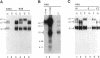Abstract
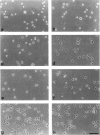
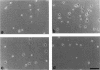
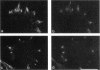
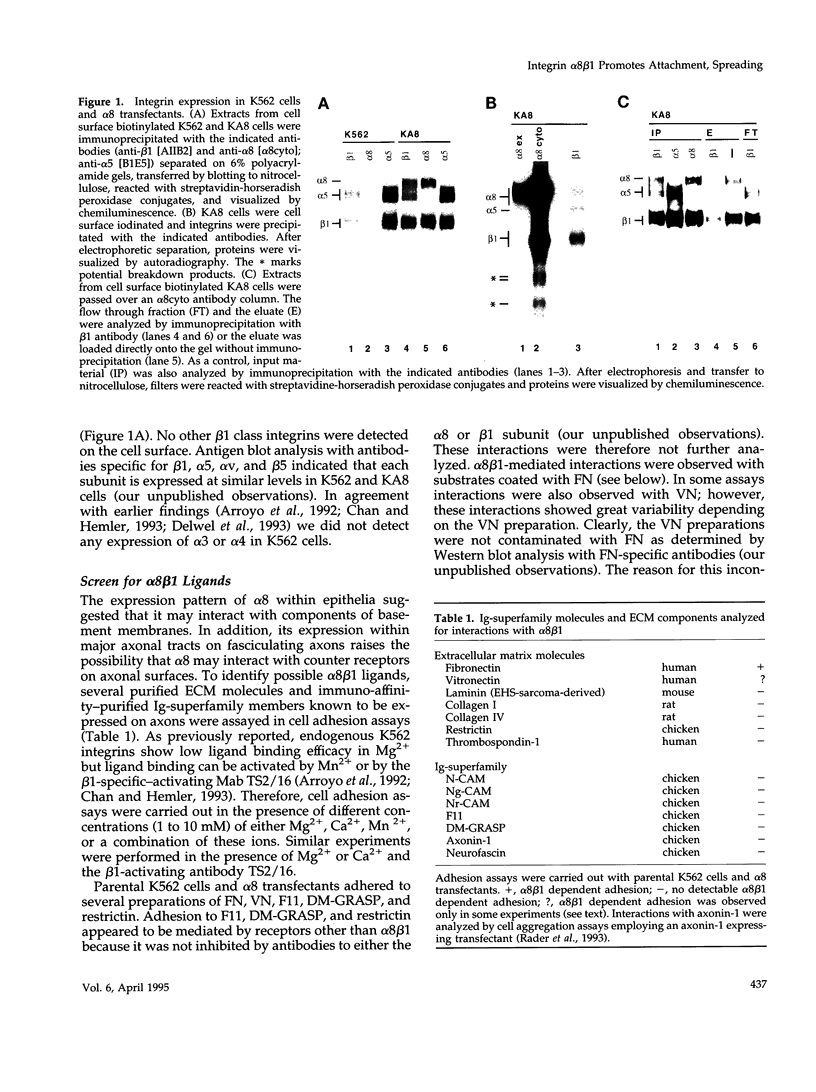
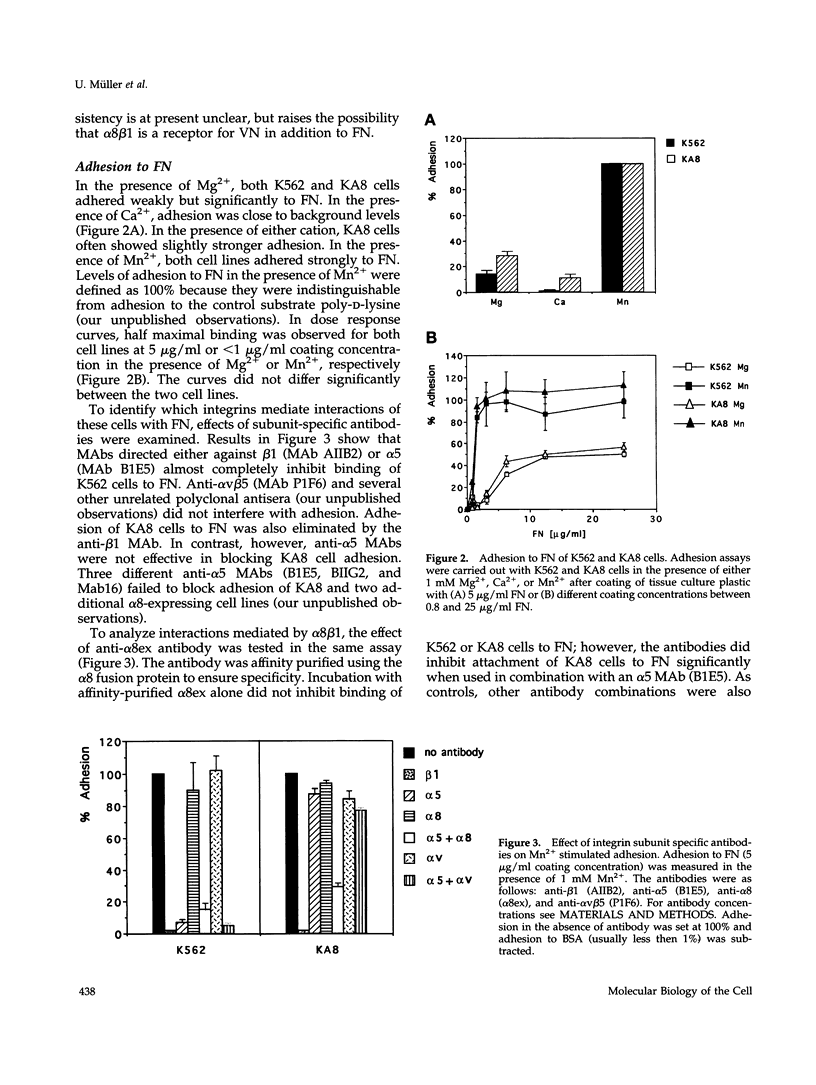
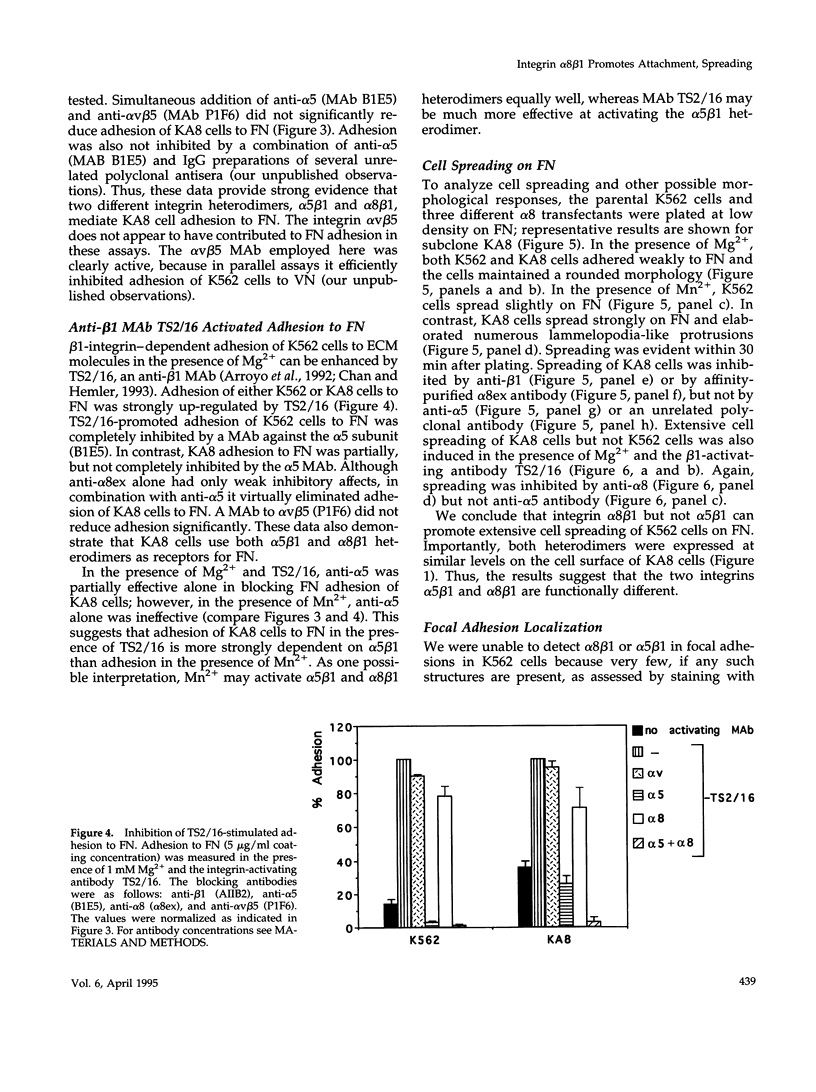
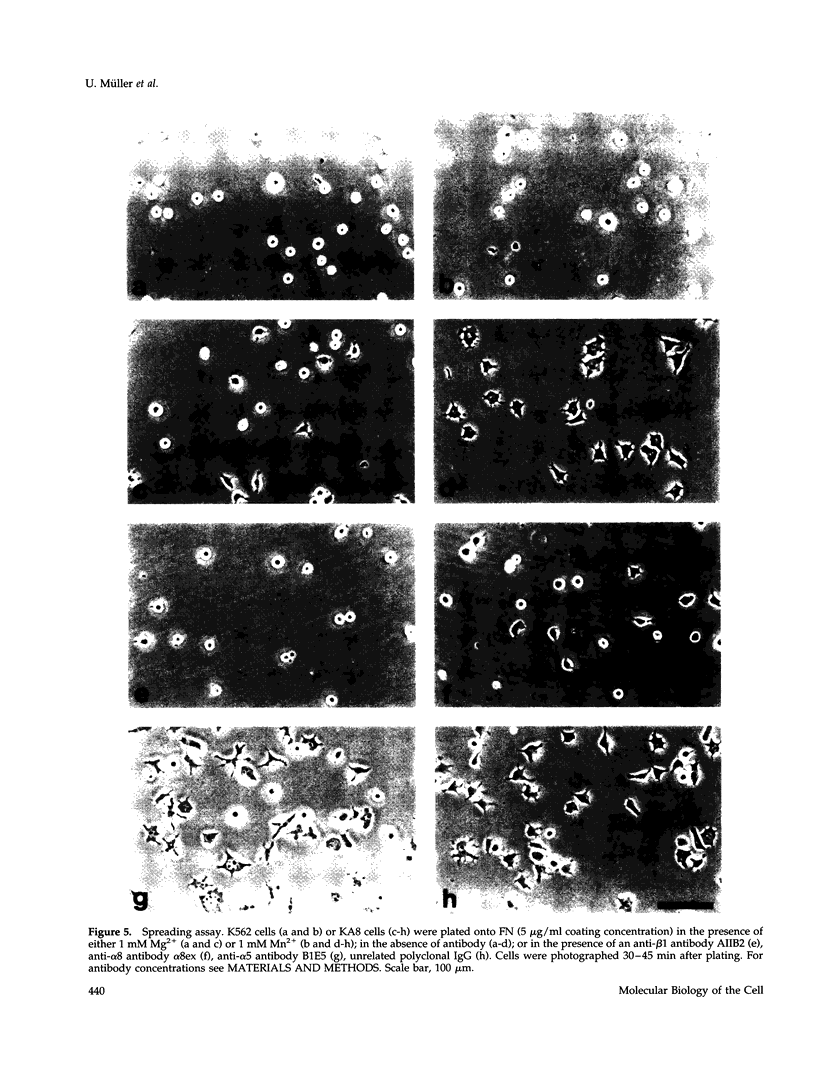
The integrin alpha 8 subunit, isolated by low stringency hybridization, is a novel integrin subunit that associates with beta 1. To identify ligands, we have prepared a function-blocking antiserum to the extracellular domain of alpha 8, and we have established by transfection K562 cell lines that stably express alpha 8 beta 1 heterodimers on the cell surface. We demonstrate here by cell adhesion and neurite outgrowth assays that alpha 8 beta 1 is a fibronectin receptor. Studies on fibronectin fragments using RGD peptides as inhibitors show that alpha 8 beta 1 binds to the RGD site of fibronectin. In contrast to the endogenous alpha 5 beta 1 fibronectin receptor in K562 cells, alpha 8 beta 1 not only promotes cell attachment but also extensive cell spreading, suggesting functional differences between the two receptors. In chick embryo fibroblasts, alpha 8 beta 1 is localized to focal adhesions. We conclude that alpha 8 beta 1 is a receptor for fibronectin and can promote attachment, cell spreading, and neurite outgrowth on fibronectin.
Full text
PDF



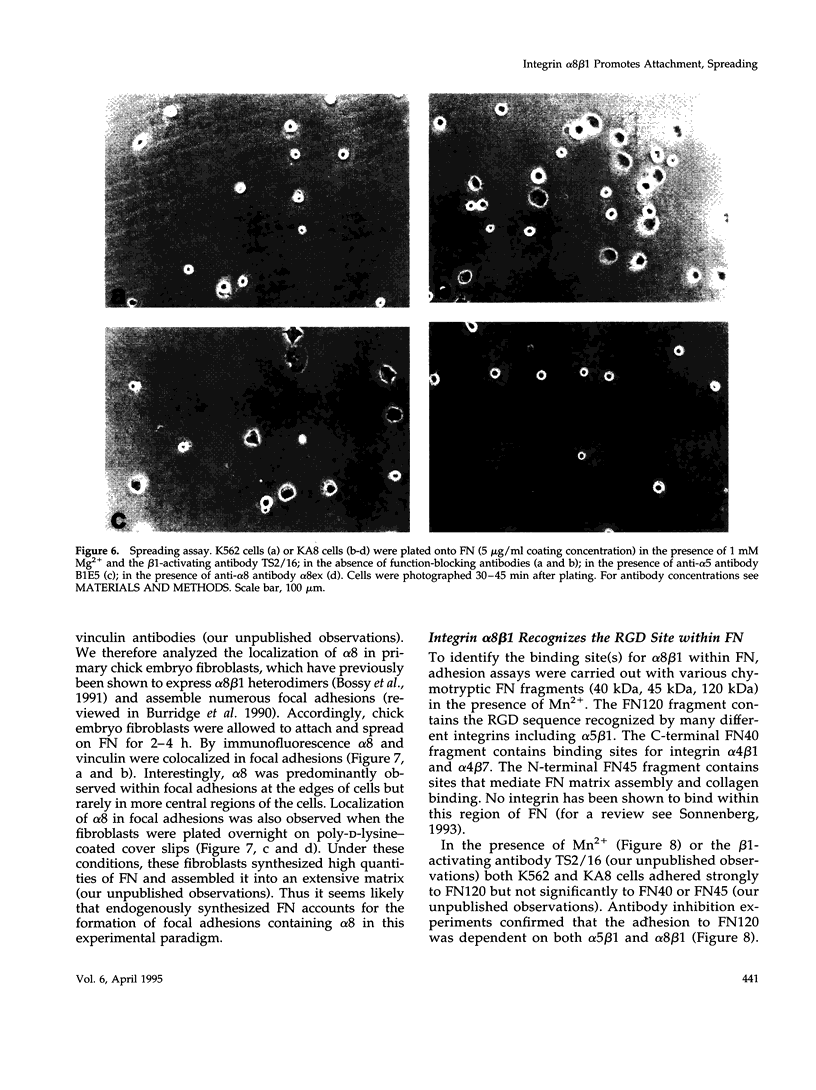
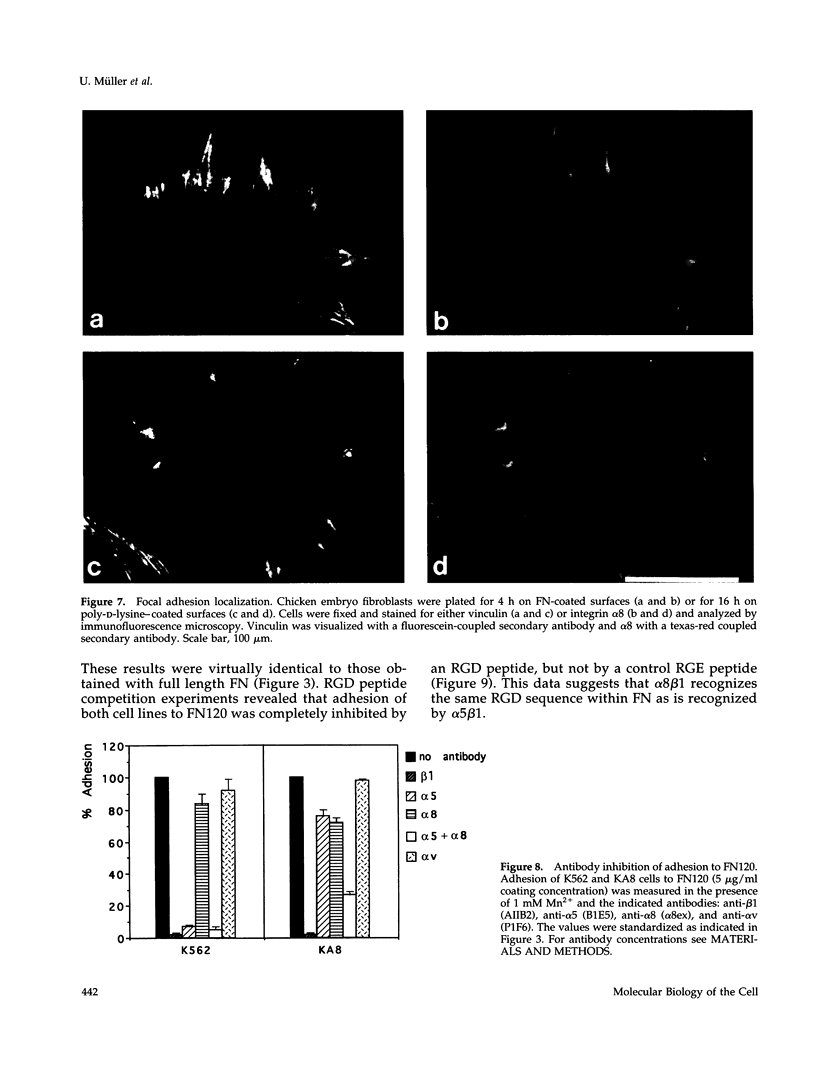

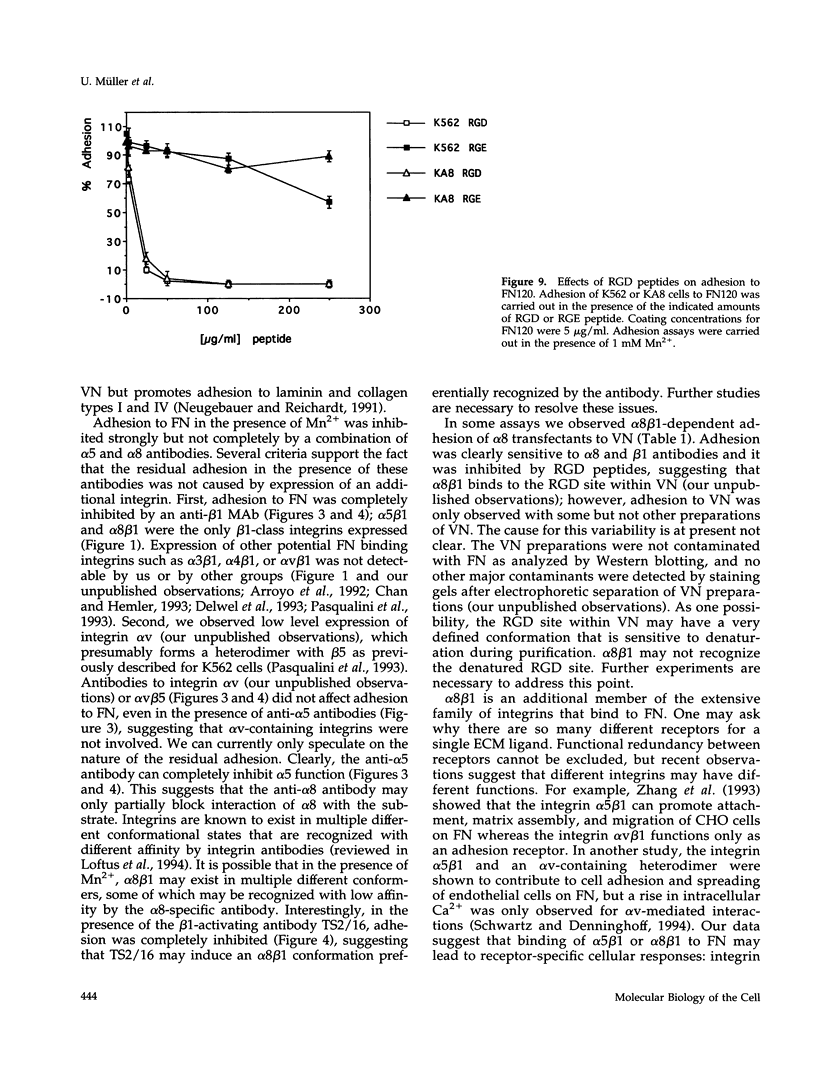




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J. C., Watt F. M. Regulation of development and differentiation by the extracellular matrix. Development. 1993 Apr;117(4):1183–1198. doi: 10.1242/dev.117.4.1183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akiyama S. K., Yamada S. S., Chen W. T., Yamada K. M. Analysis of fibronectin receptor function with monoclonal antibodies: roles in cell adhesion, migration, matrix assembly, and cytoskeletal organization. J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;109(2):863–875. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aota S., Nagai T., Yamada K. M. Characterization of regions of fibronectin besides the arginine-glycine-aspartic acid sequence required for adhesive function of the cell-binding domain using site-directed mutagenesis. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15938–15943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arroyo A. G., Sánchez-Mateos P., Campanero M. R., Martín-Padura I., Dejana E., Sánchez-Madrid F. Regulation of the VLA integrin-ligand interactions through the beta 1 subunit. J Cell Biol. 1992 May;117(3):659–670. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.3.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bossy B., Bossy-Wetzel E., Reichardt L. F. Characterization of the integrin alpha 8 subunit: a new integrin beta 1-associated subunit, which is prominently expressed on axons and on cells in contact with basal laminae in chick embryos. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2375–2385. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07776.