Abstract
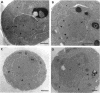
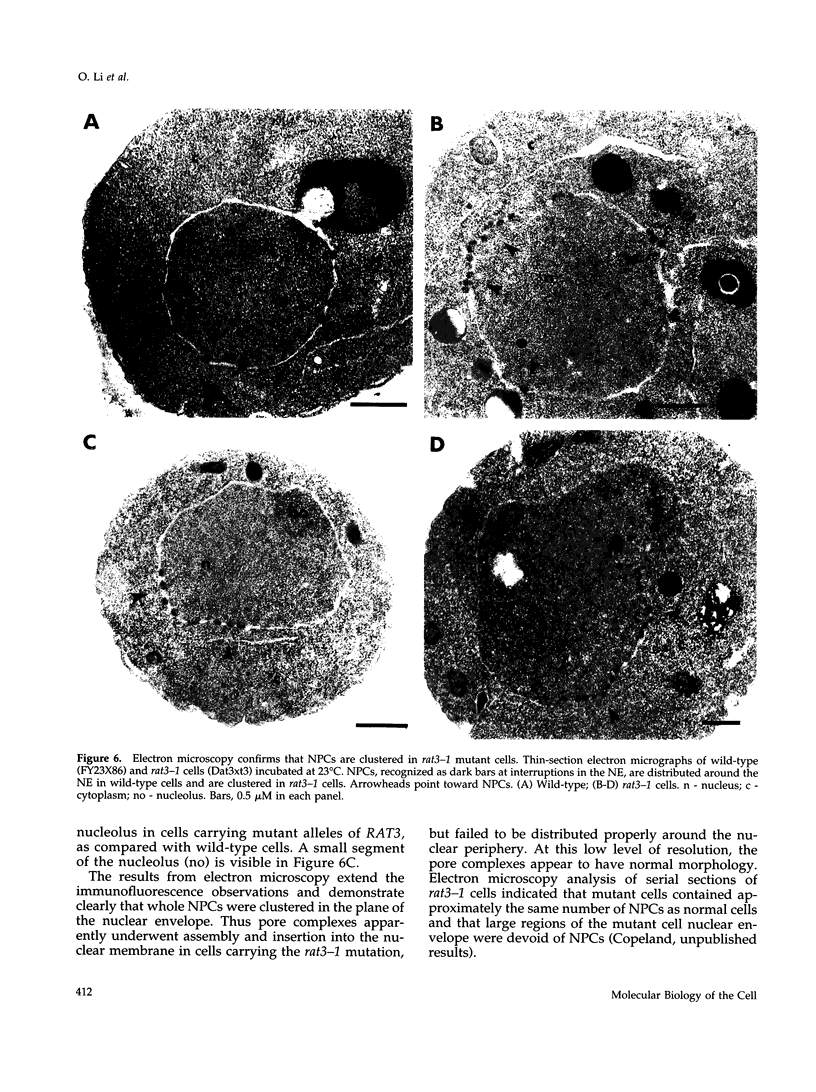
To identify genes whose products play potential roles in the nucleocytoplasmic export of messenger RNA, we isolated temperature-sensitive strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and examined them by fluorescent in situ hybridization. With the use of a digoxigen-tagged oligo-(dT)50 probe, we identified those that showed nuclear accumulation of poly(A)+ RNA when cells were shifted to the nonpermissive temperature. We describe here the properties of yeast strains bearing the rat3-1 mutation (RAT-ribonucleic acid trafficking) and the cloning of the RAT3 gene. When cultured at the permissive temperature of 23 degrees C, fewer than 10% of cells carrying the rat3-1 allele showed nuclear accumulation of poly(A)+ RNA, whereas approximately 70% showed nuclear accumulation of poly(A)+ RNA, whereas approximately 70% showed nuclear accumulation of poly(A)+ RNA after a shift to 37 degrees C for 4 h. In wild-type cells, nuclear pore complexes (NPCs) are distributed relatively evenly around the nuclear envelope. Both indirect immunofluorescence analysis and electron microscopy of rat3-1 cells indicated that NPCs were clustered into one or a few regions of the NE in mutant cells. Similar NPC clustering was seen in mutant cells cultured at temperatures between 15 degrees C and 37 degrees C. The RAT3 gene encodes an 1157-amino acid protein without similarity to other known proteins. It is essential for growth only at 37 degrees C. Cells carrying a disruption of the RAT3 gene were very similar to cells carrying the original rat3-1 mutation; they showed temperature-dependent nuclear accumulation of poly(A)+ RNA and exhibited constitutive clustering of NPCs. Epitope tagging of Rat3p demonstrated that it is located at the nuclear periphery and co-localizes with nuclear pore proteins recognized by the RL1 monoclonal antibody. We refer to this nucleoporin as Rat3p/Nup133p.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akey C. W. Probing the structure and function of the nuclear pore complex. Semin Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;2(3):167–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akey C. W., Radermacher M. Architecture of the Xenopus nuclear pore complex revealed by three-dimensional cryo-electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;122(1):1–19. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akey C. W. Visualization of transport-related configurations of the nuclear pore transporter. Biophys J. 1990 Aug;58(2):341–355. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82381-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen J. L., Douglas M. G. Organization of the nuclear pore complex in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Ultrastruct Mol Struct Res. 1989 Aug;102(2):95–108. doi: 10.1016/0889-1605(89)90047-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amberg D. C., Goldstein A. L., Cole C. N. Isolation and characterization of RAT1: an essential gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae required for the efficient nucleocytoplasmic trafficking of mRNA. Genes Dev. 1992 Jul;6(7):1173–1189. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.7.1173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belanger K. D., Kenna M. A., Wei S., Davis L. I. Genetic and physical interactions between Srp1p and nuclear pore complex proteins Nup1p and Nup2p. J Cell Biol. 1994 Aug;126(3):619–630. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.3.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogerd A. M., Hoffman J. A., Amberg D. C., Fink G. R., Davis L. I. nup1 mutants exhibit pleiotropic defects in nuclear pore complex function. J Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;127(2):319–332. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.2.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers B., Goetsch L. Preparation of yeast cells for thin-section electron microscopy. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:602–608. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94044-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland C. S., Snyder M. Nuclear pore complex antigens delineate nuclear envelope dynamics in vegetative and conjugating Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast. 1993 Mar;9(3):235–249. doi: 10.1002/yea.320090304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabauvalle M. C., Benavente R., Chaly N. Monoclonal antibodies to a Mr 68,000 pore complex glycoprotein interfere with nuclear protein uptake in Xenopus oocytes. Chromosoma. 1988 Nov;97(3):193–197. doi: 10.1007/BF00292960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis L. I., Fink G. R. The NUP1 gene encodes an essential component of the yeast nuclear pore complex. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):965–978. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90062-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doye V., Wepf R., Hurt E. C. A novel nuclear pore protein Nup133p with distinct roles in poly(A)+ RNA transport and nuclear pore distribution. EMBO J. 1994 Dec 15;13(24):6062–6075. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06953.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dujon B., Alexandraki D., André B., Ansorge W., Baladron V., Ballesta J. P., Banrevi A., Bolle P. A., Bolotin-Fukuhara M., Bossier P. Complete DNA sequence of yeast chromosome XI. Nature. 1994 Jun 2;369(6479):371–378. doi: 10.1038/369371a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabre E., Boelens W. C., Wimmer C., Mattaj I. W., Hurt E. C. Nup145p is required for nuclear export of mRNA and binds homopolymeric RNA in vitro via a novel conserved motif. Cell. 1994 Jul 29;78(2):275–289. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90297-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Featherstone C., Darby M. K., Gerace L. A monoclonal antibody against the nuclear pore complex inhibits nucleocytoplasmic transport of protein and RNA in vivo. J Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;107(4):1289–1297. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.4.1289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forbes D. J. Structure and function of the nuclear pore complex. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:495–527. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.002431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García-Cantalejo J., Baladrón V., Esteban P. F., Santos M. A., Bou G., Remacha M. A., Revuelta J. L., Ballesta J. P., Jiménez A., del Rey F. The complete sequence of an 18,002 bp segment of Saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosome XI contains the HBS1, MRP-L20 and PRP16 genes, and six new open reading frames. Yeast. 1994 Feb;10(2):231–245. doi: 10.1002/yea.320100210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerace L. Molecular trafficking across the nuclear pore complex. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;4(4):637–645. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90083-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gietz R. D., Sugino A. New yeast-Escherichia coli shuttle vectors constructed with in vitro mutagenized yeast genes lacking six-base pair restriction sites. Gene. 1988 Dec 30;74(2):527–534. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90185-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg M. W., Allen T. D. High resolution scanning electron microscopy of the nuclear envelope: demonstration of a new, regular, fibrous lattice attached to the baskets of the nucleoplasmic face of the nuclear pores. J Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;119(6):1429–1440. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.6.1429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandi P., Doye V., Hurt E. C. Purification of NSP1 reveals complex formation with 'GLFG' nucleoporins and a novel nuclear pore protein NIC96. EMBO J. 1993 Aug;12(8):3061–3071. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05975.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinshaw J. E., Carragher B. O., Milligan R. A. Architecture and design of the nuclear pore complex. Cell. 1992 Jun 26;69(7):1133–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90635-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurt E. C. The nuclear pore complex. FEBS Lett. 1993 Jun 28;325(1-2):76–80. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81417-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarnik M., Aebi U. Toward a more complete 3-D structure of the nuclear pore complex. J Struct Biol. 1991 Dec;107(3):291–308. doi: 10.1016/1047-8477(91)90054-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadowaki T., Chen S., Hitomi M., Jacobs E., Kumagai C., Liang S., Schneiter R., Singleton D., Wisniewska J., Tartakoff A. M. Isolation and characterization of Saccharomyces cerevisiae mRNA transport-defective (mtr) mutants. J Cell Biol. 1994 Aug;126(3):649–659. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.3.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadowaki T., Zhao Y., Tartakoff A. M. A conditional yeast mutant deficient in mRNA transport from nucleus to cytoplasm. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2312–2316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb J. D., Davis L. I., Fink G. R. NUP2, a novel yeast nucleoporin, has functional overlap with other proteins of the nuclear pore complex. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Feb;4(2):209–222. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.2.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maul G. G. The nuclear and the cytoplasmic pore complex: structure, dynamics, distribution, and evolution. Int Rev Cytol Suppl. 