Abstract
The crystal structure of N-(3,9-dimethyl-4-phenyl-2,5-dioxo-3,4-dihydro-2H,5H-pyrano[3,2-c]chromen-3-yl)-N-methylbenzamide methanol monosolvate, C28H23NO5·CH3OH, has been determined at room temperature by X-ray diffraction. Structural parameters are discussed with reference to ab initio calculations.
Related literature
For structures containing enol lactone fragments, see: Murray et al. (1982 ▶); Harborne & Baxter (1999 ▶); Qabaja et al. (2000 ▶). For related structures containing a coumarin fragment, see: Yu et al. (2003 ▶). For a phenylfuro[3,2-c]chromen-4-one structure, see: Bruno et al. (2001 ▶). For related furan-5-one structures, see: Grassi et al. (2002 ▶). For the Cambridge Structural Database, see: Allen (2002 ▶). For the GAUSSIAN98 software used for the ab initio calculations, see: Frisch et al. (1998 ▶). For the synthetic process used, see: Grassi et al. (2003 ▶). For background to O—C—O bond-angle asymmetry, see: Kokila et al. (1996 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C28H23NO5·CH4O
M r = 485.52
Monoclinic,
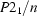
a = 10.7435 (14) Å
b = 9.9056 (17) Å
c = 23.298 (3) Å
β = 94.817 (7)°
V = 2470.7 (6) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.09 mm−1
T = 298 K
0.58 × 0.38 × 0.36 mm
Data collection
Siemens P4 diffractometer
Absorption correction: ψ scan (Kopfmann & Huber, 1968 ▶) T min = 0.870, T max = 0.968
9535 measured reflections
4347 independent reflections
2843 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.036
3 standard reflections every 197 reflections intensity decay: none
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.049
wR(F 2) = 0.132
S = 1.01
4347 reflections
331 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.18 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.31 e Å−3
Data collection: XSCANS (Bruker, 1999 ▶); cell refinement: XSCANS; data reduction: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to solve structure: SIR97 (Altomare et al., 1999 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: XPW (Siemens, 1996 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: PARST97 (Nardelli, 1995 ▶) and SHELXL97.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810043709/jh2217sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810043709/jh2217Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O35—H35⋯O27 | 0.82 | 1.99 | 2.784 (3) | 163 |
| C9—H9⋯O35i | 0.93 | 2.46 | 3.320 (4) | 153 |
| C19—H19⋯O11ii | 0.93 | 2.60 | 3.403 (3) | 144 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 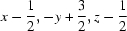 ; (ii)
; (ii) 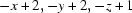 .
.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Highly functionalized enol lactones constitute an attractive class of compounds not only because of their molecular architecture but also because of the interesting biopharmacological activity often shown by compounds possessing this subunit in their molecular skeleton (Murray et al., 1982; Harborne & Baxter, 1999; Qabaja et al., 2000).
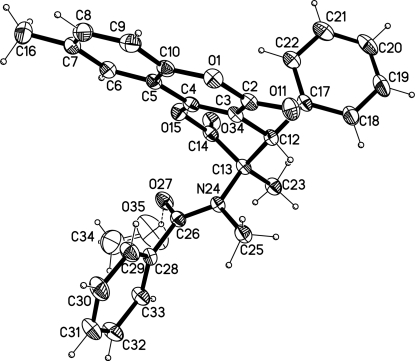
The molecule 3 is mainly constituted by a cumarine system which is further [3,2-c]-fused with a 3,4-dihydro-pyran-2-one ring carrying at posistion 3 a methyl and a methyllbenzamide group while a phenyl moiety is placed at 4. Then these C atoms at 3 and 4 are chiral centers showing the same configuration. Due to the P21/n centric space group, both the S,R and R,S diastereomers are present in the solid state and the crystals represent a perfect racemic mixture. The methyl cumarin fragment is planar within experimental error; bonds distances and angles of this moiety are in good agreement with the corresponding values reported for such fragments (Yu et al., 2003). The methylbenzamide fragment is not planar and shows the usual bond geometry values: the phenyl ring is rotated by 60.9 (3)° with respect to the amide moiety. The three carbonyl groups have very different C═O bond distances and their O atoms are involved in several intra- and intermolecular hydrogen interactions. The significant elongation of C(26)—O(27) bond might be related to the strongest hydrogen interaction of its O atom with the co-crystallized methanol molecule: O(27)···H(35) and O(27)···O(35) are 1.99 and 2.784 (3) Å, respectively, while O(35)—H(35)···O(27) is 163°. The sum of the valence angles around N(24) is 357.7 (2)° and evidences the not significant pyramidalization of the nitrogen. Therefore the nitrogen geometry appears planar and might be related to its sp2 hybridization caused by the delocalization of its lone-pair over the carbonyl fragments as also suggested by the length of the bonds involving the N(24) atom. Phenyl group bonded to C(26) is rotated with respect to this system (the N(24)—C(26)—C(28)—C(29) torsion angle is 60.5 (3)°) and does not participate to the possible π-electronic delocalization as evidenced by the C(28)—C(26) single-bond length value [1.491 (3) Å]. In the crystal lattice, each pair of molecules related by an inversion centre shows a π-interaction of 3.4 (1) Å between their planar furo[3,2-c]coumarin fragments. The substituent phenyl rings, despite their out-of-plane rotation, are directed far from the flat central molecular bulk and do not obstacle the strong π-stacking in the formation of the centrosymmetric couple, remaing at its surface as the co-crystallized methanol. Therefore crystal packing is constituted by dimeric units interconnected by several weak hydrogen bonds involving the O atoms.
