Abstract
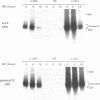
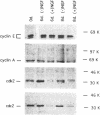
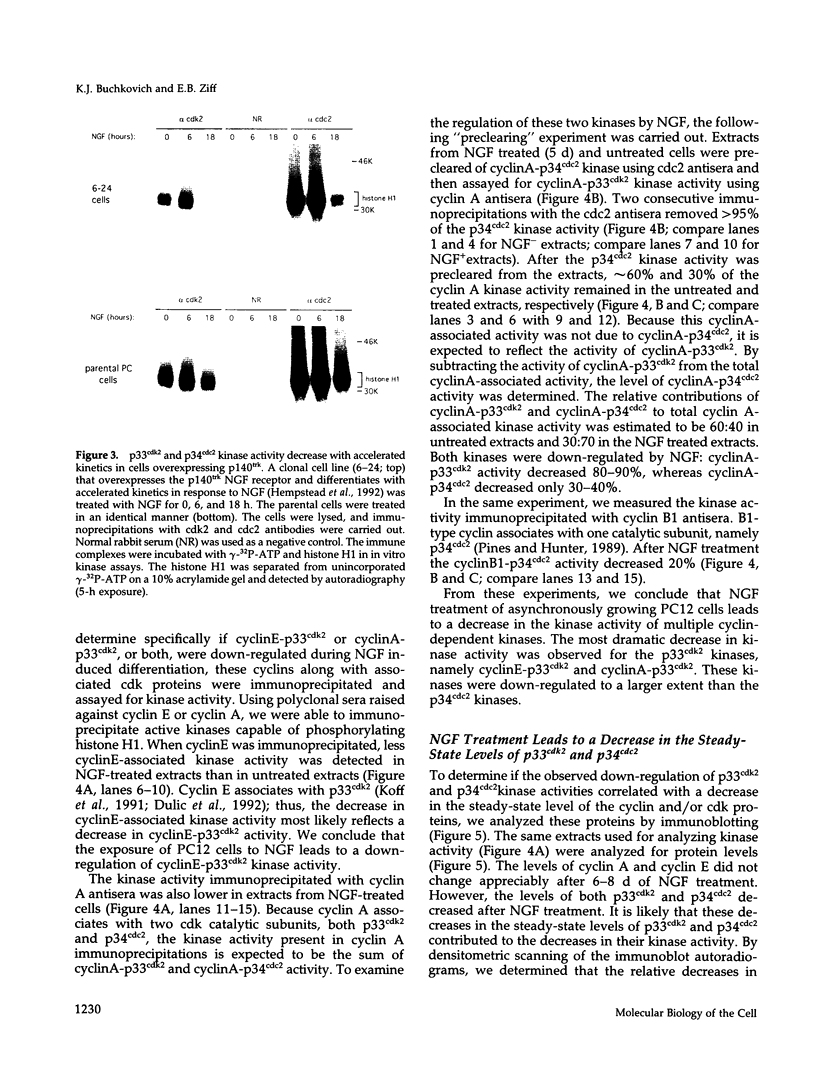
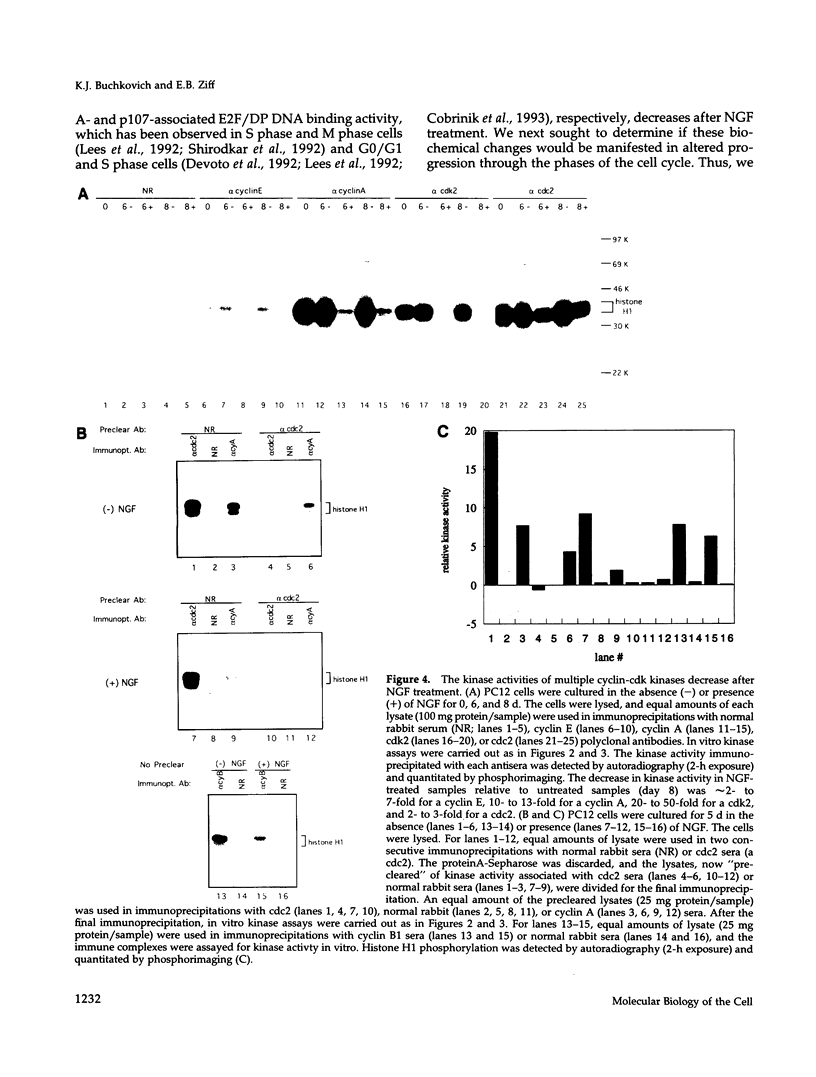
In the absence of serum, nerve growth factor (NGF) promotes the survival and differentiation of the PC12 pheochromocytoma cell line. In the presence of serum, NGF acts primarily as a differentiation factor and negative regulator of cell cycling. To investigate NGF control of cell cycling, we have analyzed the regulation of cyclin dependent kinases during PC12 cell differentiation. NGF treatment leads to a reduction in the steady-state protein levels of p33cdk2 and p34cdc2, two key regulators of cell cycle progression. The decrease in p33cdk2 and p34cdc2 coincides with a decrease in the enzymatic activity of cyclinA-p34cdc2, cyclinB-p34cdc2, cyclinE-p33cdk2, and cyclinA-p33cdk2 kinases. The decline in p33cdk2 and p34cdc2 kinase activity in response to NGF is accelerated in cells that over-express the p140trk NGF receptor, suggesting that the timing of the down- regulation is dependent on the level of p140trk and the strength of the NGF signal. The level of cyclin A, a regulatory subunit of p33cdk2 and p34cdc2, is relatively constant during PC12 differentiation. Nevertheless, the DNA binding activity of the cyclinA-associated transcription factor E2F/DP decreases. Thus, NGF down-regulates the activity of cyclin dependent kinases and cyclin-transcription factor complexes during PC12 differentiation.
Full text
PDF







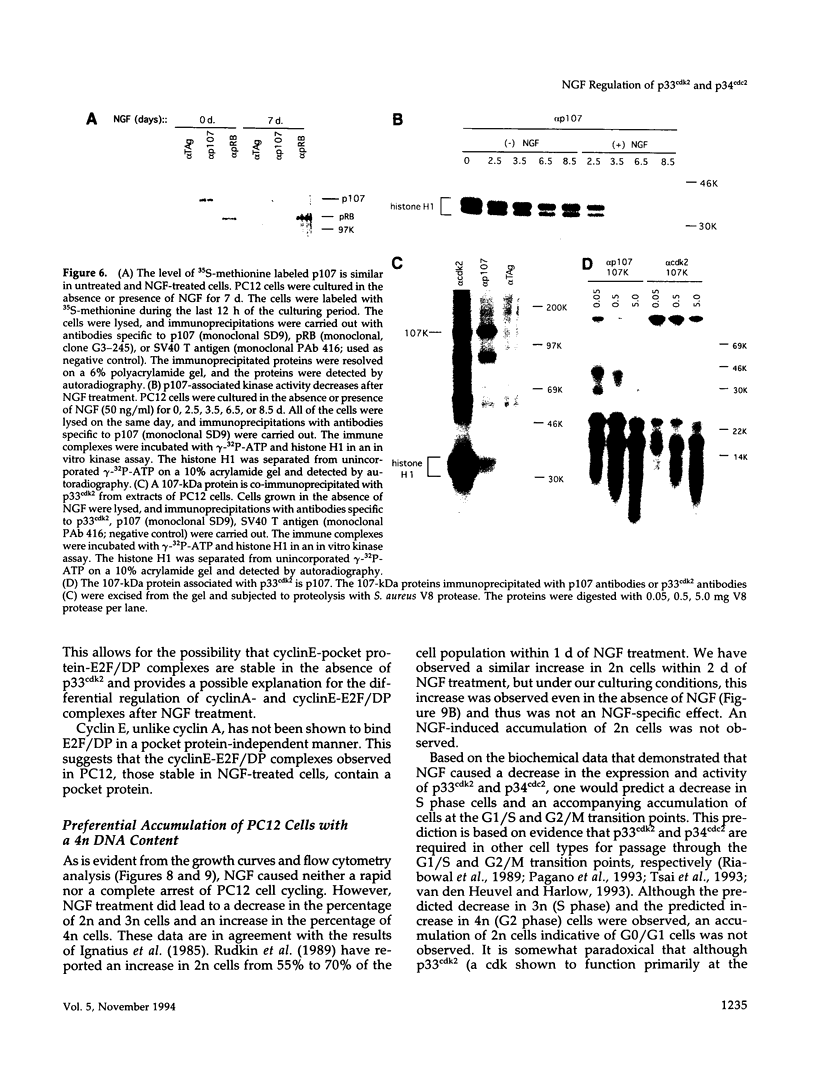
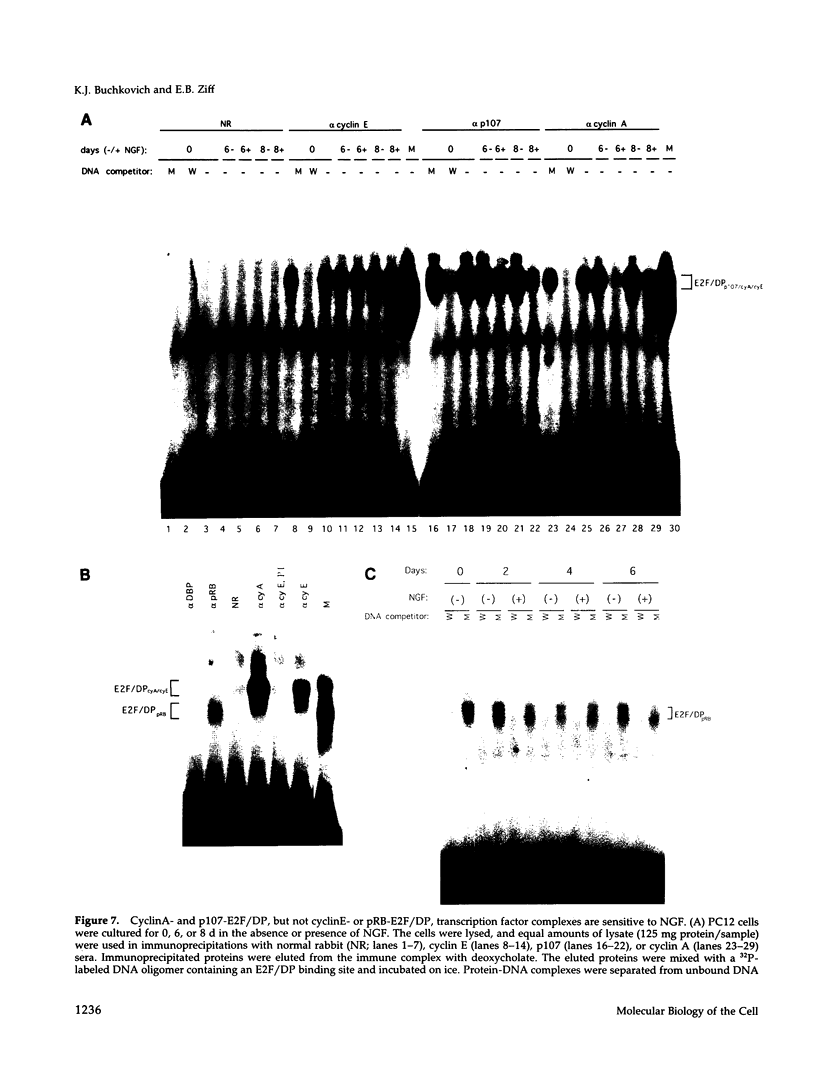
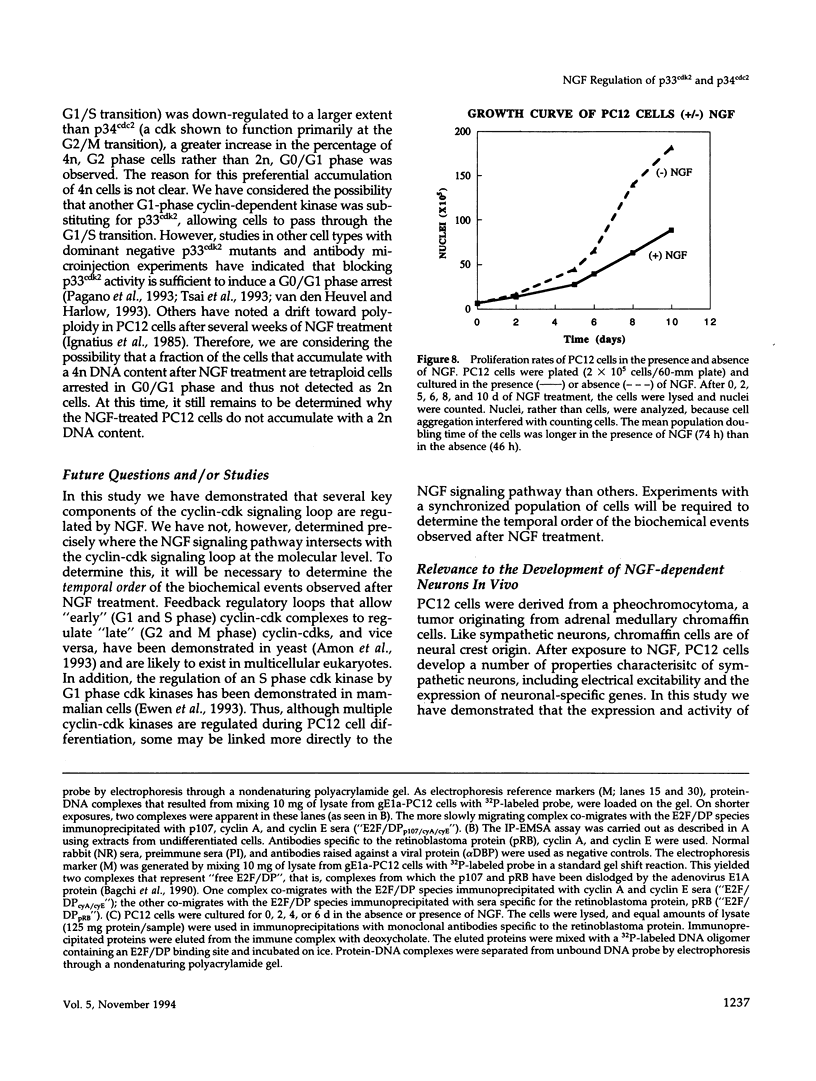
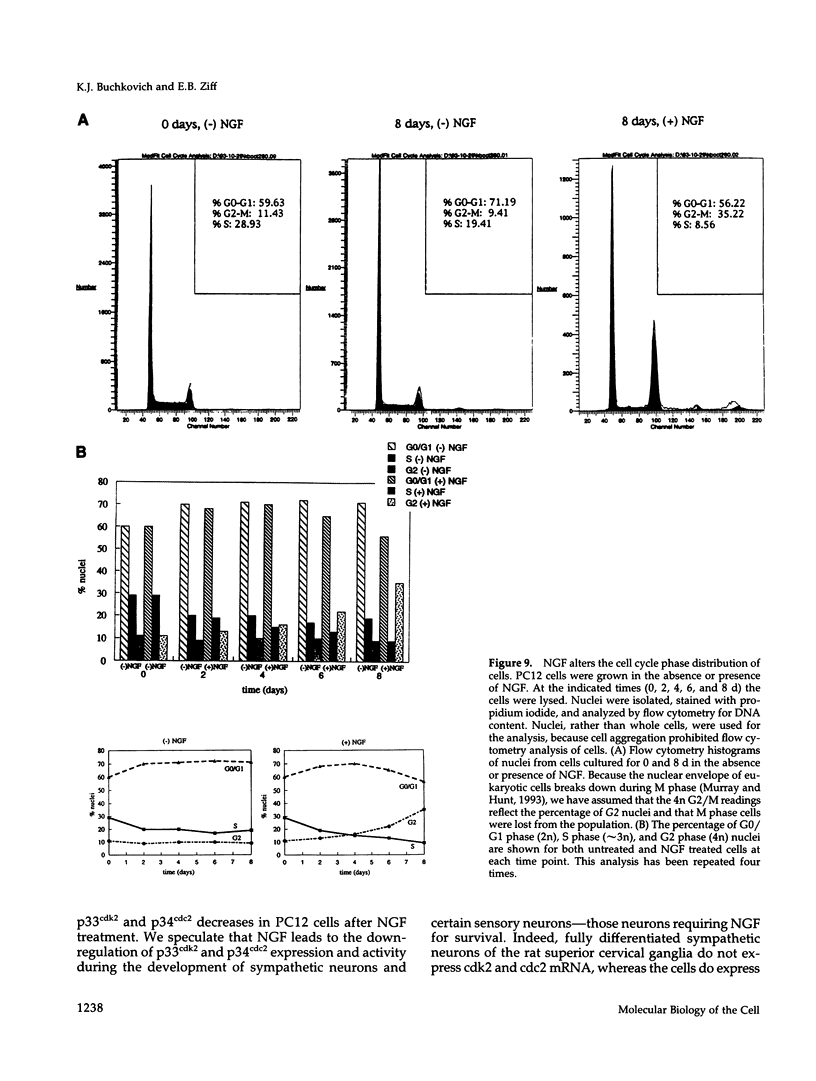



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amon A., Tyers M., Futcher B., Nasmyth K. Mechanisms that help the yeast cell cycle clock tick: G2 cyclins transcriptionally activate G2 cyclins and repress G1 cyclins. Cell. 1993 Sep 24;74(6):993–1007. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90722-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagchi S., Raychaudhuri P., Nevins J. R. Adenovirus E1A proteins can dissociate heteromeric complexes involving the E2F transcription factor: a novel mechanism for E1A trans-activation. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):659–669. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90112-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbacid M. Nerve growth factor: a tale of two receptors. Oncogene. 1993 Aug;8(8):2033–2042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulukos K. E., Ziff E. B. Adenovirus 5 E1A proteins disrupt the neuronal phenotype and growth factor responsiveness of PC12 cells by a conserved region 1-dependent mechanism. Oncogene. 1993 Feb;8(2):237–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bregnard A., Kuenzle C. C., Ruch F. Cytophotometric and autoradiographic evidence for post-natal DNA synthesis in neurons of the rat cerebral cortex. Exp Cell Res. 1977 Jun;107(1):151–157. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(77)90396-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burstein D. E., Greene L. A. Nerve growth factor has both mitogenic and antimitogenic activity. Dev Biol. 1982 Dec;94(2):477–482. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90364-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao L., Faha B., Dembski M., Tsai L. H., Harlow E., Dyson N. Independent binding of the retinoblastoma protein and p107 to the transcription factor E2F. Nature. 