Abstract
We recently determined the nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding p28, a light chain of inner dynein arms of Chlamydomonas axonemes. Here, we show that p28 is the protein encoded by the IDA4 locus. p28, and the dynein heavy chains normally associated with it, are completely absent from the flagella and cell bodies of three allelic strains of ida4, named ida4-1, ida4-2, and ida4-3. We determined the nucleotide sequence of the three alleles of the p28 gene and found in each case a single nucleotide change, affecting the splice sites of the first, second, and fourth introns, respectively. Reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction amplification of RNAs prepared from ida4 cells confirmed that these mutations prevent the correct splicing of the affected introns, thereby blocking the synthesis of full-length p28. These are the first intron splicing mutations described in Chlamydomonas and the first inner dynein arm mutations characterized at the molecular level. The absence in ida4 axonemes of the dynein heavy chains normally found in association with p28 suggests that p28 is necessary for stable assembly of a subset of inner dynein arms or for the binding of these arms to the microtubule doublets.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aebi M., Hornig H., Weissmann C. 5' cleavage site in eukaryotic pre-mRNA splicing is determined by the overall 5' splice region, not by the conserved 5' GU. Cell. 1987 Jul 17;50(2):237–246. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90219-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang D. D., Sharp P. A. Regulation by HIV Rev depends upon recognition of splice sites. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):789–795. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90602-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daar I. O., Maquat L. E. Premature translation termination mediates triosephosphate isomerase mRNA degradation. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):802–813. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuzawa H., Fujiwara S., Tachiki A., Miyachi S. Nucleotide sequences of two genes CAH1 and CAH2 which encode carbonic anhydrase polypeptides in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 11;18(21):6441–6442. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.21.6441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner L. C., O'Toole E., Perrone C. A., Giddings T., Porter M. E. Components of a "dynein regulatory complex" are located at the junction between the radial spokes and the dynein arms in Chlamydomonas flagella. J Cell Biol. 1994 Dec;127(5):1311–1325. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.5.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross C. H., Ranum L. P., Lefebvre P. A. Extensive restriction fragment length polymorphisms in a new isolate of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Curr Genet. 1988 Jun;13(6):503–508. doi: 10.1007/BF02427756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschhorn R., Yang D. R., Israni A., Huie M. L., Ownby D. R. Somatic mosaicism for a newly identified splice-site mutation in a patient with adenosine deaminase-deficient immunodeficiency and spontaneous clinical recovery. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Jul;55(1):59–68. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson I. J. A reappraisal of non-consensus mRNA splice sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 25;19(14):3795–3798. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.14.3795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. A., Rosenbaum J. L. Flagellar regeneration in Chlamydomonas: a model system for studying organelle assembly. Trends Cell Biol. 1993 May;3(5):156–161. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(93)90136-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamiya R., Hasegawa E. Intrinsic difference in beat frequency between the two flagella of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Exp Cell Res. 1987 Nov;173(1):299–304. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(87)90357-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamiya R., Kurimoto E., Muto E. Two types of Chlamydomonas flagellar mutants missing different components of inner-arm dynein. J Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;112(3):441–447. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.3.441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamiya R., Okamoto M. A mutant of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii that lacks the flagellar outer dynein arm but can swim. J Cell Sci. 1985 Mar;74:181–191. doi: 10.1242/jcs.74.1.181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeDizet M., Piperno G. Cytoplasmic microtubules containing acetylated alpha-tubulin in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: spatial arrangement and properties. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;103(1):13–22. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.1.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee V. D., Huang B. Missense mutations at lysine 350 in beta 2-tubulin confer altered sensitivity to microtubule inhibitors in Chlamydomonas. Plant Cell. 1990 Nov;2(11):1051–1057. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.11.1051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leeds P., Peltz S. W., Jacobson A., Culbertson M. R. The product of the yeast UPF1 gene is required for rapid turnover of mRNAs containing a premature translational termination codon. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12A):2303–2314. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12a.2303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legrain P., Rosbash M. Some cis- and trans-acting mutants for splicing target pre-mRNA to the cytoplasm. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):573–583. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90127-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Losson R., Lacroute F. Interference of nonsense mutations with eukaryotic messenger RNA stability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5134–5137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luck D., Piperno G., Ramanis Z., Huang B. Flagellar mutants of Chlamydomonas: studies of radial spoke-defective strains by dikaryon and revertant analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3456–3460. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malim M. H., Cullen B. R. Rev and the fate of pre-mRNA in the nucleus: implications for the regulation of RNA processing in eukaryotes. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;13(10):6180–6189. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.10.6180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mastronarde D. N., O'Toole E. T., McDonald K. L., McIntosh J. R., Porter M. E. Arrangement of inner dynein arms in wild-type and mutant flagella of Chlamydomonas. J Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;118(5):1145–1162. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.5.1145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell D. R., Kang Y. Reversion analysis of dynein intermediate chain function. J Cell Sci. 1993 Aug;105(Pt 4):1069–1078. doi: 10.1242/jcs.105.4.1069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai K., Sakamoto H. Construction of a novel database containing aberrant splicing mutations of mammalian genes. Gene. 1994 Apr 20;141(2):171–177. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)90567-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piperno G., Huang B., Ramanis Z., Luck D. J. Radial spokes of Chlamydomonas flagella: polypeptide composition and phosphorylation of stalk components. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jan;88(1):73–79. doi: 10.1083/jcb.88.1.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piperno G. Isolation of a sixth dynein subunit adenosine triphosphatase of Chlamydomonas axonemes. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;106(1):133–140. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piperno G., Mead K., Shestak W. The inner dynein arms I2 interact with a "dynein regulatory complex" in Chlamydomonas flagella. J Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;118(6):1455–1463. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.6.1455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piperno G., Ramanis Z., Smith E. F., Sale W. S. Three distinct inner dynein arms in Chlamydomonas flagella: molecular composition and location in the axoneme. J Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;110(2):379–389. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.2.379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piperno G., Ramanis Z. The proximal portion of Chlamydomonas flagella contains a distinct set of inner dynein arms. J Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;112(4):701–709. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.4.701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter M. E., Knott J. A., Gardner L. C., Mitchell D. R., Dutcher S. K. Mutations in the SUP-PF-1 locus of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii identify a regulatory domain in the beta-dynein heavy chain. J Cell Biol. 1994 Sep;126(6):1495–1507. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.6.1495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulak R., Anderson P. mRNA surveillance by the Caenorhabditis elegans smg genes. Genes Dev. 1993 Oct;7(10):1885–1897. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.10.1885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn J., Li H. H., Singer J., Morimoto B., Mets L., