Abstract
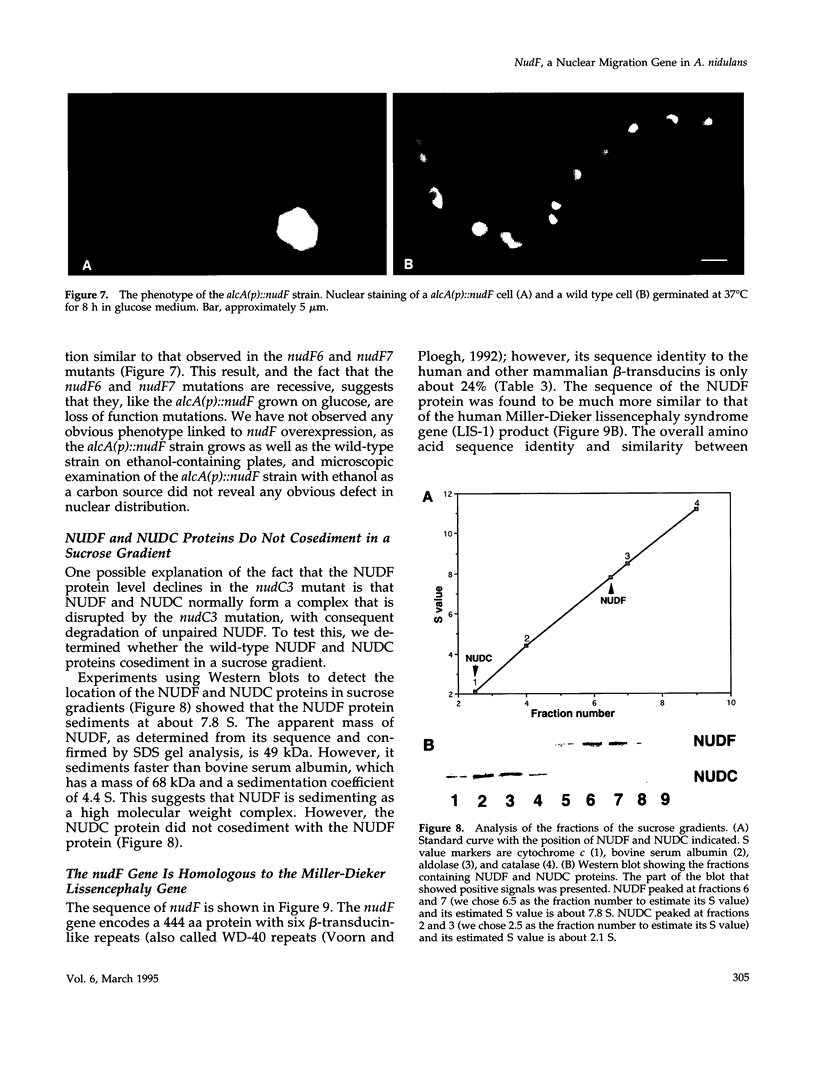
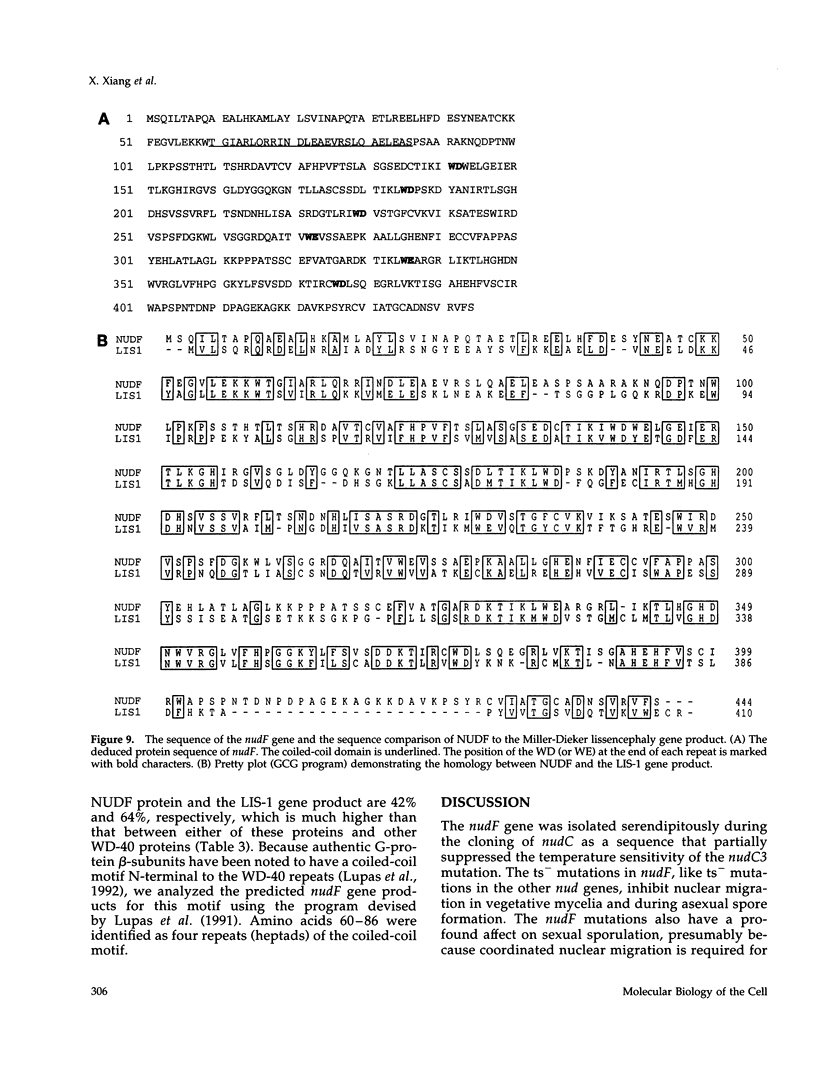
During a study of the genetics of nuclear migration in the filamentous fungus Aspergillus nidulans, we cloned a gene, nudF, which is required for nuclear migration during vegetative growth as well as development. The NUDF protein level is controlled by another protein NUDC, and extra copies of the nudF gene can suppress the nudC3 mutation. nudF encodes a protein with 42% sequence identity to the human LIS-1 (Miller-Dieker lissencephaly-1) gene, which is required for proper neuronal migration during brain development. This strong similarity suggests that the LIS-1 gene product may have a function similar to that of NUDF and supports previous findings to suggest that nuclear migration may play a role in neuronal migration.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnbaumer L. G proteins in signal transduction. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1990;30:675–705. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.30.040190.003331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Book K. J., Howard R., Morest D. K. Direct observation in vitro of how neuroblasts migrate: medulla and cochleovestibular ganglion of the chick embryo. Exp Neurol. 1991 Feb;111(2):228–243. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(91)90011-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Book K. J., Morest D. K. Migration of neuroblasts by perikaryal translocation: role of cellular elongation and axonal outgrowth in the acoustic nuclei of the chick embryo medulla. J Comp Neurol. 1990 Jul 1;297(1):55–76. doi: 10.1002/cne.902970105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clapham D. E., Neer E. J. New roles for G-protein beta gamma-dimers in transmembrane signalling. Nature. 1993 Sep 30;365(6445):403–406. doi: 10.1038/365403a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins C. A., Vallee R. B. Preparation of microtubules from rat liver and testis: cytoplasmic dynein is a major microtubule associated protein. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1989;14(4):491–500. doi: 10.1002/cm.970140407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conklin B. R., Bourne H. R. Structural elements of G alpha subunits that interact with G beta gamma, receptors, and effectors. Cell. 1993 May 21;73(4):631–641. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90245-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng X. W., Matsui M., Wei N., Wagner D., Chu A. M., Feldmann K. A., Quail P. H. COP1, an Arabidopsis regulatory gene, encodes a protein with both a zinc-binding motif and a G beta homologous domain. Cell. 1992 Nov 27;71(5):791–801. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90555-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobyns W. B., Elias E. R., Newlin A. C., Pagon R. A., Ledbetter D. H. Causal heterogeneity in isolated lissencephaly. Neurology. 1992 Jul;42(7):1375–1388. doi: 10.1212/wnl.42.7.1375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doonan J. H., MacKintosh C., Osmani S., Cohen P., Bai G., Lee E. Y., Morris N. R. A cDNA encoding rabbit muscle protein phosphatase 1 alpha complements the Aspergillus cell cycle mutation, bimG11. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 5;266(28):18889–18894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutcher S. K., Hartwell L. H. Genes that act before conjugation to prepare the Saccharomyces cerevisiae nucleus for caryogamy. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):203–210. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90349-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynlacht B. D., Weinzierl R. O., Admon A., Tjian R. The dTAFII80 subunit of Drosophila TFIID contains beta-transducin repeats. Nature. 1993 May 13;363(6425):176–179. doi: 10.1038/363176a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endow S. A., Kang S. J., Satterwhite L. L., Rose M. D., Skeen V. P., Salmon E. D. Yeast Kar3 is a minus-end microtubule motor protein that destabilizes microtubules preferentially at the minus ends. EMBO J. 1994 Jun 1;13(11):2708–2713. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06561.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Englander L. L., Rubin L. L. Acetylcholine receptor clustering and nuclear movement in muscle fibers in culture. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;104(1):87–95. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.1.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eshel D., Urrestarazu L. A., Vissers S., Jauniaux J. C., van Vliet-Reedijk J. C., Planta R. J., Gibbons I. R. Cytoplasmic dynein is required for normal nuclear segregation in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 1;90(23):11172–11176. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.11172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Adachi H., Tsujimoto M., Arai H., Inoue K. Miller-Dieker lissencephaly gene encodes a subunit of brain platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase [corrected]. Nature. 1994 Jul 21;370(6486):216–218. doi: 10.1038/370216a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Arai H., Inoue K. Purification and characterization of bovine brain platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 5;268(25):18748–18753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klominek J., Sundqvist K. G., Robért K. H. Nucleokinesis: distinct pattern of cell translocation in response to an autocrine motility factor-like substance or fibronectin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3902–3906. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koerner T. J., Hill J. E., Myers A. M., Tzagoloff A. High-expression vectors with multiple cloning sites for construction of trpE fusion genes: pATH vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:477–490. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94036-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y. Y., Yeh E., Hays T., Bloom K. Disruption of mitotic spindle orientation in a yeast dynein mutant. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 1;90(21):10096–10100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.21.10096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liscovitch M., Cantley L. C. Lipid second messengers. Cell. 1994 May 6;77(3):329–334. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90148-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lupas A. N., Lupas J. M., Stock J. B. Do G protein subunits associate via a three-stranded coiled coil? FEBS Lett. 1992 Dec 14;314(2):105–108. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80952-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meluh P. B., Rose M. D. KAR3, a kinesin-related gene required for yeast nuclear fusion. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):1029–1041. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90351-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirabito P. M., Morris N. R. BIMA, a TPR-containing protein required for mitosis, localizes to the spindle pole body in Aspergillus nidulans. J Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;120(4):959–968. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.4.959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morest D. K. A study of neurogenesis in the forebrain of opossum pouch young. Z Anat Entwicklungsgesch. 1970;130(4):265–305. doi: 10.1007/BF00520999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris N. R. Mitotic mutants of Aspergillus nidulans. Genet Res. 1975 Dec;26(3):237–254. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300016049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muhua L., Karpova T. S., Cooper J. A. A yeast actin-related protein homologous to that in vertebrate dynactin complex is important for spindle orientation and nuclear migration. Cell. 1994 Aug 26;78(4):669–679. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90531-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neer E. J., Schmidt C. J., Nambudripad R., Smith T. F. The ancient regulatory-protein family of WD-repeat proteins. Nature. 1994 Sep 22;371(6495):297–300. doi: 10.1038/371297a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakley B. R., Morris N. R. A beta-tubulin mutation in Aspergillus nidulans that blocks microtubule function without blocking assembly. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):837–845. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90109-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakley B. R., Morris N. R. Nuclear movement is beta--tubulin-dependent in Aspergillus nidulans. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):255–262. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90407-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osmani A. H., Osmani S. A., Morris N. R. The molecular cloning and identification of a gene product specifically required for nuclear movement in Aspergillus nidulans. J Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;111(2):543–551. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.2.543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osmani S. A., May G. S., Morris N. R. Regulation of the mRNA levels of nimA, a gene required for the G2-M transition in Aspergillus nidulans. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;104(6):1495–1504. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.6.1495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osmani S. A., Pu R. T., Morris N. R. Mitotic induction and maintenance by overexpression of a G2-specific gene that encodes a potential protein kinase. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):237–244. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90385-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. E., Sullivan D. S., Huffaker T., Koshland D. Role of astral microtubules and actin in spindle orientation and migration in the budding yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(3):583–593. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.3.583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plamann M., Minke P. F., Tinsley J. H., Bruno K. S. Cytoplasmic dynein and actin-related protein Arp1 are required for normal nuclear distribution in filamentous fungi. J Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;127(1):139–149. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.1.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rakic P. Neuron-glia relationship during granule cell migration in developing cerebellar cortex. A Golgi and electronmicroscopic study in Macacus Rhesus. J Comp Neurol. 1971 Mar;141(3):283–312. doi: 10.1002/cne.901410303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeve W. J., Kelly F. P. Nuclear position in the cells of the mouse early embryo. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1983 Jun;75:117–139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiner O., Carrozzo R., Shen Y., Wehnert M., Faustinella F., Dobyns W. B., Caskey C. T., Ledbetter D. H. Isolation of a Miller-Dieker lissencephaly gene containing G protein beta-subunit-like repeats. Nature. 1993 Aug 19;364(6439):717–721. doi: 10.1038/364717a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. D., Fink G. R. KAR1, a gene required for function of both intranuclear and extranuclear microtubules in yeast. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):1047–1060. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90712-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatten G. Motility during fertilization. Int Rev Cytol. 1982;79:59–163. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61673-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroer T. A. New insights into the interaction of cytoplasmic dynein with the actin-related protein, Arp1. J Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;127(1):1–4. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. L., Schoenwolf G. C. Role of cell-cycle in regulating neuroepithelial cell shape during bending of the chick neural plate. Cell Tissue Res. 1988 Jun;252(3):491–500. doi: 10.1007/BF00216636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan D. S., Huffaker T. C. Astral microtubules are not required for anaphase B in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;119(2):379–388. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.2.379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timberlake W. E., Marshall M. A. Genetic regulation of development in Aspergillus nidulans. Trends Genet. 1988 Jun;4(6):162–169. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90022-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang E., Cross R. K., Choppin P. W. Involvement of microtubules and 10-nm filaments in the movement and positioning of nuclei in syncytia. J Cell Biol. 1979 Nov;83(2 Pt 1):320–337. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.2.320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Voorn L., Ploegh H. L. The WD-40 repeat. FEBS Lett. 1992 Jul 28;307(2):131–134. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80751-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]










