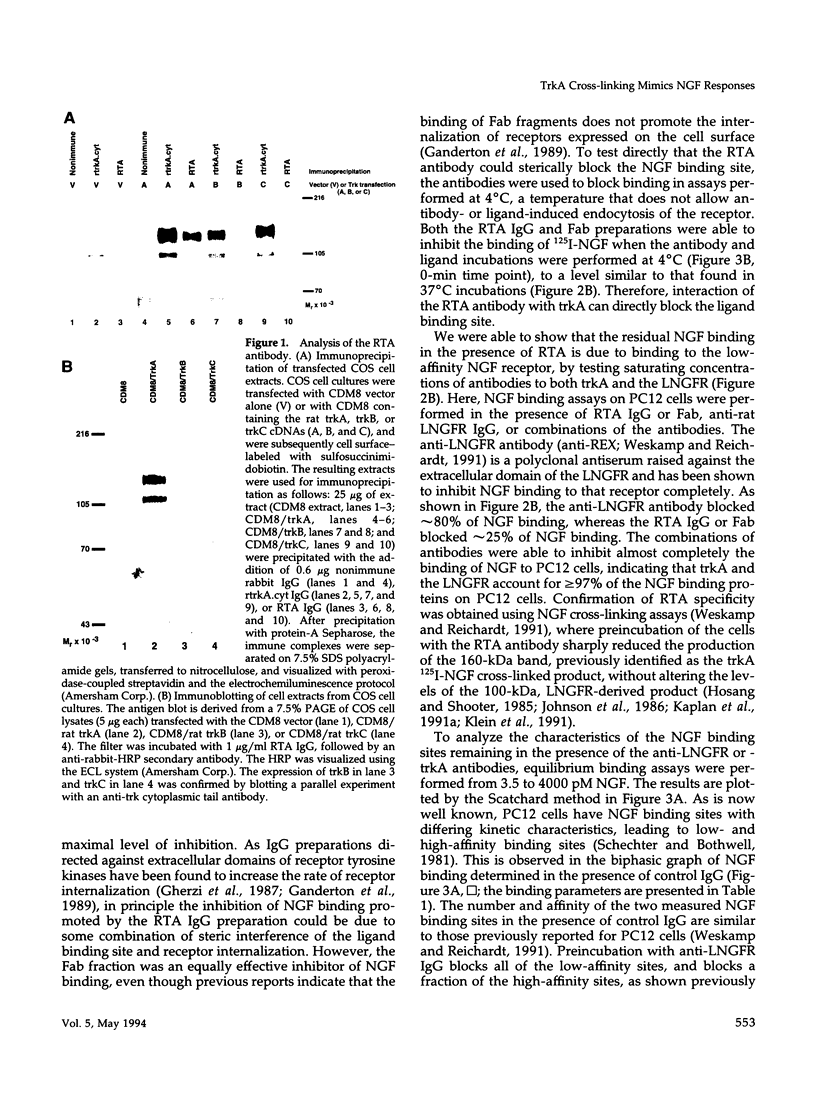
Abstract
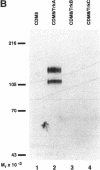
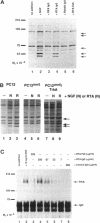
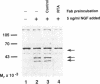
TrkA, a tyrosine kinase receptor, is an essential component of the nerve growth factor (NGF) response pathway. The binding of NGF to the receptor induces receptor autophosphorylation and activation of intracellular signaling pathways, resulting in diverse biological effects. We prepared polyclonal antibodies against the entire extracellular domain of rat trkA produced using a baculovirus expression system. These antibodies specifically recognize rat trkA on antigen blots and in immunoprecipitations. Both IgG and Fab fragments block binding of NGF to trkA expressed by the PC12 cell line. In NGF binding studies using anti-trkA and anti-low-affinity NGF receptor (LNGFR) immunoglobulin (Ig) G, essentially all binding of NGF can be inhibited. The results imply that > or = 97% of the NGF binding sites on PC12 cells are accounted for by trkA and the LNGFR. The binding data also argue that all low-affinity NGF binding sites on PC12 cells reflect interactions with the LNGFR, while all high-affinity sites are trkA dependent. A fraction of the high-affinity (or slow) binding sites seem to require both trkA and the LNGFR. Although the monovalent anti-trkA Fab fragments inhibited the biological effects of NGF, such as induction of tyrosine phosphorylation, and survival and neurite outgrowth of sympathetic neurons, the IgG preparation was not effective as an inhibitor. Instead, the IgG fraction by itself was almost as effective as NGF at stimulating receptor activation, cell survival, and neurite outgrowth. Thus, it appears oligomerization of trkA by antibody-induced cross-linking is sufficient to produce the known cellular effects of NGF.
