Abstract
In the title compound, C11H19NO5, the five-membered pyrrolidine ring adopts an envelope conformation. The dihedral angles between the carboxyl group plane, the pyrrolidine ring and the methoxy group are 59.50 (3) and 62.02 (1)°, respectively. In the crystal, intermolecular O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds link the molecules into chains along [100]. The absolute configuration is assigned in accord with that of (2R,4R)-1-(tert-butoxycarbonyl)-4-hydroxypyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid, which was the starting material in the synthesis.
Related literature
The title compound is an intermediate in the preparation of the direct FXa inhibitor, eribaxaban {systematic name: (2R,4R)-N
1-(4-chlorophenyl)-N
2-[2-fluoro-4-(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-yl)phenyl]-4-methoxypyrrolidine-1,2-dicarboxamide}. For background to the bioactivity and applications of eribaxaban, see: Perzborn (2009 ▶); Kohrt et al. (2007 ▶). For the synthesis of other derivatives with proline, see: Van Huis et al. (2009 ▶); Bigge et al. (2003 ▶).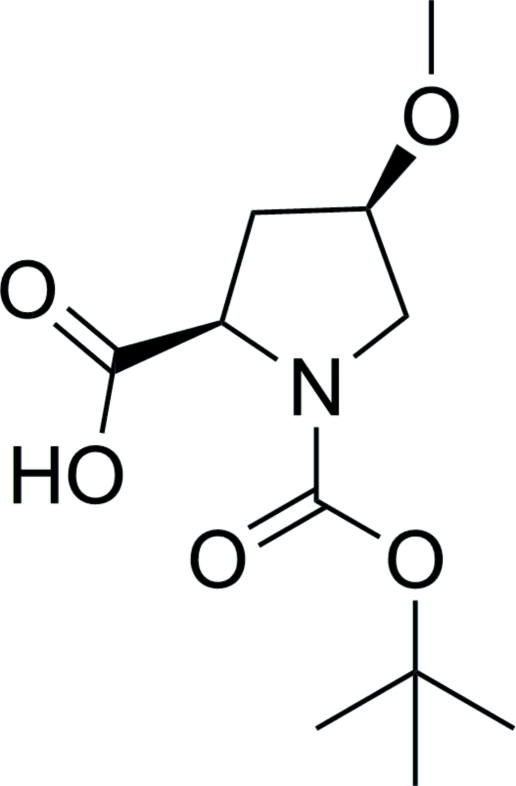
Experimental
Crystal data
C11H19NO5
M r = 245.27
Monoclinic,

a = 6.4299 (13) Å
b = 9.784 (2) Å
c = 10.279 (2) Å
β = 90.12 (3)°
V = 646.7 (2) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.10 mm−1
T = 293 K
0.26 × 0.20 × 0.10 mm
Data collection
Rigaku Saturn CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrystalClear; Rigaku/MSC, 2005) ▶ T min = 0.975, T max = 0.990
7923 measured reflections
1601 independent reflections
1059 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.059
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.037
wR(F 2) = 0.086
S = 0.94
1601 reflections
163 parameters
1 restraint
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.13 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.16 e Å−3
Data collection: CrystalClear (Rigaku, 2005) ▶; cell refinement: CrystalClear ▶; data reduction: CrystalClear ▶; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810047707/kp2285sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810047707/kp2285Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O3—H3⋯O4i | 1.00 (3) | 1.68 (4) | 2.672 (2) | 169 (4) |
Symmetry code: (i) 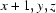 .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the State Key Laboratory of Elemento-organic Chemistry, Nankai University, for the data collection.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Eribaxaban is a direct FXa inhibitors and has a high affinity for human FXa. Clinical data with eribaxaban in the prevention of VTE in TKR patients have recently been presented (Perzborn, 2009; Kohrt et al., 2007).