Here, as well as already found in the phenyl-furo[3,2-c]chromen-4-one (Bruno et al., 2001) and in other related coumarin compounds reported in the October 2004 (Version 5.27) release of CSD (Allen, 2002), an important asymmetry in the O—C—O bond angles has been detected [β = O(1)—C(2)—O(11), 117.4 (2)° and α = C(3)—C(2)—O(11), 125.1 (2)°] Δ(α-β) = 7.7 (2)°. Even more similar significant differences have been observed in other molecules containing the furan-5-one fragment, as we have already reported (Grassi et al., 2002).
Ab initio and DFT calculations on some models have been performed in order to clarify the relevant observed asymmetry in the O—C—O bond angles of the cumarinic fragment. From these results we can conclude that the observed and calculated carbonyl distortion arises exclusively from electronic rather than steric factors. However further statistical and theoretical study are necessary to better clarify the real nature of this asymmetry.
Experimental
Fig. 2.
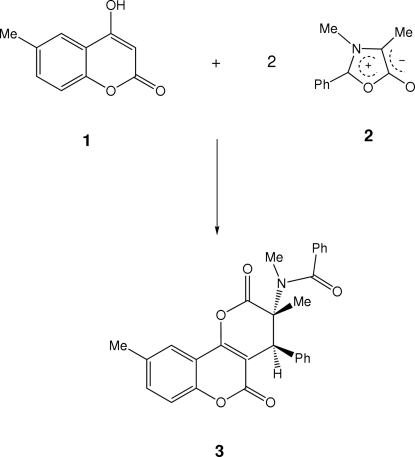
We recently described a novel kind of cyclo-condensation process that converts two equivalents of a münchnone and a 1,3-dicarbonyl compound into a functionalized enol lactone containing a protected α-amino acid (Grassi et al., 2003). Here we report structural characterization of the enol lactone 3 synthesized by 4,5-dimethyl-2-phenyl-1,3-oxazolium-5-late (DMPO) 2 and 4-hydroxy-6-methylcoumarin 1 (an unsymmetrical enolisable dicarbonyl substrate). Single crystals of 3 suitable for X-ray analysis were obtained by slow evaporation from a methanole solution.
In trying to get some insight regarding this important asymmetry in the O—C—O bond angle of the cumarinic fragment an ab initio and DFT calculations on some model compounds, such as the bicyclic 3,4-dyhidro-pyrano[4,3-b]pyran-2,5-dione, a series of 3-substituted pyran-2-one, the cumarine and 3-methyl-cumarine, were performed by using the basis set 6-31+G(d,p) in GAUSSIAN98 (Frisch et al., 1998). At all level of calculations this controversial asymmetry (Kokila et al., 1996) around carbonilic C atom is consistent with the X-ray structural observations.
Refinement
A suitable colourless single-crystal was mounted on a capillary glass fiber. The intensity data were collected at room temperature up to 2θ = 50° by using the ω-2θ scan technique with variable scan speed on a Siemens P4 4-cirlce diffractometer with graphite monochromated Mo Kα radiation. Lattice parameters were obtained from least-squares refinement of the setting angles of 59 reflections with 14 < 2θ < 35°. Intensities were corrected for Lonrentz polarization and then for absorption effetcts. No crystal deterioration was revealed during irradiation. The structure, solved by standard Direct Methods, was completed and refined by a combination of least squares technique and Fourier Syntheses. Whereas several H atoms were located on final ΔF map, the H atoms were included in the refinement among the "riding model" method with the X—H bond geometry and the H isotropic displacement parameter depending on the parent atom X. The refinement, with all non H atoms anisotropic and carried out by the full matrix least-square technique, has included a parameter for extinction correction. The last difference Fourier map showed no significant density residuals. One terminal methyl (C16) appeared to be affected by a significant rotational disorder and its H's group has to be split over two symmetric positions with equal occupancy 0.5; the disorder of the methanol molecule causes its large thermal ellipsoids.
Figures
Fig. 1.
Perspective view of the asymmetric unit with numbering scheme of compound 3. Dashed line represents H-bond with the co-crystallized methanol hydrogen. Ellipsoids are drawn at 20% of probability level while hydrogen size is arbitrary.
Fig. 2.
Reaction scheme.
