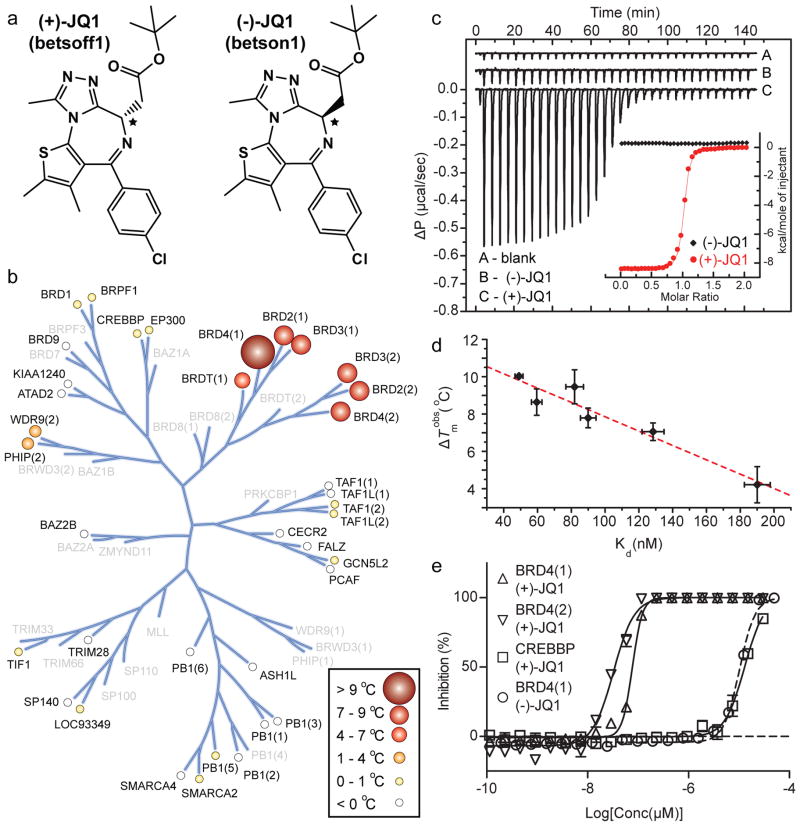
Figure 1. Structure and selectivity of JQ1.
a, Structure of the two JQ1 stereo-isomers. The stereocentre at C6 is indicated by an asterix (*). b, Assessment of inhibitor selectivity using Differential Scanning Fluorimetry (DSF). Shown are averaged temperature shifts (ΔTmobs) in °C upon binding of 10 μM (+)-JQ1. The temperature shifts are represented by spheres as indicated in the inset. Screened proteins are labelled and proteins not included in the selectivity panel are shown in grey. (−)-JQ1 did not reveal any significant temperature shifts to any of the screened bromodomains. c, Isothermal Titration Calorimetry (ITC). Raw injection heats are shown for a blank titration of (BRD4(1)) into buffer (A), and reverse titrations using the inactive isomer (−)-JQ1 (B) and the active isomer (+)-JQ1 (C). The inset shows normalized binding enthalpies corrected for the heat of dilution as a function of binding site saturation (symbols as indicated in the inset). Solid lines represent a nonlinear least squares fit using a single-site binding model. d, Thermal shifts (ΔTmobs) show good correlation to dissociation constants (Kd) determined by ITC for the BET bromodomains. The dotted red line represents a least squares fit with an R of 96 %. e, Competitive displacement of a histone peptide from human bromodomains is exhibited by JQ1 using a bead-based proximity assay. Alpha screen titrations monitoring the displacement of a tetra-acetylated histone H4 peptide by JQ1 isomers using the bromodomains BRD4(1), BRD4(2) or of an acetylated H3 peptide using CREBBP.