Abstract
In the title compound, C17H12O4·H2O, the coumarin ring system is approximately planar with a maximum atomic deviation of 0.011 (2) Å, and is nearly perpendicular to the phenyl ring at a dihedral angle of 86.63 (9)°. In the crystal, molecules are linked by classical O—H⋯O and weak C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds. π–π stacking is also present [centroid–centroid distance = 3.6898 (12) Å].
Related literature
For the biological activity of coumarins, see: Sharma et al. (2005 ▶); Iqbal et al. (2009 ▶); Siddiqui et al. (2009 ▶); Vyas et al. (2009 ▶); Rollinger et al. (2004 ▶); Brühlmann et al. (2001 ▶). For related structures, see: Yang et al. (2006 ▶, 2007 ▶, 2008 ▶).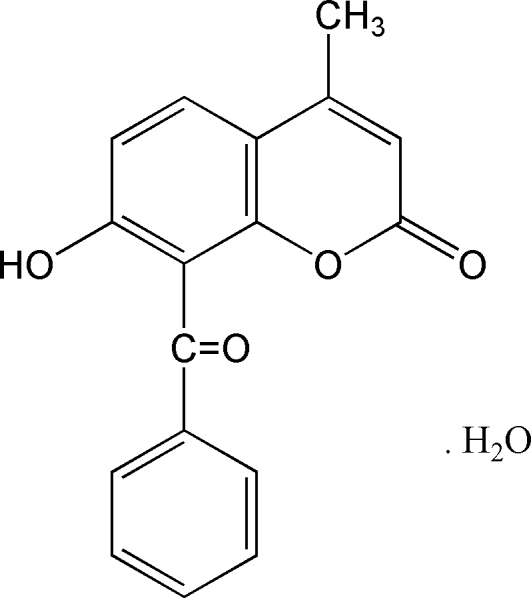
Experimental
Crystal data
C17H12O4·H2O
M r = 298.28
Monoclinic,
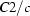
a = 14.8912 (15) Å
b = 9.6768 (11) Å
c = 20.644 (2) Å
β = 104.275 (2)°
V = 2882.9 (5) Å3
Z = 8
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.10 mm−1
T = 298 K
0.49 × 0.24 × 0.21 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996 ▶) T min = 0.952, T max = 0.979
7271 measured reflections
2549 independent reflections
1706 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.036
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.040
wR(F 2) = 0.110
S = 1.05
2549 reflections
255 parameters
All H-atom parameters refined
Δρmax = 0.15 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.19 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Siemens, 1996 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Siemens, 1996 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXTL; molecular graphics: SHELXTL; software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810046350/xu5087sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810046350/xu5087Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O3—H3⋯O5i | 0.93 (3) | 1.72 (3) | 2.650 (2) | 177 (3) |
| O5—H5A⋯O2 | 0.91 (4) | 2.00 (4) | 2.887 (3) | 166 (3) |
| O5—H5B⋯O4ii | 0.87 (3) | 2.03 (3) | 2.875 (2) | 162 (3) |
| C17—H17⋯O2iii | 0.95 (2) | 2.54 (2) | 3.422 (3) | 154.7 (16) |
Symmetry codes: (i) 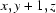 ; (ii)
; (ii) 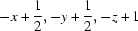 ; (iii)
; (iii) 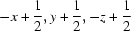 .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the financial support of the Huaihai Institute of Technology Science Foundation (No. KX10019).
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Coumarins are very well known for their biological activity, such as antioxidants (Sharma et al., 2005), antiamoebic (Iqbal et al., 2009), anticonvulsant activity (Siddiqui et al., 2009), antimicrobial (Vyas et al., 2009) and inhibitions of acetylcholinesterase and monoamine oxidase (Rollinger et al., 2004; Brühlmann et al., 2001). The crystal structures of some coumarin derivatives (Yang et al., 2006; 2007; 2008) have been decribed. As part of our study of the crystal structures of coumarin derivatives with 7-hydroxy, we report here the crystal structure of 8-Benzoyl-7-hydroxy-4-methyl-2H-1-benzopyran-2-one, (I).