Crystal data
| C28H23NO5·CH4O | F(000) = 1024 |
| Mr = 485.52 | Dx = 1.305 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2yn | Cell parameters from 59 reflections |
| a = 10.7435 (14) Å | θ = 7.7–17.5° |
| b = 9.9056 (17) Å | µ = 0.09 mm−1 |
| c = 23.298 (3) Å | T = 298 K |
| β = 94.817 (7)° | Irregular, colourless |
| V = 2470.7 (6) Å3 | 0.58 × 0.38 × 0.36 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Siemens P4 diffractometer | 2843 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Radiation source: sealed tube | Rint = 0.036 |
| graphite | θmax = 25.0°, θmin = 2.0° |
| ω scans | h = −12→12 |
| Absorption correction: ψ scan (Kopfmann & Huber, 1968) | k = −1→11 |
| Tmin = 0.870, Tmax = 0.968 | l = −27→27 |
| 9535 measured reflections | 3 standard reflections every 197 reflections |
| 4347 independent reflections | intensity decay: none |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.049 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.132 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0533P)2 + 0.7913P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.01 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 4347 reflections | Δρmax = 0.18 e Å−3 |
| 331 parameters | Δρmin = −0.31 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Extinction correction: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction coefficient: 0.0036 (8) |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R-factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | Occ. (<1) | |
| O1 | 0.50718 (15) | 0.77955 (19) | 0.49310 (6) | 0.0560 (5) | |
| C2 | 0.6021 (2) | 0.8610 (3) | 0.51636 (10) | 0.0490 (6) | |
| C3 | 0.64762 (19) | 0.8378 (2) | 0.57594 (9) | 0.0440 (6) | |
| C4 | 0.5962 (2) | 0.7392 (2) | 0.60580 (9) | 0.0456 (6) | |
| C5 | 0.4958 (2) | 0.6556 (3) | 0.58143 (10) | 0.0483 (6) | |
| C6 | 0.4409 (2) | 0.5503 (3) | 0.61028 (12) | 0.0588 (7) | |
| H6 | 0.4684 | 0.5327 | 0.6485 | 0.071* | |
| C7 | 0.3471 (2) | 0.4720 (3) | 0.58354 (14) | 0.0675 (8) | |
| C8 | 0.3087 (2) | 0.5014 (3) | 0.52619 (15) | 0.0735 (9) | |
| H8 | 0.2451 | 0.4500 | 0.5075 | 0.088* | |
| C9 | 0.3612 (2) | 0.6034 (3) | 0.49630 (12) | 0.0655 (8) | |
| H9 | 0.3340 | 0.6203 | 0.4580 | 0.079* | |
| C10 | 0.4550 (2) | 0.6802 (3) | 0.52418 (10) | 0.0512 (6) | |
| O11 | 0.64195 (16) | 0.9454 (2) | 0.48534 (7) | 0.0649 (5) | |
| C12 | 0.75139 (19) | 0.9241 (3) | 0.60261 (9) | 0.0442 (6) | |
| H12 | 0.7380 | 1.0154 | 0.5872 | 0.053* | |
| C13 | 0.7374 (2) | 0.9318 (3) | 0.66888 (9) | 0.0447 (6) | |
| C14 | 0.7351 (2) | 0.7859 (3) | 0.68848 (9) | 0.0491 (6) | |
| O15 | 0.64021 (15) | 0.70590 (17) | 0.66098 (6) | 0.0538 (4) | |
| C16 | 0.2891 (3) | 0.3579 (3) | 0.61477 (16) | 0.0964 (11) | |
| H16A | 0.2461 | 0.2984 | 0.5873 | 0.145* | 0.50 |
| H16B | 0.2310 | 0.3938 | 0.6399 | 0.145* | 0.50 |
| H16C | 0.3533 | 0.3087 | 0.6370 | 0.145* | 0.50 |
| H16D | 0.3075 | 0.3689 | 0.6555 | 0.145* | 0.50 |
| H16E | 0.3226 | 0.2735 | 0.6029 | 0.145* | 0.50 |
| H16F | 0.2003 | 0.3585 | 0.6058 | 0.145* | 0.50 |