The title compound (Fig. 1), (2R,4R)-1-(tert-butoxycarbonyl)-4-methoxypyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid is important intermediate in the preparation of Eribaxaban. Some derivatives of Eribaxaban have been reported with high affinity for human FXa (Van Huis et al., 2009; Bigge et al., 2003). Herein, the synthesis and the crystal structure of the title compound are reported; the absolute configuration is assigned by the use of (2R,4R)-1-(tert-butoxycarbonyl)-4- hydroxypyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid as the starting material for the synthesis.
The pyrrolidine ring of the title compound adopts an envelope conformation with the C3 lying out of the plane. The dihedral angles between the carboxyl group plane, pyrrolidine ring and methoxy system are 120.50 (3)° and 117.98 (1)°, respectively. In the crystal structure, intermolecular O—H···O interactions contribute to the stabilization of the packing. Each molecule is a donor and acceptor for 2 hydrogen bonds (TAble 1).
Experimental
CH3I (22 g, 0.155 mol) and 60%(w/w)NaH (15 g, 0.625 mol) were dissolved in THF(300 ml), and the resulting mixture was cooled to 273 K in an ice bath. (R,R)-4-Hydroxy-pyrrolidine-1,2-dicarboxylic acid, 1-tert-butyl ester(35 g, 0.151 mol)was then added in portions while maintaining a reaction temperature of 278 K or less. The reaction was allowed to warm to 293 K overnight. To the reaction mixture was added H2O (100 ml), 1 N HCl(100 ml) and NaCl(42 g). The layers were separated, and the organic layer was dried over MgSO4, filtered and concentrated to the white solid (37 g). Colourless single crystals suitable for X-ray diffraction were obtained by recrystallisation from methanol.
Refinement
All H atoms were geometrically positioned (C—H 0.93–0.98 Å) and treated as riding, with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The structure of C11H19NO5 with all non-H atom-labelling scheme and ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level.
Crystal data
| C11H19NO5 | F(000) = 264 |
| Mr = 245.27 | Dx = 1.260 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: P2yb | Cell parameters from 1953 reflections |
| a = 6.4299 (13) Å | θ = 3.2–27.8° |
| b = 9.784 (2) Å | µ = 0.10 mm−1 |
| c = 10.279 (2) Å | T = 293 K |
| β = 90.12 (3)° | Prism, colorless |
| V = 646.7 (2) Å3 | 0.26 × 0.20 × 0.10 mm |
| Z = 2 |
Data collection
| Rigaku Saturn CCD area-detector diffractometer | 1601 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: rotating anode | 1059 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| confocal | Rint = 0.059 |
| ω and φ scans | θmax = 27.7°, θmin = 3.2° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrystalClear; Rigaku/MSC, 2005) | h = −8→8 |
| Tmin = 0.975, Tmax = 0.990 | k = −12→12 |
