Abstract
In the title coordination polymer, [Pb(C7H5O2)(NO3)(C10H8N2)]n, the PbII ion is eight-coordinated by two N atoms from one 2,2′-bipyridine ligand, two O atoms from one benzoate anion and four O atoms from three nitrate groups (one chelating, two bridging) in a distorted dodecahedral geometry. Adjacent PbII ions are linked by bridging nitrate O atoms through the central Pb2O2 and Pb2O4N2 cores, resulting in an infinite chain structure along the b axis. The crystal structure is stabilized by π–π stacking interactions between 2,2′-bipyridine and benzoate ligands belonging to neighboring chains, with shortest centroid–centroid distances of 3.685 (8) and 3.564 (8) Å.
Related literature
For applications of complexes containing Pb(II), see: Fan & Zhu (2006 ▶); Hamilton et al. (2004 ▶); Alvarado et al. (2005 ▶). For the use of aromatic carboxylate and 2,2′-bipyridine-like ligands in the preparation of metal-organic complexes, see: Wang et al. (2006 ▶); Masaoka et al. (2001 ▶); Hagrman & Zubieta (2000 ▶); Li et al. (2002 ▶).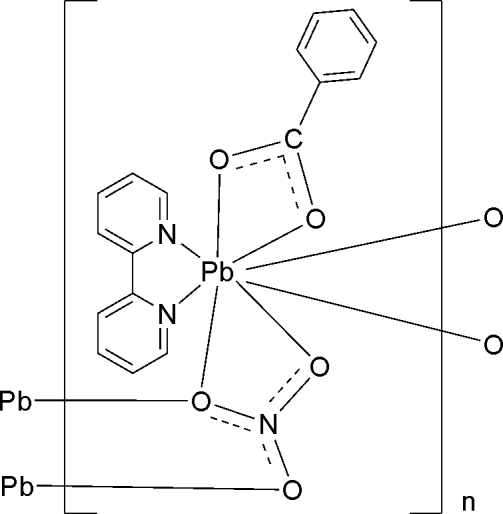
Experimental
Crystal data
[Pb(C7H5O2)(NO3)(C10H8N2)]
M r = 546.49
Triclinic,
a = 6.5389 (11) Å
b = 8.5052 (14) Å
c = 15.548 (3) Å
α = 84.566 (3)°
β = 86.593 (3)°
γ = 83.729 (2)°
V = 854.6 (3) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 9.91 mm−1
T = 296 K
0.23 × 0.21 × 0.15 mm
Data collection
Bruker APEXII CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2007 ▶) T min = 0.118, T max = 0.226
4385 measured reflections
2981 independent reflections
2769 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.030
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.037
wR(F 2) = 0.099
S = 1.02
2981 reflections
235 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 2.70 e Å−3
Δρmin = −2.79 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2007 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2007 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681004907X/gk2325sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681004907X/gk2325Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Selected bond lengths (Å).
| Pb1—O1 | 2.432 (5) |
| Pb1—N2 | 2.441 (6) |
| Pb1—N1 | 2.471 (5) |
| Pb1—O2 | 2.619 (6) |
| Pb1—O4 | 2.871 (6) |
| Pb1—O3 | 2.928 (6) |
| Pb1—O3i | 2.893 (6) |
| Pb1—O5ii | 2.887 (7) |
Symmetry codes: (i) 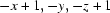 ; (ii)
; (ii) 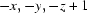 .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge financial support by the Doctoral Foundation of Henan Polytechnic University (B2008-58 648265).
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Complexes containing Pb(II) ion have recently attracted considerable interest not only because of the variety of their architectures, but also because of their potential applications, especially in environmental protection and in systems with different biological properties (Fan & Zhu, 2006; Hamilton et al., 2004; Alvarado et al., 2005). As an important family of multidentate O-donor ligands, aromatic carboxylate ligands have been extensively employed in the preparation of metal-organic complexes because of their potential properties and intriguing structural topologies (Wang et al., 2006; Masaoka et al., 2001). To our knowledge, carboxylate coordinates metal in various ways, for example, in the mode of monodentate, bidentate chelating, bidentate bridging or chelating-bridging. It is well known that the introduction of chelate ligands such as 2,2'-bipyridine are capable of passivating metal sites via the N donors of the organic groups and may induce new structural evolution (Hagrman et al., 2000; Li et al., 2002). Herein, we report the structure of the title polymer.
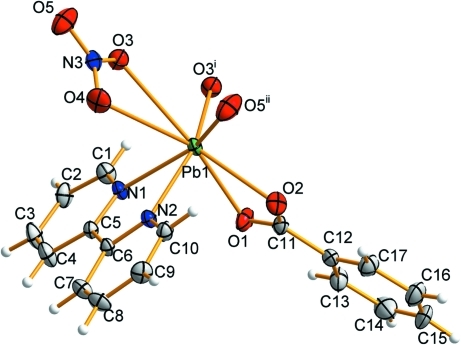
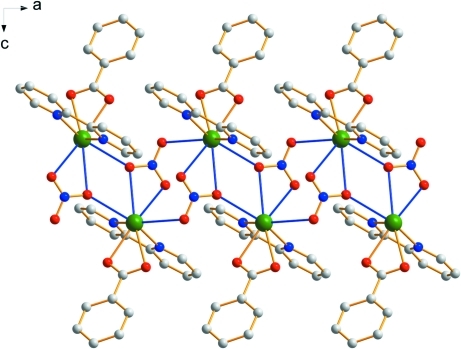
The asymmetric unit of the title compound, [Pb(C10H8N2)(C7H5O2)(NO3)], contains a PbII cation, one 2,2'-bipyridine ligand, one benzoate and one nitrate ligand, as illustrated in in Fig.1. The PbII atom is eight-coordinated by two N atoms from one 2,2'-bipyridine ligand, two O atoms from one benzoate anion and four O atoms from three chelating-bridging nitrate ligands in a distorted dodecahedron geometry. The O3 and O5 atoms of bridging nitrato ligands link the adjacent PbII ions through the central Pb2O2 and Pb2O4N2 cores, resulting in an infinite chain structure along the b axis (Fig.2). The excellent coordinating ability and large conjugated systems of 2,2'-bipyridine and benzoato ligands allow to form π..π interactions. The chains are extended into the framework through π..π stacking interactions between the ligands belonging to the neighboring chains, with the shortest centroid-centroid distance of 3.685 (8) and 3.564 (8)Å.
Experimental
A mixture of Pb(NO3)2 (0.09 g, 0.27 mmol), benzoic acid (0.102 g, 0.84 mmol), 2,2'-bipyridine (0.065 g, 0.41 mmol) and distilled water (10 ml) was sealed in a 25 ml Teflon-lined stainless autoclave. The mixture was heated at 403 K for 6 days to give the colorless crystals suitable for X-ray diffraction analysis.
Refinement
All H atoms bounded to C atoms were placed in calculated positions and treated in a riding-model approximation, with C—H = 0.93 Å and Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The coordination environment around PbII in the title compound with the atom-labeling scheme. Displacement ellipsoids for non-hydrogen atoms are drawn at the 30% probability level. Symmetry codes: (i) 1-x, -y, 1-z; (ii) -x, -y, 1-z.
Fig. 2.
The chain of the title polymer viewed down the b axis.; H atoms are omitted for clarity.
