Abstract
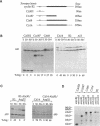
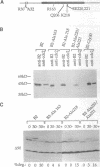
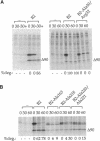
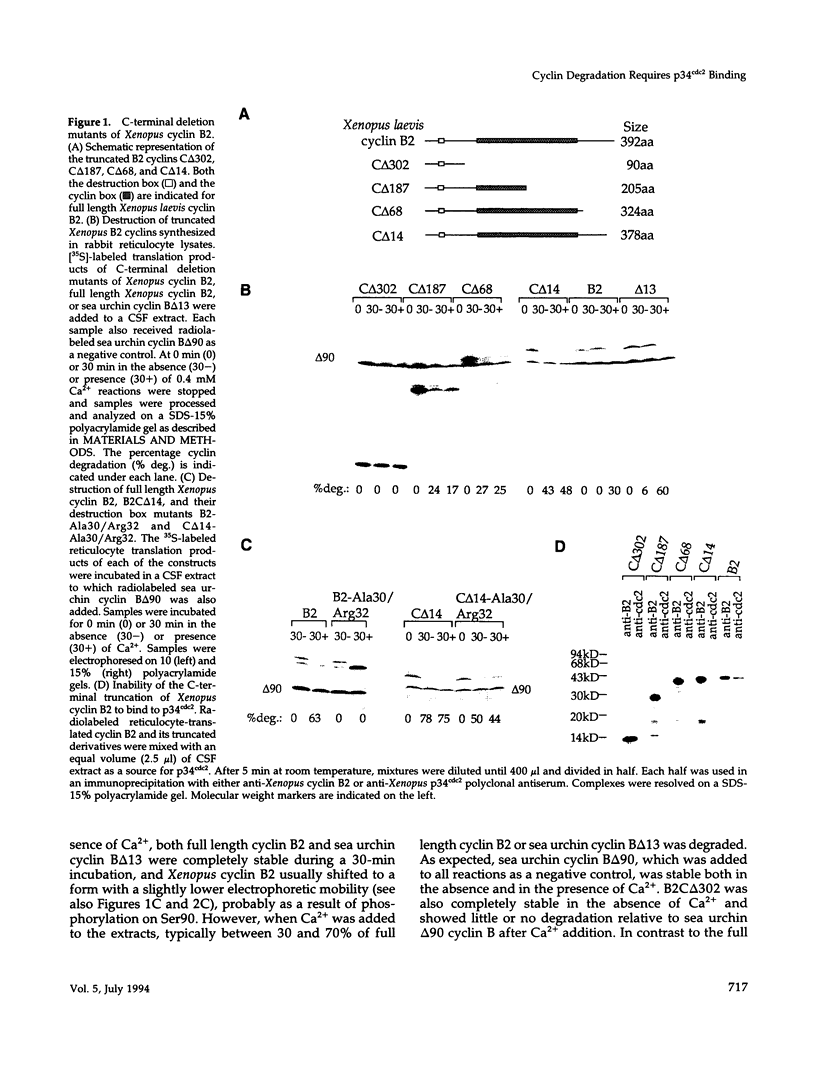
The protein kinase activity of the cell cycle regulator p34cdc2 is inactivated when the mitotic cyclin to which it is bound is degraded. The amino (N)-terminus of mitotic cyclins includes a conserved "destruction box" sequence that is essential for degradation. Although the N-terminus of sea urchin cyclin B confer cell cycle-regulated degradation to a fusion protein, a truncated protein containing only the N-terminus of Xenopus cyclin B2, including the destruction box, is stable under conditions where full length molecules are degraded. In an attempt to identify regions of cyclin B2, other than the destruction box, involved in degradation, the stability of proteins encoded by C-terminal deletion mutants of cyclin B2 was examined in Xenopus egg extracts. Truncated cyclin with only the first 90 amino acids was stable, but other C-terminal deletions lacking between 14 and 187 amino acids were unstable and were degraded by a mechanism that was neither cell cycle regulated nor dependent upon the destruction box. None of the C-terminal deletion mutants bound p34cdc2. To investigate whether the binding of p34cdc2 is required for cell cycle-regulated degradation, the behavior of proteins encoded by a series of full length Xenopus cyclin B2 cDNA with point mutations in conserved amino acids in the p34cdc2-binding domain was examined. All of the point mutants failed to form stable complexes with p34cdc, and their degradation was markedly reduced compared to wild-type cyclin. Similar results were obtained when the mutant cyclins were synthesized in reticulocyte lysates and when cyclin mRNA was translated directly in a Xenopus egg extract. These results indicate that mutations that interfere with p34cdc2 binding also interfere with cyclin destruction, suggesting that p34cdc2 binding is required for the cell cycle-regulated destruction of Xenopus cyclin B2.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chamberlain J. P. Fluorographic detection of radioactivity in polyacrylamide gels with the water-soluble fluor, sodium salicylate. Anal Biochem. 1979 Sep 15;98(1):132–135. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90716-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowdy S. F., Hinds P. W., Louie K., Reed S. I., Arnold A., Weinberg R. A. Physical interaction of the retinoblastoma protein with human D cyclins. Cell. 1993 May 7;73(3):499–511. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90137-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G., Beach D. Activation of cdc2 protein kinase during mitosis in human cells: cell cycle-dependent phosphorylation and subunit rearrangement. Cell. 1988 Jul 1;54(1):17–26. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90175-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G. Cdc2 activation: the interplay of cyclin binding and Thr161 phosphorylation. Trends Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;3(9):287–289. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(93)90001-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G. Cell cycle control in eukaryotes: molecular mechanisms of cdc2 activation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Oct;15(10):378–383. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90235-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G., Luca F., Westendorf J., Brizuela L., Ruderman J., Beach D. Cdc2 protein kinase is complexed with both cyclin A and B: evidence for proteolytic inactivation of MPF. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):829–838. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90687-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Rosenthal E. T., Youngblom J., Distel D., Hunt T. Cyclin: a protein specified by maternal mRNA in sea urchin eggs that is destroyed at each cleavage division. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):389–396. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90420-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewen M. E., Sluss H. K., Sherr C. J., Matsushime H., Kato J., Livingston D. M. Functional interactions of the retinoblastoma protein with mammalian D-type cyclins. Cell. 1993 May 7;73(3):487–497. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90136-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fesquet D., Labbé J. C., Derancourt J., Capony J. P., Galas S., Girard F., Lorca T., Shuttleworth J., Dorée M., Cavadore J. C. The MO15 gene encodes the catalytic subunit of a protein kinase that activates cdc2 and other cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) through phosphorylation of Thr161 and its homologues. EMBO J. 1993 Aug;12(8):3111–3121. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05980.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsburg S. L., Nurse P. Cell cycle regulation in the yeasts Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:227–256. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.001303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallant P., Nigg E. A. Cyclin B2 undergoes cell cycle-dependent nuclear translocation and, when expressed as a non-destructible mutant, causes mitotic arrest in HeLa cells. J Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;117(1):213–224. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.1.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier J., Minshull J., Lohka M., Glotzer M., Hunt T., Maller J. L. Cyclin is a component of maturation-promoting factor from Xenopus. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):487–494. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90599-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier J., Norbury C., Lohka M., Nurse P., Maller J. Purified maturation-promoting factor contains the product of a Xenopus homolog of the fission yeast cell cycle control gene cdc2+. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):433–439. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90206-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghiara J. B., Richardson H. E., Sugimoto K., Henze M., Lew D. J., Wittenberg C., Reed S. I. A cyclin B homolog in S. cerevisiae: chronic activation of the Cdc28 protein kinase by cyclin prevents exit from mitosis. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):163–174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90417-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghislain M., Udvardy A., Mann C. S. cerevisiae 26S protease mutants arrest cell division in G2/metaphase. Nature. 1993 Nov 25;366(6453):358–362. doi: 10.1038/366358a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glotzer M., Murray A. W., Kirschner M. W. Cyclin is degraded by the ubiquitin pathway. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):132–138. doi: 10.1038/349132a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon C., McGurk G., Dillon P., Rosen C., Hastie N. D. Defective mitosis due to a mutation in the gene for a fission yeast 26S protease subunit. Nature. 1993 Nov 25;366(6453):355–357. doi: 10.1038/366355a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Moreno S., Owen D. J., Sazer S., Nurse P. Phosphorylation at Thr167 is required for Schizosaccharomyces pombe p34cdc2 function. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3297–3309. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04894.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Nurse P. Tyrosine phosphorylation of the fission yeast cdc2+ protein kinase regulates entry into mitosis. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):39–45. doi: 10.1038/342039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershko A., Ciechanover A. The ubiquitin system for protein degradation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:761–807. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.003553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershko A., Ganoth D., Pehrson J., Palazzo R. E., Cohen L. H. Methylated ubiquitin inhibits cyclin degradation in clam embryo extracts. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 5;266(25):16376–16379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway S. L., Glotzer M., King R. W., Murray A. W. Anaphase is initiated by proteolysis rather than by the inactivation of maturation-promoting factor. Cell. 1993 Jul 2;73(7):1393–1402. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90364-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt T. Cyclins and their partners: from a simple idea to complicated reality. Semin Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;2(4):213–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt T., Luca F. C., Ruderman J. V. The requirements for protein synthesis and degradation, and the control of destruction of cyclins A and B in the meiotic and mitotic cell cycles of the clam embryo. J Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;116(3):707–724. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.3.707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izumi T., Maller J. L. Phosphorylation of Xenopus cyclins B1 and B2 is not required for cell cycle transitions. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;11(8):3860–3867. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.8.3860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi H., Minshull J., Ford C., Golsteyn R., Poon R., Hunt T. On the synthesis and destruction of A- and B-type cyclins during oogenesis and meiotic maturation in Xenopus laevis. J Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;114(4):755–765. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.4.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi H., Stewart E., Poon R., Adamczewski J. P., Gannon J., Hunt T. Identification of the domains in cyclin A required for binding to, and activation of, p34cdc2 and p32cdk2 protein kinase subunits. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Nov;3(11):1279–1294. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.11.1279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krek W., Nigg E. A. Differential phosphorylation of vertebrate p34cdc2 kinase at the G1/S and G2/M transitions of the cell cycle: identification of major phosphorylation sites. EMBO J. 1991 Feb;10(2):305–316. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07951.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lees E. M., Harlow E. Sequences within the conserved cyclin box of human cyclin A are sufficient for binding to and activation of cdc2 kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;13(2):1194–1201. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.2.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohka M. J., Maller J. L. Induction of nuclear envelope breakdown, chromosome condensation, and spindle formation in cell-free extracts. J Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;101(2):518–523. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.2.518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohka M. J., Masui Y. Effects of Ca2+ ions on the formation of metaphase chromosomes and sperm pronuclei in cell-free preparations from unactivated Rana pipiens eggs. Dev Biol. 1984 Jun;103(2):434–442. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90331-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luca F. C., Ruderman J. V. Control of programmed cyclin destruction in a cell-free system. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):1895–1909. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.1895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luca F. C., Shibuya E. K., Dohrmann C. E., Ruderman J. V. Both cyclin A delta 60 and B delta 97 are stable and arrest cells in M-phase, but only cyclin B delta 97 turns on cyclin destruction. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4311–4320. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb05009.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milarski K. L., Dunphy W. G., Russell P., Gould S. J., Newport J. W. Cloning and characterization of Xenopus cdc2, a component of MPF. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1991;56:377–384. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1991.056.01.045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minshull J., Golsteyn R., Hill C. S., Hunt T. The A- and B-type cyclin associated cdc2 kinases in Xenopus turn on and off at different times in the cell cycle. EMBO J. 1990 Sep;9(9):2865–2875. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07476.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittnacht S., Lees J. A., Desai D., Harlow E., Morgan D. O., Weinberg R. A. Distinct sub-populations of the retinoblastoma protein show a distinct pattern of phosphorylation. EMBO J. 1994 Jan 1;13(1):118–127. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06241.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittnacht S., Weinberg R. A. G1/S phosphorylation of the retinoblastoma protein is associated with an altered affinity for the nuclear compartment. Cell. 1991 May 3;65(3):381–393. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90456-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Kirschner M. W. Cyclin synthesis drives the early embryonic cell cycle. Nature. 1989 May 25;339(6222):275–280. doi: 10.1038/339275a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Solomon M. J., Kirschner M. W. The role of cyclin synthesis and degradation in the control of maturation promoting factor activity. Nature. 1989 May 25;339(6222):280–286. doi: 10.1038/339280a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norbury C., Nurse P. Animal cell cycles and their control. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:441–470. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.002301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nugent J. H., Alfa C. E., Young T., Hyams J. S. Conserved structural motifs in cyclins identified by sequence analysis. J Cell Sci. 1991 Jul;99(Pt 3):669–674. doi: 10.1242/jcs.99.3.669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurse P., Bissett Y. Gene required in G1 for commitment to cell cycle and in G2 for control of mitosis in fission yeast. Nature. 