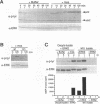
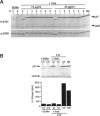
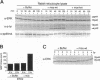
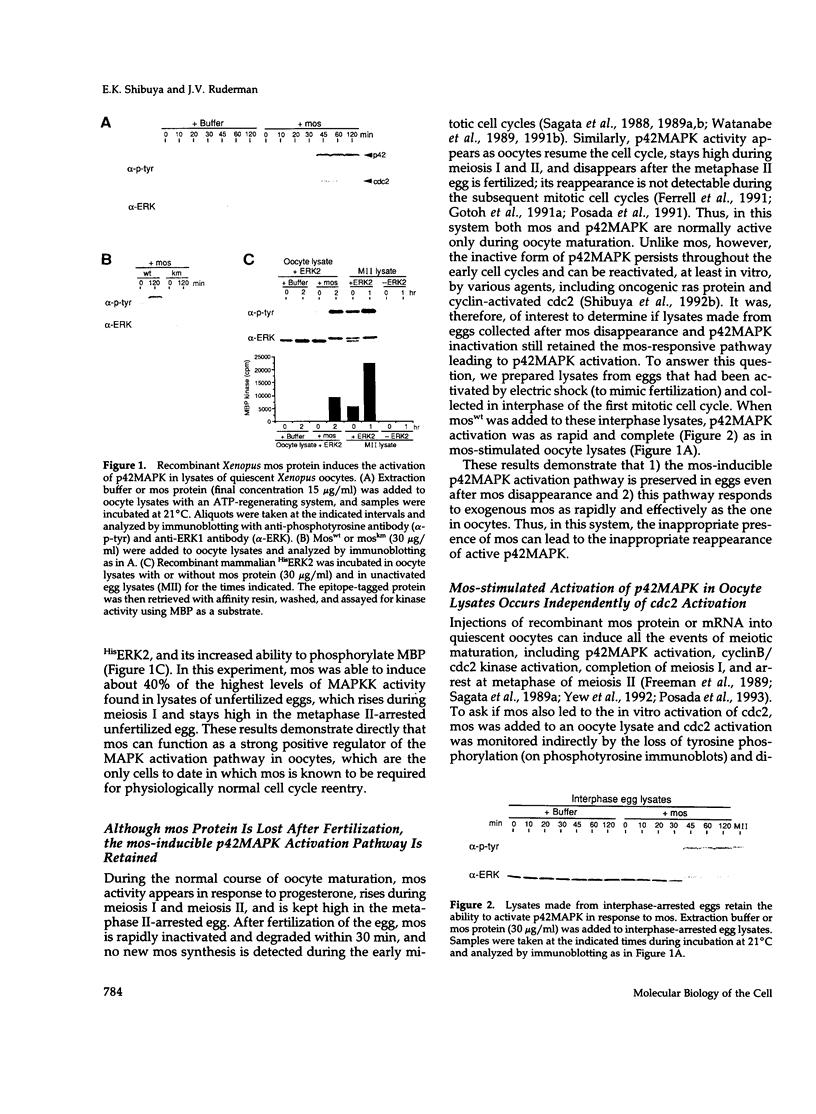
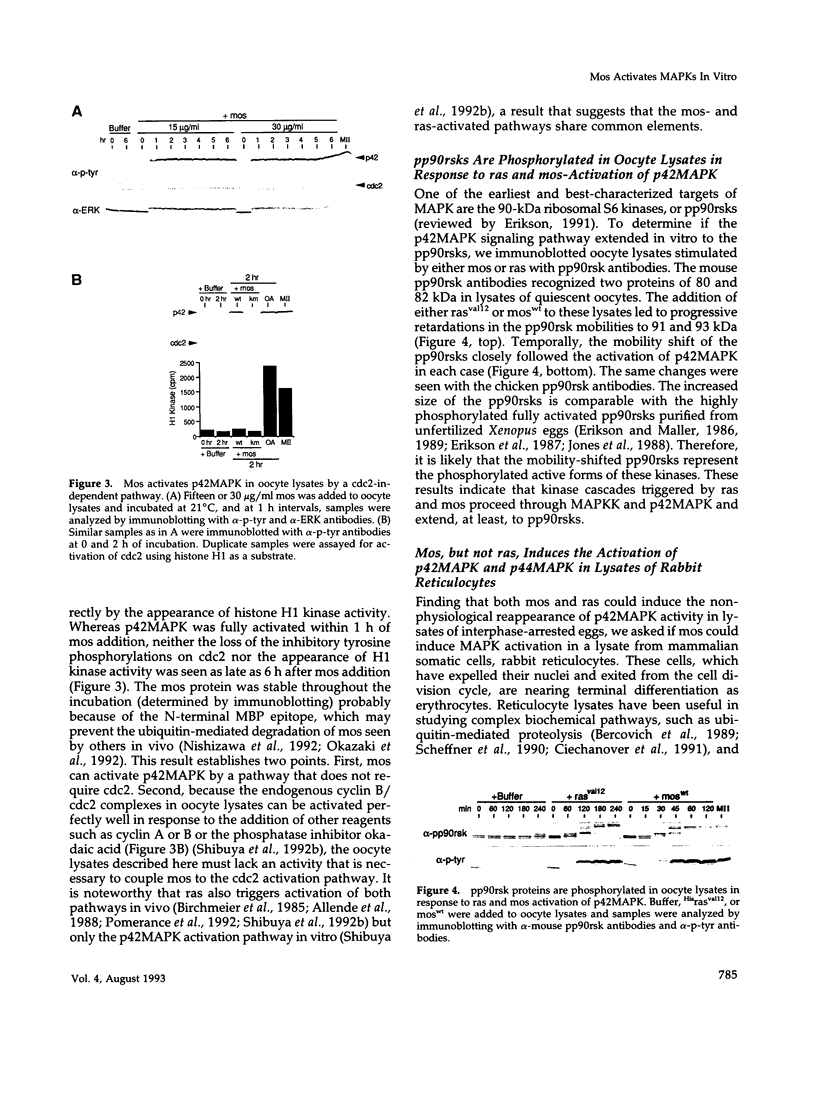
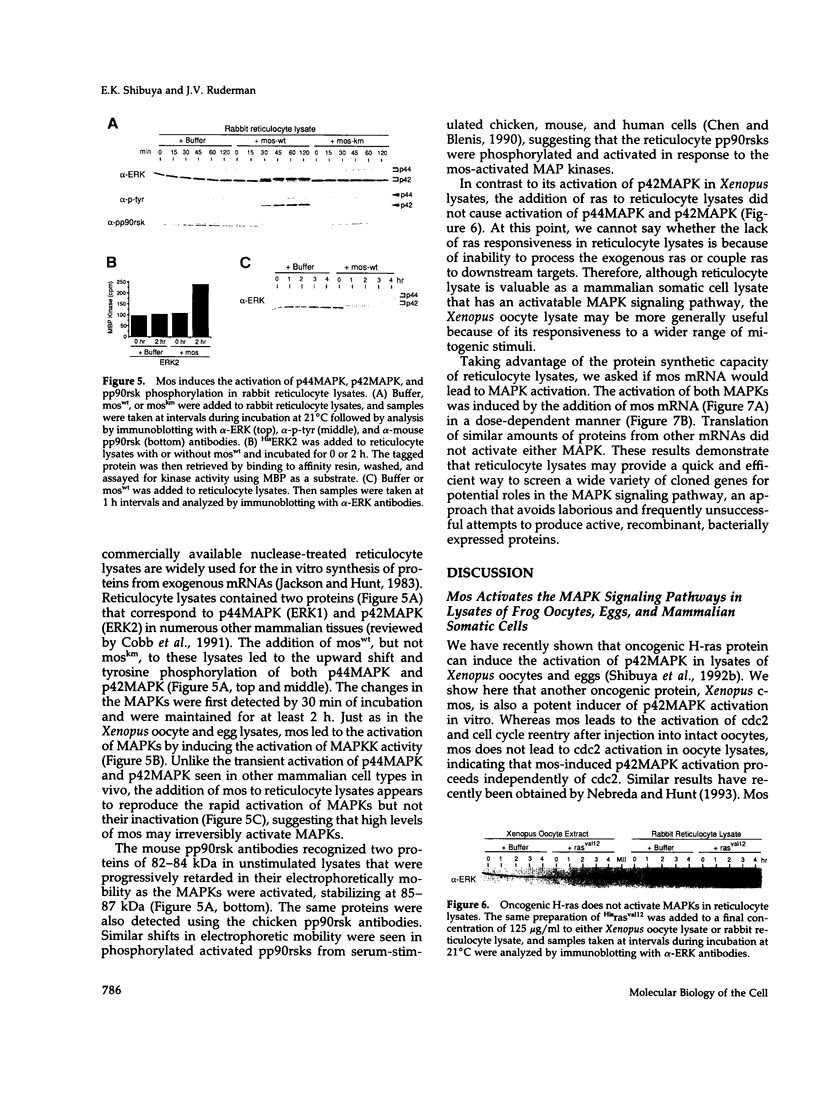
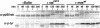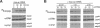Abstract
Mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) are rapidly and transiently activated when both quiescent Go-arrested cells and G2-arrested oocytes are stimulated to reenter the cell cycle. We previously developed a cell-free system from lysates of quiescent Xenopus oocytes that responds to oncogenic H-ras protein by activating a MAPK, p42MAPK. Here, we show that the oncogenic protein kinase mos is also a potent activator of p42MAPK in these lysates. Mos also induces p42MAPK activation in lysates of activated eggs taken at a time when neither mos nor p42MAPK is normally active, showing that the mos-responsive MAPK activation pathway persists beyond the stage where mos normally functions. Similarly, lysates of somatic cells (rabbit reticulocytes) also retain a mos-inducible MAPK activation pathway. The mos-induced activation of MAPKs in all three lysates leads to phosphorylation of the pp90rsk proteins, downstream targets of the MAPK signaling pathway in vivo. The in vitro activation of MAPKs by mos in cell-free systems derived from oocytes and somatic cells suggests that mos contributes to oncogenic transformation by inappropriately inducing the activation of MAPKs.
Full text
PDF


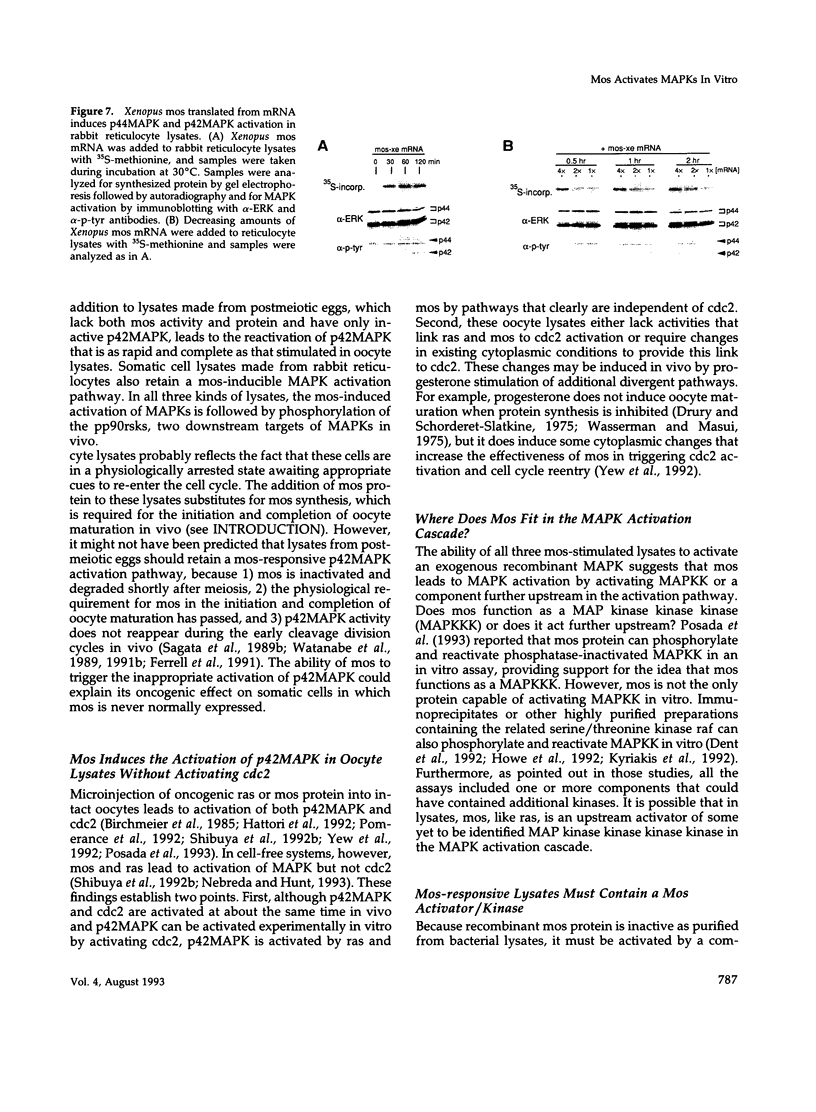



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahn N. G., Seger R., Bratlien R. L., Diltz C. D., Tonks N. K., Krebs E. G. Multiple components in an epidermal growth factor-stimulated protein kinase cascade. In vitro activation of a myelin basic protein/microtubule-associated protein 2 kinase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 5;266(7):4220–4227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alcorta D. A., Crews C. M., Sweet L. J., Bankston L., Jones S. W., Erikson R. L. Sequence and expression of chicken and mouse rsk: homologs of Xenopus laevis ribosomal S6 kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):3850–3859. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.3850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allende C. C., Hinrichs M. V., Santos E., Allende J. E. Oncogenic ras protein induces meiotic maturation of amphibian oocytes in the presence of protein synthesis inhibitors. FEBS Lett. 1988 Jul 18;234(2):426–430. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80130-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson N. G., Maller J. L., Tonks N. K., Sturgill T. W. Requirement for integration of signals from two distinct phosphorylation pathways for activation of MAP kinase. Nature. 1990 Feb 15;343(6259):651–653. doi: 10.1038/343651a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Sagi D., Feramisco J. R. Microinjection of the ras oncogene protein into PC12 cells induces morphological differentiation. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):841–848. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90280-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbacid M. ras genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:779–827. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.004023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bercovich Z., Rosenberg-Hasson Y., Ciechanover A., Kahana C. Degradation of ornithine decarboxylase in reticulocyte lysate is ATP-dependent but ubiquitin-independent. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 25;264(27):15949–15952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birchmeier C., Broek D., Wigler M. ras proteins can induce meiosis in Xenopus oocytes. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):615–621. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90233-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollag G., McCormick F. Regulators and effectors of ras proteins. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:601–632. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.003125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulton T. G., Cobb M. H. Identification of multiple extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERKs) with antipeptide antibodies. Cell Regul. 1991 May;2(5):357–371. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.5.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R. H., Blenis J. Identification of Xenopus S6 protein kinase homologs (pp90rsk) in somatic cells: phosphorylation and activation during initiation of cell proliferation. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):3204–3215. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.3204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciechanover A., DiGiuseppe J. A., Bercovich B., Orian A., Richter J. D., Schwartz A. L., Brodeur G. M. Degradation of nuclear oncoproteins by the ubiquitin system in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):139–143. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobb M. H., Boulton T. G., Robbins D. J. Extracellular signal-regulated kinases: ERKs in progress. Cell Regul. 1991 Dec;2(12):965–978. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.12.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crews C. M., Alessandrini A., Erikson R. L. The primary structure of MEK, a protein kinase that phosphorylates the ERK gene product. Science. 1992 Oct 16;258(5081):478–480. doi: 10.1126/science.1411546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crews C. M., Erikson R. L. Purification of a murine protein-tyrosine/threonine kinase that phosphorylates and activates the Erk-1 gene product: relationship to the fission yeast byr1 gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):8205–8209. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.8205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daar I., Paules R. S., Vande Woude G. F. A characterization of cytostatic factor activity from Xenopus eggs and c-mos-transformed cells. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;114(2):329–335. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.2.329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent P., Haser W., Haystead T. A., Vincent L. A., Roberts T. M., Sturgill T. W. Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase by v-Raf in NIH 3T3 cells and in vitro. Science. 1992 Sep 4;257(5075):1404–1407. doi: 10.1126/science.1326789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Druker B. J., Mamon H. J., Roberts T. M. Oncogenes, growth factors, and signal transduction. N Engl J Med. 1989 Nov 16;321(20):1383–1391. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198911163212007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drury K. C., Schorderet-Slatkine S. Effects of cycloheximide on the "autocatalytic" nature of the maturation promoting factor (MPF) in oocytes of Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1975 Mar;4(3):269–274. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90175-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumont J. N. Oogenesis in Xenopus laevis (Daudin). I. Stages of oocyte development in laboratory maintained animals. J Morphol. 1972 Feb;136(2):153–179. doi: 10.1002/jmor.1051360203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elion E. A., Brill J. A., Fink G. R. Functional redundancy in the yeast cell cycle: FUS3 and KSS1 have both overlapping and unique functions. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1991;56:41–49. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1991.056.01.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Maller J. L. In vivo phosphorylation and activation of ribosomal protein S6 kinases during Xenopus oocyte maturation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13711–13717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Maller J. L. Purification and characterization of a protein kinase from Xenopus eggs highly specific for ribosomal protein S6. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):350–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Stefanovic D., Blenis J., Erikson R. L., Maller J. L. Antibodies to Xenopus egg S6 kinase II recognize S6 kinase from progesterone- and insulin-stimulated Xenopus oocytes and from proliferating chicken embryo fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3147–3155. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson R. L. Structure, expression, and regulation of protein kinases involved in the phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6007–6010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrell J. E., Jr, Wu M., Gerhart J. C., Martin G. S. Cell cycle tyrosine phosphorylation of p34cdc2 and a microtubule-associated protein kinase homolog in Xenopus oocytes and eggs. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):1965–1971. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman R. S., Donoghue D. J. Protein kinases and protooncogenes: biochemical regulators of the eukaryotic cell cycle. Biochemistry. 1991 Mar 5;30(9):2293–2302. doi: 10.1021/bi00223a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman R. S., Meyer A. N., Li J., Donoghue D. J. Phosphorylation of conserved serine residues does not regulate the ability of mosxe protein kinase to induce oocyte maturation or function as cytostatic factor. J Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;116(3):725–735. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.3.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman R. S., Pickham K. M., Kanki J. P., Lee B. A., Pena S. V., Donoghue D. J. Xenopus homolog of the mos protooncogene transforms mammalian fibroblasts and induces maturation of Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5805–5809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotoh Y., Moriyama K., Matsuda S., Okumura E., Kishimoto T., Kawasaki H., Suzuki K., Yahara I., Sakai H., Nishida E. Xenopus M phase MAP kinase: isolation of its cDNA and activation by MPF. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2661–2668. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07809.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotoh Y., Nishida E., Matsuda S., Shiina N., Kosako H., Shiokawa K., Akiyama T., Ohta K., Sakai H. In vitro effects on microtubule dynamics of purified Xenopus M phase-activated MAP kinase. Nature. 1991 Jan 17;349(6306):251–254. doi: 10.1038/349251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gómez N., Cohen P. Dissection of the protein kinase cascade by which nerve growth factor activates MAP kinases. Nature. 1991 Sep 12;353(6340):170–173. doi: 10.1038/353170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori S., Fukuda M., Yamashita T., Nakamura S., Gotoh Y., Nishida E. Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase and its activator by ras in intact cells and in a cell-free system. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 5;267(28):20346–20351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe L. R., Leevers S. J., Gómez N., Nakielny S., Cohen P., Marshall C. J. Activation of the MAP kinase pathway by the protein kinase raf. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):335–342. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90361-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. J., Hunt T. Preparation and use of nuclease-treated rabbit reticulocyte lysates for the translation of eukaryotic messenger RNA. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:50–74. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. W., Erikson E., Blenis J., Maller J. L., Erikson R. L. A Xenopus ribosomal protein S6 kinase has two apparent kinase domains that are each similar to distinct protein kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3377–3381. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanki J. P., Donoghue D. J. Progression from meiosis I to meiosis II in Xenopus oocytes requires de novo translation of the mosxe protooncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5794–5798. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosako H., Gotoh Y., Matsuda S., Ishikawa M., Nishida E. Xenopus MAP kinase activator is a serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activated by threonine phosphorylation. EMBO J. 1992 Aug;11(8):2903–2908. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05359.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosako H., Nishida E., Gotoh Y. cDNA cloning of MAP kinase kinase reveals kinase cascade pathways in yeasts to vertebrates. EMBO J. 1993 Feb;12(2):787–794. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05713.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krohne G., Franke W. W. Proteins of pore complex--lamina structures from nuclei and nuclear membranes. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:597–608. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96052-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurata N., Akiyama H., Taniyama T., Marunouchi T. Dose-dependent regulation of macrophage differentiation by mos mRNA in a human monocytic cell line. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):457–463. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03398.