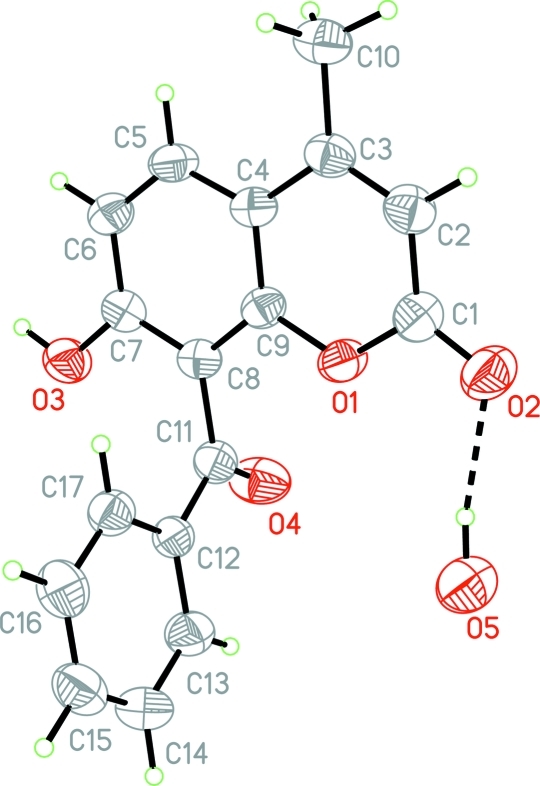
In the molecule(I), the asymmetric unit of (I) contains one coumarin molecule and one hydration water molecules, and which are linked together by one O—H···O hydrogen bond (Table 1 and Fig. 1). The coumarin moiety and phenyl ring (two r.m.s deviations 0.0060 Å) are perpendicular to each other with a dihedral angle of 86.59 (5)° between the plane of the atoms O1—O3/C1—C9 and the plane of C12—C17.
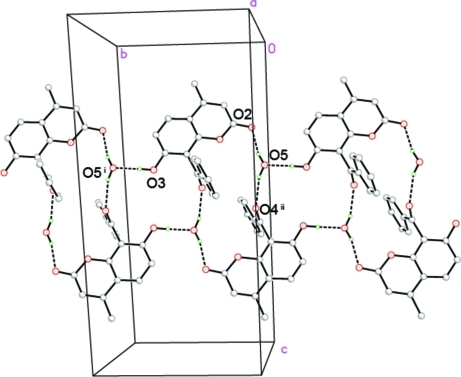
In crystal structure of (I), translationally related molecules are linked together by O3—H3···O5i [symmetry code: (i)x, 1 + y, z] hydrogen bond, forming C(10) chains parallel to the b axis; inversionally related molecular chains are linked together by O—H···O hydrogen bond O5—H5B···O4ii [symmetry codes: (ii)1/2 - x, 1/2 - y, 1 - z], generating doubled chain of R56(28)[R44(20)R44(16)] ring parallel to the b axis (Table.1 and Fig. 2). Neighboring doubled chains are linked into three-dimensional crystal structure by π–π interaction Cg1···Cg1iii [Where Cg1 is the centroid of O1/C1—C4/C9, Cg1···Cg1iii = 3.6898 (12) Å, symmetry code: (iii) -x, y,1/2 - z].
Experimental
The mixture containing 2.8 g (10 mmol) of dry, powdered 7-benzoxy-4-methylcoumarin and 4.53 g (34 mmol) of anhydrous aluminium chloride was heated at 463 K for 2 h in an oil bath, then 30 ml of dilute (1:7) hydrochloric acid is added and the mixture is heated on a steam bath for 30 min, the crude product was filtered off, washed with water. Colorless crystals of (I) suitable for X-ray structure analysis were obtained by recrystallizing from 95% water-ethanol solution [m.p. 492 K].