| 7923 measured reflections | l = −13→13 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.037 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F2) = 0.086 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0494P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 0.94 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 1601 reflections | Δρmax = 0.13 e Å−3 |
| 163 parameters | Δρmin = −0.16 e Å−3 |
| 1 restraint | Extinction correction: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction coefficient: 0.55 (4) |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.9616 (2) | 0.74085 (17) | 0.56702 (14) | 0.0482 (4) | |
| O2 | 1.2349 (3) | 0.63017 (18) | 0.30520 (17) | 0.0550 (5) | |
| O3 | 1.1022 (3) | 0.83878 (17) | 0.27707 (17) | 0.0505 (5) | |
| H3 | 1.253 (5) | 0.861 (4) | 0.262 (3) | 0.093 (11)* | |
| O4 | 0.4931 (2) | 0.92660 (17) | 0.24970 (16) | 0.0472 (5) | |
| O5 | 0.6949 (2) | 0.80182 (16) | 0.10995 (13) | 0.0462 (5) | |
| N1 | 0.7106 (2) | 0.7625 (2) | 0.32240 (16) | 0.0387 (4) | |
| C1 | 1.0873 (3) | 0.7059 (2) | 0.2972 (2) | 0.0383 (5) | |
| C2 | 0.8634 (3) | 0.6534 (2) | 0.3036 (2) | 0.0375 (5) | |
| H2 | 0.8304 | 0.6019 | 0.2244 | 0.045* | |
| C3 | 0.8259 (4) | 0.5636 (2) | 0.4235 (2) | 0.0490 (6) | |
| H3A | 0.7087 | 0.5027 | 0.4103 | 0.059* | |
| H3B | 0.9482 | 0.5099 | 0.4448 | 0.059* | |
| C4 | 0.7804 (4) | 0.6680 (2) | 0.5283 (2) | 0.0461 (6) | |
| H4 | 0.7092 | 0.6269 | 0.6028 | 0.055* | |
| C5 | 0.6428 (3) | 0.7725 (3) | 0.45841 (19) | 0.0454 (6) | |
| H5A | 0.4968 | 0.7493 | 0.4670 | 0.054* | |
| H5B | 0.6654 | 0.8638 | 0.4924 | 0.054* | |
| C6 | 1.1031 (4) | 0.6610 (3) | 0.6413 (2) | 0.0632 (8) | |
| H6A | 1.0289 | 0.6135 | 0.7084 | 0.095* | |
| H6B | 1.2057 | 0.7197 | 0.6801 | 0.095* | |
| H6C | 1.1706 | 0.5960 | 0.5856 | 0.095* | |
| C7 | 0.6240 (3) | 0.8376 (2) | 0.2284 (2) | 0.0381 (5) | |
| C8 | 0.6706 (4) | 0.8926 (2) | −0.0042 (2) | 0.0463 (6) | |
| C9 | 0.7760 (5) | 1.0273 (3) | 0.0251 (3) | 0.0712 (9) | |
| H9A | 0.7098 | 1.0697 | 0.0983 | 0.107* | |
| H9B | 0.7650 | 1.0863 | −0.0493 | 0.107* | |
| H9C | 0.9200 | 1.0115 | 0.0447 | 0.107* | |
| C10 | 0.7858 (5) | 0.8146 (4) | −0.1077 (2) | 0.0734 (9) | |
| H10A | 0.9256 | 0.7975 | −0.0791 | 0.110* | |
| H10B | 0.7884 | 0.8672 | −0.1865 | 0.110* | |
| H10C | 0.7167 | 0.7291 | −0.1235 | 0.110* | |
| C11 | 0.4450 (5) | 0.9100 (4) | −0.0410 (3) | 0.0750 (9) | |
| H11A | 0.3765 | 0.8229 | −0.0382 | 0.113* | |
| H11B | 0.4356 | 0.9469 | −0.1274 | 0.113* | |
| H11C | 0.3794 | 0.9714 | 0.0191 | 0.113* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0579 (10) | 0.0464 (10) | 0.0402 (8) | −0.0032 (8) | −0.0090 (7) | 0.0051 (7) |
| O2 | 0.0423 (9) | 0.0491 (10) | 0.0735 (11) | 0.0155 (9) | −0.0065 (7) | −0.0084 (8) |
| O3 | 0.0326 (9) | 0.0405 (10) | 0.0783 (12) | 0.0026 (8) | 0.0053 (7) | 0.0105 (9) |
| O4 | 0.0349 (9) | 0.0452 (10) | 0.0614 (10) | 0.0048 (8) | 0.0058 (7) | 0.0067 (7) |