1981 Aug 6;292(5823):558–560. doi: 10.1038/292558a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piggott J. R., Rai R., Carter B. L. A bifunctional gene product involved in two phases of the yeast cell cycle. Nature. 1982 Jul 22;298(5872):391–393. doi: 10.1038/298391a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J. Cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases: take your partners. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Jun;18(6):195–197. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90185-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J., Hunter T. Human cyclin A is adenovirus E1A-associated protein p60 and behaves differently from cyclin B. Nature. 1990 Aug 23;346(6286):760–763. doi: 10.1038/346760a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J., Hunter T. Isolation of a human cyclin cDNA: evidence for cyclin mRNA and protein regulation in the cell cycle and for interaction with p34cdc2. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):833–846. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90936-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poon R. Y., Yamashita K., Adamczewski J. P., Hunt T., Shuttleworth J. The cdc2-related protein p40MO15 is the catalytic subunit of a protein kinase that can activate p33cdk2 and p34cdc2. EMBO J. 1993 Aug;12(8):3123–3132. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05981.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. I. G1-specific cyclins: in search of an S-phase-promoting factor. Trends Genet. 1991 Mar;7(3):95–99. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90279-Y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. I. The role of p34 kinases in the G1 to S-phase transition. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:529–561. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.002525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherr C. J. Mammalian G1 cyclins. Cell. 1993 Jun 18;73(6):1059–1065. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90636-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon M. J., Glotzer M., Lee T. H., Philippe M., Kirschner M. W. Cyclin activation of p34cdc2. Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):1013–1024. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90504-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon M. J., Harper J. W., Shuttleworth J. CAK, the p34cdc2 activating kinase, contains a protein identical or closely related to p40MO15. EMBO J. 1993 Aug;12(8):3133–3142. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05982.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon M. J., Lee T., Kirschner M. W. Role of phosphorylation in p34cdc2 activation: identification of an activating kinase. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Jan;3(1):13–27. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.1.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart E., Kobayashi H., Harrison D., Hunt T. Destruction of Xenopus cyclins A and B2, but not B1, requires binding to p34cdc2. EMBO J. 1994 Feb 1;13(3):584–594. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06296.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surana U., Amon A., Dowzer C., McGrew J., Byers B., Nasmyth K. Destruction of the CDC28/CLB mitotic kinase is not required for the metaphase to anaphase transition in budding yeast. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):1969–1978. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05846.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westendorf J. M., Swenson K. I., Ruderman J. V. The role of cyclin B in meiosis I. J Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;108(4):1431–1444. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.4.1431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitfield W. G., Gonzalez C., Maldonado-Codina G., Glover D. M. The A- and B-type cyclins of Drosophila are accumulated and destroyed in temporally distinct events that define separable phases of the G2-M transition. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2563–2572. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07437.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng X. F., Ruderman J. V. Functional analysis of the P box, a domain in cyclin B required for the activation of Cdc25. Cell. 1993 Oct 8;75(1):155–164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Velden H. M., Lohka M. J. Mitotic arrest caused by the amino terminus of Xenopus cyclin B2. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1480–1488. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]