Refinement
All H atom was located in a difference Fourier map and refined freely.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The asymmetric unit of title structure, showing 50% probability displacement ellipsoids for non-H atoms and the atom-numbering scheme, intramolecular O–H···O contact is shown.
Fig. 2.
The molecular doubled chain of R56(28)[R44 (20)R44(16)]ring parallel to the b axis. [Symmetry codes: (i) x, 1 + y, z; (ii)1/2 - x, 1/2 - y, 1 - z].
Crystal data
| C17H12O4·H2O | F(000) = 1248 |
| Mr = 298.28 | Dx = 1.374 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, C2/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -C 2yc | Cell parameters from 2106 reflections |
| a = 14.8912 (15) Å | θ = 2.6–26.3° |
| b = 9.6768 (11) Å | µ = 0.10 mm−1 |
| c = 20.644 (2) Å | T = 298 K |
| β = 104.275 (2)° | Prism, colorless |
| V = 2882.9 (5) Å3 | 0.49 × 0.24 × 0.21 mm |
| Z = 8 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART CCD area-detector diffractometer | 2549 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1706 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.036 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 25.0°, θmin = 2.0° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996) | h = −17→14 |
| Tmin = 0.952, Tmax = 0.979 | k = −11→11 |
| 7271 measured reflections | l = −24→24 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.040 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.110 | All H-atom parameters refined |
| S = 1.05 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0463P)2 + 1.197P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2549 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 255 parameters | Δρmax = 0.15 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.19 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.17438 (9) | 0.30443 (14) | 0.31197 (6) | 0.0429 (4) | |
| O2 | 0.13299 (12) | 0.09551 (16) | 0.27504 (8) | 0.0590 (5) | |
| O3 | 0.27345 (10) | 0.73405 (18) | 0.40667 (7) | 0.0516 (4) | |
| H3 | 0.2699 (19) | 0.830 (3) | 0.4027 (13) | 0.093 (10)* | |
| O4 | 0.23351 (10) | 0.42720 (19) | 0.46551 (7) | 0.0621 (5) | |
| C1 | 0.12717 (15) | 0.2185 (2) | 0.26211 (10) | 0.0443 (5) | |
| C2 | 0.07607 (15) | 0.2814 (2) | 0.20096 (10) | 0.0453 (6) | |
| H2 | 0.0427 (14) | 0.218 (2) | 0.1671 (10) | 0.050 (6)* | |
| C3 | 0.07320 (13) | 0.4192 (2) | 0.19106 (9) | 0.0397 (5) | |
| C4 | 0.12370 (13) | 0.5072 (2) | 0.24429 (9) | 0.0367 (5) | |
| C5 | 0.12629 (15) | 0.6515 (2) | 0.24161 (11) | 0.0436 (5) | |
| H5 | 0.0918 (13) | 0.697 (2) | 0.2017 (10) | 0.042 (5)* | |
| C6 | 0.17489 (14) | 0.7290 (2) | 0.29421 (11) | 0.0438 (5) | |