Full text
PDF




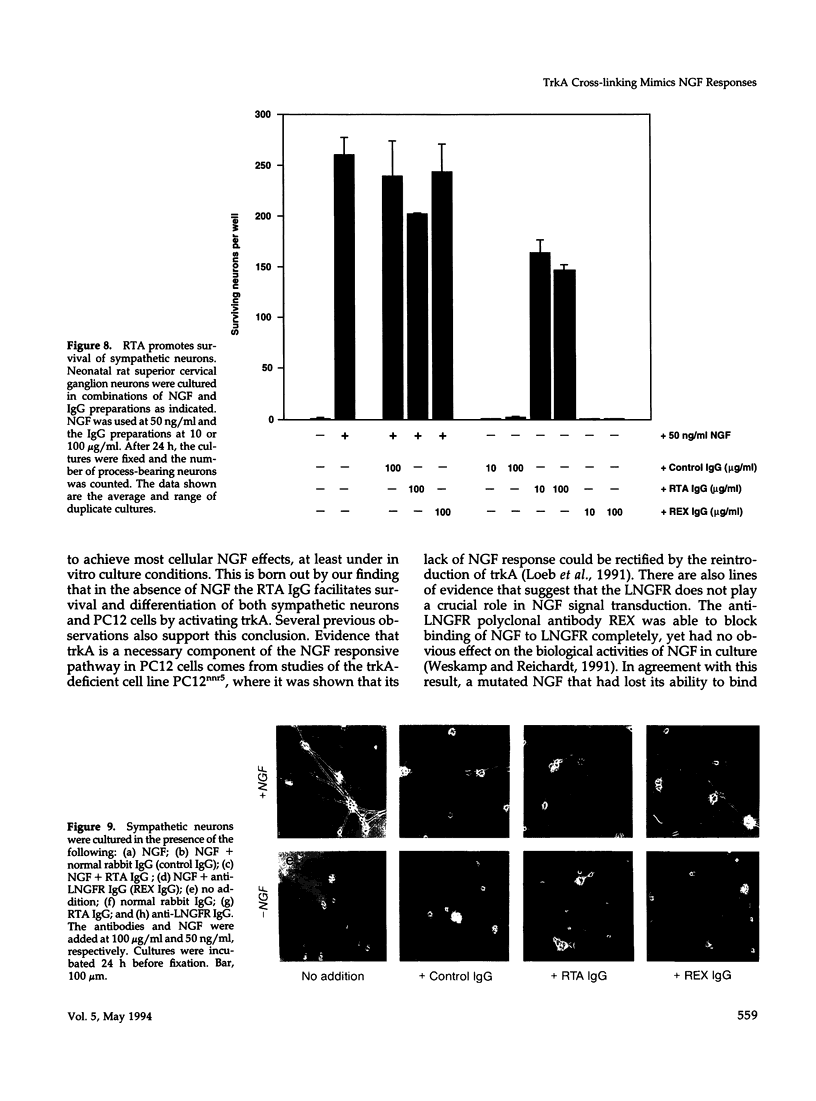
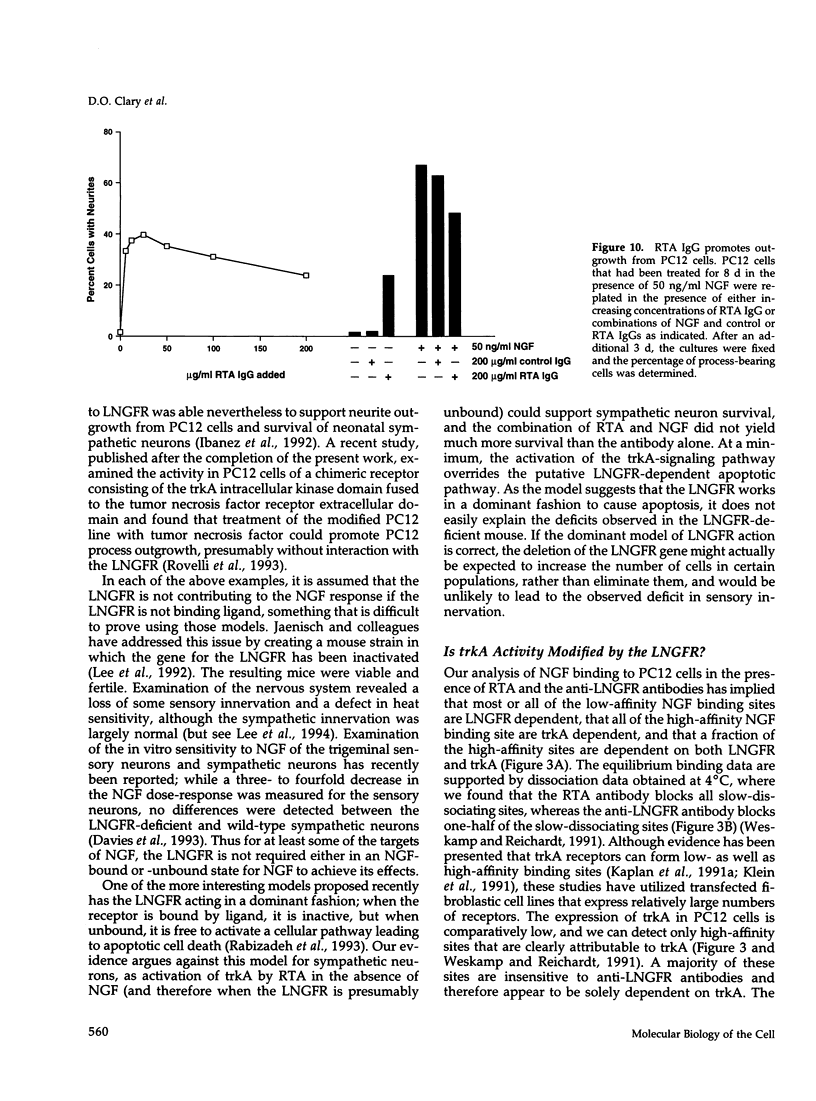



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aruffo A., Seed B. Molecular cloning of a CD28 cDNA by a high-efficiency COS cell expression system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8573–8577. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barde Y. A. Trophic factors and neuronal survival. Neuron. 1989 Jun;2(6):1525–1534. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90040-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battleman D. S., Geller A. I., Chao M. V. HSV-1 vector-mediated gene transfer of the human nerve growth factor receptor p75hNGFR defines high-affinity NGF binding. J Neurosci. 1993 Mar;13(3):941–951. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-03-00941.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benedetti M., Levi A., Chao M. V. Differential expression of nerve growth factor receptors leads to altered binding affinity and neurotrophin responsiveness. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 15;90(16):7859–7863. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.16.7859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg M. M., Sternberg D. W., Hempstead B. L., Chao M. V. The low-affinity p75 nerve growth factor (NGF) receptor mediates NGF-induced tyrosine phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7106–7110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bothwell M. Keeping track of neurotrophin receptors. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):915–918. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90540-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottenstein J. E., Skaper S. D., Varon S. S., Sato G. H. Selective survival of neurons from chick embryo sensory ganglionic dissociates utilizing serum-free supplemented medium. Exp Cell Res. 1980 Jan;125(1):183–190. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(80)90202-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler C. E., Parsons L. M., Hosang M., Shooter E. M. A monoclonal antibody modulates the interaction of nerve growth factor with PC12 cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):6882–6889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordon-Cardo C., Tapley P., Jing S. Q., Nanduri V., O'Rourke E., Lamballe F., Kovary K., Klein R., Jones K. R., Reichardt L. F. The trk tyrosine protein kinase mediates the mitogenic properties of nerve growth factor and neurotrophin-3. Cell. 1991 Jul 12;66(1):173–183. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90149-s. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies A. M., Lee K. F., Jaenisch R. p75-deficient trigeminal sensory neurons have an altered response to NGF but not to other neurotrophins. Neuron. 1993 Oct;11(4):565–574. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90069-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eide F. F., Lowenstein D. H., Reichardt L. F. Neurotrophins and their receptors--current concepts and implications for neurologic disease. Exp Neurol. 1993 Jun;121(2):200–214. doi: 10.1006/exnr.1993.1087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gherzi R., Russell D. S., Taylor S. I., Rosen O. M. Reevaluation of the evidence that an antibody to the insulin receptor is insulinmimetic without activating the protein tyrosine kinase activity of the receptor. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 15;262(35):16900–16905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass D. J., Nye S. H., Hantzopoulos P., Macchi M. J., Squinto S. P., Goldfarb M., Yancopoulos G. D. TrkB mediates BDNF/NT-3-dependent survival and proliferation in fibroblasts lacking the low affinity NGF receptor. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):405–413. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90629-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. A., Tischler A. S. Establishment of a noradrenergic clonal line of rat adrenal pheochromocytoma cells which respond to nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2424–2428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grob P. M., Bothwell M. A. Modification of nerve growth factor receptor properties by wheat germ agglutinin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14136–14143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. M., Maddux B. A., Patel R. G., Wong K. Y., Mamula P. W., Firestone G. L., Brunetti A., Verspohl E., Goldfine I. D. Insulin receptor monoclonal antibodies that mimic insulin action without activating tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 15;264(5):2438–2444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawrot E., Patterson P. H. Long-term culture of dissociated sympathetic neurons. Methods Enzymol. 1979;58:574–584. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(79)58174-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hempstead B. L., Martin-Zanca D., Kaplan D. R., Parada L. F., Chao M. V. High-affinity NGF binding requires coexpression of the trk proto-oncogene and the low-affinity NGF receptor. Nature. 1991 Apr 25;350(6320):678–683. doi: 10.1038/350678a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holtzman D. M., Li Y., Parada L. F., Kinsman S., Chen C. K., Valletta J. S., Zhou J., Long J. B., Mobley W. C. p140trk mRNA marks NGF-responsive forebrain neurons: evidence that trk gene expression is induced by NGF. Neuron. 