Crystal data
| [Pb(C7H5O2)(NO3)(C10H8N2)] | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 546.49 | F(000) = 516 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 2.124 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 6.5389 (11) Å | Cell parameters from 3772 reflections |
| b = 8.5052 (14) Å | θ = 2.6–28.2° |
| c = 15.548 (3) Å | µ = 9.90 mm−1 |
| α = 84.566 (3)° | T = 296 K |
| β = 86.593 (3)° | Column, colorless |
| γ = 83.729 (2)° | 0.23 × 0.21 × 0.15 mm |
| V = 854.6 (3) Å3 |
Data collection
| Bruker APEXII CCD area-detector diffractometer | 2981 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2769 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.030 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 25.0°, θmin = 2.7° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2007) | h = −7→7 |
| Tmin = 0.118, Tmax = 0.226 | k = −9→10 |
| 4385 measured reflections | l = −18→15 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.037 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.099 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.02 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0675P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2981 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 235 parameters | Δρmax = 2.70 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −2.79 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Experimental. Refinement Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2sigma(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. Geometry All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Pb1 | 0.31380 (3) | 0.02444 (2) | 0.362929 (15) | 0.02612 (13) | |
| O3 | 0.3180 (9) | 0.0845 (7) | 0.5451 (4) | 0.0433 (14) | |
| O2 | 0.2641 (8) | −0.0974 (7) | 0.2180 (4) | 0.0409 (13) | |
| O4 | 0.0370 (9) | 0.1789 (8) | 0.4866 (4) | 0.0546 (16) | |
| O1 | 0.5402 (9) | 0.0249 (7) | 0.2331 (4) | 0.0443 (14) | |
| O5 | 0.0478 (10) | 0.1446 (10) | 0.6257 (5) | 0.064 (2) | |
| N3 | 0.1340 (9) | 0.1372 (8) | 0.5520 (5) | 0.0339 (15) | |
| N1 | 0.4378 (8) | 0.2885 (6) | 0.3637 (4) | 0.0278 (13) | |
| N2 | 0.1021 (8) | 0.2377 (6) | 0.2836 (4) | 0.0282 (12) | |
| C1 | 0.6040 (10) | 0.3077 (9) | 0.4070 (5) | 0.0351 (17) | |
| H1 | 0.6739 | 0.2188 | 0.4357 | 0.042* | |
| C16 | 0.5298 (18) | −0.2934 (13) | −0.0021 (7) | 0.064 (3) | |
| H16 | 0.4584 | −0.3589 | −0.0314 | 0.076* | |
| C11 | 0.4407 (11) | −0.0630 (9) | 0.1930 (5) | 0.0328 (17) | |
| C14 | 0.8340 (17) | −0.1765 (12) | 0.0162 (8) | 0.067 (3) | |
| H14 | 0.9697 | −0.1615 | −0.0009 | 0.081* | |
| C10 | −0.0635 (12) | 0.2054 (10) | 0.2451 (5) | 0.0349 (18) | |
| H10 | −0.0986 | 0.1017 | 0.2507 | 0.042* | |
| C8 | −0.1339 (12) | 0.4738 (10) | 0.1900 (6) | 0.045 (2) | |
| H8 | −0.2144 | 0.5531 | 0.1583 | 0.054* | |
