Abstract
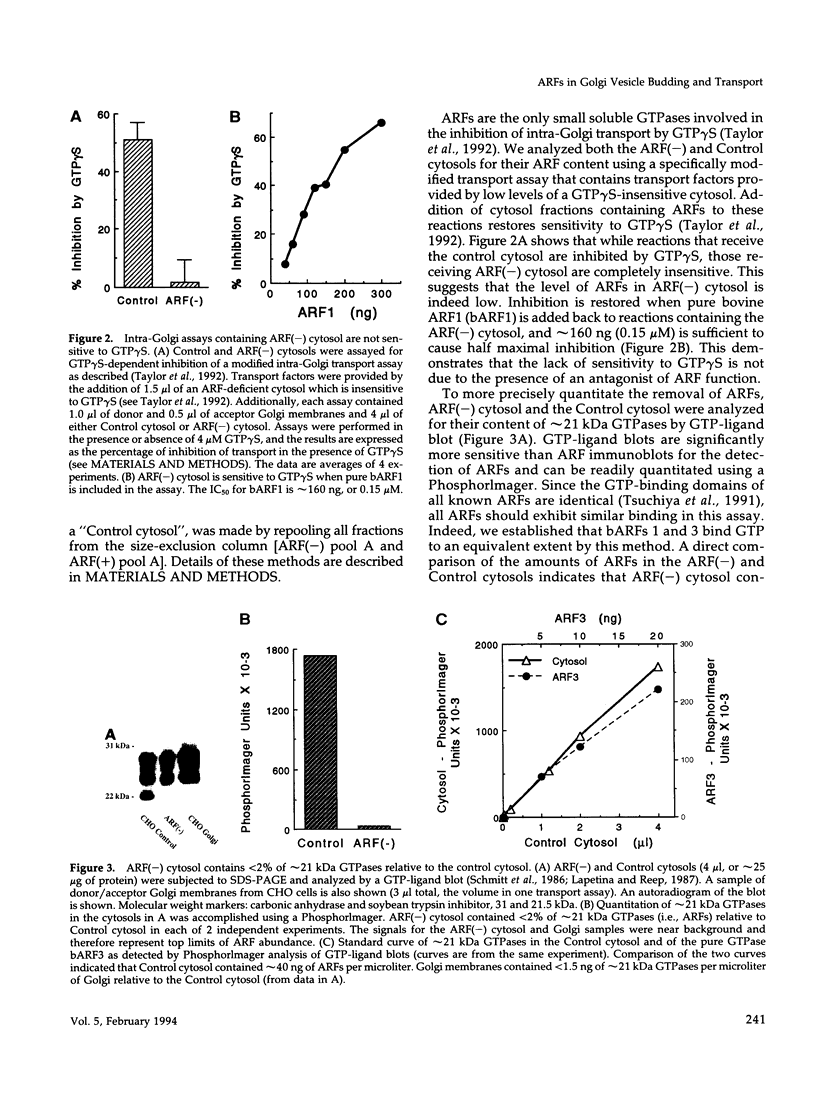
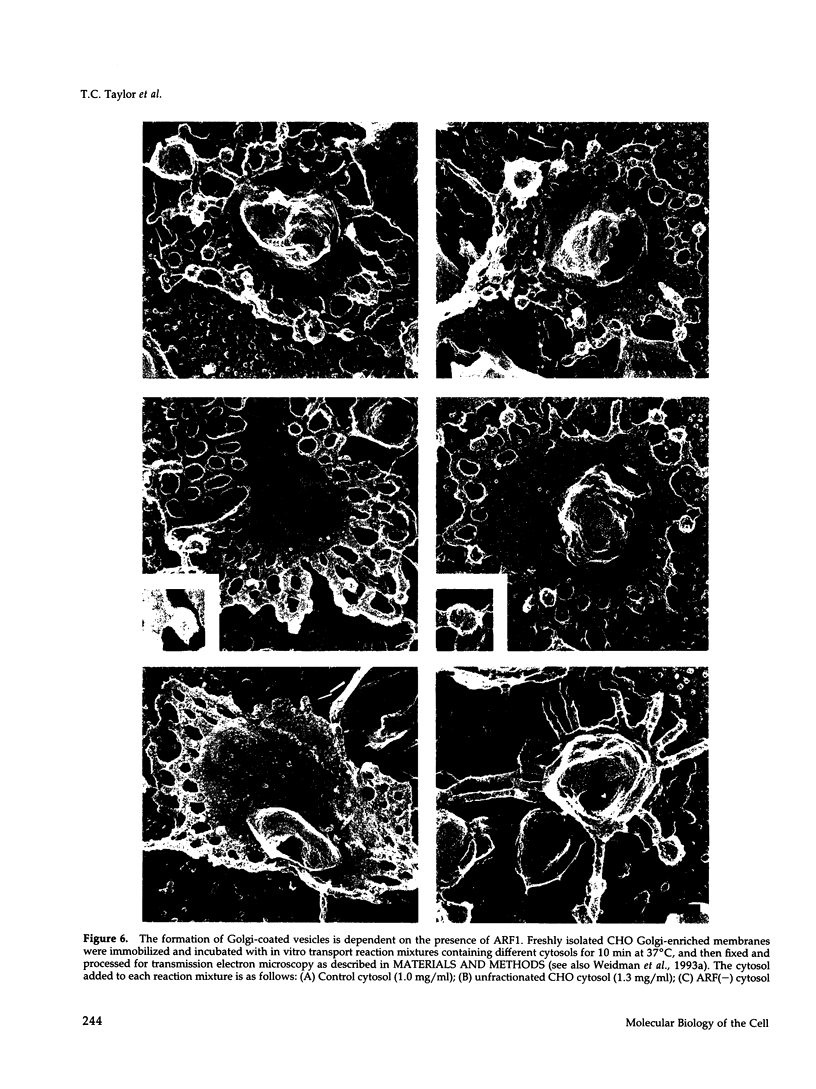
We investigated the role of ADP-ribosylation factors (ARFs) in Golgi function using biochemical and morphological cell-free assays. An ARF-free cytosol produced from soluble Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) extracts supports intra-Golgi transport by a mechanism that is biochemically indistinguishable from control transport reactions: ARF-free transport reactions are NSF-dependent, remain sensitive to the donor Golgi-specific inhibitor ilimaquinone, and exhibit kinetics that are identical to that of control reactions containing ARFs. In contrast, ARF-free cytosol does not support the formation of coated vesicles on Golgi cisternae. However, vesicle formation is reconstituted upon the addition of ARF1. These data suggest that neither soluble ARFs nor coated vesicle formation are essential for transport. We conclude that cell-free intra-Golgi transport proceeds via a coated vesicle-independent mechanism regardless of vesicle formation on Golgi cisternae.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balch W. E., Dunphy W. G., Braell W. A., Rothman J. E. Reconstitution of the transport of protein between successive compartments of the Golgi measured by the coupled incorporation of N-acetylglucosamine. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(2 Pt 1):405–416. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90019-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balch W. E., Glick B. S., Rothman J. E. Sequential intermediates in the pathway of intercompartmental transport in a cell-free system. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):525–536. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90459-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balch W. E., Rothman J. E. Characterization of protein transport between successive compartments of the Golgi apparatus: asymmetric properties of donor and acceptor activities in a cell-free system. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Jul;240(1):413–425. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90046-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
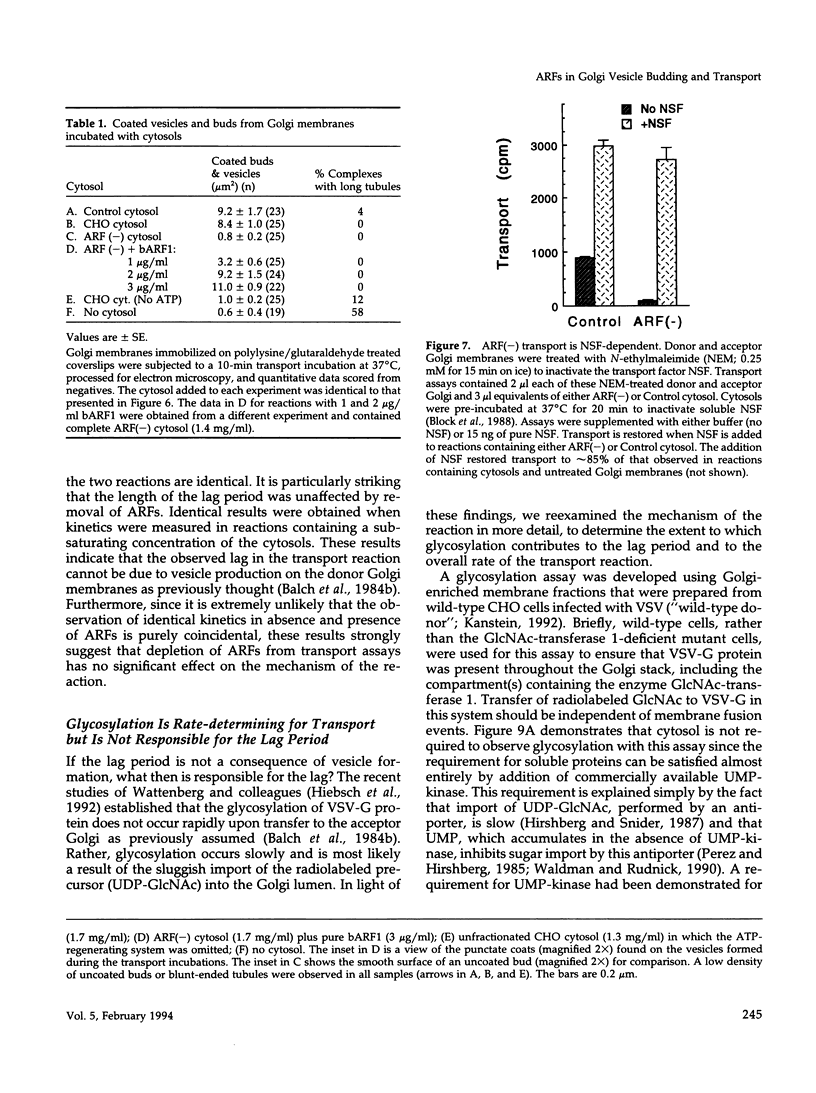
- Block M. R., Glick B. S., Wilcox C. A., Wieland F. T., Rothman J. E. Purification of an N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive protein catalyzing vesicular transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7852–7856. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braell W. A., Balch W. E., Dobbertin D. C., Rothman J. E. The glycoprotein that is transported between successive compartments of the Golgi in a cell-free system resides in stacks of cisternae. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):511–524. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90458-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown H. A., Gutowski S., Moomaw C. R., Slaughter C., Sternweis P. C. ADP-ribosylation factor, a small GTP-dependent regulatory protein, stimulates phospholipase D activity. Cell. 1993 Dec 17;75(6):1137–1144. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90323-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clary D. O., Rothman J. E. Purification of three related peripheral membrane proteins needed for vesicular transport. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 15;265(17):10109–10117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colombo M. I., Gonzalo S., Weidman P., Stahl P. Characterization of trypsin-sensitive factor(s) required for endosome-endosome fusion. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 5;266(34):23438–23445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper M. S., Cornell-Bell A. H., Chernjavsky A., Dani J. W., Smith S. J. Tubulovesicular processes emerge from trans-Golgi cisternae, extend along microtubules, and interlink adjacent trans-golgi elements into a reticulum. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):135–145. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90221-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson J. G., Cassel D., Kahn R. A., Klausner R. D. ADP-ribosylation factor, a small GTP-binding protein, is required for binding of the coatomer protein beta-COP to Golgi membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6408–6412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson J. G., Finazzi D., Klausner R. D. Brefeldin A inhibits Golgi membrane-catalysed exchange of guanine nucleotide onto ARF protein. Nature. 1992 Nov 26;360(6402):350–352. doi: 10.1038/360350a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson J. G., Lippincott-Schwartz J., Klausner R. D. Guanine nucleotides modulate the effects of brefeldin A in semipermeable cells: regulation of the association of a 110-kD peripheral membrane protein with the Golgi apparatus. J Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;112(4):579–588. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.4.579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duden R., Allan V., Kreis T. Involvement of beta-COP in membrane traffic through the Golgi complex. Trends Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;1(1):14–19. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(91)90064-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farquhar M. G., Palade G. E. The Golgi apparatus (complex)-(1954-1981)-from artifact to center stage. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 2):77s–103s. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.77s. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groesch M. E., Ruohola H., Bacon R., Rossi G., Ferro-Novick S. Isolation of a functional vesicular intermediate that mediates ER to Golgi transport in yeast. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;111(1):45–53. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.1.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruenberg J., Howell K. E. Membrane traffic in endocytosis: insights from cell-free assays. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1989;5:453–481. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.05.110189.002321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helms J. B., Palmer D. J., Rothman J. E. Two distinct populations of ARF bound to Golgi membranes. J Cell Biol. 1993 May;121(4):751–760. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.4.751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helms J. B., Rothman J. E. Inhibition by brefeldin A of a Golgi membrane enzyme that catalyses exchange of guanine nucleotide bound to ARF. Nature. 