1992 Sep;9(3):465–478. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90184-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosang M., Shooter E. M. Molecular characteristics of nerve growth factor receptors on PC12 cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):655–662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosang M., Shooter E. M. The internalization of nerve growth factor by high-affinity receptors on pheochromocytoma PC12 cells. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1197–1202. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02354.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibáez C. F., Ebendal T., Barbany G., Murray-Rust J., Blundell T. L., Persson H. Disruption of the low affinity receptor-binding site in NGF allows neuronal survival and differentiation by binding to the trk gene product. Cell. 1992 Apr 17;69(2):329–341. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90413-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibáez C. F., Ilag L. L., Murray-Rust J., Persson H. An extended surface of binding to Trk tyrosine kinase receptors in NGF and BDNF allows the engineering of a multifunctional pan-neurotrophin. EMBO J. 1993 Jun;12(6):2281–2293. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05882.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh N., Yonehara S., Ishii A., Yonehara M., Mizushima S., Sameshima M., Hase A., Seto Y., Nagata S. The polypeptide encoded by the cDNA for human cell surface antigen Fas can mediate apoptosis. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):233–243. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90614-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jing S., Tapley P., Barbacid M. Nerve growth factor mediates signal transduction through trk homodimer receptors. Neuron. 1992 Dec;9(6):1067–1079. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90066-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D., Lanahan A., Buck C. R., Sehgal A., Morgan C., Mercer E., Bothwell M., Chao M. Expression and structure of the human NGF receptor. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):545–554. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90619-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan D. R., Hempstead B. L., Martin-Zanca D., Chao M. V., Parada L. F. The trk proto-oncogene product: a signal transducing receptor for nerve growth factor. Science. 1991 Apr 26;252(5005):554–558. doi: 10.1126/science.1850549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan D. R., Martin-Zanca D., Parada L. F. Tyrosine phosphorylation and tyrosine kinase activity of the trk proto-oncogene product induced by NGF. Nature. 