1977;(6):75–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehlin H., Daneholt B., Skoglund U. Translocation of a specific premessenger ribonucleoprotein particle through the nuclear pore studied with electron microscope tomography. Cell. 1992 May 15;69(4):605–613. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90224-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melchior F., Paschal B., Evans J., Gerace L. Inhibition of nuclear protein import by nonhydrolyzable analogues of GTP and identification of the small GTPase Ran/TC4 as an essential transport factor. J Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;123(6 Pt 2):1649–1659. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.6.1649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirzayan C., Copeland C. S., Snyder M. The NUF1 gene encodes an essential coiled-coil related protein that is a potential component of the yeast nucleoskeleton. J Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;116(6):1319–1332. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.6.1319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M. S., Blobel G. The GTP-binding protein Ran/TC4 is required for protein import into the nucleus. Nature. 1993 Oct 14;365(6447):661–663. doi: 10.1038/365661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreland R. B., Langevin G. L., Singer R. H., Garcea R. L., Hereford L. M. Amino acid sequences that determine the nuclear localization of yeast histone 2B. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):4048–4057. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.4048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nehrbass U., Kern H., Mutvei A., Horstmann H., Marshallsay B., Hurt E. C. NSP1: a yeast nuclear envelope protein localized at the nuclear pores exerts its essential function by its carboxy-terminal domain. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):979–989. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90063-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newmeyer D. D. The nuclear pore complex and nucleocytoplasmic transport. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;5(3):395–407. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90003-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panté N., Aebi U. The nuclear pore complex. J Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;122(5):977–984. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.5.977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichelt R., Holzenburg A., Buhle E. L., Jr, Jarnik M., Engel A., Aebi U. Correlation between structure and mass distribution of the nuclear pore complex and of distinct pore complex components. J Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;110(4):883–894. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.4.883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ren M., Drivas G., D'Eustachio P., Rush M. G. Ran/TC4: a small nuclear GTP-binding protein that regulates DNA synthesis. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;120(2):313–323. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.2.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson W. D., Mills A. D., Dilworth S. M., Laskey R. A., Dingwall C. Nuclear protein migration involves two steps: rapid binding at the nuclear envelope followed by slower translocation through nuclear pores. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):655–664. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90403-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riles L., Dutchik J. E., Baktha A., McCauley B. K., Thayer E. C., Leckie M. P., Braden V. V., Depke J. E., Olson M. V. Physical maps of the six smallest chromosomes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae at a resolution of 2.6 kilobase pairs. Genetics. 1993 May;134(1):81–150. doi: 10.1093/genetics/134.1.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ris H., Malecki M. High-resolution field emission scanning electron microscope imaging of internal cell structures after Epon extraction from sections: a new approach to correlative ultrastructural and immunocytochemical studies. J Struct Biol. 1993 Sep-Oct;111(2):148–157. doi: 10.1006/jsbi.1993.1045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. Targeting, disruption, replacement, and allele rescue: integrative DNA transformation in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:281–301. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94022-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rout M. P., Blobel G. Isolation of the yeast nuclear pore complex. J Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;123(4):771–783. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.4.771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rout M. P., Wente S. R. Pores for thought: nuclear pore complex proteins. Trends Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;4(10):357–365. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(94)90085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlenstedt G., Hurt E., Doye V., Silver P. A. Reconstitution of nuclear protein transport with semi-intact yeast cells. J Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;123(4):785–798. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.4.785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlenstedt G., Saavedra C., Loeb J. D., Cole C. N., Silver P. A. The GTP-bound form of the yeast Ran/TC4 homologue blocks nuclear protein import and appearance of poly(A)+ RNA in the cytoplasm. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jan 3;92(1):225–229. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.1.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Severs N. J., Jordan E. G., Williamson D. H. Nuclear pore absence from areas of close association between nucleus and vacuole in synchronous yeast cultures. J Ultrastruct Res. 1976 Mar;54(3):374–387. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(76)80023-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman F. Getting started with yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:3–21. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94004-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Hieter P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver P. A. How proteins enter the nucleus. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):489–497. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90233-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snow C. M., Senior A., Gerace L. Monoclonal antibodies identify a group of nuclear pore complex glycoproteins. J Cell Biol. 1987 May;104(5):1143–1156. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.5.1143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens B. J., Swift H. RNA transport from nucleus to cytoplasm in Chironomus salivary glands. J Cell Biol. 1966 Oct;31(1):55–77. doi: 10.1083/jcb.31.1.55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart M. Nuclear pore structure and function. Semin Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;3(4):267–277. doi: 10.1016/1043-4682(92)90028-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sukegawa J., Blobel G. A nuclear pore complex protein that contains zinc finger motifs, binds DNA, and faces the nucleoplasm. Cell. 1993 Jan 15;72(1):29–38. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90047-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unwin P. N., Milligan R. A. A large particle associated with the perimeter of the nuclear pore complex. J Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;93(1):63–75. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.1.63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wente S. R., Blobel G. A temperature-sensitive NUP116 null mutant forms a nuclear envelope seal over the yeast nuclear pore complex thereby blocking nucleocytoplasmic traffic. J Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;123(2):275–284. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.2.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wente S. R., Blobel G. NUP145 encodes a novel yeast glycine-leucine-phenylalanine-glycine (GLFG) nucleoporin required for nuclear envelope structure. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;125(5):955–969. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.5.955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wente S. R., Rout M. P., Blobel G. A new family of yeast nuclear pore complex proteins. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(4):705–723. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.4.705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wimmer C., Doye V., Grandi P., Nehrbass U., Hurt E. C. A new subclass of nucleoporins that functionally interact with nuclear pore protein NSP1. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):5051–5061. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05612.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wozniak R. W., Blobel G., Rout M. P. POM152 is an integral protein of the pore membrane domain of the yeast nuclear envelope. J Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;125(1):31–42. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yano R., Oakes M. L., Tabb M. M., Nomura M. Yeast Srp1p has homology to armadillo/plakoglobin/beta-catenin and participates in apparently multiple nuclear functions including the maintenance of the nucleolar structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 19;91(15):6880–6884. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.15.6880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yano R., Oakes M., Yamaghishi M., Dodd J. A., Nomura M. Cloning and characterization of SRP1, a suppressor of temperature-sensitive RNA polymerase I mutations, in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;12(12):5640–5651. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.12.5640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]