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowditch R. D., Halloran C. E., Aota S., Obara M., Plow E. F., Yamada K. M., Ginsberg M. H. Integrin alpha IIb beta 3 (platelet GPIIb-IIIa) recognizes multiple sites in fibronectin. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 5;266(34):23323–23328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowditch R. D., Hariharan M., Tominna E. F., Smith J. W., Yamada K. M., Getzoff E. D., Ginsberg M. H. Identification of a novel integrin binding site in fibronectin. Differential utilization by beta 3 integrins. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 8;269(14):10856–10863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brümmendorf T., Hubert M., Treubert U., Leuschner R., Tárnok A., Rathjen F. G. The axonal recognition molecule F11 is a multifunctional protein: specific domains mediate interactions with Ng-CAM and restrictin. Neuron. 1993 Apr;10(4):711–727. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90172-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burridge K., Nuckolls G., Otey C., Pavalko F., Simon K., Turner C. Actin-membrane interaction in focal adhesions. Cell Differ Dev. 1990 Dec 2;32(3):337–342. doi: 10.1016/0922-3371(90)90048-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busk M., Pytela R., Sheppard D. Characterization of the integrin alpha v beta 6 as a fibronectin-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):5790–5796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan B. M., Hemler M. E. Multiple functional forms of the integrin VLA-2 can be derived from a single alpha 2 cDNA clone: interconversion of forms induced by an anti-beta 1 antibody. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;120(2):537–543. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.2.537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan B. M., Kassner P. D., Schiro J. A., Byers H. R., Kupper T. S., Hemler M. E. Distinct cellular functions mediated by different VLA integrin alpha subunit cytoplasmic domains. Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):1051–1060. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90077-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charo I. F., Nannizzi L., Smith J. W., Cheresh D. A. The vitronectin receptor alpha v beta 3 binds fibronectin and acts in concert with alpha 5 beta 1 in promoting cellular attachment and spreading on fibronectin. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 1):2795–2800. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.2795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheresh D. A., Spiro R. C. Biosynthetic and functional properties of an Arg-Gly-Asp-directed receptor involved in human melanoma cell attachment to vitronectin, fibrinogen, and von Willebrand factor. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17703–17711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuong C. M., Crossin K. L., Edelman G. M. Sequential expression and differential function of multiple adhesion molecules during the formation of cerebellar cortical layers. J Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;104(2):331–342. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.2.