1991 Mar 14;350(6314):158–160. doi: 10.1038/350158a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R., Jing S. Q., Nanduri V., O'Rourke E., Barbacid M. The trk proto-oncogene encodes a receptor for nerve growth factor. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):189–197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90419-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R., Parada L. F., Coulier F., Barbacid M. trkB, a novel tyrosine protein kinase receptor expressed during mouse neural development. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3701–3709. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08545.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korsching S. The neurotrophic factor concept: a reexamination. J Neurosci. 1993 Jul;13(7):2739–2748. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-07-02739.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamballe F., Klein R., Barbacid M. trkC, a new member of the trk family of tyrosine protein kinases, is a receptor for neurotrophin-3. Cell. 1991 Sep 6;66(5):967–979. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90442-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. F., Bachman K., Landis S., Jaenisch R. Dependence on p75 for innervation of some sympathetic targets. Science. 1994 Mar 11;263(5152):1447–1449. doi: 10.1126/science.8128229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. F., Li E., Huber L. J., Landis S. C., Sharpe A. H., Chao M. V., Jaenisch R. Targeted mutation of the gene encoding the low affinity NGF receptor p75 leads to deficits in the peripheral sensory nervous system. Cell. 1992 May 29;69(5):737–749. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90286-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Montalcini R. The nerve growth factor 35 years later. Science. 1987 Sep 4;237(4819):1154–1162. doi: 10.1126/science.3306916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb D. M., Maragos J., Martin-Zanca D., Chao M. V., Parada L. F., Greene L. A. The trk proto-oncogene rescues NGF responsiveness in mutant NGF-nonresponsive PC12 cell lines. Cell. 1991 Sep 6;66(5):961–966. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90441-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb D. M., Tsao H., Cobb M. H., Greene L. A. NGF and other growth factors induce an association between ERK1 and the NGF receptor, gp140prototrk. Neuron. 1992 Dec;9(6):1053–1065. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90065-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
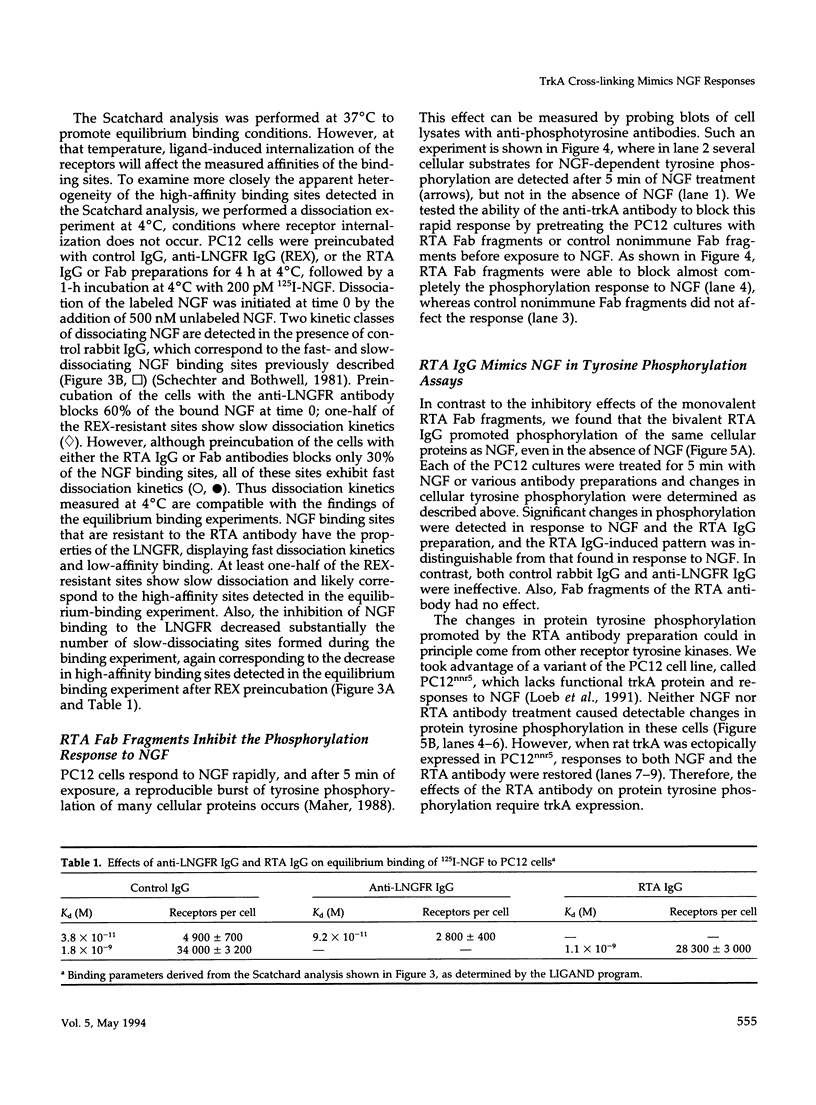
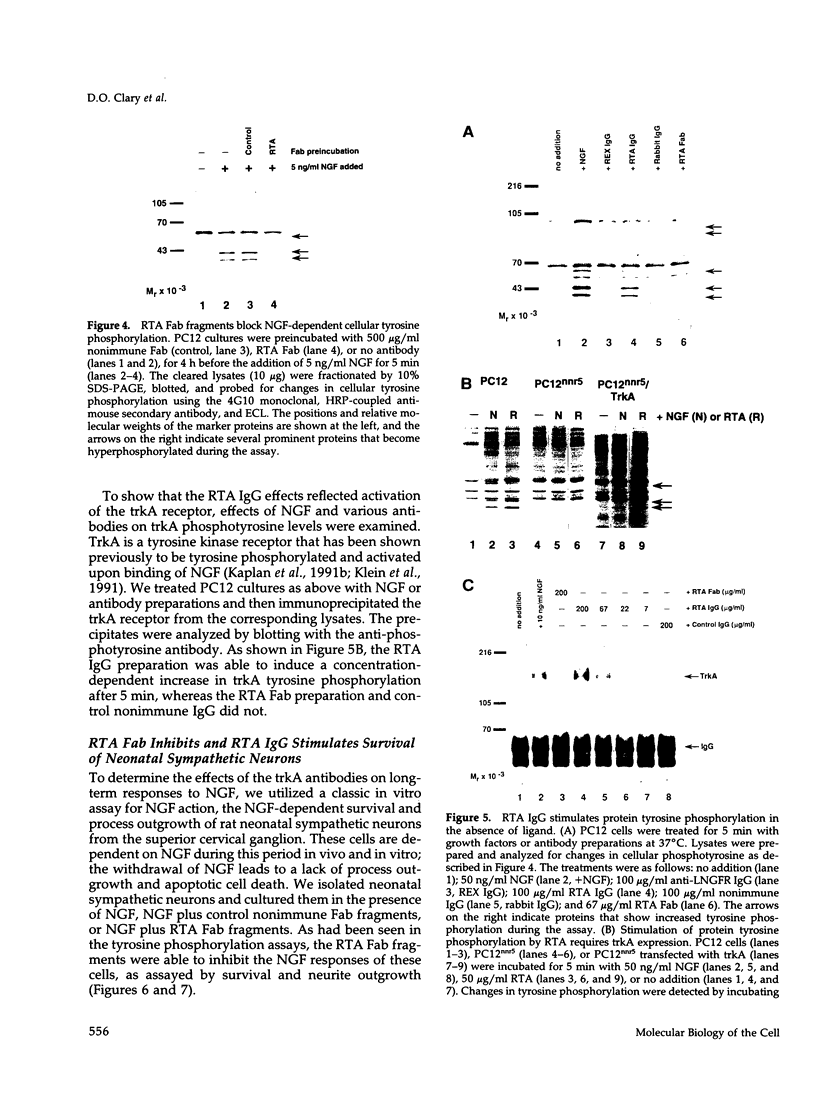
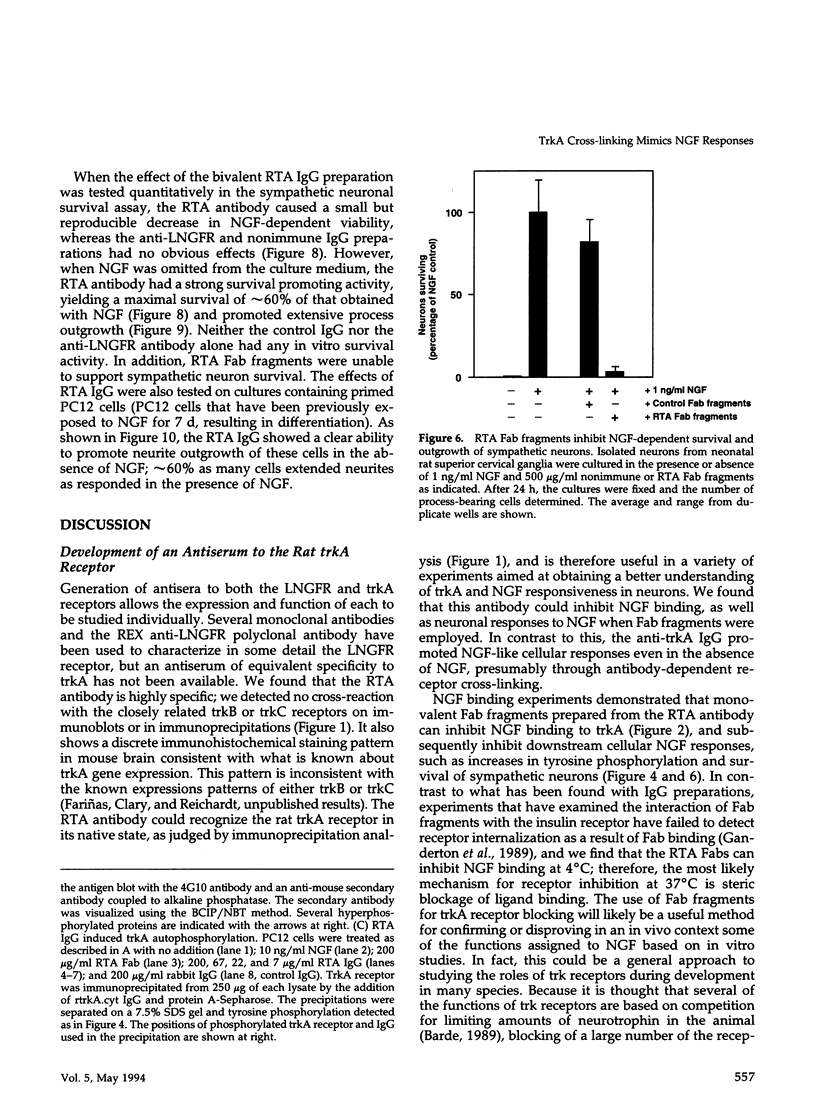