| H6 | 0.1748 (14) | 0.829 (2) | 0.2898 (10) | 0.050 (6)* | |
| C7 | 0.22368 (14) | 0.6637 (2) | 0.35315 (10) | 0.0395 (5) | |
| C8 | 0.22316 (13) | 0.5202 (2) | 0.35827 (9) | 0.0364 (5) | |
| C9 | 0.17343 (13) | 0.4459 (2) | 0.30380 (9) | 0.0359 (5) | |
| C10 | 0.01805 (19) | 0.4821 (3) | 0.12713 (12) | 0.0522 (6) | |
| H10A | −0.0231 (17) | 0.414 (3) | 0.0985 (12) | 0.074 (8)* | |
| H10B | −0.0219 (17) | 0.555 (3) | 0.1356 (12) | 0.071 (8)* | |
| H10C | 0.0575 (16) | 0.525 (3) | 0.1039 (12) | 0.064 (8)* | |
| C11 | 0.27364 (14) | 0.4473 (2) | 0.42133 (9) | 0.0390 (5) | |
| C12 | 0.37057 (13) | 0.4036 (2) | 0.42734 (9) | 0.0360 (5) | |
| H13 | 0.3868 (14) | 0.308 (2) | 0.5173 (11) | 0.056 (7)* | |
| C13 | 0.41872 (16) | 0.3316 (2) | 0.48382 (11) | 0.0484 (6) | |
| C14 | 0.51066 (17) | 0.2977 (3) | 0.49076 (13) | 0.0568 (7) | |
| H14 | 0.5453 (14) | 0.250 (2) | 0.5300 (11) | 0.057 (6)* | |
| C15 | 0.55516 (17) | 0.3334 (3) | 0.44212 (12) | 0.0552 (6) | |
| H15 | 0.6208 (17) | 0.309 (2) | 0.4484 (11) | 0.063 (7)* | |
| C16 | 0.50801 (16) | 0.4022 (3) | 0.38535 (12) | 0.0523 (6) | |
| H16 | 0.5390 (16) | 0.430 (2) | 0.3503 (12) | 0.070 (7)* | |
| C17 | 0.41556 (15) | 0.4371 (2) | 0.37787 (10) | 0.0417 (5) | |
| H17 | 0.3830 (13) | 0.483 (2) | 0.3384 (10) | 0.046 (6)* | |
| O5 | 0.25946 (14) | 0.00677 (18) | 0.39756 (10) | 0.0631 (5) | |
| H5A | 0.220 (2) | 0.049 (4) | 0.3623 (17) | 0.125 (13)* | |
| H5B | 0.258 (2) | 0.045 (3) | 0.4355 (16) | 0.101 (11)* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0533 (9) | 0.0359 (9) | 0.0360 (8) | 0.0039 (7) | 0.0042 (6) | 0.0021 (6) |
| O2 | 0.0815 (12) | 0.0410 (10) | 0.0500 (9) | 0.0009 (9) | 0.0076 (8) | 0.0008 (8) |
| O3 | 0.0539 (10) | 0.0458 (11) | 0.0477 (9) | −0.0017 (8) | −0.0015 (7) | −0.0047 (8) |
| O4 | 0.0535 (10) | 0.0921 (13) | 0.0436 (9) | 0.0117 (9) | 0.0173 (8) | 0.0148 (8) |
| C1 | 0.0524 (14) | 0.0411 (14) | 0.0403 (12) | 0.0011 (11) | 0.0133 (10) | −0.0015 (10) |
| C2 | 0.0499 (14) | 0.0491 (15) | 0.0357 (12) | −0.0010 (11) | 0.0086 (10) | −0.0057 (10) |
| C3 | 0.0376 (12) | 0.0496 (14) | 0.0324 (10) | 0.0032 (10) | 0.0095 (9) | 0.0010 (10) |
| C4 | 0.0360 (11) | 0.0409 (13) | 0.0327 (10) | 0.0051 (9) | 0.0078 (9) | 0.0034 (9) |
| C5 | 0.0431 (13) | 0.0445 (14) | 0.0393 (12) | 0.0072 (11) | 0.0031 (10) | 0.0094 (11) |
| C6 | 0.0454 (13) | 0.0354 (13) | 0.0479 (13) | 0.0045 (10) | 0.0065 (10) | 0.0046 (10) |
| C7 | 0.0366 (12) | 0.0425 (13) | 0.0383 (11) | 0.0014 (10) | 0.0074 (9) | −0.0020 (10) |
| C8 | 0.0351 (11) | 0.0401 (13) | 0.0339 (10) | 0.0035 (9) | 0.0080 (9) | 0.0017 (9) |
| C9 | 0.0373 (11) | 0.0340 (12) | 0.0374 (11) | 0.0049 (9) | 0.0108 (9) | 0.0027 (9) |
