Abstract
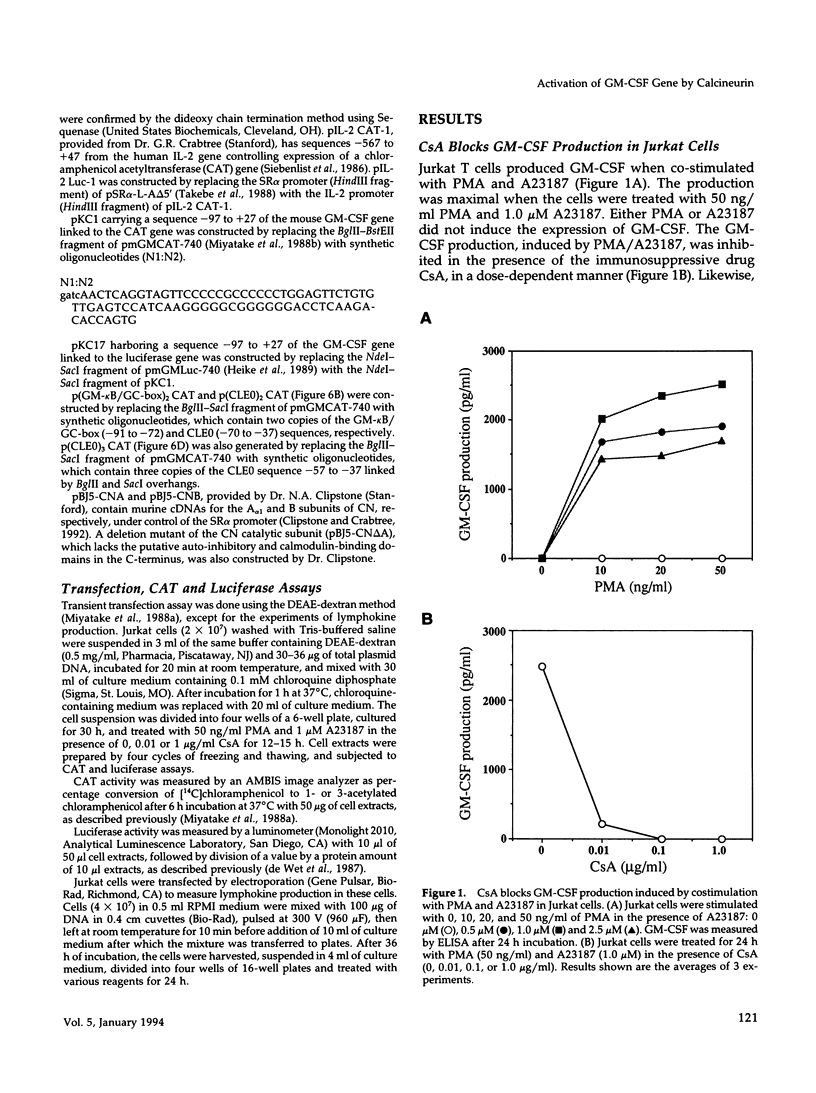
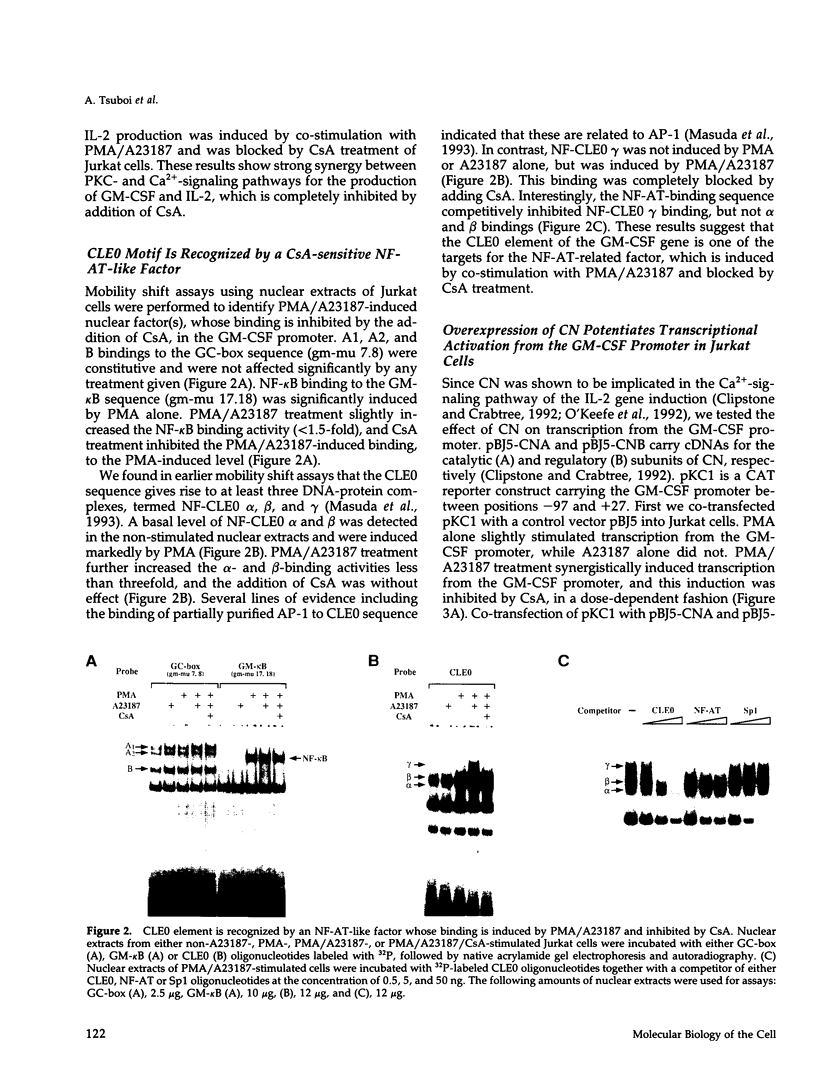
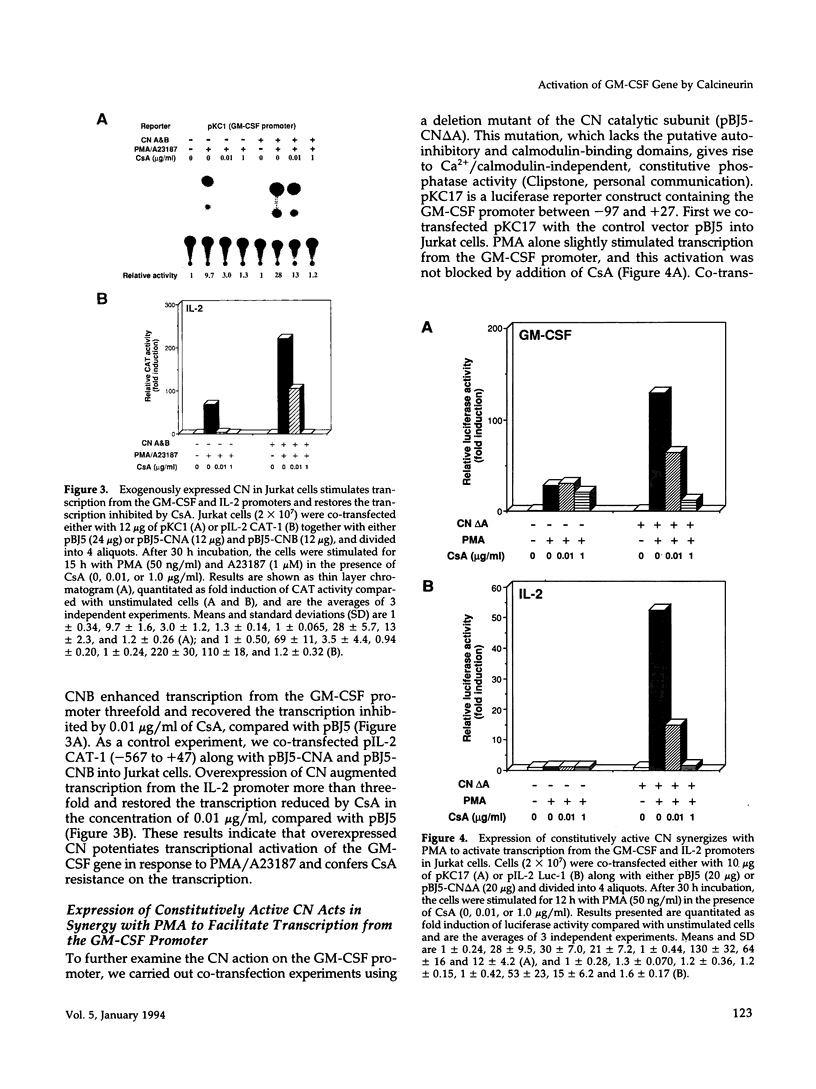
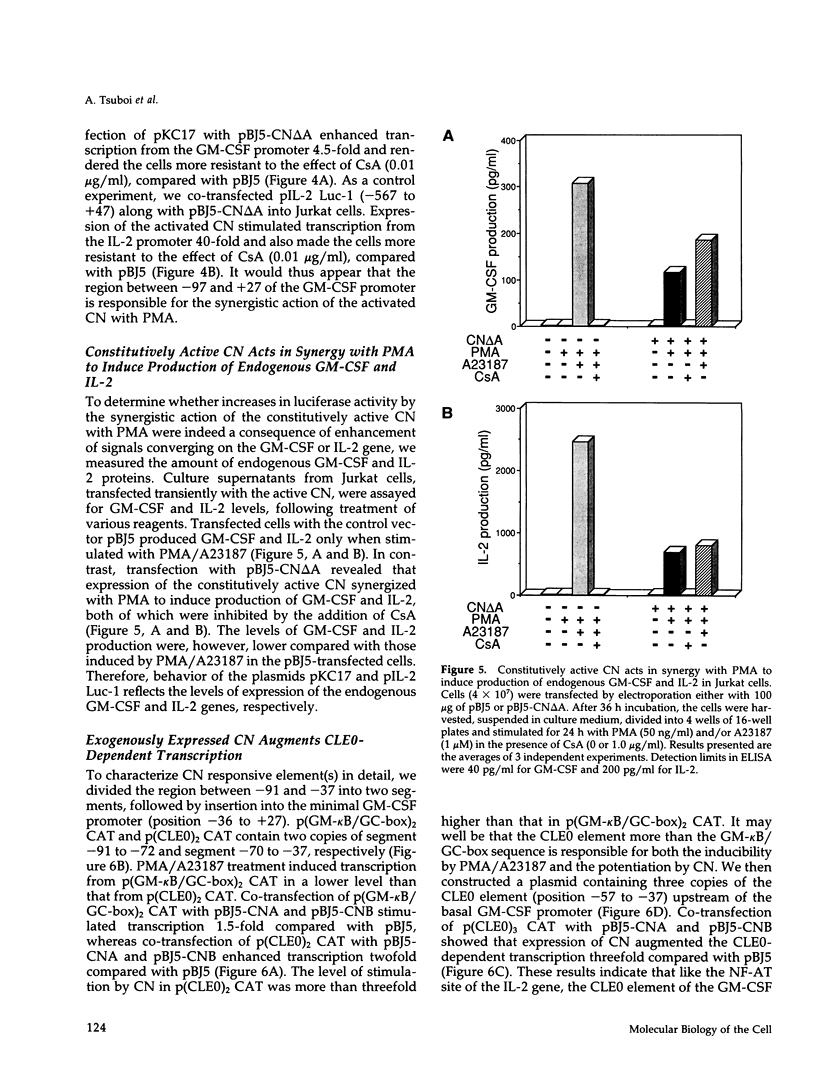
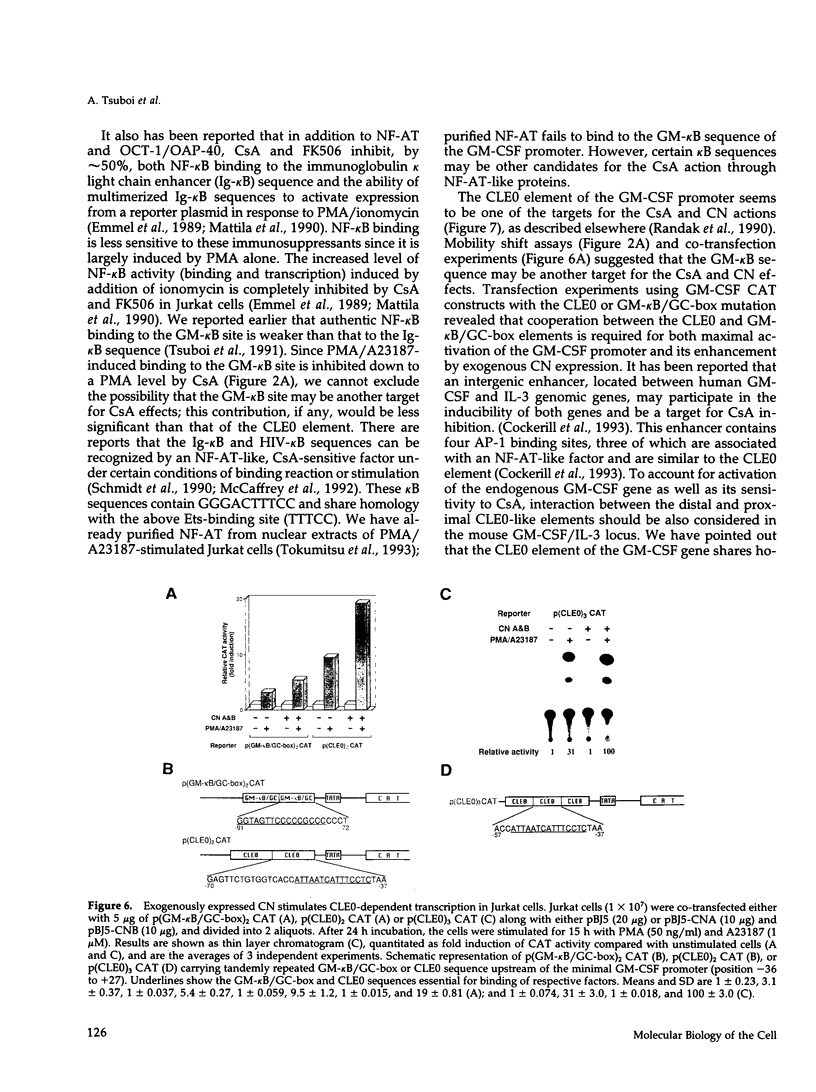
Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) and interleukin-2 (IL-2) are produced by stimulation with phorbol-12-myristate acetate (PMA) and calcium ionophore (A23187) in human T cell leukemia Jurkat cells. The expression of GM-CSF and IL-2 is inhibited by immunosuppressive drugs such as cyclosporin A (CsA) and FK506. Earlier studies on the IL-2 gene expression showed that overexpression of calcineurin (CN), a Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein phosphatase, can stimulate transcription from the IL-2 promoter through the NF-AT-binding site. In this study, we obtained evidence that transfection of the cDNAs for CN A (catalytic) and CN B (regulatory) subunits also augments transcription from the GM-CSF promoter and recovers the transcription inhibited by CsA. The constitutively active type of the CN A subunit, which lacks the auto-inhibitory and calmodulin-binding domains, acts in synergy with PMA to activate transcription from the GM-CSF promoter. We also found that the active CN partially replaces calcium ionophore in synergy with PMA to induce expression of endogenous GM-CSF and IL-2. By multimerizing the regulatory elements of the GM-CSF promoter, we found that one of the target sites for the CN action is the conserved lymphokine element 0 (CLE0), located at positions between -54 and -40. Mobility shift assays showed that the CLE0 sequence has an AP1-binding site and is associated with an NF-AT-like factor, termed NF-CLE0 gamma. NF-CLE0 gamma binding is induced by PMA/A23187 and is inhibited by treatment with CsA. These results suggest that CN is involved in the coordinated induction of the GM-CSF and IL-2 genes and that the CLE0 sequence of the GM-CSF gene is a functional analogue of the NF-AT-binding site in the IL-2 promoter, which mediates signals downstream of T cell activation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrams J. S., Roncarolo M. G., Yssel H., Andersson U., Gleich G. J., Silver J. E. Strategies of anti-cytokine monoclonal antibody development: immunoassay of IL-10 and IL-5 in clinical samples. Immunol Rev. 1992 Jun;127:5–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1992.tb01406.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai K. I., Lee F., Miyajima A., Miyatake S., Arai N., Yokota T. Cytokines: coordinators of immune and inflammatory responses. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:783–836. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.004031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai N., Naito Y., Watanabe M., Masuda E. S., Yamaguchi-Iwai Y., Tsuboi A., Heike T., Matsuda I., Yokota K., Koyano-Nakagawa N. Activation of lymphokine genes in T cells: role of cis-acting DNA elements that respond to T cell activation signals. Pharmacol Ther. 1992;55(3):303–318. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(92)90054-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and calcium signalling. Nature. 1993 Jan 28;361(6410):315–325. doi: 10.1038/361315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boise L. H., Petryniak B., Mao X., June C. H., Wang C. Y., Lindsten T., Bravo R., Kovary K., Leiden J. M., Thompson C. B. The NFAT-1 DNA binding complex in activated T cells contains Fra-1 and JunB. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1911–1919. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clipstone N. A., Crabtree G. R. Identification of calcineurin as a key signalling enzyme in T-lymphocyte activation. Nature. 1992 Jun 25;357(6380):695–697. doi: 10.1038/357695a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockerill P. N., Shannon M. F., Bert A. G., Ryan G. R., Vadas M. A. The granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor/interleukin 3 locus is regulated by an inducible cyclosporin A-sensitive enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2466–2470. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. The promoter-specific transcription factor Sp1 binds to upstream sequences in the SV40 early promoter. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90210-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmel E. A., Verweij C. L., Durand D. B., Higgins K. M., Lacy E., Crabtree G. R. Cyclosporin A specifically inhibits function of nuclear proteins involved in T cell activation. Science. 1989 Dec 22;246(4937):1617–1620. doi: 10.1126/science.2595372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan W. M., Corthésy B., Bram R. J., Crabtree G. R. Nuclear association of a T-cell transcription factor blocked by FK-506 and cyclosporin A. Nature. 1991 Aug 29;352(6338):803–807. doi: 10.1038/352803a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser J. D., Weiss A. Regulation of T-cell lymphokine gene transcription by the accessory molecule CD28. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4357–4363. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fruman D. A., Klee C. B., Bierer B. E., Burakoff S. J. Calcineurin phosphatase activity in T lymphocytes is inhibited by FK 506 and cyclosporin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):3686–3690. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.3686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto Y., Perrino B. A., Soderling T. R. Identification of an autoinhibitory domain in calcineurin. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 5;265(4):1924–1927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heike T., Miyatake S., Yoshida M., Arai K., Arai N. Bovine papilloma virus encoded E2 protein activates lymphokine genes through DNA elements, distinct from the consensus motif, in the long control region of its own genome. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1411–1417. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03522.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain J., McCaffrey P. G., Valge-Archer V. E., Rao A. Nuclear factor of activated T cells contains Fos and Jun. Nature. 1992 Apr 30;356(6372):801–804. doi: 10.1038/356801a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kincaid R. L., Giri P. R., Higuchi S., Tamura J., Dixon S. C., Marietta C. A., Amorese D. A., Martin B. M. Cloning and characterization of molecular isoforms of the catalytic subunit of calcineurin using nonisotopic methods. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 5;265(19):11312–11319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kincaid R. L., Takayama H., Billingsley M. L., Sitkovsky M. V. Differential expression of calmodulin-binding proteins in B, T lymphocytes and thymocytes. Nature. 1987 Nov 12;330(6144):176–178. doi: 10.1038/330176a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuda E. S., Tokumitsu H., Tsuboi A., Shlomai J., Hung P., Arai K., Arai N. The granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor promoter cis-acting element CLE0 mediates induction signals in T cells and is recognized by factors related to AP1 and NFAT. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;13(12):7399–7407. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.12.7399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattila P. S., Ullman K. S., Fiering S., Emmel E. A., McCutcheon M., Crabtree G. R., Herzenberg L. A. The actions of cyclosporin A and FK506 suggest a novel step in the activation of T lymphocytes. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4425–4433. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07893.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCaffrey P. G., Jain J., Jamieson C., Sen R., Rao A. A T cell nuclear factor resembling NF-AT binds to an NF-kappa B site and to the conserved lymphokine promoter sequence "cytokine-1". J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 25;267(3):1864–1871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCaffrey P. G., Perrino B. A., Soderling T. R., Rao A. NF-ATp, a T lymphocyte DNA-binding protein that is a target for calcineurin and immunosuppressive drugs. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 15;268(5):3747–3752. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyatake S., Seiki M., Malefijt R. D., Heike T., Fujisawa J., Takebe Y., Nishida J., Shlomai J., Yokota T., Yoshida M. Activation of T cell-derived lymphokine genes in T cells and fibroblasts: effects of human T cell leukemia virus type I p40x protein and bovine papilloma virus encoded E2 protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 25;16(14A):6547–6566. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.14.6547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyatake S., Seiki M., Yoshida M., Arai K. T-cell activation signals and human T-cell leukemia virus type I-encoded p40x protein activate the mouse granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor gene through a common DNA element. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;8(12):5581–5587. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.12.5581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyatake S., Shlomai J., Arai K., Arai N. Characterization of the mouse granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) gene promoter: nuclear factors that interact with an element shared by three lymphokine genes--those for GM-CSF, interleukin-4 (IL-4), and IL-5. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;11(12):5894–5901. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.12.5894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyatake S., Yokota T., Lee F., Arai K. Structure of the chromosomal gene for murine interleukin 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):316–320. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northrop J. P., Ullman K. S., Crabtree G. R. Characterization of the nuclear and cytoplasmic components of the lymphoid-specific nuclear factor of activated T cells (NF-AT) complex. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 5;268(4):2917–2923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Keefe S. J., Tamura J., Kincaid R. L., Tocci M. J., O'Neill E. A. FK-506- and CsA-sensitive activation of the interleukin-2 promoter by calcineurin. Nature. 1992 Jun 25;357(6380):692–694. doi: 10.1038/357692a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randak C., Brabletz T., Hergenröther M., Sobotta I., Serfling E. Cyclosporin A suppresses the expression of the interleukin 2 gene by inhibiting the binding of lymphocyte-specific factors to the IL-2 enhancer. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2529–2536. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07433.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riegel J. S., Corthesy B., Flanagan W. M., Crabtree G. R. Regulation of the interleukin-2 gene. Chem Immunol. 1992;51:266–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risse G., Jooss K., Neuberg M., Brüller H. J., Müller R. Asymmetrical recognition of the palindromic AP1 binding site (TRE) by Fos protein complexes. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3825–3832. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08560.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt A., Hennighausen L., Siebenlist U. Inducible nuclear factor binding to the kappa B elements of the human immunodeficiency virus enhancer in T cells can be blocked by cyclosporin A in a signal-dependent manner. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):4037–4041. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.4037-4041.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber E., Matthias P., Müller M. M., Schaffner W. Rapid detection of octamer binding proteins with 'mini-extracts', prepared from a small number of cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 11;17(15):6419–6419. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.15.6419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber S. L., Crabtree G. R. The mechanism of action of cyclosporin A and FK506. Immunol Today. 1992 Apr;13(4):136–142. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90111-J. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Durand D. B., Bressler P., Holbrook N. J., Norris C. A., Kamoun M., Kant J. A., Crabtree G. R. Promoter region of interleukin-2 gene undergoes chromatin structure changes and confers inducibility on chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene during activation of T cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;6(9):3042–3049. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.9.3042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigal N. H., Dumont F. J. Cyclosporin A, FK-506, and rapamycin: pharmacologic probes of lymphocyte signal transduction. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992;10:519–560. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.10.040192.002511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto K., Tsuboi A., Miyatake S., Arai K., Arai N. Inducible and non-inducible factors co-operatively activate the GM-CSF promoter by interacting with two adjacent DNA motifs. Int Immunol. 