| O5 | 0.0514 (9) | 0.0497 (10) | 0.0374 (9) | 0.0110 (8) | −0.0016 (6) | 0.0051 (7) |
| N1 | 0.0300 (9) | 0.0469 (11) | 0.0393 (10) | 0.0032 (9) | 0.0017 (7) | 0.0045 (8) |
| C1 | 0.0368 (13) | 0.0415 (13) | 0.0364 (11) | 0.0045 (10) | −0.0013 (9) | −0.0039 (9) |
| C2 | 0.0378 (11) | 0.0365 (12) | 0.0384 (11) | −0.0004 (10) | −0.0062 (8) | −0.0033 (9) |
| C3 | 0.0561 (16) | 0.0360 (13) | 0.0548 (14) | −0.0073 (11) | −0.0064 (11) | 0.0074 (10) |
| C4 | 0.0509 (14) | 0.0451 (15) | 0.0424 (12) | −0.0089 (11) | 0.0027 (10) | 0.0084 (10) |
| C5 | 0.0411 (12) | 0.0557 (15) | 0.0393 (12) | −0.0021 (12) | 0.0076 (9) | 0.0029 (11) |
| C6 | 0.0698 (17) | 0.073 (2) | 0.0469 (15) | 0.0031 (16) | −0.0158 (12) | 0.0085 (13) |
| C7 | 0.0270 (10) | 0.0422 (13) | 0.0451 (12) | −0.0051 (10) | 0.0012 (9) | 0.0042 (10) |
| C8 | 0.0563 (15) | 0.0457 (14) | 0.0367 (12) | −0.0018 (11) | −0.0070 (10) | 0.0064 (9) |
| C9 | 0.100 (2) | 0.0617 (19) | 0.0519 (16) | −0.0284 (18) | 0.0041 (15) | 0.0033 (13) |
| C10 | 0.103 (2) | 0.076 (2) | 0.0412 (14) | 0.0196 (19) | 0.0010 (14) | 0.0007 (14) |
| C11 | 0.072 (2) | 0.076 (2) | 0.078 (2) | 0.0082 (17) | −0.0301 (15) | 0.0039 (16) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| O1—C6 | 1.421 (3) | C4—H4 | 0.9800 |
| O1—C4 | 1.422 (3) | C5—H5A | 0.9700 |
| O2—C1 | 1.206 (3) | C5—H5B | 0.9700 |
| O3—C1 | 1.320 (3) | C6—H6A | 0.9600 |
| O3—H3 | 1.00 (3) | C6—H6B | 0.9600 |
| O4—C7 | 1.231 (3) | C6—H6C | 0.9600 |
| O5—C7 | 1.347 (3) | C8—C10 | 1.506 (3) |
| O5—C8 | 1.480 (3) | C8—C11 | 1.508 (4) |
| N1—C7 | 1.335 (3) | C8—C9 | 1.512 (4) |
| N1—C2 | 1.464 (3) | C9—H9A | 0.9600 |
| N1—C5 | 1.469 (3) | C9—H9B | 0.9600 |
| C1—C2 | 1.530 (3) | C9—H9C | 0.9600 |
| C2—C3 | 1.533 (3) | C10—H10A | 0.9600 |
| C2—H2 | 0.9800 | C10—H10B | 0.9600 |
| C3—C4 | 1.513 (3) | C10—H10C | 0.9600 |
| C3—H3A | 0.9700 | C11—H11A | 0.9600 |
| C3—H3B | 0.9700 | C11—H11B | 0.9600 |
| C4—C5 | 1.530 (3) | C11—H11C | 0.9600 |
| C6—O1—C4 | 113.5 (2) | O1—C6—H6A | 109.5 |
| C1—O3—H3 | 108 (2) | O1—C6—H6B | 109.5 |
| C7—O5—C8 | 121.67 (18) | H6A—C6—H6B | 109.5 |
| C7—N1—C2 | 125.79 (17) | O1—C6—H6C | 109.5 |
| C7—N1—C5 | 121.89 (19) | H6A—C6—H6C | 109.5 |
| C2—N1—C5 | 112.03 (17) | H6B—C6—H6C | 109.5 |
| O2—C1—O3 | 123.9 (2) | O4—C7—N1 | 123.01 (19) |
| O2—C1—C2 | 122.1 (2) | O4—C7—O5 | 125.3 (2) |
| O3—C1—C2 | 113.93 (19) | N1—C7—O5 | 111.70 (19) |
| N1—C2—C1 | 113.13 (18) | O5—C8—C10 | 101.8 (2) |
| N1—C2—C3 | 101.81 (17) | O5—C8—C11 | 111.5 (2) |
| C1—C2—C3 | 112.11 (17) | C10—C8—C11 | 110.7 (2) |
| N1—C2—H2 | 109.8 | O5—C8—C9 | 108.62 (19) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 109.8 | C10—C8—C9 | 111.2 (2) |