| C17 | 0.8802 (2) | 0.8790 (3) | 0.58752 (9) | 0.0493 (6) | |
| C18 | 0.9676 (2) | 0.9762 (3) | 0.57662 (11) | 0.0684 (8) | |
| H18 | 0.9468 | 1.0670 | 0.5789 | 0.082* | |
| C19 | 1.0865 (3) | 0.9398 (4) | 0.56224 (12) | 0.0835 (10) | |
| H19 | 1.1443 | 1.0064 | 0.5552 | 0.100* | |
| C20 | 1.1177 (3) | 0.8095 (5) | 0.55848 (13) | 0.0848 (11) | |
| H20 | 1.1971 | 0.7857 | 0.5490 | 0.102* | |
| C21 | 1.0328 (3) | 0.7111 (4) | 0.56862 (13) | 0.0832 (10) | |
| H21 | 1.0546 | 0.6207 | 0.5658 | 0.100* | |
| C22 | 0.9136 (2) | 0.7461 (3) | 0.58313 (11) | 0.0633 (7) | |
| H22 | 0.8563 | 0.6787 | 0.5899 | 0.076* | |
| C23 | 0.8437 (2) | 1.0061 (3) | 0.70278 (10) | 0.0583 (7) | |
| H23A | 0.8475 | 1.0973 | 0.6891 | 0.087* | |
| H23B | 0.9212 | 0.9613 | 0.6977 | 0.087* | |
| H23C | 0.8294 | 1.0067 | 0.7429 | 0.087* | |
| N24 | 0.61573 (15) | 0.9977 (2) | 0.67699 (7) | 0.0444 (5) | |
| C25 | 0.5853 (2) | 1.1225 (3) | 0.64515 (11) | 0.0613 (7) | |
| H25A | 0.6605 | 1.1728 | 0.6412 | 0.092* | |
| H25B | 0.5290 | 1.1756 | 0.6657 | 0.092* | |
| H25C | 0.5467 | 1.1007 | 0.6076 | 0.092* | |
| C26 | 0.5548 (2) | 0.9634 (3) | 0.72315 (10) | 0.0490 (6) | |
| O27 | 0.59794 (16) | 0.8770 (2) | 0.75754 (7) | 0.0659 (5) | |
| C28 | 0.4305 (2) | 1.0259 (3) | 0.73030 (10) | 0.0502 (6) | |
| C29 | 0.3308 (2) | 1.0086 (3) | 0.68954 (12) | 0.0716 (8) | |
| H29 | 0.3414 | 0.9615 | 0.6558 | 0.086* | |
| C30 | 0.2151 (2) | 1.0614 (4) | 0.69901 (14) | 0.0843 (10) | |
| H30 | 0.1477 | 1.0472 | 0.6719 | 0.101* | |
| C31 | 0.1984 (3) | 1.1333 (4) | 0.74701 (14) | 0.0807 (9) | |
| H31 | 0.1206 | 1.1700 | 0.7526 | 0.097* | |
| C32 | 0.2965 (3) | 1.1516 (4) | 0.78720 (13) | 0.0806 (9) | |
| H32 | 0.2856 | 1.2013 | 0.8203 | 0.097* | |
| C33 | 0.4116 (2) | 1.0973 (3) | 0.77930 (11) | 0.0657 (8) | |
| H33 | 0.4773 | 1.1091 | 0.8075 | 0.079* | |
| O34 | 0.81109 (15) | 0.7302 (2) | 0.72014 (7) | 0.0637 (5) | |
| C34 | 0.5741 (5) | 0.8527 (5) | 0.8947 (2) | 0.1397 (17) | |
| H34A | 0.5325 | 0.7866 | 0.8698 | 0.210* | |
| H34B | 0.5214 | 0.9305 | 0.8969 | 0.210* | |
| H34C | 0.5915 | 0.8150 | 0.9325 | 0.210* | |
| O35 | 0.6784 (3) | 0.8881 (7) | 0.87417 (13) | 0.208 (2) | |
| H35 | 0.6675 | 0.8947 | 0.8390 | 0.312* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0512 (9) | 0.0702 (12) | 0.0453 (9) | 0.0038 (9) | −0.0040 (7) | −0.0002 (9) |
| C2 | 0.0414 (12) | 0.0628 (17) | 0.0433 (12) | 0.0088 (12) | 0.0060 (10) | −0.0008 (13) |
| C3 | 0.0388 (11) | 0.0561 (15) | 0.0378 (11) | 0.0061 (11) | 0.0068 (9) | 0.0007 (11) |
| C4 | 0.0450 (12) | 0.0535 (15) | 0.0383 (11) | 0.0068 (12) | 0.0044 (9) | −0.0019 (11) |
| C5 | 0.0400 (12) | 0.0528 (15) | 0.0533 (14) | 0.0048 (11) | 0.0110 (10) | −0.0051 (12) |
| C6 | 0.0509 (14) | 0.0589 (17) | 0.0680 (16) | 0.0005 (13) | 0.0135 (12) | −0.0055 (14) |
| C7 | 0.0489 (15) | 0.0576 (18) | 0.099 (2) | −0.0006 (14) | 0.0214 (15) | −0.0127 (17) |
| C8 | 0.0433 (14) | 0.074 (2) | 0.102 (2) | −0.0026 (15) | 0.0015 (15) | −0.0291 (19) |
| C9 | 0.0494 (15) | 0.076 (2) | 0.0696 (17) | 0.0070 (15) | −0.0045 (13) | −0.0197 (16) |
| C10 | 0.0397 (12) | 0.0585 (17) | 0.0553 (14) | 0.0072 (12) | 0.0041 (11) | −0.0069 (13) |
| O11 | 0.0640 (11) | 0.0864 (14) | 0.0446 (9) | −0.0029 (10) | 0.0072 (8) | 0.0148 (10) |
| C12 | 0.0405 (12) | 0.0535 (15) | 0.0390 (11) | 0.0011 (11) | 0.0058 (9) | 0.0027 (11) |
| C13 | 0.0387 (12) | 0.0575 (16) | 0.0382 (11) | 0.0040 (11) | 0.0043 (9) | −0.0002 (11) |
| C14 | 0.0447 (12) | 0.0655 (17) | 0.0373 (11) | 0.0055 (13) | 0.0060 (10) | 0.0006 (12) |
| O15 | 0.0619 (10) | 0.0573 (11) | 0.0417 (8) | −0.0035 (9) | 0.0011 (7) | 0.0069 (8) |
| C16 | 0.076 (2) | 0.076 (2) | 0.141 (3) | −0.0171 (18) | 0.029 (2) | −0.003 (2) |
| C17 | 0.0421 (12) | 0.0686 (18) | 0.0378 (12) | −0.0006 (13) | 0.0079 (10) | −0.0013 (12) |
| C18 | 0.0584 (16) | 0.086 (2) | 0.0632 (16) | −0.0079 (16) | 0.0182 (13) | −0.0048 (16) |
| C19 | 0.0550 (17) | 0.129 (3) | 0.0698 (19) | −0.015 (2) | 0.0224 (14) | −0.009 (2) |
| C20 | 0.0500 (16) | 0.138 (3) | 0.0687 (19) | 0.014 (2) | 0.0170 (14) | −0.014 (2) |
| C21 | 0.0671 (19) | 0.103 (3) | 0.081 (2) | 0.027 (2) | 0.0170 (16) | −0.0044 (19) |
| C22 | 0.0546 (15) | 0.073 (2) | 0.0631 (16) | 0.0080 (15) | 0.0110 (12) | −0.0009 (14) |
| C23 | 0.0463 (13) | 0.0765 (19) | 0.0518 (13) | −0.0025 (14) | 0.0015 (11) | −0.0070 (14) |
| N24 | 0.0397 (10) | 0.0542 (12) | 0.0397 (9) | 0.0036 (9) | 0.0068 (8) | 0.0038 (9) |
| C25 | 0.0583 (15) | 0.0686 (19) | 0.0586 (15) | 0.0116 (14) | 0.0158 (12) | 0.0123 (14) |
| C26 | 0.0455 (13) | 0.0591 (16) | 0.0427 (12) | 0.0009 (12) | 0.0049 (10) | −0.0023 (12) |
| O27 | 0.0669 (11) | 0.0826 (14) | 0.0501 (10) | 0.0178 (11) | 0.0156 (8) | 0.0156 (10) |
| C28 | 0.0417 (12) | 0.0607 (16) | 0.0490 (13) | −0.0030 (12) | 0.0091 (10) | 0.0024 (12) |
| C29 | 0.0502 (15) | 0.100 (2) | 0.0642 (16) | −0.0008 (16) | 0.0047 (12) | −0.0214 (17) |
| C30 | 0.0403 (15) | 0.128 (3) | 0.084 (2) | −0.0023 (17) | −0.0005 (14) | −0.011 (2) |
| C31 | 0.0505 (16) | 0.113 (3) | 0.081 (2) | 0.0139 (17) | 0.0204 (15) | −0.002 (2) |
| C32 | 0.0637 (18) | 0.107 (3) | 0.0732 (19) | 0.0124 (18) | 0.0176 (15) | −0.0207 (18) |
| C33 | 0.0503 (14) | 0.091 (2) | 0.0564 (15) | 0.0016 (15) | 0.0070 (12) | −0.0154 (15) |
| O34 | 0.0554 (10) | 0.0799 (13) | 0.0549 (10) | 0.0163 (10) | −0.0014 (8) | 0.0164 (10) |
| C34 | 0.159 (4) | 0.135 (4) | 0.128 (4) | 0.009 (4) | 0.024 (3) | 0.029 (3) |
| O35 | 0.140 (3) | 0.398 (7) | 0.0822 (19) | 0.048 (4) | −0.0186 (19) | 0.013 (3) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| O1—C10 | 1.369 (3) | C18—H18 | 0.9300 |
| O1—C2 | 1.376 (3) | C19—C20 | 1.339 (5) |
| C2—O11 | 1.206 (3) | C19—H19 | 0.9300 |
| C2—C3 | 1.451 (3) | C20—C21 | 1.369 (5) |
| C3—C4 | 1.344 (3) | C20—H20 | 0.9300 |
| C3—C12 | 1.498 (3) | C21—C22 | 1.395 (4) |
| C4—O15 | 1.372 (3) | C21—H21 | 0.9300 |
| C4—C5 | 1.438 (3) | C22—H22 | 0.9300 |
| C5—C10 | 1.390 (3) | C23—H23A | 0.9600 |
| C5—C6 | 1.398 (3) | C23—H23B | 0.9600 |
| C6—C7 | 1.379 (4) | C23—H23C | 0.9600 |
| C6—H6 | 0.9300 | N24—C26 | 1.349 (3) |
| C7—C8 | 1.396 (4) | N24—C25 | 1.464 (3) |
