Abstract
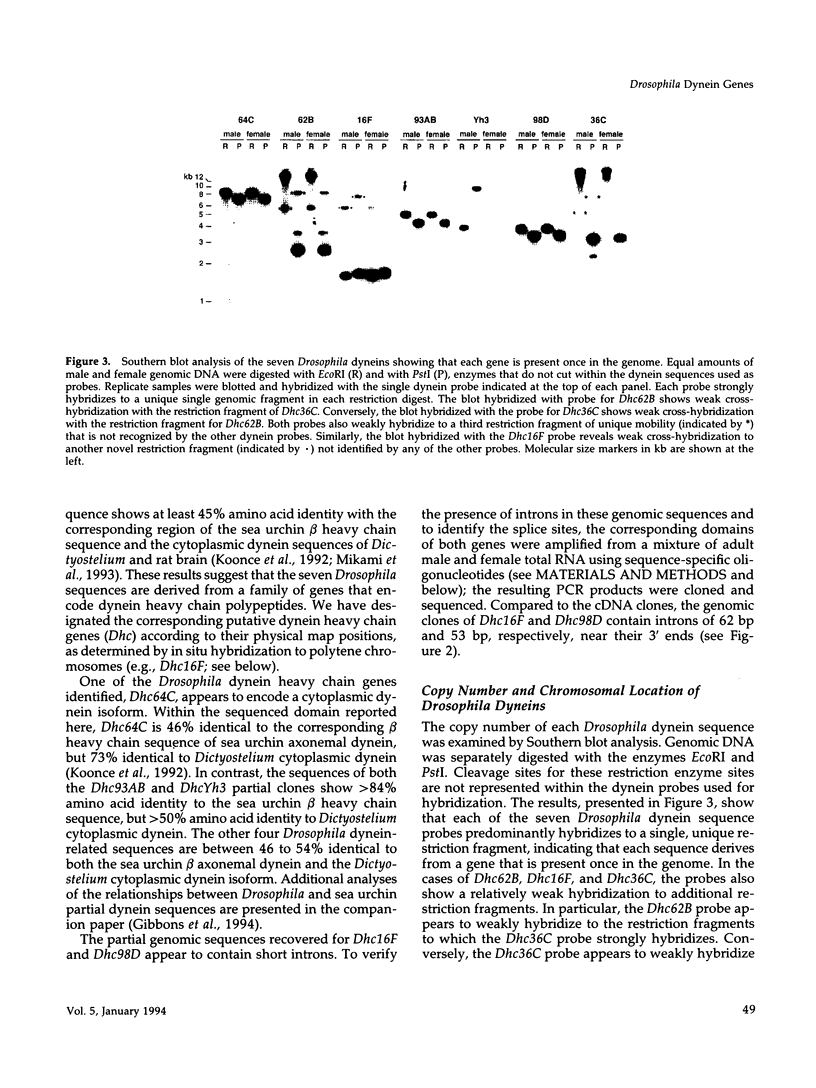
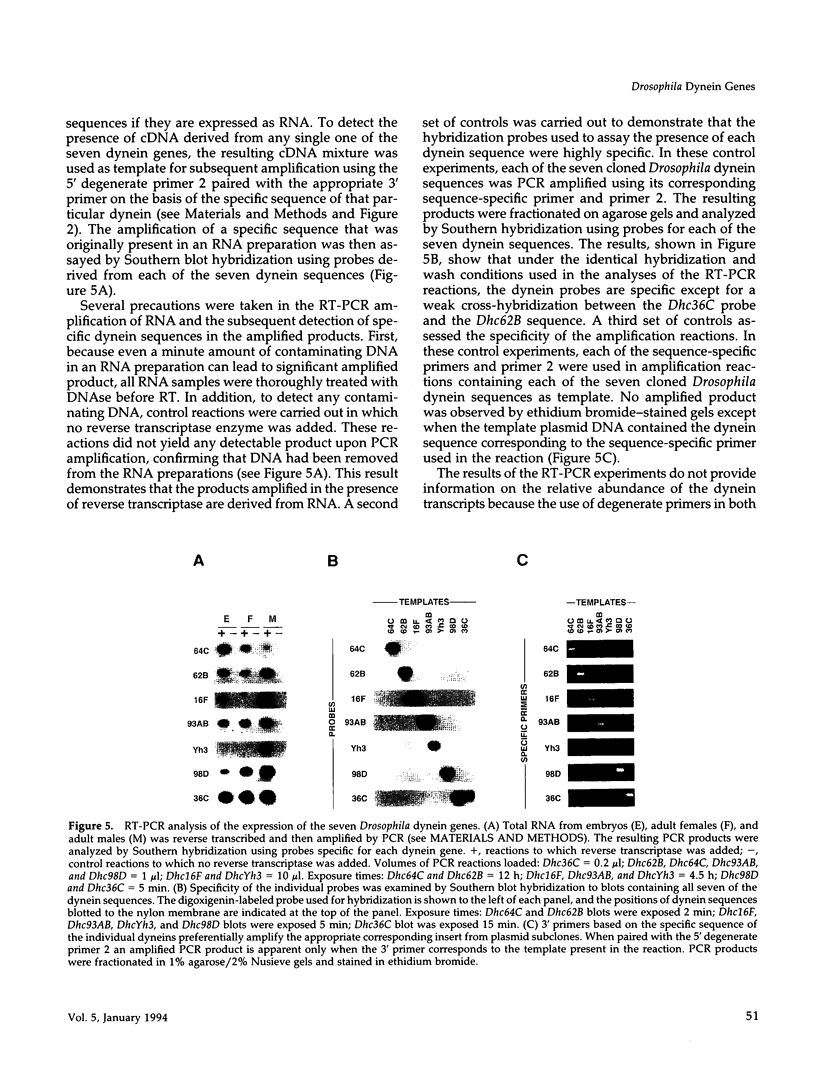
We report the identification and initial characterization of seven Drosophila dynein heavy chain genes. Each gene is single copy and maps to a unique genomic location. Sequence analysis of partial clones reveals that each encodes a highly conserved portion of the putative dynein hydrolytic ATP-binding site in dyneins that includes a consensus phosphate-binding (P-loop) motif. One of the clones is derived from a Drosophila cytoplasmic dynein heavy chain gene, Dhc64C, that shows extensive amino acid identity to cytoplasmic dynein isoforms from other organisms. Two other Drosophila dynein clones are 85 and 90% identical at the amino acid level to the corresponding region of the beta heavy chain of sea urchin axonemal dynein. Probes for all seven of the dynein-related sequences hybridize to transcripts that are of the appropriate size, approximately 14 kilobases, to encode the characteristic high molecular weight dynein heavy chain polypeptides. The Dhc64C transcript is readily detected in RNA from ovaries, embryos, and testes. Transcripts from five of the six remaining genes are also detected in much lesser amounts in tissues other than testes. All but one of the dynein transcripts are expressed at comparable levels in testes suggesting their participation in flagellar axoneme assembly and motility.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bloom G. S. Motor proteins for cytoplasmic microtubules. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;4(1):66–73. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90060-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brokaw C. J., Kamiya R. Bending patterns of Chlamydomonas flagella: IV. Mutants with defects in inner and outer dynein arms indicate differences in dynein arm function. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1987;8(1):68–75. doi: 10.1002/cm.970080110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosseau G E. Genetic Analysis of the Male Fertility Factors on the Y Chromosome of Drosophila Melanogaster. Genetics. 1960 Mar;45(3):257–274. doi: 10.1093/genetics/45.3.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole D. G., Cande W. Z., Baskin R. J., Skoufias D. A., Hogan C. J., Scholey J. M. Isolation of a sea urchin egg kinesin-related protein using peptide antibodies. J Cell Sci. 1992 Feb;101(Pt 2):291–301. doi: 10.1242/jcs.101.2.291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endow S. A., Hatsumi M. A multimember kinesin gene family in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4424–4427. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endow S. A., Titus M. A. Genetic approaches to molecular motors. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:29–66. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.000333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engels W. R., Johnson-Schlitz D. M., Eggleston W. B., Sved J. High-frequency P element loss in Drosophila is homolog dependent. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):515–525. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eshel D., Urrestarazu L. A., Vissers S., Jauniaux J. C., van Vliet-Reedijk J. C., Planta R. J., Gibbons I. R. Cytoplasmic dynein is required for normal nuclear segregation in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 1;90(23):11172–11176. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.11172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasset M., Baldwin M. A., Fletterick R. J., Prusiner S. B. Perturbation of the secondary structure of the scrapie prion protein under conditions that alter infectivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 1;90(1):1–5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gepner J., Hays T. S. A fertility region on the Y chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster encodes a dynein microtubule motor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 1;90(23):11132–11136. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.11132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons B. H., Asai D. J., Tang W. J., Hays T. S., Gibbons I. R. Phylogeny and expression of axonemal and cytoplasmic dynein genes in sea urchins. Mol Biol Cell. 1994 Jan;5(1):57–70. doi: 10.1091/mbc.5.1.57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons B. H., Gibbons I. R. Vanadate-sensitized cleavage of dynein heavy chains by 365-nm irradiation of demembranated sperm flagella and its effect on the flagellar motility. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 15;262(17):8354–8359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons I. R. Cilia and flagella of eukaryotes. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 2):107s–124s. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.107s. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons I. R. Dynein ATPases as microtubule motors. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):15837–15840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons I. R., Gibbons B. H., Mocz G., Asai D. J. Multiple nucleotide-binding sites in the sequence of dynein beta heavy chain. Nature. 1991 Aug 15;352(6336):640–643. doi: 10.1038/352640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein L. S., Hardy R. W., Lindsley D. L. Structural genes on the Y chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7405–7409. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein L. S. The kinesin superfamily: tails of functional redundancy. Trends Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;1(4):93–98. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(91)90036-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodenough U. W., Gebhart B., Mermall V., Mitchell D. R., Heuser J. E. High-pressure liquid chromatography fractionation of Chlamydomonas dynein extracts and characterization of inner-arm dynein subunits. J Mol Biol. 1987 Apr 5;194(3):481–494. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90676-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy R. W., Tokuyasu K. T., Lindsley D. L. Analysis of spermatogenesis in Drosophila melanogaster bearing deletions for Y-chromosome fertility genes. Chromosoma. 1981;83(5):593–617. doi: 10.1007/BF00328522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang B., Piperno G., Luck D. J. Paralyzed flagella mutants of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Defective for axonemal doublet microtubule arms. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):3091–3099. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamiya R. Mutations at twelve independent loci result in absence of outer dynein arms in Chylamydomonas reinhardtii. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 1):2253–2258. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawasaki E. S., Clark S. S., Coyne M. Y., Smith S. D., Champlin R., Witte O. N., McCormick F. P. Diagnosis of chronic myeloid and acute lymphocytic leukemias by detection of leukemia-specific mRNA sequences amplified in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5698–5702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koonce M. P., Grissom P. M., McIntosh J. R. Dynein from Dictyostelium: primary structure comparisons between a cytoplasmic motor enzyme and flagellar dynein. J Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;119(6):1597–1604. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.6.1597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughon A., Boulet A. M., Bermingham J. R., Jr, Laymon R. A., Scott M. P. Structure of transcripts from the homeotic Antennapedia gene of Drosophila melanogaster: two promoters control the major protein-coding region. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4676–4689. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald H. B., Goldstein L. S. Identification and characterization of a gene encoding a kinesin-like protein in Drosophila. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):991–1000. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90064-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medberry S. L., Lockhart B. E., Olszewski N. E. Properties of Commelina yellow mottle virus's complete DNA sequence, genomic discontinuities and transcript suggest that it is a pararetrovirus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 25;18(18):5505–5513. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.18.5505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikami A., Paschal B. M., Mazumdar M., Vallee R. B. Molecular cloning of the retrograde transport motor cytoplasmic dynein (MAP 1C). Neuron. 1993 May;10(5):787–796. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90195-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa K. Four ATP-binding sites in the midregion of the beta heavy chain of dynein. Nature. 1991 Aug 15;352(6336):643–645. doi: 10.1038/352643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paschal B. M., Shpetner H. S., Vallee R. B. MAP 1C is a microtubule-activated ATPase which translocates microtubules in vitro and has dynein-like properties. J Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;105(3):1273–1282. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.3.1273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry M. M. Further studies on the development of the of Drosophila melanogaster. II. The interommatidial bristles. J Morphol. 1968 Feb;124(2):249–262. doi: 10.1002/jmor.1051240209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piperno G., Ramanis Z., Smith E. F., Sale W. S. Three distinct inner dynein arms in Chlamydomonas flagella: molecular composition and location in the axoneme. J Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;110(2):379–389. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.2.379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter M. E., Johnson K. A. Dynein structure and function. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1989;5:119–151. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.05.110189.001003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter M. E., Power J., Dutcher S. K. Extragenic suppressors of paralyzed flagellar mutations in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii identify loci that alter the inner dynein arms. J Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;118(5):1163–1176. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.5.1163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roof D. M., Meluh P. B., Rose M. D. Kinesin-related proteins required for assembly of the mitotic spindle. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;118(1):95–108. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakakibara H., Mitchell D. R., Kamiya R. A Chlamydomonas outer arm dynein mutant missing the alpha heavy chain. J Cell Biol. 1991 May;113(3):615–622. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.3.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saraste M., Sibbald P. R., Wittinghofer A. The P-loop--a common motif in ATP- and GTP-binding proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Nov;15(11):430–434. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90281-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawin K. E., Mitchison T. J., Wordeman L. G. Evidence for kinesin-related proteins in the mitotic apparatus using peptide antibodies. J Cell Sci. 1992 Feb;101(Pt 2):303–313. doi: 10.1242/jcs.101.2.303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholey J. M., Heuser J., Yang J. T., Goldstein L. S. Identification of globular mechanochemical heads of kinesin. Nature. 1989 Mar 23;338(6213):355–357. doi: 10.1038/338355a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skoufias D. A., Scholey J. M. Cytoplasmic microtubule-based motor proteins. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;5(1):95–104. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(05)80014-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart R. J., Pesavento P. A., Woerpel D. N., Goldstein L. S. Identification and partial characterization of six members of the kinesin superfamily in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8470–8474. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamkun J. W., Kahn R. A., Kissinger M., Brizuela B. J., Rulka C., Scott M. P., Kennison J. A. The arflike gene encodes an essential GTP-binding protein in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3120–3124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vale R. D., Schnapp B. J., Reese T. S., Sheetz M. P. Organelle, bead, and microtubule translocations promoted by soluble factors from the squid giant axon. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):559–569. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90204-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallee R. B., Shpetner H. S. Motor proteins of cytoplasmic microtubules. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:909–932. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.004401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Gillespie D. Preparative and analytical purification of DNA from agarose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):615–619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. E., Saraste M., Runswick M. J., Gay N. J. Distantly related sequences in the alpha- and beta-subunits of ATP synthase, myosin, kinases and other ATP-requiring enzymes and a common nucleotide binding fold. EMBO J. 1982;1(8):945–951. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01276.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witman G. B. Axonemal dyneins. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;4(1):74–79. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90061-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J. T., Laymon R. A., Goldstein L. S. A three-domain structure of kinesin heavy chain revealed by DNA sequence and microtubule binding analyses. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):879–889. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90692-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J. T., Saxton W. M., Stewart R. J., Raff E. C., Goldstein L. S. Evidence that the head of kinesin is sufficient for force generation and motility in vitro. Science. 1990 Jul 6;249(4964):42–47. doi: 10.1126/science.2142332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