| C3—C2—H2 | 109.8 | C11—C8—C9 | 112.5 (2) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 102.49 (18) | C8—C9—H9A | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—H3A | 111.3 | C8—C9—H9B | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—H3A | 111.3 | H9A—C9—H9B | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—H3B | 111.3 | C8—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—H3B | 111.3 | H9A—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| H3A—C3—H3B | 109.2 | H9B—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| O1—C4—C3 | 112.24 (19) | C8—C10—H10A | 109.5 |
| O1—C4—C5 | 105.62 (19) | C8—C10—H10B | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 103.28 (17) | H10A—C10—H10B | 109.5 |
| O1—C4—H4 | 111.7 | C8—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 111.7 | H10A—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 111.7 | H10B—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| N1—C5—C4 | 103.27 (19) | C8—C11—H11A | 109.5 |
| N1—C5—H5A | 111.1 | C8—C11—H11B | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—H5A | 111.1 | H11A—C11—H11B | 109.5 |
| N1—C5—H5B | 111.1 | C8—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—H5B | 111.1 | H11A—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| H5A—C5—H5B | 109.1 | H11B—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| C7—N1—C2—C1 | 85.8 (2) | C7—N1—C5—C4 | 179.02 (19) |
| C5—N1—C2—C1 | −100.3 (2) | C2—N1—C5—C4 | 4.8 (2) |
| C7—N1—C2—C3 | −153.7 (2) | O1—C4—C5—N1 | 89.6 (2) |
| C5—N1—C2—C3 | 20.2 (2) | C3—C4—C5—N1 | −28.4 (2) |
| O2—C1—C2—N1 | 166.64 (19) | C2—N1—C7—O4 | 178.7 (2) |
| O3—C1—C2—N1 | −16.0 (2) | C5—N1—C7—O4 | 5.3 (3) |
| O2—C1—C2—C3 | 52.2 (3) | C2—N1—C7—O5 | −0.3 (3) |
| O3—C1—C2—C3 | −130.4 (2) | C5—N1—C7—O5 | −173.6 (2) |
| N1—C2—C3—C4 | −37.2 (2) | C8—O5—C7—O4 | 18.7 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 84.0 (2) | C8—O5—C7—N1 | −162.41 (18) |
| C6—O1—C4—C3 | −71.9 (2) | C7—O5—C8—C10 | 175.9 (2) |
| C6—O1—C4—C5 | 176.29 (19) | C7—O5—C8—C11 | −65.9 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—O1 | −72.3 (2) | C7—O5—C8—C9 | 58.5 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 40.9 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O3—H3···O4i | 1.00 (3) | 1.68 (4) | 2.672 (2) | 169 (4) |
Symmetry codes: (i) x+1, y, z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: KP2285).
References
- Bigge, C. F., et al. (2003). Patent WO 03045912A1.
- Kohrt, J. T., et al. (2007). Chem. Biol. Drug Des.17, 100–112. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Perzborn, E. (2009). Hamostaseologie, 29, 260–267. [PubMed]
- Rigaku (1998). RAPID-AUTO Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan.
- Rigaku/MSC (2005). CrystalClear Rigaku/MSC, The Woodlands, Texas, USA.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Van Huis, C. A., et al. (2009). Bioorg. Med. Chem.17, 2501–2511.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810047707/kp2285sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810047707/kp2285Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report