1992 Nov 26;360(6402):352–354. doi: 10.1038/360352a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuser J. E., Reese T. S., Dennis M. J., Jan Y., Jan L., Evans L. Synaptic vesicle exocytosis captured by quick freezing and correlated with quantal transmitter release. J Cell Biol. 1979 May;81(2):275–300. doi: 10.1083/jcb.81.2.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuser J. Three-dimensional visualization of coated vesicle formation in fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1980 Mar;84(3):560–583. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.3.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
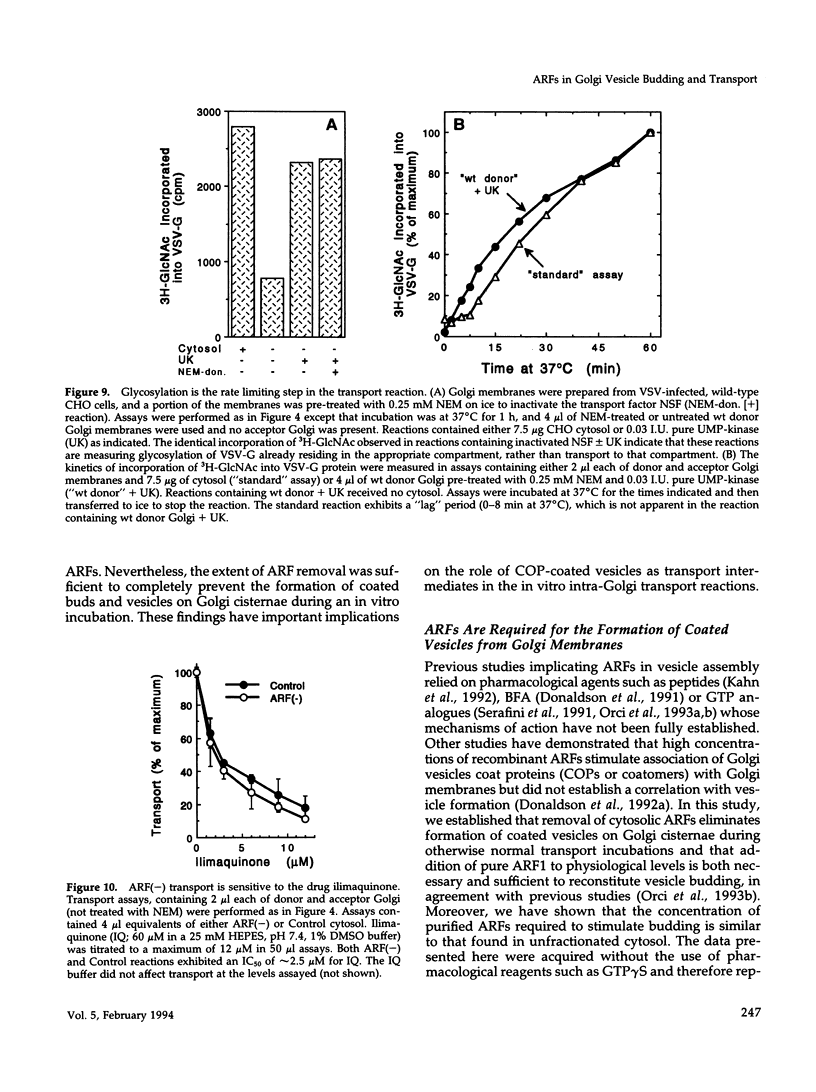
- Hiebsch R. R., Raub T. J., Wattenberg B. W. Primaquine blocks transport by inhibiting the formation of functional transport vesicles. Studies in a cell-free assay of protein transport through the Golgi apparatus. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):20323–20328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiebsch R. R., Wattenberg B. W. Vesicle fusion in protein transport through the Golgi in vitro does not involve long-lived prefusion intermediates. A reassessment of the kinetics of transport as measured by glycosylation. Biochemistry. 1992 Jul 7;31(26):6111–6118. doi: 10.1021/bi00141a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschberg C. B., Snider M. D. Topography of glycosylation in the rough endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:63–87. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.000431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosobuchi M., Kreis T., Schekman R. SEC21 is a gene required for ER to Golgi protein transport that encodes a subunit of a yeast coatomer. Nature. 1992 Dec 10;360(6404):603–605. doi: 10.1038/360603a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson J. D., Palade G. E. Intracellular transport of secretory proteins in the pancreatic exocrine cell. I. Role of the peripheral elements of the Golgi complex. J Cell Biol. 1967 Aug;34(2):577–596. doi: 10.1083/jcb.34.2.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn R. A. Fluoride is not an activator of the smaller (20-25 kDa) GTP-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15595–15597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn R. A., Randazzo P., Serafini T., Weiss O., Rulka C., Clark J., Amherdt M., Roller P., Orci L., Rothman J. E. The amino terminus of ADP-ribosylation factor (ARF) is a critical determinant of ARF activities and is a potent and specific inhibitor of protein transport. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 25;267(18):13039–13046. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn R. A., Yucel J. K., Malhotra V. ARF signaling: a potential role for phospholipase D in membrane traffic. Cell. 1993 Dec 17;75(6):1045–1048. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90314-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausner R. D., Donaldson J. G., Lippincott-Schwartz J. Brefeldin A: insights into the control of membrane traffic and organelle structure. J Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;116(5):1071–1080. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.5.1071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang L., Kornfeld S. A simplified procedure for synthesizing large quantities of highly purified uridine [beta-32P]diphospho-N-acetylglucosamine. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jul;140(1):264–269. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90163-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G., Reep B. R. Specific binding of [alpha-32P]GTP to cytosolic and membrane-bound proteins of human platelets correlates with the activation of phospholipase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2261–2265. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippincott-Schwartz J. Bidirectional membrane traffic between the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus. Trends Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;3(3):81–88. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(93)90078-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melançon P., Glick B. S., Malhotra V., Weidman P. J., Serafini T., Gleason M. L., Orci L., Rothman J. E. Involvement of GTP-binding "G" proteins in transport through the Golgi stack. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1053–1062. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90591-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellman I., Simons K. The Golgi complex: in vitro veritas? Cell. 1992 Mar 6;68(5):829–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90027-A. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Glick B. S., Rothman J. E. A new type of coated vesicular carrier that appears not to contain clathrin: its possible role in protein transport within the Golgi stack. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):171–184. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90734-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Malhotra V., Amherdt M., Serafini T., Rothman J. E. Dissection of a single round of vesicular transport: sequential intermediates for intercisternal movement in the Golgi stack. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):357–368. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90239-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Palmer D. J., Ravazzola M., Perrelet A., Amherdt M., Rothman J. E. Budding from Golgi membranes requires the coatomer complex of non-clathrin coat proteins. Nature. 1993 Apr 15;362(6421):648–652. doi: 10.1038/362648a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Tagaya M., Amherdt M., Perrelet A., Donaldson J. G., Lippincott-Schwartz J., Klausner R. D., Rothman J. E. Brefeldin A, a drug that blocks secretion, prevents the assembly of non-clathrin-coated buds on Golgi cisternae. Cell. 1991 Mar 22;64(6):1183–1195. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90273-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orcl L., Palmer D. J., Amherdt M., Rothman J. E. Coated vesicle assembly in the Golgi requires only coatomer and ARF proteins from the cytosol. Nature. 1993 Aug 19;364(6439):732–734. doi: 10.1038/364732a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostermann J., Orci L., Tani K., Amherdt M., Ravazzola M., Elazar Z., Rothman J. E. Stepwise assembly of functionally active transport vesicles. Cell. 1993 Dec 3;75(5):1015–1025. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90545-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palade G. Intracellular aspects of the process of protein synthesis. Science. 1975 Aug 1;189(4200):347–358. doi: 10.1126/science.1096303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepperkok R., Scheel J., Horstmann H., Hauri H. P., Griffiths G., Kreis T. E. Beta-COP is essential for biosynthetic membrane transport from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi complex in vivo. Cell. 1993 Jul 16;74(1):71–82. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90295-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez M., Hirschberg C. B. Translocation of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine into vesicles derived from rat liver rough endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 25;260(8):4671–4678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randazzo P. A., Yang Y. C., Rulka C., Kahn R. A. Activation of ADP-ribosylation factor by Golgi membranes. Evidence for a brefeldin A- and protease-sensitive activating factor on Golgi membranes. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 5;268(13):9555–9563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rexach M. F., Schekman R. W. Distinct biochemical requirements for the budding, targeting, and fusion of ER-derived transport vesicles. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;114(2):219–229. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.2.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E., Miller R. L., Urbani L. J. Intercompartmental transport in the Golgi complex is a dissociative process: facile transfer of membrane protein between two Golgi populations. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;99(1 Pt 1):260–271. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.1.260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E., Orci L. Molecular dissection of the secretory pathway. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):409–415. doi: 10.1038/355409a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E., Orci L. Movement of proteins through the Golgi stack: a molecular dissection of vesicular transport. FASEB J. 1990 Mar;4(5):1460–1468. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.5.2407590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E., Urbani L. J., Brands R. Transport of protein between cytoplasmic membranes of fused cells: correspondence to processes reconstituted in a cell-free system. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;99(1 Pt 1):248–259. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.1.248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saraste J., Kuismanen E. Pathways of protein sorting and membrane traffic between the rough endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi complex. Semin Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;3(5):343–355. doi: 10.1016/1043-4682(92)90020-V. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt H. D., Wagner P., Pfaff E., Gallwitz D. The ras-related YPT1 gene product in yeast: a GTP-binding protein that might be involved in microtubule organization. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):401–412. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90597-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwaninger R., Beckers C. J., Balch W. E. Sequential transport of protein between the endoplasmic reticulum and successive Golgi compartments in semi-intact cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 15;266(20):13055–13063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serafini T., Orci L., Amherdt M., Brunner M., Kahn R. A., Rothman J. E. ADP-ribosylation factor is a subunit of the coat of Golgi-derived COP-coated vesicles: a novel role for a GTP-binding protein. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):239–253. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90176-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley P., Caillibot V., Siminovitch L. Selection and characterization of eight phenotypically distinct lines of lectin-resistant Chinese hamster ovary cell. Cell. 1975 Oct;6(2):121–128. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90002-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stearns T., Kahn R. A., Botstein D., Hoyt M. A. ADP ribosylation factor is an essential protein in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and is encoded by two genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6690–6699. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sztul E., Kaplin A., Saucan L., Palade G. Protein traffic between distinct plasma membrane domains: isolation and characterization of vesicular carriers involved in transcytosis. Cell. 1991 Jan 11;64(1):81–89. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90210-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söllner T., Bennett M. K., Whiteheart S. W., Scheller R. H., Rothman J. E. A protein assembly-disassembly pathway in vitro that may correspond to sequential steps of synaptic vesicle docking, activation, and fusion. Cell. 1993 Nov 5;75(3):409–418. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90376-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söllner T., Whiteheart S. W., Brunner M., Erdjument-Bromage H., Geromanos S., Tempst P., Rothman J. E. SNAP receptors implicated in vesicle targeting and fusion. Nature. 1993 Mar 25;362(6418):318–324. doi: 10.1038/362318a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C., De Camilli P., Niemann H., Jahn R. Membrane fusion machinery: insights from synaptic proteins. Cell. 1993 Oct 8;75(1):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takizawa P. A., Malhotra V. Coatomers and SNAREs in promoting membrane traffic. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):593–596. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90477-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takizawa P. A., Yucel J. K., Veit B., Faulkner D. J., Deerinck T., Soto G., Ellisman M., Malhotra V. Complete vesiculation of Golgi membranes and inhibition of protein transport by a novel sea sponge metabolite, ilimaquinone. Cell. 1993 Jun 18;73(6):1079–1090. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90638-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanigawa G., Orci L., Amherdt M., Ravazzola M., Helms J. B., Rothman J. E. Hydrolysis of bound GTP by ARF protein triggers uncoating of Golgi-derived COP-coated vesicles. J Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;123(6 Pt 1):1365–1371. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.6.1365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor T. C., Kahn R. A., Melançon P. Two distinct members of the ADP-ribosylation factor family of GTP-binding proteins regulate cell-free intra-Golgi transport. Cell. 1992 Jul 10;70(1):69–79. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90534-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchiya M., Price S. R., Tsai S. C., Moss J., Vaughan M. Molecular identification of ADP-ribosylation factor mRNAs and their expression in mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 15;266(5):2772–2777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldman B. C., Rudnick G. UDP-GlcNAc transport across the Golgi membrane: electroneutral exchange for dianionic UMP. Biochemistry. 1990 Jan 9;29(1):44–52. doi: 10.1021/bi00453a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker M. W., Bobak D. A., Tsai S. C., Moss J., Vaughan M. GTP but not GDP analogues promote association of ADP-ribosylation factors, 20-kDa protein activators of cholera toxin, with phospholipids and PC-12 cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):3230–3235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walworth N. C., Novick P. J. Purification and characterization of constitutive secretory vesicles from yeast. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;105(1):163–174. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.1.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren G. Cell biology. Bridging the gap. Nature. 1993 Mar 25;362(6418):297–298. doi: 10.1038/362297a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters M. G., Clary D. O., Rothman J. E. A novel 115-kD peripheral membrane protein is required for intercisternal transport in the Golgi stack. J Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;118(5):1015–1026. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.5.1015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters M. G., Serafini T., Rothman J. E. 'Coatomer': a cytosolic protein complex containing subunits of non-clathrin-coated Golgi transport vesicles. Nature. 1991 Jan 17;349(6306):248–251. doi: 10.1038/349248a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidman P. J., Melançon P., Block M. R., Rothman J. E. Binding of an N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive fusion protein to Golgi membranes requires both a soluble protein(s) and an integral membrane receptor. J Cell Biol. 1989 May;108(5):1589–1596. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.5.1589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidman P., Roth R., Heuser J. Golgi membrane dynamics imaged by freeze-etch electron microscopy: views of different membrane coatings involved in tubulation versus vesiculation. Cell. 1993 Oct 8;75(1):123–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodman P. G., Warren G. Isolation of functional, coated, endocytic vesicles. J Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;112(6):1133–1141. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.6.1133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Curtis I., Simons K. Isolation of exocytic carrier vesicles from BHK cells. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):719–727. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90106-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]