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conforti G., Zanetti A., Pasquali-Ronchetti I., Quaglino D., Jr, Neyroz P., Dejana E. Modulation of vitronectin receptor binding by membrane lipid composition. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):4011–4019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dedhar S., Gray V. Isolation of a novel integrin receptor mediating Arg-Gly-Asp-directed cell adhesion to fibronectin and type I collagen from human neuroblastoma cells. Association of a novel beta 1-related subunit with alpha v. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;110(6):2185–2193. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.6.2185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delwel G. O., Hogervorst F., Kuikman I., Paulsson M., Timpl R., Sonnenberg A. Expression and function of the cytoplasmic variants of the integrin alpha 6 subunit in transfected K562 cells. Activation-dependent adhesion and interaction with isoforms of laminin. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 5;268(34):25865–25875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dufour S., Duband J. L., Humphries M. J., Obara M., Yamada K. M., Thiery J. P. Attachment, spreading and locomotion of avian neural crest cells are mediated by multiple adhesion sites on fibronectin molecules. EMBO J. 1988 Sep;7(9):2661–2671. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03119.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elices M. J., Hemler M. E. The human integrin VLA-2 is a collagen receptor on some cells and a collagen/laminin receptor on others. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9906–9910. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elices M. J., Osborn L., Takada Y., Crouse C., Luhowskyj S., Hemler M. E., Lobb R. R. VCAM-1 on activated endothelium interacts with the leukocyte integrin VLA-4 at a site distinct from the VLA-4/fibronectin binding site. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):577–584. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90661-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elices M. J., Urry L. A., Hemler M. E. Receptor functions for the integrin VLA-3: fibronectin, collagen, and laminin binding are differentially influenced by Arg-Gly-Asp peptide and by divalent cations. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;112(1):169–181. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.1.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ffrench-Constant C., Hynes R. O. Alternative splicing of fibronectin is temporally and spatially regulated in the chicken embryo. Development. 1989 Jun;106(2):375–388. doi: 10.1242/dev.106.2.375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Pardo A., Wayner E. A., Carter W. G., Ferreira O. C., Jr Human B lymphocytes define an alternative mechanism of adhesion to fibronectin. The interaction of the alpha 4 beta 1 integrin with the LHGPEILDVPST sequence of the type III connecting segment is sufficient to promote cell attachment. J Immunol. 