| C7—C16 | 1.507 (4) | C25—H25A | 0.9600 |
| C8—C9 | 1.375 (4) | C25—H25B | 0.9600 |
| C8—H8 | 0.9300 | C25—H25C | 0.9600 |
| C9—C10 | 1.381 (4) | C26—O27 | 1.236 (3) |
| C9—H9 | 0.9300 | C26—C28 | 1.493 (3) |
| C12—C17 | 1.524 (3) | C28—C33 | 1.373 (3) |
| C12—C13 | 1.566 (3) | C28—C29 | 1.382 (3) |
| C12—H12 | 0.9800 | C29—C30 | 1.383 (4) |
| C13—N24 | 1.488 (3) | C29—H29 | 0.9300 |
| C13—C14 | 1.516 (4) | C30—C31 | 1.351 (4) |
| C13—C23 | 1.523 (3) | C30—H30 | 0.9300 |
| C14—O34 | 1.189 (3) | C31—C32 | 1.362 (4) |
| C14—O15 | 1.403 (3) | C31—H31 | 0.9300 |
| C16—H16A | 0.9600 | C32—C33 | 1.374 (4) |
| C16—H16B | 0.9600 | C32—H32 | 0.9300 |
| C16—H16C | 0.9600 | C33—H33 | 0.9300 |
| C16—H16D | 0.9600 | C34—O35 | 1.302 (5) |
| C16—H16E | 0.9600 | C34—H34A | 0.9600 |
| C16—H16F | 0.9600 | C34—H34B | 0.9600 |
| C17—C22 | 1.371 (4) | C34—H34C | 0.9600 |
| C17—C18 | 1.382 (4) | O35—H35 | 0.8200 |
| C18—C19 | 1.395 (4) | ||
| C10—O1—C2 | 122.43 (19) | H16D—C16—H16F | 109.5 |
| O11—C2—O1 | 117.3 (2) | H16E—C16—H16F | 109.5 |
| O11—C2—C3 | 125.1 (2) | C22—C17—C18 | 118.0 (2) |
| O1—C2—C3 | 117.6 (2) | C22—C17—C12 | 123.1 (2) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 119.4 (2) | C18—C17—C12 | 118.8 (2) |
| C4—C3—C12 | 121.6 (2) | C17—C18—C19 | 120.9 (3) |
| C2—C3—C12 | 119.0 (2) | C17—C18—H18 | 119.5 |
| C3—C4—O15 | 122.4 (2) | C19—C18—H18 | 119.5 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 122.8 (2) | C20—C19—C18 | 120.3 (3) |
| O15—C4—C5 | 114.8 (2) | C20—C19—H19 | 119.9 |
| C10—C5—C6 | 118.7 (2) | C18—C19—H19 | 119.9 |
| C10—C5—C4 | 116.3 (2) | C19—C20—C21 | 120.1 (3) |
| C6—C5—C4 | 124.9 (2) | C19—C20—H20 | 120.0 |
| C7—C6—C5 | 121.6 (3) | C21—C20—H20 | 120.0 |
| C7—C6—H6 | 119.2 | C20—C21—C22 | 120.3 (3) |
| C5—C6—H6 | 119.2 | C20—C21—H21 | 119.9 |
| C6—C7—C8 | 117.5 (3) | C22—C21—H21 | 119.9 |
| C6—C7—C16 | 121.4 (3) | C17—C22—C21 | 120.5 (3) |
| C8—C7—C16 | 121.2 (3) | C17—C22—H22 | 119.8 |
| C9—C8—C7 | 122.5 (3) | C21—C22—H22 | 119.8 |
| C9—C8—H8 | 118.8 | C13—C23—H23A | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—H8 | 118.8 | C13—C23—H23B | 109.5 |
| C8—C9—C10 | 118.8 (3) | H23A—C23—H23B | 109.5 |
| C8—C9—H9 | 120.6 | C13—C23—H23C | 109.5 |
| C10—C9—H9 | 120.6 | H23A—C23—H23C | 109.5 |
| O1—C10—C9 | 117.6 (2) | H23B—C23—H23C | 109.5 |
| O1—C10—C5 | 121.5 (2) | C26—N24—C25 | 121.0 (2) |
| C9—C10—C5 | 120.9 (3) | C26—N24—C13 | 118.76 (19) |
| C3—C12—C17 | 113.34 (19) | C25—N24—C13 | 117.86 (18) |
| C3—C12—C13 | 107.90 (17) | N24—C25—H25A | 109.5 |
| C17—C12—C13 | 113.96 (17) | N24—C25—H25B | 109.5 |
| C3—C12—H12 | 107.1 | H25A—C25—H25B | 109.5 |
| C17—C12—H12 | 107.1 | N24—C25—H25C | 109.5 |
| C13—C12—H12 | 107.1 | H25A—C25—H25C | 109.5 |
| N24—C13—C14 | 110.10 (18) | H25B—C25—H25C | 109.5 |
| N24—C13—C23 | 110.53 (19) | O27—C26—N24 | 120.7 (2) |
| C14—C13—C23 | 109.6 (2) | O27—C26—C28 | 120.3 (2) |
| N24—C13—C12 | 107.74 (16) | N24—C26—C28 | 118.9 (2) |
| C14—C13—C12 | 104.82 (19) | C33—C28—C29 | 118.3 (2) |
| C23—C13—C12 | 113.90 (18) | C33—C28—C26 | 120.2 (2) |