| C9 | −0.1831 (11) | 0.3195 (10) | 0.1977 (6) | 0.0412 (18) | |
| H9 | −0.2966 | 0.2933 | 0.1709 | 0.049* | |
| C12 | 0.5419 (13) | −0.1335 (9) | 0.1145 (5) | 0.0360 (18) | |
| C15 | 0.7274 (19) | −0.2662 (12) | −0.0304 (7) | 0.067 (3) | |
| H15 | 0.7873 | −0.3080 | −0.0802 | 0.080* | |
| C3 | 0.5708 (13) | 0.5819 (10) | 0.3691 (7) | 0.050 (2) | |
| H3 | 0.6165 | 0.6812 | 0.3708 | 0.060* | |
| C2 | 0.6744 (12) | 0.4517 (10) | 0.4106 (6) | 0.0420 (19) | |
| H2 | 0.7907 | 0.4609 | 0.4406 | 0.050* | |
| C13 | 0.7444 (14) | −0.1082 (10) | 0.0878 (6) | 0.049 (2) | |
| H13 | 0.8178 | −0.0458 | 0.1181 | 0.058* | |
| C17 | 0.4357 (15) | −0.2243 (11) | 0.0694 (6) | 0.049 (2) | |
| H17 | 0.3002 | −0.2400 | 0.0864 | 0.058* | |
| C6 | 0.1514 (10) | 0.3891 (7) | 0.2771 (5) | 0.0268 (14) | |
| C7 | 0.0347 (11) | 0.5089 (9) | 0.2296 (5) | 0.0395 (18) | |
| H7 | 0.0708 | 0.6123 | 0.2246 | 0.047* | |
| C5 | 0.3344 (10) | 0.4157 (7) | 0.3236 (5) | 0.0275 (14) | |
| C4 | 0.3976 (13) | 0.5674 (9) | 0.3244 (7) | 0.047 (2) | |
| H4 | 0.3258 | 0.6557 | 0.2959 | 0.057* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Pb1 | 0.02844 (18) | 0.01828 (18) | 0.0322 (2) | −0.00253 (11) | −0.00343 (11) | −0.00370 (12) |
| O3 | 0.039 (3) | 0.049 (4) | 0.041 (3) | 0.004 (3) | −0.007 (2) | −0.008 (3) |
| O2 | 0.030 (3) | 0.042 (3) | 0.053 (4) | −0.014 (2) | 0.003 (2) | −0.010 (3) |
| O4 | 0.041 (3) | 0.060 (4) | 0.060 (4) | 0.015 (3) | −0.022 (3) | −0.004 (3) |
| O1 | 0.048 (3) | 0.047 (3) | 0.043 (3) | −0.023 (3) | 0.007 (3) | −0.019 (3) |
| O5 | 0.050 (4) | 0.093 (6) | 0.056 (4) | −0.025 (4) | 0.012 (3) | −0.025 (4) |
| N3 | 0.031 (3) | 0.029 (3) | 0.043 (4) | −0.006 (3) | −0.002 (3) | −0.007 (3) |
| N1 | 0.028 (3) | 0.020 (3) | 0.036 (3) | −0.003 (2) | −0.005 (2) | −0.004 (3) |
| N2 | 0.029 (3) | 0.024 (3) | 0.032 (3) | −0.004 (2) | −0.003 (2) | −0.004 (3) |
| C1 | 0.027 (3) | 0.033 (4) | 0.046 (5) | −0.005 (3) | −0.010 (3) | −0.004 (4) |
| C16 | 0.089 (8) | 0.062 (7) | 0.043 (6) | 0.003 (6) | −0.014 (5) | −0.023 (5) |
| C11 | 0.034 (4) | 0.032 (4) | 0.031 (4) | 0.006 (3) | 0.002 (3) | −0.006 (3) |
| C14 | 0.067 (6) | 0.055 (6) | 0.073 (8) | 0.000 (5) | 0.030 (6) | 0.001 (6) |
| C10 | 0.039 (4) | 0.032 (4) | 0.035 (4) | −0.002 (3) | −0.007 (3) | −0.010 (3) |
| C8 | 0.040 (4) | 0.040 (5) | 0.051 (5) | 0.005 (3) | −0.011 (4) | 0.008 (4) |
| C9 | 0.033 (4) | 0.048 (5) | 0.044 (5) | −0.005 (3) | −0.011 (3) | −0.006 (4) |
| C12 | 0.050 (5) | 0.026 (4) | 0.031 (4) | 0.004 (3) | −0.002 (3) | −0.002 (3) |
| C15 | 0.102 (8) | 0.057 (6) | 0.038 (6) | 0.012 (6) | 0.012 (5) | −0.022 (5) |
| C3 | 0.050 (5) | 0.028 (4) | 0.076 (7) | −0.010 (4) | −0.017 (4) | −0.013 (4) |
| C2 | 0.040 (4) | 0.041 (5) | 0.051 (5) | −0.012 (4) | −0.008 (4) | −0.019 (4) |