1992 Jan 9;355(6356):176–179. doi: 10.1038/355176a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardoso M. C., Leonhardt H., Nadal-Ginard B. Reversal of terminal differentiation and control of DNA replication: cyclin A and Cdk2 specifically localize at subnuclear sites of DNA replication. Cell. 1993 Sep 24;74(6):979–992. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90721-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chellappan S. P., Hiebert S., Mudryj M., Horowitz J. M., Nevins J. R. The E2F transcription factor is a cellular target for the RB protein. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1053–1061. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90557-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke A. R., Maandag E. R., van Roon M., van der Lugt N. M., van der Valk M., Hooper M. L., Berns A., te Riele H. Requirement for a functional Rb-1 gene in murine development. Nature. 1992 Sep 24;359(6393):328–330. doi: 10.1038/359328a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke P. R., Karsenti E. Regulation of p34cdc2 protein kinase: new insights into protein phosphorylation and the cell cycle. J Cell Sci. 1991 Nov;100(Pt 3):409–414. doi: 10.1242/jcs.100.3.409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobrinik D., Whyte P., Peeper D. S., Jacks T., Weinberg R. A. Cell cycle-specific association of E2F with the p130 E1A-binding protein. Genes Dev. 1993 Dec;7(12A):2392–2404. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.12a.2392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connell-Crowley L., Solomon M. J., Wei N., Harper J. W. Phosphorylation independent activation of human cyclin-dependent kinase 2 by cyclin A in vitro. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Jan;4(1):79–92. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.1.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowley C., Spencer S. D., Nishimura M. C., Chen K. S., Pitts-Meek S., Armanini M. P., Ling L. H., McMahon S. B., Shelton D. L., Levinson A. D. Mice lacking nerve growth factor display perinatal loss of sensory and sympathetic neurons yet develop basal forebrain cholinergic neurons. Cell. 1994 Mar 25;76(6):1001–1011. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90378-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devoto S. H., Mudryj M., Pines J., Hunter T., Nevins J. R. A cyclin A-protein kinase complex possesses sequence-specific DNA binding activity: p33cdk2 is a component of the E2F-cyclin A complex. Cell. 1992 Jan 10;68(1):167–176. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90215-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G., Beach D. Activation of cdc2 protein kinase during mitosis in human cells: cell cycle-dependent phosphorylation and subunit rearrangement. Cell. 1988 Jul 1;54(1):17–26. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90175-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G., Beach D., Moran E. Synthesis of p34, the mammalian homolog of the yeast cdc2+/CDC28 protein kinase, is stimulated during adenovirus-induced proliferation of primary baby rat kidney cells. Oncogene. 1988 Jun;2(6):553–557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulić V., Lees E., Reed S. I. Association of human cyclin E with a periodic G1-S phase protein kinase. Science. 1992 Sep 25;257(5078):1958–1961. doi: 10.1126/science.1329201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynlacht B. D., Flores O., Lees J. A., Harlow E. Differential regulation of E2F transactivation by cyclin/cdk2 complexes. Genes Dev. 1994 Aug 1;8(15):1772–1786. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.15.1772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyson N., Dembski M., Fattaey A., Ngwu C., Ewen M., Helin K. Analysis of p107-associated proteins: p107 associates with a form of E2F that differs from pRB-associated E2F-1. J Virol. 1993 Dec;67(12):7641–7647. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.12.7641-7647.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elledge S. J., Richman R., Hall F. L., Williams R. T., Lodgson N., Harper J. W. CDK2 encodes a 33-kDa cyclin A-associated protein kinase and is expressed before CDC2 in the cell cycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2907–2911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewen M. E., Sluss H. K., Whitehouse L. L., Livingston D. M. TGF beta inhibition of Cdk4 synthesis is linked to cell cycle arrest. Cell. 1993 Sep 24;74(6):1009–1020. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90723-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feddersen R. M., Ehlenfeldt R., Yunis W. S., Clark H. B., Orr H. T. Disrupted cerebellar cortical development and progressive degeneration of Purkinje cells in SV40 T antigen transgenic mice. Neuron. 1992 Nov;9(5):955–966. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90247-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fesquet D., Labbé J. C., Derancourt J., Capony J. P., Galas S., Girard F., Lorca T., Shuttleworth J., Dorée M., Cavadore J. C. The MO15 gene encodes the catalytic subunit of a protein kinase that activates cdc2 and other cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) through phosphorylation of Thr161 and its homologues. EMBO J. 1993 Aug;12(8):3111–3121. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05980.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman R. S., Estus S., Johnson E. M., Jr Analysis of cell cycle-related gene expression in postmitotic neurons: selective induction of Cyclin D1 during programmed cell death. Neuron. 1994 Feb;12(2):343–355. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90276-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. A., Tischler A. S. Establishment of a noradrenergic clonal line of rat adrenal pheochromocytoma cells which respond to nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2424–2428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu Y., Rosenblatt J., Morgan D. O. Cell cycle regulation of CDK2 activity by phosphorylation of Thr160 and Tyr15. EMBO J. 1992 Nov;11(11):3995–4005. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05493.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu Y., Turck C. W., Morgan D. O. Inhibition of CDK2 activity in vivo by an associated 20K regulatory subunit. Nature. 1993 Dec 16;366(6456):707–710. doi: 10.1038/366707a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunning P. W., Landreth G. E., Layer P., Ignatius M., Shooter E. M. Nerve growth factor-induced differentiation of PC12 cells: evaluation of changes in RNA and DNA metabolism. J Neurosci. 1981 Apr;1(4):368–379. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.01-04-00368.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyuris J., Golemis E., Chertkov H., Brent R. Cdi1, a human G1 and S phase protein phosphatase that associates with Cdk2. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):791–803. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90498-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halegoua S., Armstrong R. C., Kremer N. E. Dissecting the mode of action of a neuronal growth factor. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1991;165:119–170. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-75747-1_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammang J. P., Behringer R. R., Baetge E. E., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L., Messing A. Oncogene expression in retinal horizontal cells of transgenic mice results in a cascade of neurodegeneration. Neuron. 1993 Jun;10(6):1197–1209. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90067-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannon G. J., Demetrick D., Beach D. Isolation of the Rb-related p130 through its interaction with CDK2 and cyclins. Genes Dev. 1993 Dec;7(12A):2378–2391. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.12a.2378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlow E., Crawford L. V., Pim D. C., Williamson N. M. Monoclonal antibodies specific for simian virus 40 tumor antigens. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):861–869. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.861-869.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J. W., Adami G. R., Wei N., Keyomarsi K., Elledge S. J. The p21 Cdk-interacting protein Cip1 is a potent inhibitor of G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):805–816. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90499-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes T. E., Valtz N. L., McKay R. D. Downregulation of CDC2 upon terminal differentiation of neurons. New Biol. 1991 Mar;3(3):259–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintz N. Cell death and the cell cycle: a relationship between transformation and neurodegeneration? Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 May;18(5):157–159. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90103-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hempstead B. L., Rabin S. J., Kaplan L., Reid S., Parada L. F., Kaplan D. R. Overexpression of the trk tyrosine kinase rapidly accelerates nerve growth factor-induced differentiation. Neuron. 1992 Nov;9(5):883–896. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90241-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann C. H., Su L. K., Harlow E. Adenovirus E1A is associated with a serine/threonine protein kinase. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5848–5859. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5848-5859.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huff K. R., Guroff G. Nerve growth factor-induced reduction in epidermal growth factor responsiveness and epidermal growth factor receptors in PC12 cells: an aspect of cell differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Jul 12;89(1):175–180. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90960-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignatius M. J., Chandler C. R., Shooter E. M. Nerve growth factor-treated, neurite-bearing PC12 cells continue to synthesize DNA. J Neurosci. 1985 Feb;5(2):343–351. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-02-00343.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacks T., Fazeli A., Schmitt E. M., Bronson R. T., Goodell M. A., Weinberg R. A. Effects of an Rb mutation in the mouse. Nature. 1992 Sep 24;359(6393):295–300. doi: 10.1038/359295a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalman D., Whittaker K., Bishop J. M., O'Lague P. H. Domains of E1A that bind p105Rb, p130, and p300 are required to block nerve growth factor-induced neurite growth in PC12 cells. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Apr;4(4):353–361. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.4.353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan D. R., Hempstead B. L., Martin-Zanca D., Chao M. V., Parada L. F. The trk proto-oncogene product: a signal transducing receptor for nerve growth factor. Science. 