Abstract
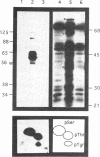
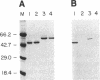
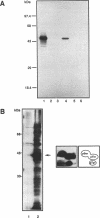
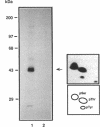
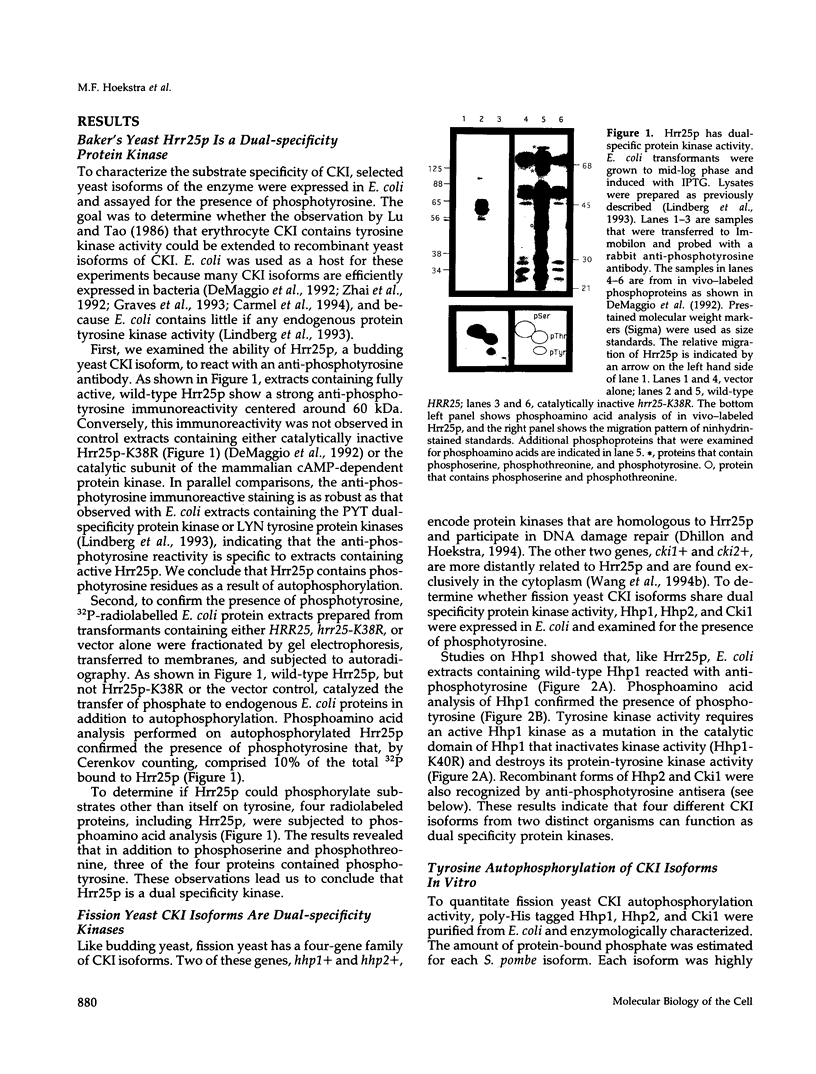
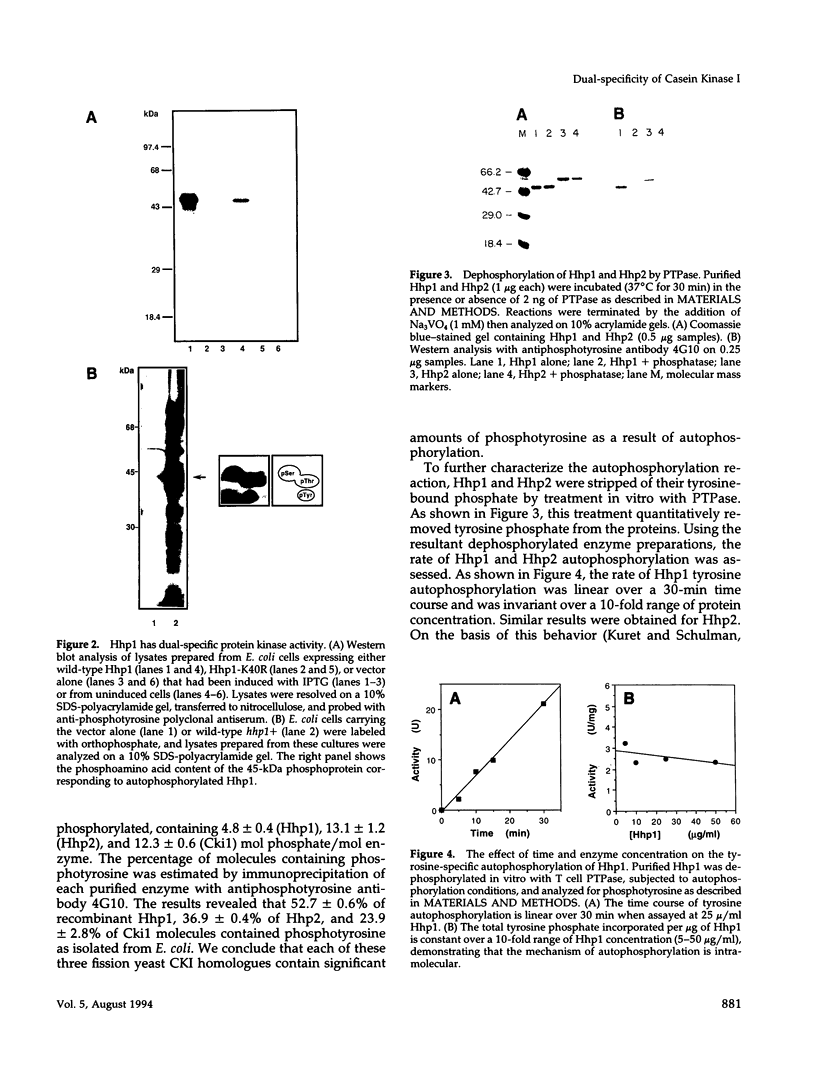
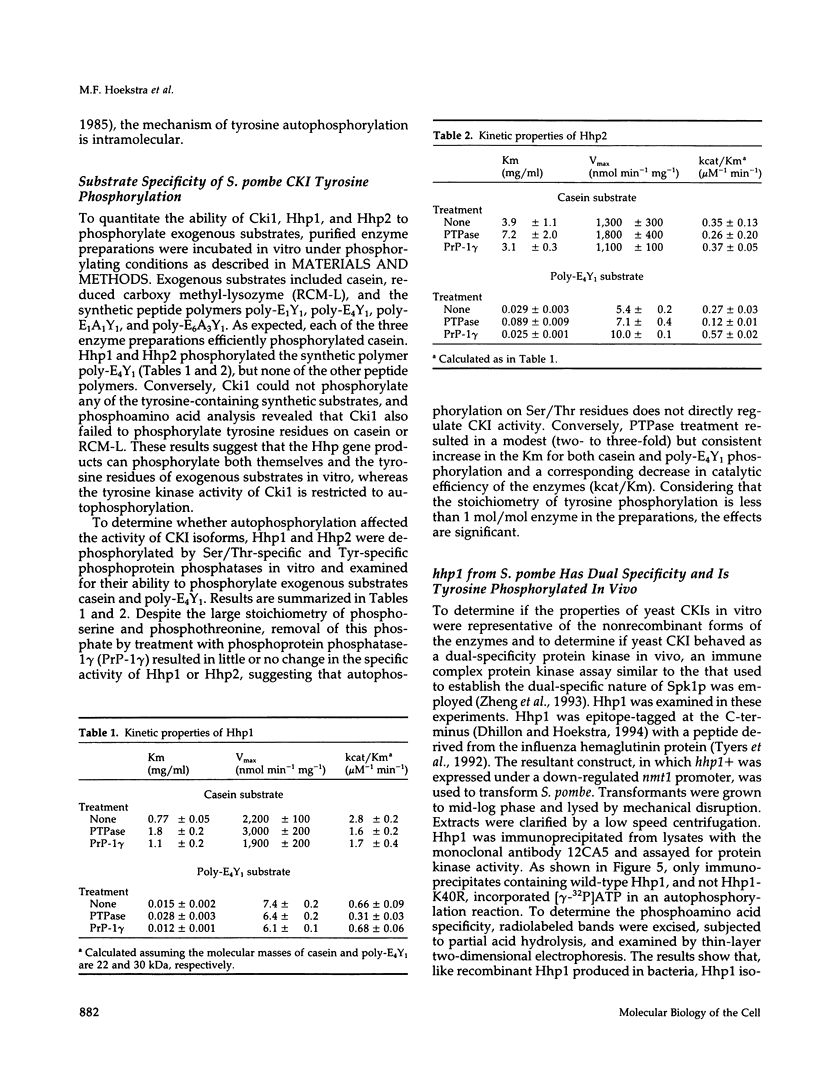
We have examined the activity and substrate specificity of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae Hrr25p and the Schizosaccharomyces pombe Hhp1, Hhp2, and Cki1 protein kinase isoforms. These four gene products are isotypes of casein kinase I (CKI), and the sequence of these protein kinases predicts that they are protein serine/threonine kinases. However, each of these four protein kinases, when expressed in Escherichia coli in an active form, was recognized by anti-phosphotyrosine antibodies. Phosphoamino acid analysis of 32P-labeled proteins showed phosphorylation on serine, threonine, and tyrosine residues. The E. coli produced forms of Hhp1, Hhp2, and Cki1 were autophosphorylated on tyrosine, and both Hhp1 and Hhp2 were capable of phosphorylating the tyrosine-protein kinase synthetic peptide substrate polymer poly-E4Y1. Immune complex protein kinases assays from S. pombe cells showed that Hhp1-containing precipitates were associated with a protein-tyrosine kinase activity, and the Hhp1 present in these immunoprecipitates was phosphorylated on tyrosine residues. Although dephosphorylation of Hhp1 and Hhp2 by Ser/Thr phosphatase had little effect on the specific activity, tyrosine dephosphorylation of Hhp1 and Hhp2 caused a 1.8-to 3.1-fold increase in the Km for poly-E4Y1 and casein. These data demonstrate that four different CKI isoforms from two different yeasts are capable of protein-tyrosine kinase activity and encode dual-specificity protein kinases.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyle W. J., van der Geer P., Hunter T. Phosphopeptide mapping and phosphoamino acid analysis by two-dimensional separation on thin-layer cellulose plates. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:110–149. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01013-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockman J. L., Anderson R. A. Casein kinase I is regulated by phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in native membranes. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 5;266(4):2508–2512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockman J. L., Gross S. D., Sussman M. R., Anderson R. A. Cell cycle-dependent localization of casein kinase I to mitotic spindles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9454–9458. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmel G., Leichus B., Cheng X., Patterson S. D., Mirza U., Chait B. T., Kuret J. Expression, purification, crystallization, and preliminary x-ray analysis of casein kinase-1 from Schizosaccharomyces pombe. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 11;269(10):7304–7309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cegielska A., Virshup D. M. Control of simian virus 40 DNA replication by the HeLa cell nuclear kinase casein kinase I. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;13(2):1202–1211. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.2.1202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobb M. H., Rosen O. M. Description of a protein kinase derived from insulin-treated 3T3-L1 cells that catalyzes the phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 and casein. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12472–12481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dailey D., Schieven G. L., Lim M. Y., Marquardt H., Gilmore T., Thorner J., Martin G. S. Novel yeast protein kinase (YPK1 gene product) is a 40-kilodalton phosphotyrosyl protein associated with protein-tyrosine kinase activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6244–6256. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. J. The mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathway. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 15;268(20):14553–14556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMaggio A. J., Lindberg R. A., Hunter T., Hoekstra M. F. The budding yeast HRR25 gene product is a casein kinase I isoform. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):7008–7012. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.7008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhillon N., Hoekstra M. F. Characterization of two protein kinases from Schizosaccharomyces pombe involved in the regulation of DNA repair. EMBO J. 1994 Jun 15;13(12):2777–2788. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06571.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Featherstone C., Russell P. Fission yeast p107wee1 mitotic inhibitor is a tyrosine/serine kinase. Nature. 1991 Feb 28;349(6312):808–811. doi: 10.1038/349808a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flotow H., Graves P. R., Wang A. Q., Fiol C. J., Roeske R. W., Roach P. J. Phosphate groups as substrate determinants for casein kinase I action. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 25;265(24):14264–14269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flotow H., Roach P. J. Role of acidic residues as substrate determinants for casein kinase I. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 25;266(6):3724–3727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves P. R., Haas D. W., Hagedorn C. H., DePaoli-Roach A. A., Roach P. J. Molecular cloning, expression, and characterization of a 49-kilodalton casein kinase I isoform from rat testis. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 25;268(9):6394–6401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guesdon F., Freshney N., Waller R. J., Rawlinson L., Saklatvala J. Interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor stimulate two novel protein kinases that phosphorylate the heat shock protein hsp27 and beta-casein. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 25;268(6):4236–4243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy G. R., Chua S. P., Wong N. S., Ng S. B., Tan Y. H. Interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor activate common multiple protein kinases in human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 5;266(22):14343–14352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochuli E., Döbeli H., Schacher A. New metal chelate adsorbent selective for proteins and peptides containing neighbouring histidine residues. J Chromatogr. 1987 Dec 18;411:177–184. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)93969-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoekstra M. F., Liskay R. M., Ou A. C., DeMaggio A. J., Burbee D. G., Heffron F. HRR25, a putative protein kinase from budding yeast: association with repair of damaged DNA. Science. 1991 Aug 30;253(5023):1031–1034. doi: 10.1126/science.1887218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosey M. M., Tao M. Protein kinases of rabbit and human erythrocyte membranes. Solubilization and characterization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jun 10;482(2):348–357. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(77)90248-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes K., Nikolakaki E., Plyte S. E., Totty N. F., Woodgett J. R. Modulation of the glycogen synthase kinase-3 family by tyrosine phosphorylation. EMBO J. 1993 Feb;12(2):803–808. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05715.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Sefton B. M. Identification of multiple novel polypeptide substrates of the v-src, v-yes, v-fps, v-ros, and v-erb-B oncogenic tyrosine protein kinases utilizing antisera against phosphotyrosine. Oncogene. 1988 Apr;2(4):305–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuret J., Schulman H. Mechanism of autophosphorylation of the multifunctional Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):6427–6433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim M. Y., Dailey D., Martin G. S., Thorner J. Yeast MCK1 protein kinase autophosphorylates at tyrosine and serine but phosphorylates exogenous substrates at serine and threonine. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 5;268(28):21155–21164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg R. A., Fischer W. H., Hunter T. Characterization of a human protein threonine kinase isolated by screening an expression library with antibodies to phosphotyrosine. Oncogene. 1993 Feb;8(2):351–359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg R. A., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. Dual-specificity protein kinases: will any hydroxyl do? Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Mar;17(3):114–119. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90248-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu P. W., Tao M. Phosphorylation of protein tyrosine by human erythrocyte casein kinase A. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Sep 30;139(3):855–860. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80256-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald J. K., Culbertson J. T., Owers N. O. Identification and localization of a novel cathepsin S-like proteinase in guinea pig spermatozoa. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1993 Aug 15;305(1):1–8. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1993.1386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milne D. M., Palmer R. H., Campbell D. G., Meek D. W. Phosphorylation of the p53 tumour-suppressor protein at three N-terminal sites by a novel casein kinase I-like enzyme. Oncogene. 1992 Jul;7(7):1361–1369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neigeborn L., Mitchell A. P. The yeast MCK1 gene encodes a protein kinase homolog that activates early meiotic gene expression. Genes Dev. 1991 Apr;5(4):533–548. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.4.533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neiman A. M., Stevenson B. J., Xu H. P., Sprague G. F., Jr, Herskowitz I., Wigler M., Marcus S. Functional homology of protein kinases required for sexual differentiation in Schizosaccharomyces pombe and Saccharomyces cerevisiae suggests a conserved signal transduction module in eukaryotic organisms. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Jan;4(1):107–120. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.1.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racker E. Use of synthetic amino acid polymers for assay of protein-tyrosine and protein-serine kinases. Methods Enzymol. 1991;200:107–111. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)00131-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roach P. J. Control of glycogen synthase by hierarchal protein phosphorylation. FASEB J. 1990 Sep;4(12):2961–2968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson L. C., Hubbard E. J., Graves P. R., DePaoli-Roach A. A., Roach P. J., Kung C., Haas D. W., Hagedorn C. H., Goebl M., Culbertson M. R. Yeast casein kinase I homologues: an essential gene pair. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):28–32. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.28. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowles J., Slaughter C., Moomaw C., Hsu J., Cobb M. H. Purification of casein kinase I and isolation of cDNAs encoding multiple casein kinase I-like enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9548–9552. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shero J. H., Hieter P. A suppressor of a centromere DNA mutation encodes a putative protein kinase (MCK1). Genes Dev. 1991 Apr;5(4):549–560. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.4.549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. F., Zheng P., Beidler D. R., Zerillo C. Spk1, a new kinase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae, phosphorylates proteins on serine, threonine, and tyrosine. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):987–1001. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuazon P. T., Traugh J. A. Casein kinase I and II--multipotential serine protein kinases: structure, function, and regulation. Adv Second Messenger Phosphoprotein Res. 1991;23:123–164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyers M., Tokiwa G., Nash R., Futcher B. The Cln3-Cdc28 kinase complex of S. cerevisiae is regulated by proteolysis and phosphorylation. EMBO J. 1992 May;11(5):1773–1784. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05229.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILKINSON G. N. Statistical estimations in enzyme kinetics. Biochem J. 1961 Aug;80:324–332. doi: 10.1042/bj0800324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang P. C., Vancura A., Desai A., Carmel G., Kuret J. Cytoplasmic forms of fission yeast casein kinase-1 associate primarily with the particulate fraction of the cell. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 22;269(16):12014–12023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang P. C., Vancura A., Mitcheson T. G., Kuret J. Two genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae encode a membrane-bound form of casein kinase-1. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Mar;3(3):275–286. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.3.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Q. M., Fiol C. J., DePaoli-Roach A. A., Roach P. J. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta is a dual specificity kinase differentially regulated by tyrosine and serine/threonine phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 20;269(20):14566–14574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhai L., Graves P. R., Longenecker K. L., DePaoli-Roach A. A., Roach P. J. Recombinant rabbit muscle casein kinase I alpha is inhibited by heparin and activated by polylysine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Dec 15;189(2):944–949. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)92295-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng P., Fay D. S., Burton J., Xiao H., Pinkham J. L., Stern D. F. SPK1 is an essential S-phase-specific gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae that encodes a nuclear serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;13(9):5829–5842. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.9.5829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Z., Gartner A., Cade R., Ammerer G., Errede B. Pheromone-induced signal transduction in Saccharomyces cerevisiae requires the sequential function of three protein kinases. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2069–2080. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Groot R. P., den Hertog J., Vandenheede J. R., Goris J., Sassone-Corsi P. Multiple and cooperative phosphorylation events regulate the CREM activator function. EMBO J. 1993 Oct;12(10):3903–3911. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06068.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]