| C13 | 0.051 (5) | 0.040 (5) | 0.056 (6) | −0.008 (4) | 0.009 (4) | −0.018 (4) |
| C17 | 0.056 (5) | 0.050 (5) | 0.042 (5) | −0.004 (4) | −0.009 (4) | −0.012 (4) |
| C6 | 0.027 (3) | 0.021 (3) | 0.032 (4) | 0.003 (3) | −0.003 (3) | −0.003 (3) |
| C7 | 0.042 (4) | 0.027 (4) | 0.048 (5) | 0.000 (3) | −0.004 (4) | 0.004 (4) |
| C5 | 0.031 (3) | 0.022 (3) | 0.029 (4) | −0.003 (3) | −0.001 (3) | −0.006 (3) |
| C4 | 0.050 (5) | 0.023 (4) | 0.070 (6) | −0.002 (3) | −0.013 (4) | −0.007 (4) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Pb1—O1 | 2.432 (5) | C16—C17 | 1.387 (13) |
| Pb1—N2 | 2.441 (6) | C11—C12 | 1.498 (11) |
| Pb1—N1 | 2.471 (5) | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| Pb1—O2 | 2.619 (6) | C14—H14 | 0.9300 |
| Pb1—C11 | 2.863 (7) | C14—C13 | 1.375 (13) |
| Pb1—O4 | 2.871 (6) | C14—C15 | 1.368 (16) |
| Pb1—O3 | 2.928 (6) | C10—C9 | 1.365 (12) |
| Pb1—O3i | 2.893 (6) | C8—H8 | 0.9300 |
| Pb1—O5ii | 2.887 (7) | C9—H9 | 0.9300 |
| O3—N3 | 1.239 (9) | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| O2—C11 | 1.252 (9) | C8—C7 | 1.368 (12) |
| O4—N3 | 1.234 (9) | C8—C9 | 1.378 (11) |
| O1—C11 | 1.270 (10) | C12—C17 | 1.359 (12) |
| O5—N3 | 1.251 (9) | C17—H17 | 0.9300 |
| N1—C5 | 1.333 (9) | C12—C13 | 1.397 (12) |
| N1—C1 | 1.344 (9) | C3—C4 | 1.386 (12) |
| N2—C10 | 1.334 (10) | C3—C2 | 1.361 (12) |
| N2—C6 | 1.355 (8) | C6—C7 | 1.386 (10) |
| C1—C2 | 1.362 (10) | C7—H7 | 0.9300 |
| C1—H1 | 0.9300 | C6—C5 | 1.483 (9) |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C5—C4 | 1.399 (10) |
| C16—C15 | 1.376 (16) | C3—H3 | 0.9300 |
| C16—H16 | 0.9300 | C4—H4 | 0.9300 |
| C15—H15 | 0.9300 | ||
| O1—Pb1—N2 | 85.6 (2) | O2—C11—C12 | 118.6 (7) |
| O1—Pb1—N1 | 80.21 (18) | O1—C11—C12 | 118.6 (7) |
| N2—Pb1—N1 | 66.18 (18) | O2—C11—Pb1 | 66.1 (4) |
| O1—Pb1—O2 | 51.83 (16) | O1—C11—Pb1 | 57.6 (4) |
| N2—Pb1—O2 | 77.48 (18) | C12—C11—Pb1 | 167.3 (6) |
| N1—Pb1—O2 | 121.47 (18) | C15—C14—C13 | 121.3 (10) |
| O1—Pb1—C11 | 26.2 (2) | N2—C10—C9 | 122.2 (7) |
| N2—Pb1—C11 | 83.2 (2) | C7—C8—C9 | 119.2 (8) |
| N1—Pb1—C11 | 102.9 (2) | C10—C9—C8 | 119.3 (7) |
| O2—Pb1—C11 | 25.91 (19) | C17—C12—C13 | 119.8 (8) |
| O1—Pb1—O4 | 152.8 (2) | C17—C12—C11 | 119.5 (8) |
| N2—Pb1—O4 | 72.48 (18) | C13—C12—C11 | 120.7 (8) |
| N1—Pb1—O4 | 76.30 (19) | C14—C15—C16 | 118.7 (9) |
| O2—Pb1—O4 | 133.87 (16) | C2—C3—C4 | 120.5 (7) |
| C11—Pb1—O4 | 153.8 (2) | C3—C2—C1 | 118.5 (7) |
| O1—Pb1—O3 | 139.88 (17) | C14—C13—C12 | 119.3 (9) |
| N2—Pb1—O3 | 110.35 (18) | C12—C17—C16 | 119.9 (9) |
| N1—Pb1—O3 | 73.97 (19) | N2—C6—C7 | 120.8 (6) |
| O2—Pb1—O3 | 164.48 (18) | N2—C6—C5 | 115.7 (6) |
| C11—Pb1—O3 | 162.4 (2) | C7—C6—C5 | 123.5 (6) |
| O4—Pb1—O3 | 43.33 (16) | C8—C7—C6 | 119.4 (7) |
| O1—Pb1—O5ii | 120.12 (20) | N1—C5—C4 | 121.4 (7) |