1991 Apr 26;252(5005):554–558. doi: 10.1126/science.1850549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R., Jing S. Q., Nanduri V., O'Rourke E., Barbacid M. The trk proto-oncogene encodes a receptor for nerve growth factor. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):189–197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90419-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koff A., Cross F., Fisher A., Schumacher J., Leguellec K., Philippe M., Roberts J. M. Human cyclin E, a new cyclin that interacts with two members of the CDC2 gene family. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1217–1228. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90044-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krek W., Ewen M. E., Shirodkar S., Arany Z., Kaelin W. G., Jr, Livingston D. M. Negative regulation of the growth-promoting transcription factor E2F-1 by a stably bound cyclin A-dependent protein kinase. Cell. 1994 Jul 15;78(1):161–172. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90582-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Thangue N. B. DRTF1/E2F: an expanding family of heterodimeric transcription factors implicated in cell-cycle control. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Mar;19(3):108–114. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90202-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee E. Y., Chang C. Y., Hu N., Wang Y. C., Lai C. C., Herrup K., Lee W. H., Bradley A. Mice deficient for Rb are nonviable and show defects in neurogenesis and haematopoiesis. Nature. 1992 Sep 24;359(6393):288–294. doi: 10.1038/359288a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. G., Norbury C. J., Spurr N. K., Nurse P. Regulated expression and phosphorylation of a possible mammalian cell-cycle control protein. Nature. 1988 Jun 16;333(6174):676–679. doi: 10.1038/333676a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lees E., Faha B., Dulic V., Reed S. I., Harlow E. Cyclin E/cdk2 and cyclin A/cdk2 kinases associate with p107 and E2F in a temporally distinct manner. Genes Dev. 1992 Oct;6(10):1874–1885. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.10.1874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lees J. A., Saito M., Vidal M., Valentine M., Look T., Harlow E., Dyson N., Helin K. The retinoblastoma protein binds to a family of E2F transcription factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;13(12):7813–7825. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.12.7813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lentz R. D., Lapham L. W. A quantitative cytochemical study of the DNA content of neurons of rat cerebellar cortex. J Neurochem. 1969 Mar;16(3):379–384. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1969.tb10377.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Montalcini R. The nerve growth factor 35 years later. Science. 1987 Sep 4;237(4819):1154–1162. doi: 10.1126/science.3306916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Graham C., Lacy S., Duncan A. M., Whyte P. The adenovirus E1A-associated 130-kD protein is encoded by a member of the retinoblastoma gene family and physically interacts with cyclins A and E. Genes Dev. 1993 Dec;7(12A):2366–2377. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.12a.2366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb D. M., Tsao H., Cobb M. H., Greene L. A. NGF and other growth factors induce an association between ERK1 and the NGF receptor, gp140prototrk. Neuron. 