| C10 | 0.0494 (15) | 0.0626 (18) | 0.0403 (13) | 0.0049 (14) | 0.0029 (12) | 0.0046 (12) |
| C11 | 0.0427 (12) | 0.0404 (12) | 0.0329 (11) | −0.0018 (10) | 0.0076 (9) | −0.0017 (9) |
| C12 | 0.0390 (11) | 0.0333 (12) | 0.0329 (10) | −0.0020 (9) | 0.0039 (9) | −0.0018 (9) |
| C13 | 0.0480 (14) | 0.0536 (15) | 0.0419 (12) | 0.0010 (11) | 0.0079 (11) | 0.0088 (11) |
| C14 | 0.0501 (15) | 0.0607 (17) | 0.0526 (15) | 0.0086 (12) | −0.0007 (12) | 0.0109 (12) |
| C15 | 0.0391 (14) | 0.0596 (16) | 0.0636 (16) | 0.0030 (12) | 0.0064 (12) | −0.0049 (13) |
| C16 | 0.0473 (14) | 0.0588 (16) | 0.0534 (14) | −0.0038 (12) | 0.0176 (12) | −0.0056 (12) |
| C17 | 0.0464 (13) | 0.0402 (13) | 0.0363 (11) | −0.0016 (10) | 0.0065 (10) | 0.0000 (10) |
| O5 | 0.0828 (13) | 0.0548 (12) | 0.0488 (11) | 0.0045 (9) | 0.0106 (10) | −0.0027 (9) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| O1—C1 | 1.374 (2) | C8—C11 | 1.509 (3) |
| O1—C9 | 1.379 (2) | C10—H10A | 0.99 (3) |
| O2—C1 | 1.218 (2) | C10—H10B | 0.96 (3) |
| O3—C7 | 1.352 (2) | C10—H10C | 0.94 (2) |
| O3—H3 | 0.93 (3) | C11—C12 | 1.479 (3) |
| O4—C11 | 1.223 (2) | C12—C17 | 1.391 (3) |
| C1—C2 | 1.438 (3) | C12—C13 | 1.395 (3) |
| C2—C3 | 1.348 (3) | C13—C14 | 1.381 (3) |
| C2—H2 | 0.97 (2) | C13—H13 | 0.96 (2) |
| C3—C4 | 1.446 (3) | C14—C15 | 1.376 (3) |
| C3—C10 | 1.501 (3) | C14—H14 | 0.96 (2) |
| C4—C5 | 1.398 (3) | C15—C16 | 1.380 (3) |
| C4—C9 | 1.400 (3) | C15—H15 | 0.98 (2) |
| C5—C6 | 1.370 (3) | C16—C17 | 1.389 (3) |
| C5—H5 | 0.96 (2) | C16—H16 | 0.99 (2) |
| C6—C7 | 1.404 (3) | C17—H17 | 0.95 (2) |
| C6—H6 | 0.97 (2) | O5—H5A | 0.91 (4) |
| C7—C8 | 1.393 (3) | O5—H5B | 0.87 (3) |
| C8—C9 | 1.385 (3) | ||
| C1—O1—C9 | 121.41 (15) | C3—C10—H10A | 112.3 (14) |
| C7—O3—H3 | 114.9 (17) | C3—C10—H10B | 111.4 (15) |
| O2—C1—O1 | 115.56 (19) | H10A—C10—H10B | 106 (2) |
| O2—C1—C2 | 126.8 (2) | C3—C10—H10C | 110.6 (14) |
| O1—C1—C2 | 117.6 (2) | H10A—C10—H10C | 111 (2) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 122.8 (2) | H10B—C10—H10C | 105 (2) |
| C3—C2—H2 | 121.6 (12) | O4—C11—C12 | 122.57 (18) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 115.7 (12) | O4—C11—C8 | 119.13 (18) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 118.45 (18) | C12—C11—C8 | 118.30 (16) |
| C2—C3—C10 | 121.6 (2) | C17—C12—C13 | 119.26 (19) |
| C4—C3—C10 | 119.9 (2) | C17—C12—C11 | 120.57 (18) |
| C5—C4—C9 | 116.35 (19) | C13—C12—C11 | 120.15 (17) |
| C5—C4—C3 | 124.92 (19) | C14—C13—C12 | 119.8 (2) |
| C9—C4—C3 | 118.73 (19) | C14—C13—H13 | 121.6 (13) |
| C6—C5—C4 | 122.0 (2) | C12—C13—H13 | 118.6 (13) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.5 (12) | C15—C14—C13 | 120.5 (2) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 118.5 (12) | C15—C14—H14 | 118.6 (12) |