- Maher P. A. Nerve growth factor induces protein-tyrosine phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6788–6791. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin-Zanca D., Barbacid M., Parada L. F. Expression of the trk proto-oncogene is restricted to the sensory cranial and spinal ganglia of neural crest origin in mouse development. Genes Dev. 1990 May;4(5):683–694. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.5.683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin-Zanca D., Oskam R., Mitra G., Copeland T., Barbacid M. Molecular and biochemical characterization of the human trk proto-oncogene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):24–33. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meakin S. O., Shooter E. M. Molecular investigations on the high-affinity nerve growth factor receptor. Neuron. 1991 Jan;6(1):153–163. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90130-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meakin S. O., Shooter E. M. The nerve growth factor family of receptors. Trends Neurosci. 1992 Sep;15(9):323–331. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(92)90047-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meakin S. O., Suter U., Drinkwater C. C., Welcher A. A., Shooter E. M. The rat trk protooncogene product exhibits properties characteristic of the slow nerve growth factor receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2374–2378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middlemas D. S., Lindberg R. A., Hunter T. trkB, a neural receptor protein-tyrosine kinase: evidence for a full-length and two truncated receptors. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):143–153. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobley W. C., Schenker A., Shooter E. M. Characterization and isolation of proteolytically modified nerve growth factor. Biochemistry. 1976 Dec 14;15(25):5543–5552. doi: 10.1021/bi00670a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obermeier A., Halfter H., Wiesmüller K. H., Jung G., Schlessinger J., Ullrich A. Tyrosine 785 is a major determinant of Trk--substrate interaction. EMBO J. 1993 Mar;12(3):933–941. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05734.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabizadeh S., Oh J., Zhong L. T., Yang J., Bitler C. M., Butcher L. L., Bredesen D. E. Induction of apoptosis by the low-affinity NGF receptor. Science. 1993 Jul 16;261(5119):345–348. doi: 10.1126/science.8332899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radeke M. J., Feinstein S. C. Analytical purification of the slow, high affinity NGF receptor: identification of a novel 135 kd polypeptide. Neuron. 