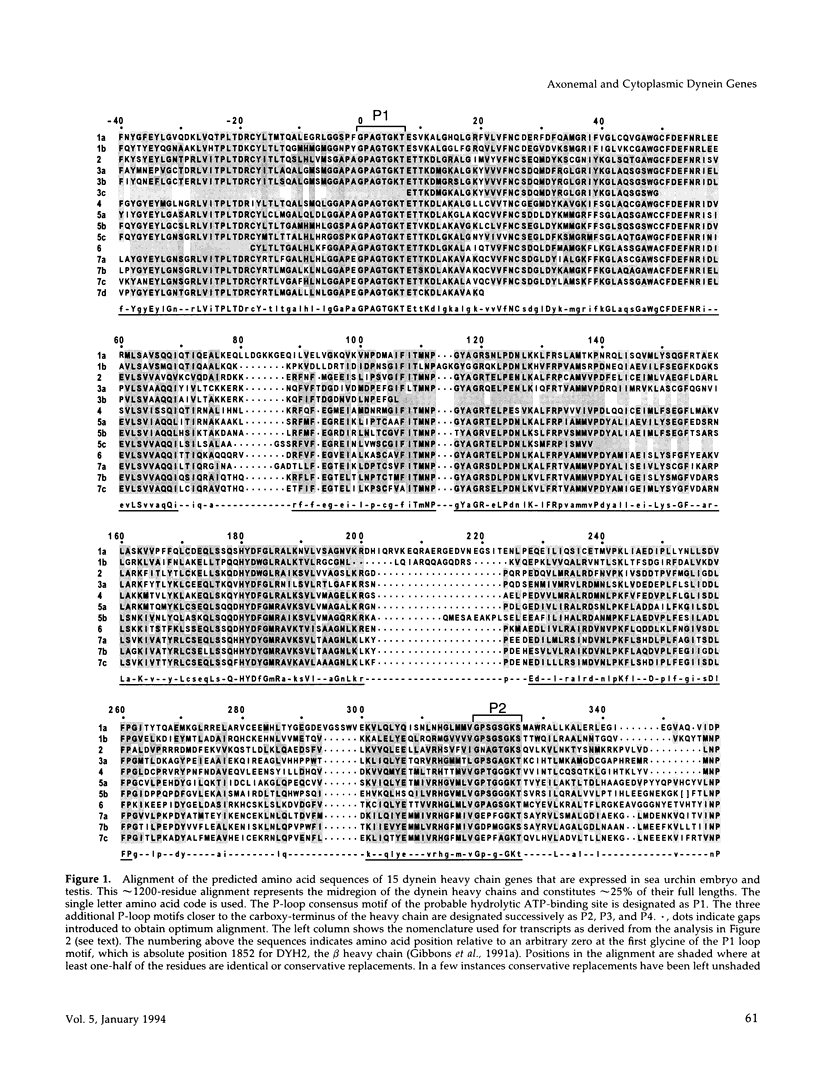
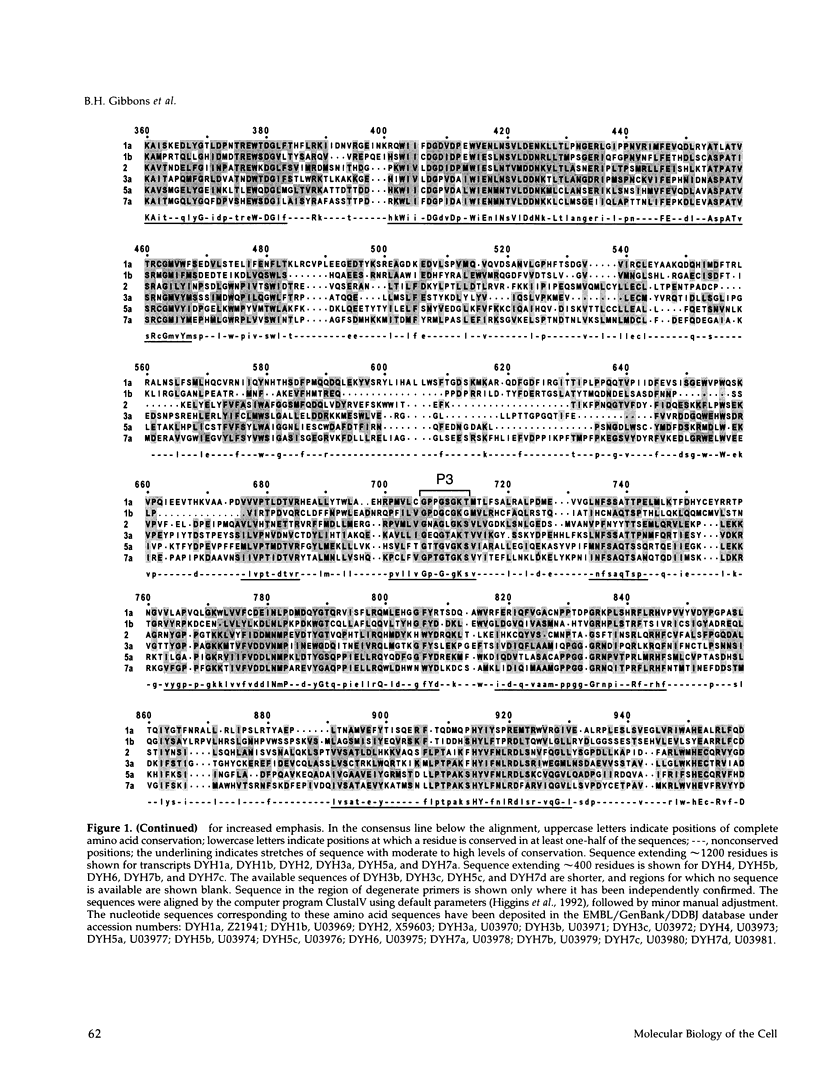
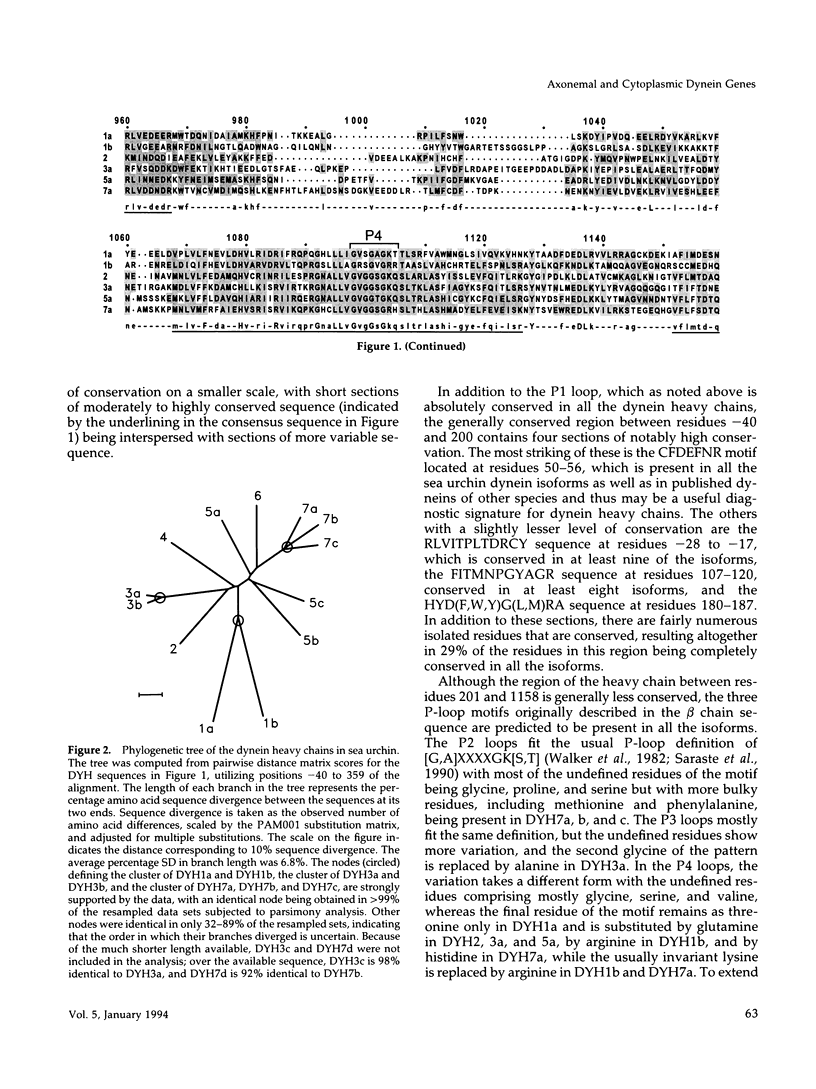
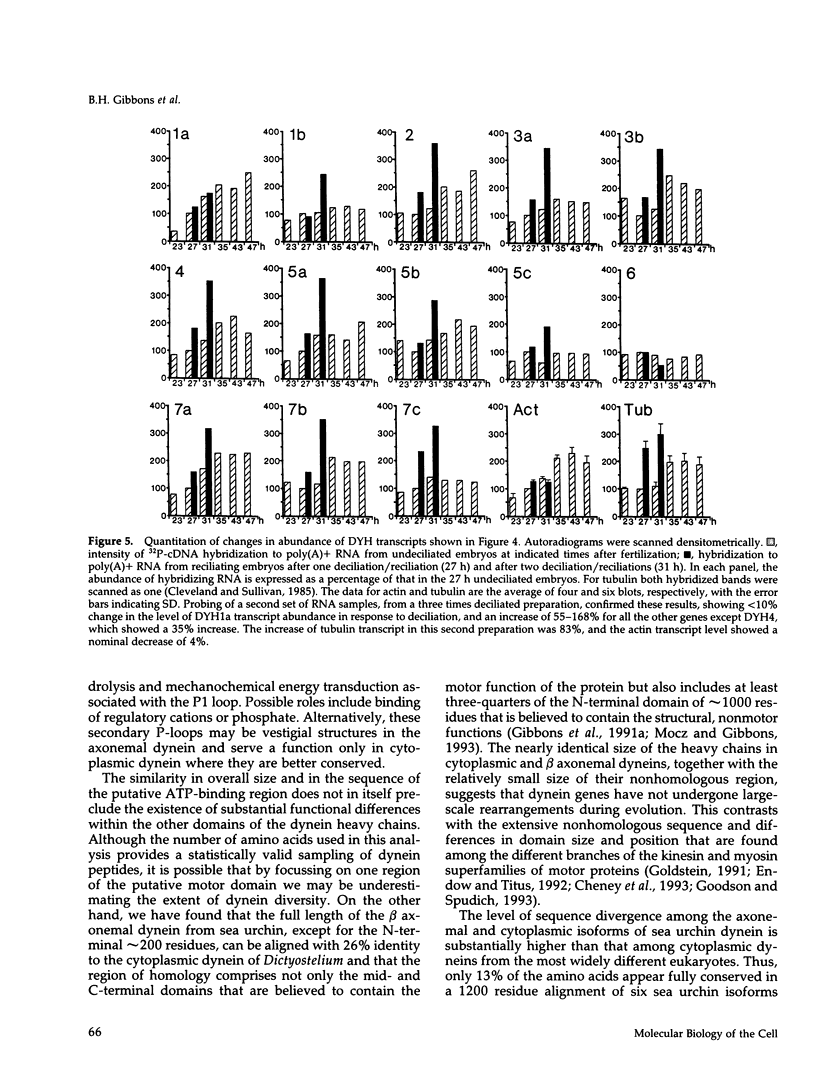
Abstract
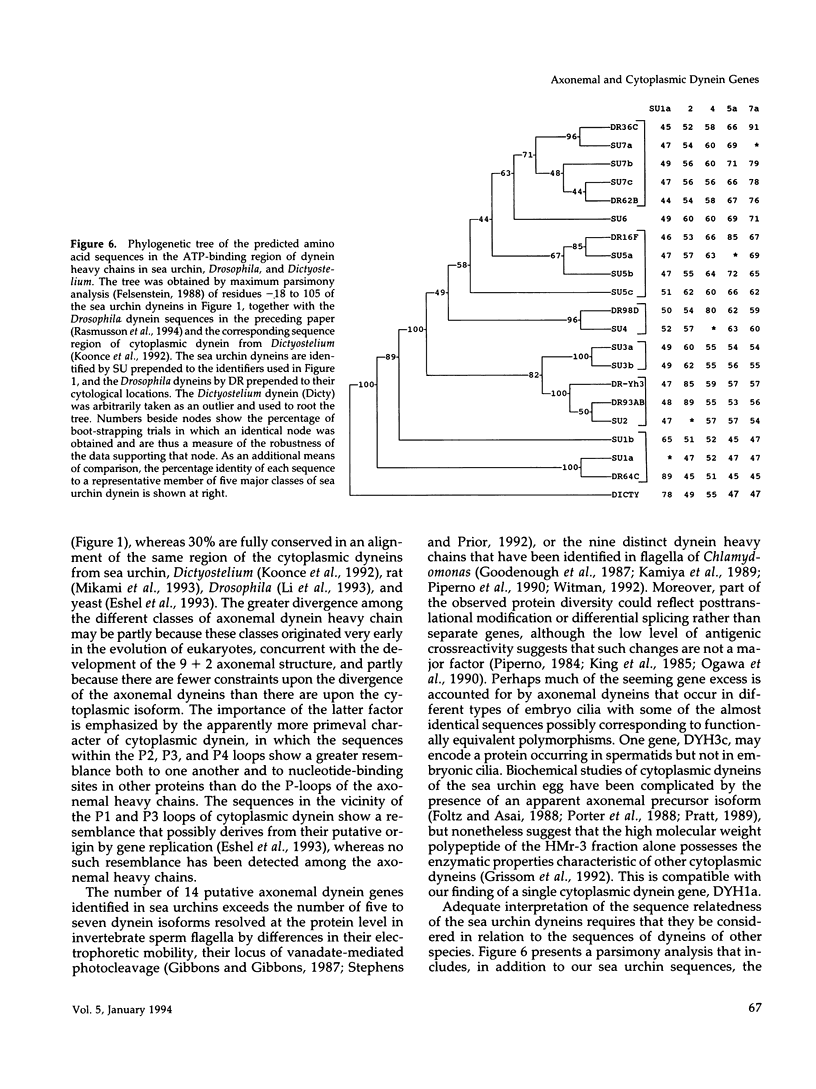
Transcripts approximately 14.5 kilobases in length from 14 different genes that encode for dynein heavy chains have been identified in poly(A)+ RNA from sea urchin embryos. Analysis of the changes in level of these dynein transcripts in response to deciliation, together with their sequence relatedness, suggests that 11 or more of these genes encode dynein isoforms that participate in regeneration of external cilia on the embryo, whereas the single gene whose deduced sequence closely resembles that of cytoplasmic dynein in other organisms appears not to be involved in this regeneration. The four consensus motifs for phosphate binding found previously in the beta heavy chain of sea urchin dynein are present in all five additional isoforms for which extended sequences have been obtained, suggesting that these sites play a significant role in dynein function. Sequence analysis of a approximately 400 amino acid region encompassing the putative hydrolytic ATP-binding site shows that the dynein genes fall into at least six distinct classes. Most of these classes in sea urchin have a high degree of sequence identity with one of the dynein heavy chain genes identified in Drosophila, indicating that the radiation of the dynein gene family into the present classes occurred at an early stage in the evolution of eukaryotes. Evolutionary changes in cytoplasmic dynein have been more constrained than those in the axonemal dyneins.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Britten R. J., Cetta A., Davidson E. H. The single-copy DNA sequence polymorphism of the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1175–1186. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90044-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheney R. E., Riley M. A., Mooseker M. S. Phylogenetic analysis of the myosin superfamily. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1993;24(4):215–223. doi: 10.1002/cm.970240402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Sullivan K. F. Molecular biology and genetics of tubulin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:331–365. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.001555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corthésy-Theulaz I., Pauloin A., Pfeffer S. R. Cytoplasmic dynein participates in the centrosomal localization of the Golgi complex. J Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;118(6):1333–1345. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.6.1333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dentler W. L., Pratt M. M., Stephens R. E. Microtubule-membrane interactions in cilia. II. Photochemical cross-linking of bridge structures and the identification of a membrane-associated dynein-like ATPase. J Cell Biol. 1980 Feb;84(2):381–403. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.2.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endow S. A., Hatsumi M. A multimember kinesin gene family in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4424–4427. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endow S. A., Titus M. A. Genetic approaches to molecular motors. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:29–66. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.000333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eshel D., Urrestarazu L. A., Vissers S., Jauniaux J. C., van Vliet-Reedijk J. C., Planta R. J., Gibbons I. R. Cytoplasmic dynein is required for normal nuclear segregation in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 1;90(23):11172–11176. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.11172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felsenstein J. Phylogenies from molecular sequences: inference and reliability. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:521–565. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.002513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foltz K. R., Asai D. J. Ionic strength-dependent isoforms of sea urchin egg dynein. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):2878–2883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fregien N., Dolecki G. J., Mandel M., Humphreys T. Molecular cloning of five individual stage- and tissue-specific mRNA sequences from sea urchin pluteus embryos. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;3(6):1021–1031. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.6.1021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons B. H., Gibbons I. R. Vanadate-sensitized cleavage of dynein heavy chains by 365-nm irradiation of demembranated sperm flagella and its effect on the flagellar motility. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 15;262(17):8354–8359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons I. R., Asai D. J., Ching N. S., Dolecki G. J., Mocz G., Phillipson C. A., Ren H., Tang W. J., Gibbons B. H. A PCR procedure to determine the sequence of large polypeptides by rapid walking through a cDNA library. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8563–8567. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons I. R., Asai D. J., Tang W. J., Gibbons B. H. A cytoplasmic dynein heavy chain in sea urchin embryos. Biol Cell. 1992;76(3):303–309. doi: 10.1016/0248-4900(92)90432-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons I. R. Cilia and flagella of eukaryotes. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 2):107s–124s. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.107s. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons I. R. Dynein ATPases as microtubule motors. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):15837–15840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons I. R., Gibbons B. H., Mocz G., Asai D. J. Multiple nucleotide-binding sites in the sequence of dynein beta heavy chain. Nature. 1991 Aug 15;352(6336):640–643. doi: 10.1038/352640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons I. R., Lee-Eiford A., Mocz G., Phillipson C. A., Tang W. J., Gibbons B. H. Photosensitized cleavage of dynein heavy chains. Cleavage at the "V1 site" by irradiation at 365 nm in the presence of ATP and vanadate. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 25;262(6):2780–2786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein L. S. The kinesin superfamily: tails of functional redundancy. Trends Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;1(4):93–98. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(91)90036-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gong Z. Y., Brandhorst B. P. Stimulation of tubulin gene transcription by deciliation of sea urchin embryos. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4238–4246. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodenough U. W., Gebhart B., Mermall V., Mitchell D. R., Heuser J. E. High-pressure liquid chromatography fractionation of Chlamydomonas dynein extracts and characterization of inner-arm dynein subunits. J Mol Biol. 1987 Apr 5;194(3):481–494. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90676-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodson H. V., Spudich J. A. Molecular evolution of the myosin family: relationships derived from comparisons of amino acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):659–663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grissom P. M., Porter M. E., McIntosh J. R. Two distinct isoforms of sea urchin egg dynein. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1992;21(4):281–292. doi: 10.1002/cm.970210404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlow P., Nemer M. Coordinate and selective beta-tubulin gene expression associated with cilium formation in sea urchin embryos. Genes Dev. 1987 Dec;1(10):1293–1304. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.10.1293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins D. G., Bleasby A. J., Fuchs R. CLUSTAL V: improved software for multiple sequence alignment. Comput Appl Biosci. 1992 Apr;8(2):189–191. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/8.2.189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King S. M., Otter T., Witman G. B. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies against Chlamydomonas flagellar dyneins by high-resolution protein blotting. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4717–4721. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King S. M., Witman G. B. Localization of an intermediate chain of outer arm dynein by immunoelectron microscopy. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 15;265(32):19807–19811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King S. M., Witman G. B. Structure of the alpha and beta heavy chains of the outer arm dynein from Chlamydomonas flagella. Location of epitopes and protease-sensitive sites. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9244–9255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koonce M. P., Grissom P. M., McIntosh J. R. Dynein from Dictyostelium: primary structure comparisons between a cytoplasmic motor enzyme and flagellar dynein. J Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;119(6):1597–1604. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.6.1597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koonce M. P., McIntosh J. R. Identification and immunolocalization of cytoplasmic dynein in Dictyostelium. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1990;15(1):51–62. doi: 10.1002/cm.970150108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefebvre P. A., Rosenbaum J. L. Regulation of the synthesis and assembly of ciliary and flagellar proteins during regeneration. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:517–546. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.002505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lye R. J., Porter M. E., Scholey J. M., McIntosh J. R. Identification of a microtubule-based cytoplasmic motor in the nematode C. elegans. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):309–318. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90157-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikami A., Paschal B. M., Mazumdar M., Vallee R. B. Molecular cloning of the retrograde transport motor cytoplasmic dynein (MAP 1C). Neuron. 1993 May;10(5):787–796. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90195-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mocz G., Gibbons I. R. ATP-insensitive interaction of the amino-terminal region of the beta heavy chain of dynein with microtubules. Biochemistry. 1993 Apr 6;32(13):3456–3460. doi: 10.1021/bi00064a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neely M. D., Erickson H. P., Boekelheide K. HMW-2, the Sertoli cell cytoplasmic dynein from rat testis, is a dimer composed of nearly identical subunits. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 25;265(15):8691–8698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa K. Four ATP-binding sites in the midregion of the beta heavy chain of dynein. Nature. 1991 Aug 15;352(6336):643–645. doi: 10.1038/352643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallini V., Mencarelli C., Bracci L., Contorni M., Ruggiero P., Tiezzi A., Manetti R. Cytoplasmic nucleoside-triphosphatase similar to axonemal dynein occur widely in different cell types. J Submicrosc Cytol. 