| N2—Pb1—O5ii | 85.50 (19) | N1—C5—C6 | 117.2 (5) |
| N1—Pb1—O5ii | 144.52 (19) | C4—C5—C6 | 121.4 (7) |
| O2—Pb1—O5ii | 68.42 (19) | C3—C4—C5 | 117.8 (8) |
| C11—Pb1—O5ii | 93.96 (21) | N1—C1—H1 | 118.6 |
| O4—Pb1—O5ii | 74.99 (19) | C2—C1—H1 | 118.6 |
| O3—Pb1—O5ii | 98.23 (19) | C1—C2—H2 | 120.8 |
| O1—Pb1—O3i | 85.60 (19) | C3—C2—H2 | 120.7 |
| N2—Pb1—O3i | 149.75 (17) | C2—C3—H3 | 120.0 |
| N1—Pb1—O3i | 83.81 (17) | C4—C3—H3 | 120.0 |
| O2—Pb1—O3i | 118.16 (17) | H4—C4—C3 | 121.1 |
| C11—Pb1—O3i | 100.76 (19) | H4—C4—C5 | 121.1 |
| O4—Pb1—O3i | 105.12 (17) | C6—C7—H7 | 120.3 |
| O3—Pb1—O3i | 61.80 (17) | H7—C7—C8 | 120.3 |
| O5ii—Pb1—O3i | 123.69 (18) | H8—C8—C7 | 120.4 |
| N3—O3—Pb1 | 95.6 (5) | H8—C8—C9 | 120.4 |
| C11—O2—Pb1 | 88.0 (5) | C8—C9—H9 | 120.4 |
| N3—O4—Pb1 | 98.6 (4) | H9—C9—C10 | 120.3 |
| C11—O1—Pb1 | 96.2 (4) | C9—C10—H10 | 118.9 |
| O4—N3—O3 | 120.0 (7) | H10—C10—N2 | 118.9 |
| O4—N3—O5 | 120.7 (7) | C12—C13—H13 | 120.4 |
| O3—N3—O5 | 119.3 (7) | H13—C13—C14 | 120.3 |
| C5—N1—C1 | 119.0 (6) | H14—C14—C13 | 119.4 |
| C5—N1—Pb1 | 119.9 (4) | H14—C14—C15 | 119.3 |
| C1—N1—Pb1 | 121.0 (5) | H15—C15—C14 | 120.7 |
| C10—N2—C6 | 119.1 (6) | H15—C15—C16 | 120.6 |
| C10—N2—Pb1 | 119.9 (5) | C15—C16—H16 | 119.5 |
| C6—N2—Pb1 | 121.0 (4) | C17—C16—H16 | 119.6 |
| N1—C1—C2 | 122.8 (7) | H17—C17—C12 | 120.1 |
| C15—C16—C17 | 120.9 (10) | H17—C17—C16 | 120.0 |
| O2—C11—O1 | 122.8 (7) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y, −z+1; (ii) −x, −y, −z+1.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: GK2325).
References
- Alvarado, R. J., Rosenberg, J. M., Andreu, A., Bryan, J. C., Chen, W.-Z., Ren, T. & Kavallieratos, K. (2005). Inorg. Chem.44, 7951–7959. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Bruker (2007). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Fan, S. R. & Zhu, L. G. (2006). Inorg. Chem.45, 7935–7942. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Hagrman, P. J. & Zubieta, J. (2000). Inorg. Chem.39, 3252–3260. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, B. H., Kelley, K. A., Wagler, T. A., Espe, M. P. & Ziegler, C. J. (2004). Inorg. Chem.43, 50–56. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Li, Y. G., Wang, E. B., Zhang, H., Luan, G. L. & Hu, C. W. (2002). J. Solid State Chem.163, 10–16.
- Masaoka, S., Furukawa, S., Chang, H. C., Mizutani, T. & Kitagawa, S. (2001). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.40, 3817–3819. [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Wang, X. L., Qin, C. & Wang, E. B. (2006). Cryst. Growth Des.6, 439–443.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681004907X/gk2325sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681004907X/gk2325Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report