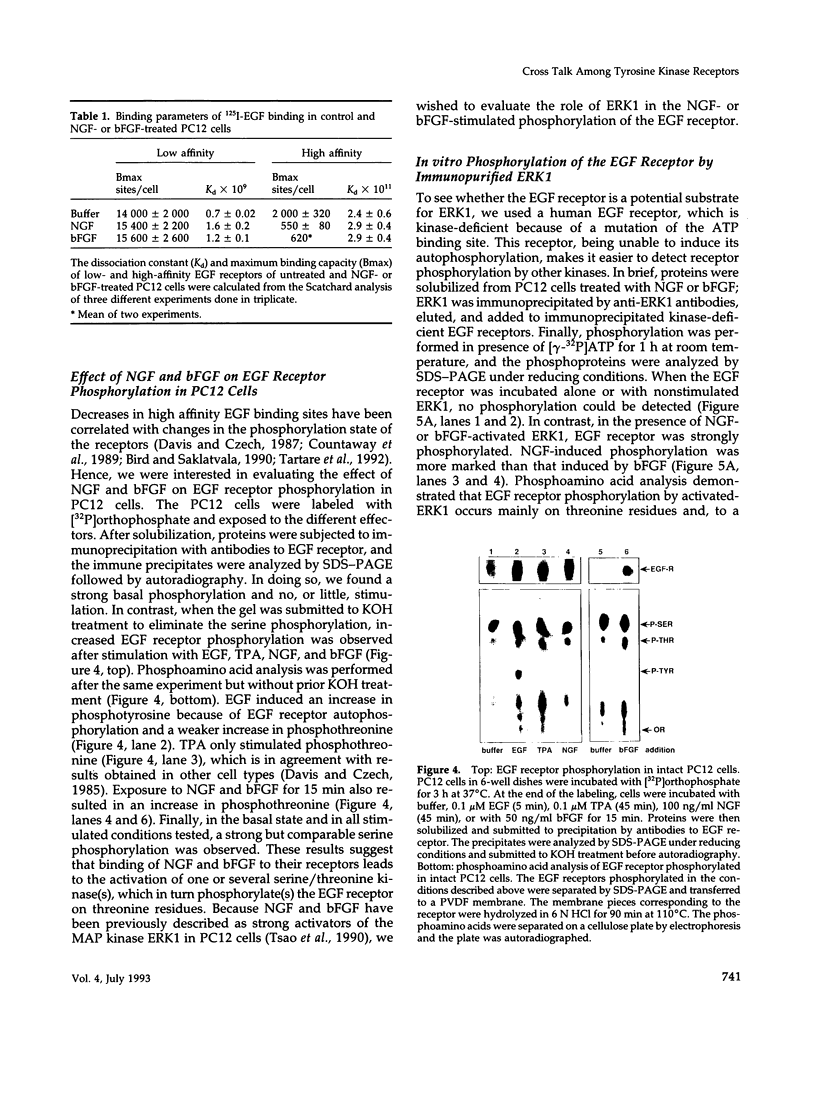
- Friedman B. A., van Amsterdam J., Fujiki H., Rosner M. R. Phosphorylation at threonine-654 is not required for negative regulation of the epidermal growth factor receptor by non-phorbol tumor promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):812–816. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. A., Raden D. L., Davis R. J. Identification of substrate recognition determinants for human ERK1 and ERK2 protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 25;266(33):22159–22163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. A., Tischler A. S. Establishment of a noradrenergic clonal line of rat adrenal pheochromocytoma cells which respond to nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2424–2428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hempstead B. L., Martin-Zanca D., Kaplan D. R., Parada L. F., Chao M. V. High-affinity NGF binding requires coexpression of the trk proto-oncogene and the low-affinity NGF receptor. Nature. 1991 Apr 25;350(6320):678–683. doi: 10.1038/350678a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hicks K., Friedman B., Rosner M. R. Basic and acidic fibroblast growth factors modulate the epidermal growth factor receptor by a protein kinase C-independent pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Oct 31;164(2):796–803. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91529-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honegger A. M., Dull T. J., Felder S., Van Obberghen E., Bellot F., Szapary D., Schmidt A., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Point mutation at the ATP binding site of EGF receptor abolishes protein-tyrosine kinase activity and alters cellular routing. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):199–209. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90147-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honegger A. M., Kris R. M., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Evidence that autophosphorylation of solubilized receptors for epidermal growth factor is mediated by intermolecular cross-phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):925–929. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huff K., End D., Guroff G. Nerve growth factor-induced alteration in the response of PC12 pheochromocytoma cells to epidermal growth factor. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jan;88(1):189–198. doi: 10.1083/jcb.88.1.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan D. R., Martin-Zanca D., Parada L. F. Tyrosine phosphorylation and tyrosine kinase activity of the trk proto-oncogene product induced by NGF. Nature. 1991 Mar 14;350(6314):158–160. doi: 10.1038/350158a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kase H., Iwahashi K., Nakanishi S., Matsuda Y., Yamada K., Takahashi M., Murakata C., Sato A., Kaneko M. K-252 compounds, novel and potent inhibitors of protein kinase C and cyclic nucleotide-dependent protein kinases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jan 30;142(2):436–440. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90293-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R., Jing S. Q., Nanduri V., O'Rourke E., Barbacid M. The trk proto-oncogene encodes a receptor for nerve growth factor. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):189–197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90419-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koizumi S., Contreras M. L., Matsuda Y., Hama T., Lazarovici P., Guroff G. K-252a: a specific inhibitor of the action of nerve growth factor on PC 12 cells. J Neurosci. 1988 Feb;8(2):715–721. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-02-00715.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee L. S., Weinstein I. B. Tumor-promoting phorbol esters inhibit binding of epidermal growth factor to cellular receptors. Science. 1978 Oct 20;202(4365):313–315. doi: 10.1126/science.308698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C. R., Chen W. S., Lazar C. S., Carpenter C. D., Gill G. N., Evans R. M., Rosenfeld M. G. Protein kinase C phosphorylation at Thr 654 of the unoccupied EGF receptor and EGF binding regulate functional receptor loss by independent mechanisms. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):839–848. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90006-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B., Li N., Koch A., Mohammadi M., Hurwitz D. R., Zilberstein A., Ullrich A., Pawson T., Schlessinger J. The tyrosine phosphorylated carboxyterminus of the EGF receptor is a binding site for GAP and PLC-gamma. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4375–4380. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07887.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen T. T., Scimeca J. C., Filloux C., Peraldi P., Carpentier J. L., Van Obberghen E. Co-regulation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase, extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1, and the 90-kDa ribosomal S6 kinase in PC12 cells. Distinct effects of the neurotrophic factor, nerve growth factor, and the mitogenic factor, epidermal growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 5;268(13):9803–9810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northwood I. C., Gonzalez F. A., Wartmann M., Raden D. L., Davis R. J. Isolation and characterization of two growth factor-stimulated protein kinases that phosphorylate the epidermal growth factor receptor at threonine 669. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):15266–15276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olashaw N. E., O'Keefe E. J., Pledger W. J. Platelet-derived growth factor modulates epidermal growth factor receptors by a mechanism distinct from that of phorbol esters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3834–3838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotin D., Margolis B., Mohammadi M., Daly R. J., Daum G., Li N., Fischer E. H., Burgess W. H., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. SH2 domains prevent tyrosine dephosphorylation of the EGF receptor: identification of Tyr992 as the high-affinity binding site for SH2 domains of phospholipase C gamma. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):559–567. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05087.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rydel R. E., Greene L. A. Acidic and basic fibroblast growth factors promote stable neurite outgrowth and neuronal differentiation in cultures of PC12 cells. J Neurosci. 1987 Nov;7(11):3639–3653. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-11-03639.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoscheck C. M., Carpenter G. Down regulation of epidermal growth factor receptors: direct demonstration of receptor degradation in human fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;98(3):1048–1053. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.3.1048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartare S., Ballotti R., Lammers R., Alengrin F., Dull T., Schlessinger J., Ullrich A., Van Obberghen E. Insulin-EGF receptor chimerae mediate tyrosine transphosphorylation and serine/threonine phosphorylation of kinase-deficient EGF receptors. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 25;266(15):9900–9906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartare S., Ballotti R., Lammers R., Filloux C., Chauvel A., Schlessinger J., Ullrich A., Van Obberghen E. Activation of insulin-epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor chimerae regulates EGF receptor binding affinity. J Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;116(3):627–633. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.3.627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsao H., Aletta J. M., Greene L. A. Nerve growth factor and fibroblast growth factor selectively activate a protein kinase that phosphorylates high molecular weight microtubule-associated proteins. Detection, partial purification, and characterization in PC12 cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 15;265(26):15471–15480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90801-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker F., Burgess A. W. Reconstitution of the high affinity epidermal growth factor receptor on cell-free membranes after transmodulation by platelet-derived growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 15;266(5):2746–2752. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilden U., Hall S. W., Kühn H. Phosphodiesterase activation by photoexcited rhodopsin is quenched when rhodopsin is phosphorylated and binds the intrinsic 48-kDa protein of rod outer segments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1174–1178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachary I., Sinnett-Smith J. W., Rozengurt E. Early events elicited by bombesin and structurally related peptides in quiescent Swiss 3T3 cells. I. Activation of protein kinase C and inhibition of epidermal growth factor binding. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;102(6):2211–2222. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.6.2211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]