1990 May 1;144(9):3361–3366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grumet M., Hoffman S., Crossin K. L., Edelman G. M. Cytotactin, an extracellular matrix protein of neural and non-neural tissues that mediates glia-neuron interaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8075–8079. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu M., Wang W., Song W. K., Cooper D. N., Kaufman S. J. Selective modulation of the interaction of alpha 7 beta 1 integrin with fibronectin and laminin by L-14 lectin during skeletal muscle differentiation. J Cell Sci. 1994 Jan;107(Pt 1):175–181. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.1.175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan J. L., Hynes R. O. Lymphoid cells recognize an alternatively spliced segment of fibronectin via the integrin receptor alpha 4 beta 1. Cell. 1990 Jan 12;60(1):53–61. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90715-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall D. E., Neugebauer K. M., Reichardt L. F. Embryonic neural retinal cell response to extracellular matrix proteins: developmental changes and effects of the cell substratum attachment antibody (CSAT). J Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;104(3):623–634. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.3.623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall D. E., Reichardt L. F., Crowley E., Holley B., Moezzi H., Sonnenberg A., Damsky C. H. The alpha 1/beta 1 and alpha 6/beta 1 integrin heterodimers mediate cell attachment to distinct sites on laminin. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;110(6):2175–2184. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.6.2175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz A., Duggan K., Greggs R., Decker C., Buck C. The cell substrate attachment (CSAT) antigen has properties of a receptor for laminin and fibronectin. J Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;101(6):2134–2144. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.6.2134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries M. J., Akiyama S. K., Komoriya A., Olden K., Yamada K. M. Identification of an alternatively spliced site in human plasma fibronectin that mediates cell type-specific adhesion. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 2):2637–2647. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries M. J., Akiyama S. K., Komoriya A., Olden K., Yamada K. M. Neurite extension of chicken peripheral nervous system neurons on fibronectin: relative importance of specific adhesion sites in the central cell-binding domain and the alternatively spliced type III connecting segment. J Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;106(4):1289–1297. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.4.1289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries M. J., Komoriya A., Akiyama S. K., Olden K., Yamada K. M. Identification of two distinct regions of the type III connecting segment of human plasma fibronectin that promote cell type-specific adhesion. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6886–6892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: versatility, modulation, and signaling in cell adhesion. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):11–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90115-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R., Tran Van Nhieu G. Binding and internalization of microorganisms by integrin receptors. Trends Microbiol. 1994 Jan;2(1):10–14. doi: 10.1016/0966-842x(94)90338-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimizuka F., Ohdate Y., Kawase Y., Shimojo T., Taguchi Y., Hashino K., Goto S., Hashi H., Kato I., Sekiguchi K. Role of type III homology repeats in cell adhesive function within the cell-binding domain of fibronectin. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 15;266(5):3045–3051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchhofer D., Languino L. R., Ruoslahti E., Pierschbacher M. D. Alpha 2 beta 1 integrins from different cell types show different binding specificities. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):615–618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krotoski D. M., Domingo C., Bronner-Fraser M. Distribution of a putative cell surface receptor for fibronectin and laminin in the avian embryo. J Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;103(3):1061–1071. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.3.1061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagenaur C., Lemmon V. An L1-like molecule, the 8D9 antigen, is a potent substrate for neurite extension. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7753–7757. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefcort F., Venstrom K., McDonald J. A., Reichardt L. F. Regulation of expression of fibronectin and its receptor, alpha 5 beta 1, during development and regeneration of peripheral nerve. Development. 1992 Nov;116(3):767–782. doi: 10.1242/dev.116.3.767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loftus J. C., Smith J. W., Ginsberg M. H. Integrin-mediated cell adhesion: the extracellular face. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 14;269(41):25235–25238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masumoto A., Hemler M. E. Multiple activation states of VLA-4. Mechanistic differences between adhesion to CS1/fibronectin and to vascular cell adhesion molecule-1. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 5;268(1):228–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masumoto A., Hemler M. E. Mutation of putative divalent cation sites in the alpha 4 subunit of the integrin VLA-4: distinct effects on adhesion to CS1/fibronectin, VCAM-1, and invasin. J Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;123(1):245–253. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.1.245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mould A. P., Humphries M. J. Identification of a novel recognition sequence for the integrin alpha 4 beta 1 in the COOH-terminal heparin-binding domain of fibronectin. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4089–4095. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04985.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mould A. P., Komoriya A., Yamada K. M., Humphries M. J. The CS5 peptide is a second site in the IIICS region of fibronectin recognized by the integrin alpha 4 beta 1. Inhibition of alpha 4 beta 1 function by RGD peptide homologues. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 25;266(6):3579–3585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mould A. P., Wheldon L. A., Komoriya A., Wayner E. A., Yamada K. M., Humphries M. J. Affinity chromatographic isolation of the melanoma adhesion receptor for the IIICS region of fibronectin and its identification as the integrin alpha 4 beta 1. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):4020–4024. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller U., Kleinberger T., Shenk T. Adenovirus E4orf4 protein reduces phosphorylation of c-Fos and E1A proteins while simultaneously reducing the level of AP-1. J Virol. 1992 Oct;66(10):5867–5878. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.10.5867-5878.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai T., Yamakawa N., Aota S., Yamada S. S., Akiyama S. K., Olden K., Yamada K. M. Monoclonal antibody characterization of two distant sites required for function of the central cell-binding domain of fibronectin in cell adhesion, cell migration, and matrix assembly. J Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;114(6):1295–1305. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.6.1295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neff N. T., Lowrey C., Decker C., Tovar A., Damsky C., Buck C., Horwitz A. F. A monoclonal antibody detaches embryonic skeletal muscle from extracellular matrices. J Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;95(2 Pt 1):654–666. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.2.654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neugebauer K. M., Reichardt L. F. Cell-surface regulation of beta 1-integrin activity on developing retinal neurons. Nature. 1991 Mar 7;350(6313):68–71. doi: 10.1038/350068a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newgreen D., Thiery J. P. Fibronectin in early avian embryos: synthesis and distribution along the migration pathways of neural crest cells. Cell Tissue Res. 1980;211(2):269–291. doi: 10.1007/BF00236449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obara M., Kang M. S., Yamada K. M. Site-directed mutagenesis of the cell-binding domain of human fibronectin: separable, synergistic sites mediate adhesive function. Cell. 1988 May 20;53(4):649–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90580-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasqualini R., Bodorova J., Ye S., Hemler M. E. A study of the structure, function and distribution of beta 5 integrins using novel anti-beta 5 monoclonal antibodies. J Cell Sci. 1993 May;105(Pt 1):101–111. doi: 10.1242/jcs.105.1.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasqualini R., Hemler M. E. Contrasting roles for integrin beta 1 and beta 5 cytoplasmic domains in subcellular localization, cell proliferation, and cell migration. J Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;125(2):447–460. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.2.447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pytela R., Pierschbacher M. D., Ginsberg M. H., Plow E. F., Ruoslahti E. Platelet membrane glycoprotein IIb/IIIa: member of a family of Arg-Gly-Asp--specific adhesion receptors. Science. 