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurata S., Kurata N., Ikawa Y. Production of recombinant rat viruses as a method of oncogene isolation in coculture medium. Cancer Res. 1987 Nov 15;47(22):5908–5912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyriakis J. M., App H., Zhang X. F., Banerjee P., Brautigan D. L., Rapp U. R., Avruch J. Raf-1 activates MAP kinase-kinase. Nature. 1992 Jul 30;358(6385):417–421. doi: 10.1038/358417a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodish H. F., Small B. Different lifetimes of reticulocyte messenger RNA. Cell. 1976 Jan;7(1):59–65. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90255-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohka M. J., Maller J. L. Induction of nuclear envelope breakdown, chromosome condensation, and spindle formation in cell-free extracts. J Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;101(2):518–523. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.2.518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masui Y. Relative roles of the pituitary, follicle cells, and progesterone in the induction of oocyte maturation in Rana pipiens. J Exp Zool. 1967 Dec;166(3):365–375. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401660309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Kirschner M. W. Cyclin synthesis drives the early embryonic cell cycle. Nature. 1989 May 25;339(6222):275–280. doi: 10.1038/339275a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakielny S., Cohen P., Wu J., Sturgill T. MAP kinase activator from insulin-stimulated skeletal muscle is a protein threonine/tyrosine kinase. EMBO J. 1992 Jun;11(6):2123–2129. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05271.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebreda A. R., Hunt T. The c-mos proto-oncogene protein kinase turns on and maintains the activity of MAP kinase, but not MPF, in cell-free extracts of Xenopus oocytes and eggs. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):1979–1986. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05847.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizawa M., Okazaki K., Furuno N., Watanabe N., Sagata N. The 'second-codon rule' and autophosphorylation govern the stability and activity of Mos during the meiotic cell cycle in Xenopus oocytes. EMBO J. 1992 Jul;11(7):2433–2446. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05308.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Ko M., Ogura A., Liu D. G., Amano T., Takano T., Ikawa Y. Sarcoma viruses carrying ras oncogenes induce differentiation-associated properties in a neuronal cell line. Nature. 1985 Nov 7;318(6041):73–75. doi: 10.1038/318073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Keefe S. J., Wolfes H., Kiessling A. A., Cooper G. M. Microinjection of antisense c-mos oligonucleotides prevents meiosis II in the maturing mouse egg. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):7038–7042. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.7038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okazaki K., Nishizawa M., Furuno N., Yasuda H., Sagata N. Differential occurrence of CSF-like activity and transforming activity of Mos during the cell cycle in fibroblasts. EMBO J. 1992 Jul;11(7):2447–2456. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05309.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paules R. S., Buccione R., Moschel R. C., Vande Woude G. F., Eppig J. J. Mouse Mos protooncogene product is present and functions during oogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5395–5399. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomerance M., Schweighoffer F., Tocque B., Pierre M. Stimulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase by oncogenic Ras p21 in Xenopus oocytes. Requirement for Ras p21-GTPase-activating protein interaction. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16155–16160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posada J., Cooper J. A. Molecular signal integration. Interplay between serine, threonine, and tyrosine phosphorylation. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Jun;3(6):583–592. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.6.583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posada J., Cooper J. A. Requirements for phosphorylation of MAP kinase during meiosis in Xenopus oocytes. Science. 1992 Jan 10;255(5041):212–215. doi: 10.1126/science.1313186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posada J., Sanghera J., Pelech S., Aebersold R., Cooper J. A. Tyrosine phosphorylation and activation of homologous protein kinases during oocyte maturation and mitogenic activation of fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2517–2528. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posada J., Yew N., Ahn N. G., Vande Woude G. F., Cooper J. A. Mos stimulates MAP kinase in Xenopus oocytes and activates a MAP kinase kinase in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2546–2553. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp U. R., Goldsborough M. D., Mark G. E., Bonner T. I., Groffen J., Reynolds F. H., Jr, Stephenson J. R. Structure and biological activity of v-raf, a unique oncogene transduced by a retrovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4218–4222. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruderman J. V. MAP kinase and the activation of quiescent cells. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;5(2):207–213. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90104-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagata N., Daar I., Oskarsson M., Showalter S. D., Vande Woude G. F. The product of the mos proto-oncogene as a candidate "initiator" for oocyte maturation. Science. 1989 Aug 11;245(4918):643–646. doi: 10.1126/science.2474853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagata N., Oskarsson M., Copeland T., Brumbaugh J., Vande Woude G. F. Function of c-mos proto-oncogene product in meiotic maturation in Xenopus oocytes. Nature. 1988 Oct 6;335(6190):519–525. doi: 10.1038/335519a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagata N., Watanabe N., Vande Woude G. F., Ikawa Y. The c-mos proto-oncogene product is a cytostatic factor responsible for meiotic arrest in vertebrate eggs. Nature. 1989 Nov 30;342(6249):512–518. doi: 10.1038/342512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanghera J. S., Paddon H. B., Bader S. A., Pelech S. L. Purification and characterization of a maturation-activated myelin basic protein kinase from sea star oocytes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):52–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffner M., Werness B. A., Huibregtse J. M., Levine A. J., Howley P. M. The E6 oncoprotein encoded by human papillomavirus types 16 and 18 promotes the degradation of p53. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1129–1136. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90409-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seger R., Seger D., Lozeman F. J., Ahn N. G., Graves L. M., Campbell J. S., Ericsson L., Harrylock M., Jensen A. M., Krebs E. G. Human T-cell mitogen-activated protein kinase kinases are related to yeast signal transduction kinases. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 25;267(36):25628–25631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibuya E. K., Boulton T. G., Cobb M. H., Ruderman J. V. Activation of p42 MAP kinase and the release of oocytes from cell cycle arrest. EMBO J. 1992 Nov;11(11):3963–3975. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05490.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibuya E. K., Polverino A. J., Chang E., Wigler M., Ruderman J. V. Oncogenic ras triggers the activation of 42-kDa mitogen-activated protein kinase in extracts of quiescent Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9831–9835. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas S. M., DeMarco M., D'Arcangelo G., Halegoua S., Brugge J. S. Ras is essential for nerve growth factor- and phorbol ester-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of MAP kinases. Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):1031–1040. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90075-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman W. J., Masui Y. A cytoplasmic factor promoting oocyte maturation: its extraction and preliminary characterization. Science. 1976 Mar 26;191(4233):1266–1268. doi: 10.1126/science.1083070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman W. J., Masui Y. Effects of cyclohexamide on a cytoplasmic factor initiating meiotic naturation in Xenopus oocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1975 Mar 15;91(2):381–388. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(75)90118-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe N., Hunt T., Ikawa Y., Sagata N. Independent inactivation of MPF and cytostatic factor (Mos) upon fertilization of Xenopus eggs. Nature. 1991 Jul 18;352(6332):247–248. doi: 10.1038/352247a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe N., Vande Woude G. F., Ikawa Y., Sagata N. Specific proteolysis of the c-mos proto-oncogene product by calpain on fertilization of Xenopus eggs. Nature. 1989 Nov 30;342(6249):505–511. doi: 10.1038/342505a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood K. W., Sarnecki C., Roberts T. M., Blenis J. ras mediates nerve growth factor receptor modulation of three signal-transducing protein kinases: MAP kinase, Raf-1, and RSK. Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):1041–1050. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90076-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J., Harrison J. K., Vincent L. A., Haystead C., Haystead T. A., Michel H., Hunt D. F., Lynch K. R., Sturgill T. W. Molecular structure of a protein-tyrosine/threonine kinase activating p42 mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase: MAP kinase kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 1;90(1):173–177. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.1.173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yew N., Mellini M. L., Vande Woude G. F. Meiotic initiation by the mos protein in Xenopus. Nature. 1992 Feb 13;355(6361):649–652. doi: 10.1038/355649a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]