1983 Jan;15(1):229–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paschal B. M., Shpetner H. S., Vallee R. B. MAP 1C is a microtubule-activated ATPase which translocates microtubules in vitro and has dynein-like properties. J Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;105(3):1273–1282. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.3.1273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfarr C. M., Coue M., Grissom P. M., Hays T. S., Porter M. E., McIntosh J. R. Cytoplasmic dynein is localized to kinetochores during mitosis. Nature. 1990 May 17;345(6272):263–265. doi: 10.1038/345263a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piperno G. Monoclonal antibodies to dynein subunits reveal the existence of cytoplasmic antigens in sea urchin egg. J Cell Biol. 1984 May;98(5):1842–1850. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.5.1842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piperno G., Ramanis Z., Smith E. F., Sale W. S. Three distinct inner dynein arms in Chlamydomonas flagella: molecular composition and location in the axoneme. J Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;110(2):379–389. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.2.379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter M. E., Grissom P. M., Scholey J. M., Salmon E. D., McIntosh J. R. Dynein isoforms in sea urchin eggs. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6759–6771. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter M. E., Johnson K. A. Dynein structure and function. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1989;5:119–151. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.05.110189.001003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puissant C., Houdebine L. M. An improvement of the single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Biotechniques. 1990 Feb;8(2):148–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmusson K., Serr M., Gepner J., Gibbons I., Hays T. S. A family of dynein genes in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Biol Cell. 1994 Jan;5(1):45–55. doi: 10.1091/mbc.5.1.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sale W. S., Fox L. A. Isolated beta-heavy chain subunit of dynein translocates microtubules in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;107(5):1793–1797. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.5.1793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sale W. S., Goodenough U. W., Heuser J. E. The substructure of isolated and in situ outer dynein arms of sea urchin sperm flagella. J Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;101(4):1400–1412. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.4.1400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saraste M., Sibbald P. R., Wittinghofer A. The P-loop--a common motif in ATP- and GTP-binding proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Nov;15(11):430–434. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90281-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder C. C., Fok A. K., Allen R. D. Vesicle transport along microtubular ribbons and isolation of cytoplasmic dynein from Paramecium. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 1):2553–2562. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.2553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shpetner H. S., Paschal B. M., Vallee R. B. Characterization of the microtubule-activated ATPase of brain cytoplasmic dynein (MAP 1C). J Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;107(3):1001–1009. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.3.1001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmen F. A., Mandel M., Humphreys T. Length and sequence polymorphisms in the ribosomal gene spacer of the Hawaiian sea urchin, T. gratilla. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jun 13;137(2):834–840. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)91155-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. E. Differential protein synthesis and utilization during cilia formation in sea urchin embryos. Dev Biol. 1977 Dec;61(2):311–329. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90301-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. E., Prior G. Dynein from serotonin-activated cilia and flagella: extraction characteristics and distinct sites for cAMP-dependent protein phosphorylation. J Cell Sci. 1992 Dec;103(Pt 4):999–1012. doi: 10.1242/jcs.103.4.999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steuer E. R., Wordeman L., Schroer T. A., Sheetz M. P. Localization of cytoplasmic dynein to mitotic spindles and kinetochores. Nature. 1990 May 17;345(6272):266–268. doi: 10.1038/345266a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart R. J., Pesavento P. A., Woerpel D. N., Goldstein L. S. Identification and partial characterization of six members of the kinesin superfamily in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8470–8474. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vale R. D., Toyoshima Y. Y. Rotation and translocation of microtubules in vitro induced by dyneins from Tetrahymena cilia. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):459–469. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80038-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. E., Saraste M., Runswick M. J., Gay N. J. Distantly related sequences in the alpha- and beta-subunits of ATP synthase, myosin, kinases and other ATP-requiring enzymes and a common nucleotide binding fold. EMBO J. 1982;1(8):945–951. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01276.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witman G. B. Axonemal dyneins. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;4(1):74–79. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90061-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