1986 Mar 28;231(4745):1559–1562. doi: 10.1126/science.2420006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pytela R., Pierschbacher M. D., Ruoslahti E. A 125/115-kDa cell surface receptor specific for vitronectin interacts with the arginine-glycine-aspartic acid adhesion sequence derived from fibronectin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5766–5770. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pytela R., Pierschbacher M. D., Ruoslahti E. Identification and isolation of a 140 kd cell surface glycoprotein with properties expected of a fibronectin receptor. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):191–198. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90322-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rader C., Stoeckli E. T., Ziegler U., Osterwalder T., Kunz B., Sonderegger P. Cell-cell adhesion by homophilic interaction of the neuronal recognition molecule axonin-1. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Jul 1;215(1):133–141. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18015.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rein A., Rubin H. Effects of local cell concentrations upon the growth of chick embryo cells in tissue culture. Exp Cell Res. 1968 Mar;49(3):666–678. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(68)90213-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers S. L., Letourneau P. C., Palm S. L., McCarthy J., Furcht L. T. Neurite extension by peripheral and central nervous system neurons in response to substratum-bound fibronectin and laminin. Dev Biol. 1983 Jul;98(1):212–220. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90350-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüegg C., Postigo A. A., Sikorski E. E., Butcher E. C., Pytela R., Erle D. J. Role of integrin alpha 4 beta 7/alpha 4 beta P in lymphocyte adherence to fibronectin and VCAM-1 and in homotypic cell clustering. J Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;117(1):179–189. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.1.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M. A., Denninghoff K. Alpha v integrins mediate the rise in intracellular calcium in endothelial cells on fibronectin even though they play a minor role in adhesion. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 15;269(15):11133–11137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu Y., Mobley J. L. Distinct divalent cation requirements for integrin-mediated CD4+ T lymphocyte adhesion to ICAM-1, fibronectin, VCAM-1, and invasin. J Immunol. 1993 Oct 15;151(8):4106–4115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonderegger P., Rathjen F. G. Regulation of axonal growth in the vertebrate nervous system by interactions between glycoproteins belonging to two subgroups of the immunoglobulin superfamily. J Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;119(6):1387–1394. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.6.1387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenberg A. Integrins and their ligands. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1993;184:7–35. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-78253-4_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Aparicio P., Dominguez-Jiménez C., Garcia-Pardo A. Activation of the alpha 4 beta 1 integrin through the beta 1 subunit induces recognition of the RGDS sequence in fibronectin. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;126(1):271–279. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.1.271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timpl R., Rohde H., Robey P. G., Rennard S. I., Foidart J. M., Martin G. R. Laminin--a glycoprotein from basement membranes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9933–9937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomaselli K. J., Damsky C. H., Reichardt L. F. Purification and characterization of mammalian integrins expressed by a rat neuronal cell line (PC12): evidence that they function as alpha/beta heterodimeric receptors for laminin and type IV collagen. J Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;107(3):1241–1252. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.3.1241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomaselli K. J., Reichardt L. F., Bixby J. L. Distinct molecular interactions mediate neuronal process outgrowth on non-neuronal cell surfaces and extracellular matrices. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 2):2659–2672. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel B. E., Tarone G., Giancotti F. G., Gailit J., Ruoslahti E. A novel fibronectin receptor with an unexpected subunit composition (alpha v beta 1). J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 15;265(11):5934–5937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wayner E. A., Garcia-Pardo A., Humphries M. J., McDonald J. A., Carter W. G. Identification and characterization of the T lymphocyte adhesion receptor for an alternative cell attachment domain (CS-1) in plasma fibronectin. J Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;109(3):1321–1330. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.3.1321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinacker A., Chen A., Agrez M., Cone R. I., Nishimura S., Wayner E., Pytela R., Sheppard D. Role of the integrin alpha v beta 6 in cell attachment to fibronectin. Heterologous expression of intact and secreted forms of the receptor. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 4;269(9):6940–6948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werb Z., Tremble P. M., Behrendtsen O., Crowley E., Damsky C. H. Signal transduction through the fibronectin receptor induces collagenase and stromelysin gene expression. J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;109(2):877–889. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Z., Morla A. O., Vuori K., Bauer J. S., Juliano R. L., Ruoslahti E. The alpha v beta 1 integrin functions as a fibronectin receptor but does not support fibronectin matrix assembly and cell migration on fibronectin. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;122(1):235–242. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.1.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]