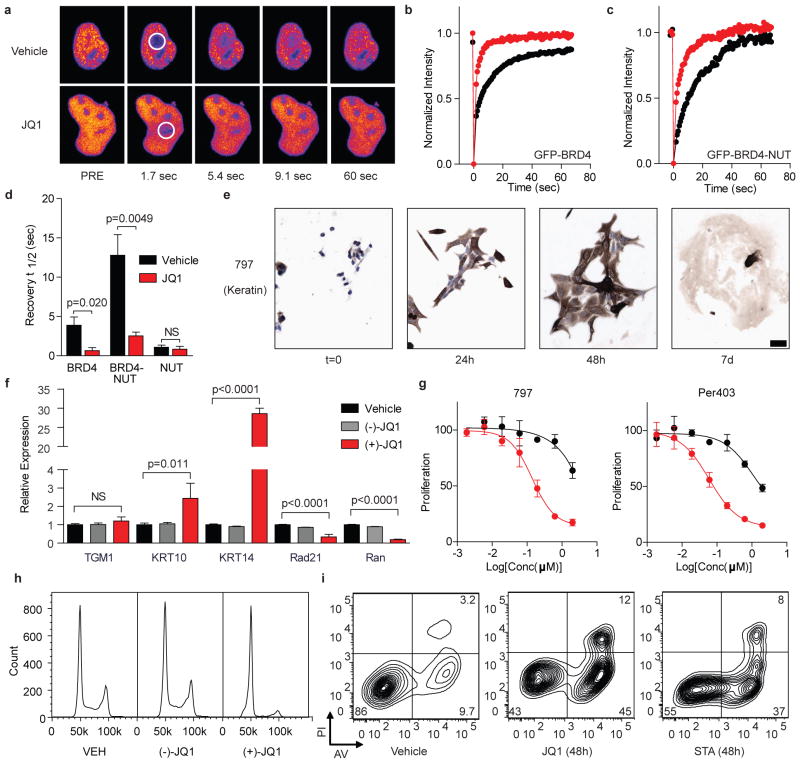
Figure 4. JQ1 binds BRD4 competitively with chromatin resulting in differentiation and growth arrest of NMC cells.
a, Fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP) of GFP-BRD4 demonstrates enhanced recovery in the presence of JQ1. Nuclei are false-colored in proportion to fluorescence intensity. White circles indicate target regions of photobleaching. b–c, JQ1 accelerates fluorescence recovery in FRAP experiments performed with transfected (b) GFP-BRD4 and (c) GFP-BRD4-NUT. d, Quantitative comparison of time to half-maximal fluorescence recovery for FRAP studies (b–c, Supplementary Fig. 3a). Data represent the mean ± s.d. (n = 5), and are annotated with p-values as obtained from a two-tailed t-test. e, Differentiation of NMC cells by JQ1 (500 nM) is prompt and characterized by a marked increase in cytokeratin expression (AE1/AE3; 10x, scale bar is 50 μm). f, Comparative gene expression studies of (+)-JQ1 (red; 250 nM, 48 h) versus (−)-JQ1 (gray; 250 nM, 48 h) and vehicle (black) confirm squamous differentiation. Data represent the mean ± s.d. (n = 3), and are annotated with p-values as obtained from a two-tailed t-test. g, Growth effects of BRD4 inhibition on BRD4-NUT dependent cell lines. Cells were incubated with (+)-JQ1 (red circles) or (−)-JQ1 (black circles) and monitored for proliferation after 72 hours. (+)-JQ1 uniquely attenuates proliferation by NMC cell lines. Data is presented as mean ± s.d. (n = 3). Curve fit was calculated by logistic regression. h, Flow cytometry for DNA content in NMC 797 cells. (+)-JQ1 (250 nM, 48 h) induces a G1 arrest compared to (−)-JQ1 (250 nM) and vehicle control. i, Flow cytometric analysis of NMC 797 squamous carcinoma cells treated with vehicle, JQ1 or staurosporine (STA), as indicated. PI, propidium iodide. AV, annexin-V.