1990;2(8):787–794. doi: 10.1093/intimm/2.8.787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takebe Y., Seiki M., Fujisawa J., Hoy P., Yokota K., Arai K., Yoshida M., Arai N. SR alpha promoter: an efficient and versatile mammalian cDNA expression system composed of the simian virus 40 early promoter and the R-U5 segment of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 long terminal repeat. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):466–472. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tocci M. J., Matkovich D. A., Collier K. A., Kwok P., Dumont F., Lin S., Degudicibus S., Siekierka J. J., Chin J., Hutchinson N. I. The immunosuppressant FK506 selectively inhibits expression of early T cell activation genes. J Immunol. 1989 Jul 15;143(2):718–726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokumitsu H., Masuda E. S., Tsuboi A., Arai K., Arai N. Purification of the 120 kDa component of the human nuclear factor of activated T cells (NF-AT): reconstitution of binding activity to the cis-acting element of the GM-CSF and IL-2 promoter with AP-1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Oct 29;196(2):737–744. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.2311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuboi A., Sugimoto K., Yodoi J., Miyatake S., Arai K., Arai N. A nuclear factor NF-GM2 that interacts with a regulatory region of the GM-CSF gene essential for its induction in responses to T-cell activation: purification from human T-cell leukemia line Jurkat cells and similarity to NF-kappa B. Int Immunol. 1991 Aug;3(8):807–817. doi: 10.1093/intimm/3.8.807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullman K. S., Northrop J. P., Admon A., Crabtree G. R. Jun family members are controlled by a calcium-regulated, cyclosporin A-sensitive signaling pathway in activated T lymphocytes. Genes Dev. 1993 Feb;7(2):188–196. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.2.188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullman K. S., Northrop J. P., Verweij C. L., Crabtree G. R. Transmission of signals from the T lymphocyte antigen receptor to the genes responsible for cell proliferation and immune function: the missing link. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:421–452. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.002225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Hahn S. L., Giovane A. The Ets family of transcription factors. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Jan 15;211(1-2):7–18. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-78757-7_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet J. R., Wood K. V., DeLuca M., Helinski D. R., Subramani S. Firefly luciferase gene: structure and expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):725–737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]