1992 Dec;9(6):1053–1065. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90065-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher P. A. Nerve growth factor induces protein-tyrosine phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6788–6791. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marraccino R. L., Firpo E. J., Roberts J. M. Activation of the p34 CDC2 protein kinase at the start of S phase in the human cell cycle. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Apr;3(4):389–401. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.4.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushime H., Ewen M. E., Strom D. K., Kato J. Y., Hanks S. K., Roussel M. F., Sherr C. J. Identification and properties of an atypical catalytic subunit (p34PSK-J3/cdk4) for mammalian D type G1 cyclins. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):323–334. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90360-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. E2F: a link between the Rb tumor suppressor protein and viral oncoproteins. Science. 1992 Oct 16;258(5081):424–429. doi: 10.1126/science.1411535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norbury C., Nurse P. Animal cell cycles and their control. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:441–470. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.002301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obermeier A., Lammers R., Wiesmüller K. H., Jung G., Schlessinger J., Ullrich A. Identification of Trk binding sites for SHC and phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase and formation of a multimeric signaling complex. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 5;268(31):22963–22966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okano H. J., Pfaff D. W., Gibbs R. B. RB and Cdc2 expression in brain: correlations with 3H-thymidine incorporation and neurogenesis. J Neurosci. 1993 Jul;13(7):2930–2938. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-07-02930.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagano M., Pepperkok R., Lukas J., Baldin V., Ansorge W., Bartek J., Draetta G. Regulation of the cell cycle by the cdk2 protein kinase in cultured human fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;121(1):101–111. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.1.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peeper D. S., Parker L. L., Ewen M. E., Toebes M., Hall F. L., Xu M., Zantema A., van der Eb A. J., Piwnica-Worms H. A- and B-type cyclins differentially modulate substrate specificity of cyclin-cdk complexes. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):1947–1954. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05844.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J., Hunter T. Human cyclin A is adenovirus E1A-associated protein p60 and behaves differently from cyclin B. Nature. 1990 Aug 23;346(6286):760–763. doi: 10.1038/346760a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J., Hunter T. Isolation of a human cyclin cDNA: evidence for cyclin mRNA and protein regulation in the cell cycle and for interaction with p34cdc2. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):833–846. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90936-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polyak K., Kato J. Y., Solomon M. J., Sherr C. J., Massague J., Roberts J. M., Koff A. p27Kip1, a cyclin-Cdk inhibitor, links transforming growth factor-beta and contact inhibition to cell cycle arrest. Genes Dev. 1994 Jan;8(1):9–22. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.1.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poon R. Y., Yamashita K., Adamczewski J. P., Hunt T., Shuttleworth J. The cdc2-related protein p40MO15 is the catalytic subunit of a protein kinase that can activate p33cdk2 and p34cdc2. EMBO J. 1993 Aug;12(8):3123–3132. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05981.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qui M. S., Green S. H. PC12 cell neuronal differentiation is associated with prolonged p21ras activity and consequent prolonged ERK activity. Neuron. 1992 Oct;9(4):705–717. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90033-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabin S. J., Cleghon V., Kaplan D. R. SNT, a differentiation-specific target of neurotrophic factor-induced tyrosine kinase activity in neurons and PC12 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2203–2213. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riabowol K., Draetta G., Brizuela L., Vandre D., Beach D. The cdc2 kinase is a nuclear protein that is essential for mitosis in mammalian cells. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):393–401. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90914-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins D. J., Cheng M., Zhen E., Vanderbilt C. A., Feig L. A., Cobb M. H. Evidence for a Ras-dependent extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase (ERK) cascade. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):6924–6928. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.6924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblatt J., Gu Y., Morgan D. O. Human cyclin-dependent kinase 2 is activated during the S and G2 phases of the cell cycle and associates with cyclin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2824–2828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudkin B. B., Lazarovici P., Levi B. Z., Abe Y., Fujita K., Guroff G. Cell cycle-specific action of nerve growth factor in PC12 cells: differentiation without proliferation. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3319–3325. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08493.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirodkar S., Ewen M., DeCaprio J. A., Morgan J., Livingston D. M., Chittenden T. The transcription factor E2F interacts with the retinoblastoma product and a p107-cyclin A complex in a cell cycle-regulated manner. Cell. 1992 Jan 10;68(1):157–166. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90214-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon M. J., Harper J. W., Shuttleworth J. CAK, the p34cdc2 activating kinase, contains a protein identical or closely related to p40MO15. EMBO J. 1993 Aug;12(8):3133–3142. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05982.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soltoff S. P., Rabin S. L., Cantley L. C., Kaplan D. R. Nerve growth factor promotes the activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and its association with the trk tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 25;267(24):17472–17477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soto A. M., Sonnenschein C. The role of estrogens on the proliferation of human breast tumor cells (MCF-7). J Steroid Biochem. 1985 Jul;23(1):87–94. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(85)90265-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. M., Loeb D. M., Copeland T. D., Pawson T., Greene L. A., Kaplan D. R. Trk receptors use redundant signal transduction pathways involving SHC and PLC-gamma 1 to mediate NGF responses. Neuron. 