| C5—C6—C7 | 120.0 (2) | C13—C14—H14 | 120.8 (12) |
| C5—C6—H6 | 118.9 (12) | C14—C15—C16 | 120.3 (2) |
| C7—C6—H6 | 121.1 (12) | C14—C15—H15 | 119.2 (13) |
| O3—C7—C8 | 116.86 (18) | C16—C15—H15 | 120.5 (13) |
| O3—C7—C6 | 123.0 (2) | C15—C16—C17 | 119.7 (2) |
| C8—C7—C6 | 120.16 (19) | C15—C16—H16 | 121.4 (14) |
| C9—C8—C7 | 117.90 (18) | C17—C16—H16 | 118.9 (14) |
| C9—C8—C11 | 120.69 (19) | C16—C17—C12 | 120.4 (2) |
| C7—C8—C11 | 121.40 (18) | C16—C17—H17 | 119.5 (12) |
| O1—C9—C8 | 115.39 (16) | C12—C17—H17 | 120.1 (12) |
| O1—C9—C4 | 121.00 (17) | H5A—O5—H5B | 112 (3) |
| C8—C9—C4 | 123.60 (19) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O3—H3···O5i | 0.93 (3) | 1.72 (3) | 2.650 (2) | 177 (3) |
| O5—H5A···O2 | 0.91 (4) | 2.00 (4) | 2.887 (3) | 166 (3) |
| O5—H5B···O4ii | 0.87 (3) | 2.03 (3) | 2.875 (2) | 162 (3) |
| C17—H17···O2iii | 0.95 (2) | 2.54 (2) | 3.422 (3) | 154.7 (16) |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, y+1, z; (ii) −x+1/2, −y+1/2, −z+1; (iii) −x+1/2, y+1/2, −z+1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: XU5087).
References
- Brühlmann, C., Ooms, F., Carrupt, P.-A., Testa, B., Catto, M., Leonetti, F., Altomare, C. & Carotti, A. (2001). J. Med. Chem.44, 3195–3198. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, P. F., Bhat, A. R. & Azam, A. (2009). Eur. J. Med. Chem.44, 2252–2259. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Rollinger, J. M., Hornick, A., Langer, T., Stuppner, H. & Prast, H. (2004). J. Med. Chem.47, 6248–6254. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S. D., Rajor, H. K., Chopra, S. & Sharma, R. K. (2005). Biometals, 18, 143–154. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (1996). SADABS University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, N., Arshad, M. F. & Khan, S. A. (2009). Acta Pol. Pharm. Drug Res.66, 161–167. [PubMed]
- Siemens (1996). SMART and SAINT Siemens Analytical X-ray Instruments Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Vyas, K. B., Nimavat, K. S., Jani, G. R. & Hathi, M. V. (2009). Orbital, 1, 183–192.
- Yang, S.-P., Han, L.-J., Wang, D.-Q. & Ding, T.-Z. (2006). Acta Cryst. E62, o5196–o5198.
- Yang, S.-P., Han, L.-J., Wang, D.-Q. & Xia, H.-T. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, o4785.
- Yang, S.-P., Wang, D.-Q., Han, L.-J. & Liu, Y.-F. (2008). Acta Cryst. E64, o2088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810046350/xu5087sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810046350/xu5087Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report