| O34—C14—O15 | 117.1 (2) | C29—C28—C26 | 121.4 (2) |
| O34—C14—C13 | 127.0 (2) | C28—C29—C30 | 119.9 (3) |
| O15—C14—C13 | 115.49 (19) | C28—C29—H29 | 120.0 |
| C4—O15—C14 | 118.16 (18) | C30—C29—H29 | 120.0 |
| C7—C16—H16A | 109.5 | C31—C30—C29 | 121.0 (3) |
| C7—C16—H16B | 109.5 | C31—C30—H30 | 119.5 |
| H16A—C16—H16B | 109.5 | C29—C30—H30 | 119.5 |
| C7—C16—H16C | 109.5 | C30—C31—C32 | 119.4 (3) |
| H16A—C16—H16C | 109.5 | C30—C31—H31 | 120.3 |
| H16B—C16—H16C | 109.5 | C32—C31—H31 | 120.3 |
| C7—C16—H16D | 109.5 | C31—C32—C33 | 120.6 (3) |
| H16A—C16—H16D | 141.1 | C31—C32—H32 | 119.7 |
| H16B—C16—H16D | 56.3 | C33—C32—H32 | 119.7 |
| H16C—C16—H16D | 56.3 | C28—C33—C32 | 120.7 (3) |
| C7—C16—H16E | 109.5 | C28—C33—H33 | 119.6 |
| H16A—C16—H16E | 56.3 | C32—C33—H33 | 119.6 |
| H16B—C16—H16E | 141.1 | O35—C34—H34A | 109.5 |
| H16C—C16—H16E | 56.3 | O35—C34—H34B | 109.5 |
| H16D—C16—H16E | 109.5 | H34A—C34—H34B | 109.5 |
| C7—C16—H16F | 109.5 | O35—C34—H34C | 109.5 |
| H16A—C16—H16F | 56.3 | H34A—C34—H34C | 109.5 |
| H16B—C16—H16F | 56.3 | H34B—C34—H34C | 109.5 |
| H16C—C16—H16F | 141.1 | C34—O35—H35 | 109.5 |
| C10—O1—C2—O11 | 179.8 (2) | N24—C13—C14—O15 | 57.6 (2) |
| C10—O1—C2—C3 | 0.6 (3) | C23—C13—C14—O15 | 179.33 (17) |
| O11—C2—C3—C4 | −179.2 (2) | C12—C13—C14—O15 | −58.1 (2) |
| O1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.1 (3) | C3—C4—O15—C14 | 5.6 (3) |
| O11—C2—C3—C12 | 0.5 (3) | C5—C4—O15—C14 | −177.71 (18) |
| O1—C2—C3—C12 | 179.67 (19) | O34—C14—O15—C4 | −144.9 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—O15 | 175.6 (2) | C13—C14—O15—C4 | 28.2 (3) |
| C12—C3—C4—O15 | −4.2 (3) | C3—C12—C17—C22 | −38.0 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.8 (3) | C13—C12—C17—C22 | 85.9 (3) |
| C12—C3—C4—C5 | 179.5 (2) | C3—C12—C17—C18 | 140.8 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—C10 | 1.1 (3) | C13—C12—C17—C18 | −95.3 (3) |
| O15—C4—C5—C10 | −175.52 (19) | C22—C17—C18—C19 | −0.7 (4) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 178.7 (2) | C12—C17—C18—C19 | −179.5 (2) |
| O15—C4—C5—C6 | 2.0 (3) | C17—C18—C19—C20 | 0.3 (5) |
| C10—C5—C6—C7 | −0.7 (4) | C18—C19—C20—C21 | 0.1 (5) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | −178.2 (2) | C19—C20—C21—C22 | −0.2 (5) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | 0.1 (4) | C18—C17—C22—C21 | 0.6 (4) |
| C5—C6—C7—C16 | 179.5 (2) | C12—C17—C22—C21 | 179.4 (2) |
| C6—C7—C8—C9 | 0.4 (4) | C20—C21—C22—C17 | −0.1 (4) |
| C16—C7—C8—C9 | −178.9 (3) | C14—C13—N24—C26 | 35.9 (3) |
| C7—C8—C9—C10 | −0.4 (4) | C23—C13—N24—C26 | −85.3 (3) |
| C2—O1—C10—C9 | −179.3 (2) | C12—C13—N24—C26 | 149.6 (2) |
| C2—O1—C10—C5 | −0.3 (3) | C14—C13—N24—C25 | −161.6 (2) |
| C8—C9—C10—O1 | 178.8 (2) | C23—C13—N24—C25 | 77.2 (2) |
| C8—C9—C10—C5 | −0.1 (4) | C12—C13—N24—C25 | −47.8 (3) |
| C6—C5—C10—O1 | −178.3 (2) | C25—N24—C26—O27 | −163.2 (2) |
| C4—C5—C10—O1 | −0.6 (3) | C13—N24—C26—O27 | −1.3 (3) |
| C6—C5—C10—C9 | 0.7 (3) | C25—N24—C26—C28 | 20.1 (3) |
| C4—C5—C10—C9 | 178.4 (2) | C13—N24—C26—C28 | −177.9 (2) |