1994 Mar;12(3):691–705. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90223-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szeberényi J., Cai H., Cooper G. M. Effect of a dominant inhibitory Ha-ras mutation on neuronal differentiation of PC12 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5324–5332. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas S. M., DeMarco M., D'Arcangelo G., Halegoua S., Brugge J. S. Ras is essential for nerve growth factor- and phorbol ester-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of MAP kinases. Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):1031–1040. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90075-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troppmair J., Bruder J. T., App H., Cai H., Liptak L., Szeberényi J., Cooper G. M., Rapp U. R. Ras controls coupling of growth factor receptors and protein kinase C in the membrane to Raf-1 and B-Raf protein serine kinases in the cytosol. Oncogene. 1992 Sep;7(9):1867–1873. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai L. H., Harlow E., Meyerson M. Isolation of the human cdk2 gene that encodes the cyclin A- and adenovirus E1A-associated p33 kinase. Nature. 1991 Sep 12;353(6340):174–177. doi: 10.1038/353174a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai L. H., Lees E., Faha B., Harlow E., Riabowol K. The cdk2 kinase is required for the G1-to-S transition in mammalian cells. Oncogene. 1993 Jun;8(6):1593–1602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vetter M. L., Martin-Zanca D., Parada L. F., Bishop J. M., Kaplan D. R. Nerve growth factor rapidly stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-gamma 1 by a kinase activity associated with the product of the trk protooncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5650–5654. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner J. A. The fibroblast growth factors: an emerging family of neural growth factors. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1991;165:95–118. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-75747-1_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood K. W., Sarnecki C., Roberts T. M., Blenis J. ras mediates nerve growth factor receptor modulation of three signal-transducing protein kinases: MAP kinase, Raf-1, and RSK. Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):1041–1050. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90076-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong Y., Hannon G. J., Zhang H., Casso D., Kobayashi R., Beach D. p21 is a universal inhibitor of cyclin kinases. Nature. 1993 Dec 16;366(6456):701–704. doi: 10.1038/366701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong Y., Zhang H., Beach D. D type cyclins associate with multiple protein kinases and the DNA replication and repair factor PCNA. Cell. 1992 Oct 30;71(3):505–514. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90518-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- al-Ubaidi M. R., Hollyfield J. G., Overbeek P. A., Baehr W. Photoreceptor degeneration induced by the expression of simian virus 40 large tumor antigen in the retina of transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 15;89(4):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.4.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Heuvel S., Harlow E. Distinct roles for cyclin-dependent kinases in cell cycle control. Science. 1993 Dec 24;262(5142):2050–2054. doi: 10.1126/science.8266103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]