1991 Jul;7(1):141–150. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90082-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radeke M. J., Misko T. P., Hsu C., Herzenberg L. A., Shooter E. M. Gene transfer and molecular cloning of the rat nerve growth factor receptor. Nature. 1987 Feb 12;325(6105):593–597. doi: 10.1038/325593a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovelli G., Heller R. A., Canossa M., Shooter E. M. Chimeric tumor necrosis factor-TrkA receptors reveal that ligand-dependent activation of the TrkA tyrosine kinase is sufficient for differentiation and survival of PC12 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 15;90(18):8717–8721. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.18.8717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter A. L., Bothwell M. A. Nerve growth factor receptors on PC12 cells: evidence for two receptor classes with differing cytoskeletal association. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):867–874. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90112-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schecterson L. C., Bothwell M. Novel roles for neurotrophins are suggested by BDNF and NT-3 mRNA expression in developing neurons. Neuron. 1992 Sep;9(3):449–463. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90183-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed B. An LFA-3 cDNA encodes a phospholipid-linked membrane protein homologous to its receptor CD2. 1987 Oct 29-Nov 4Nature. 329(6142):840–842. doi: 10.1038/329840a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed B., Aruffo A. Molecular cloning of the CD2 antigen, the T-cell erythrocyte receptor, by a rapid immunoselection procedure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3365–3369. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soos M. A., O'Brien R. M., Brindle N. P., Stigter J. M., Okamoto A. K., Whittaker J., Siddle K. Monoclonal antibodies to the insulin receptor mimic metabolic effects of insulin but do not stimulate receptor autophosphorylation in transfected NIH 3T3 fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5217–5221. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soppet D., Escandon E., Maragos J., Middlemas D. S., Reid S. W., Blair J., Burton L. E., Stanton B. R., Kaplan D. R., Hunter T. The neurotrophic factors brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-3 are ligands for the trkB tyrosine kinase receptor. Cell. 1991 May 31;65(5):895–903. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90396-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaargaren M., Defize L. H., Boonstra J., de Laat S. W. Antibody-induced dimerization activates the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 25;266(3):1733–1739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squinto S. P., Stitt T. N., Aldrich T. H., Davis S., Bianco S. M., Radziejewski C., Glass D. J., Masiakowski P., Furth M. E., Valenzuela D. M. trkB encodes a functional receptor for brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-3 but not nerve growth factor. Cell. 1991 May 31;65(5):885–893. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90395-F. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutter A., Riopelle R. J., Harris-Warrick R. M., Shooter E. M. Nerve growth factor receptors. Characterization of two distinct classes of binding sites on chick embryo sensory ganglia cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):5972–5982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vetter M. L., Martin-Zanca D., Parada L. F., Bishop J. M., Kaplan D. R. Nerve growth factor rapidly stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-gamma 1 by a kinase activity associated with the product of the trk protooncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5650–5654. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
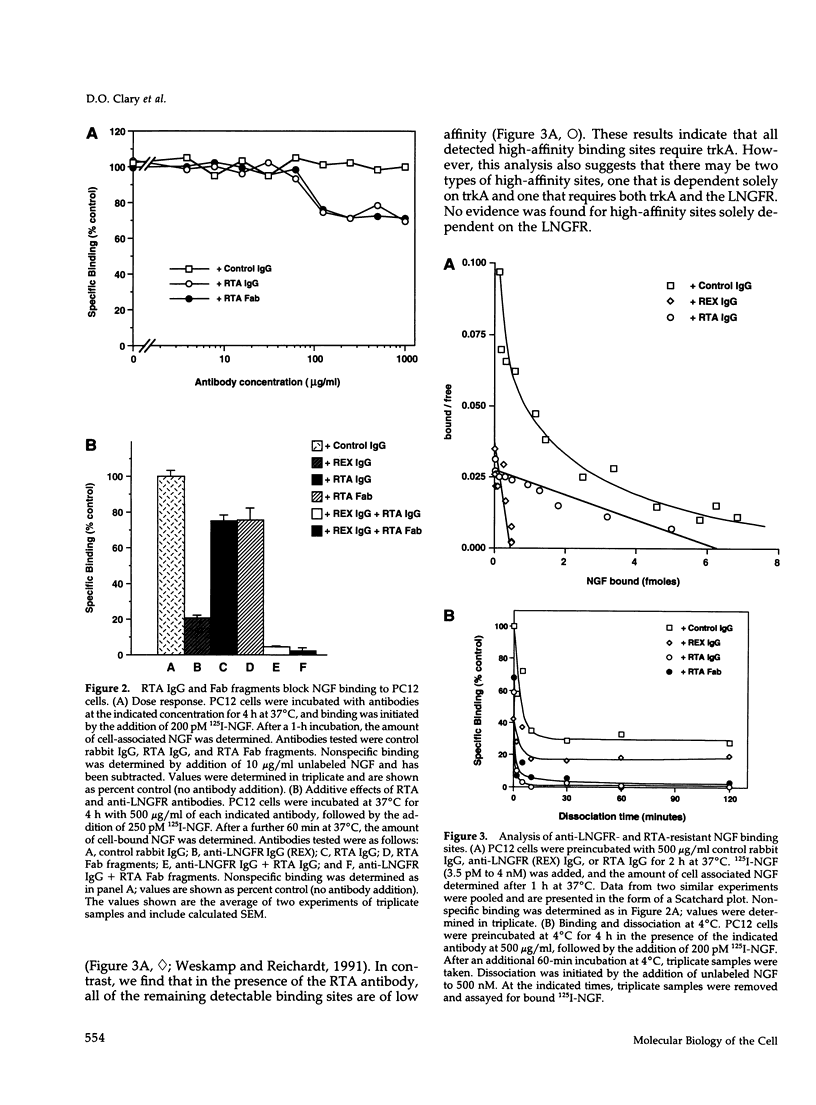
- Weskamp G., Reichardt L. F. Evidence that biological activity of NGF is mediated through a novel subclass of high affinity receptors. Neuron. 1991 Apr;6(4):649–663. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90067-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler E. F., Bothwell M. Spatiotemporal patterns of expression of NGF and the low-affinity NGF receptor in rat embryos suggest functional roles in tissue morphogenesis and myogenesis. J Neurosci. 1992 Mar;12(3):930–945. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-03-00930.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley H. S., Cunningham D. D. A steady state model for analyzing the cellular binding, internalization and degradation of polypeptide ligands. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):433–440. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90061-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt S., Shooter E. M., Davies A. M. Expression of the NGF receptor gene in sensory neurons and their cutaneous targets prior to and during innervation. Neuron. 1990 Mar;4(3):421–427. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90054-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong L., Kasuya J., Li S. L., Kato J., Fujita-Yamaguchi Y. Growth-stimulatory monoclonal antibodies against human insulin-like growth factor I receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5356–5360. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]