| C4—C3—C12—C17 | 98.8 (2) | O27—C26—C28—C33 | 61.0 (4) |
| C2—C3—C12—C17 | −80.9 (3) | N24—C26—C28—C33 | −122.4 (3) |
| C4—C3—C12—C13 | −28.3 (3) | O27—C26—C28—C29 | −116.1 (3) |
| C2—C3—C12—C13 | 151.9 (2) | N24—C26—C28—C29 | 60.5 (3) |
| C3—C12—C13—N24 | −62.3 (2) | C33—C28—C29—C30 | −0.8 (4) |
| C17—C12—C13—N24 | 170.9 (2) | C26—C28—C29—C30 | 176.3 (3) |
| C3—C12—C13—C14 | 55.0 (2) | C28—C29—C30—C31 | 1.9 (5) |
| C17—C12—C13—C14 | −71.8 (2) | C29—C30—C31—C32 | −1.4 (5) |
| C3—C12—C13—C23 | 174.7 (2) | C30—C31—C32—C33 | −0.2 (5) |
| C17—C12—C13—C23 | 47.9 (3) | C29—C28—C33—C32 | −0.8 (4) |
| N24—C13—C14—O34 | −130.1 (2) | C26—C28—C33—C32 | −177.9 (3) |
| C23—C13—C14—O34 | −8.3 (3) | C31—C32—C33—C28 | 1.3 (5) |
| C12—C13—C14—O34 | 114.3 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O35—H35···O27 | 0.82 | 1.99 | 2.784 (3) | 163 |
| C9—H9···O35i | 0.93 | 2.46 | 3.320 (4) | 153 |
| C19—H19···O11ii | 0.93 | 2.60 | 3.403 (3) | 144 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x−1/2, −y+3/2, z−1/2; (ii) −x+2, −y+2, −z+1.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: JH2217).
References
- Allen, F. H. (2002). Acta Cryst. B58, 380–388. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Altomare, A., Burla, M. C., Camalli, M., Cascarano, G. L., Giacovazzo, C., Guagliardi, A., Moliterni, A. G. G., Polidori, G. & Spagna, R. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst.32, 115–119.
- Bruker (1999). XSCANS Release 2.31. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Bruno, G., Nicoló, F., Rotondo, A., Foti, F., Risitano, F., Grassi, G. & Bilardo, C. (2001). Acta Cryst. C57, 493–494. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Frisch, M. J. et al. (1998). GAUSSIAN98 Gaussian, Inc., Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, USA.
- Grassi, G., Cordaro, M., Bruno, G. & Nicolò, F. (2002). Helv. Chim. Acta, 85, 196–205.
- Grassi, G., Risitano, F., Foti, F., Cordaro, M., Bruno, G. & Nicolò, F. (2003). Chem. Commun. pp. 1868–1869. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Harborne, J. B. & Baxter, H. (1999). The Handbook of Natural Flavonoids Chichester: Wiley.
- Kokila, M. K., Puttaraja, Kulkarni, M. V. & Shivaprakash, N. C. (1996). Acta Cryst. C52, 2078–2081.
- Kopfmann, G. & Huber, R. (1968). Acta Cryst. A24, 348–351.
- Murray, R. D. H., Medez, J. & Brown, S. A. (1982). In The Natural Coumarins: Occurence, Chemistry and Biochemistry New York: Wiley.
- Nardelli, M. (1995). J. Appl. Cryst.28, 659.
- Qabaja, G. E., Perchellet, M., Perchellet, J. P. & Jones, G. B. (2000). Tetrahedron Lett.41, 3007–3010.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Siemens (1996). XPW Siemens Analytical X-ray Instruments Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Yu, X. L., Scheller, D., Rademacher, O. & Wolff, T. (2003). J. Org. Chem.68, 7386–7399. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810043709/jh2217sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810043709/jh2217Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report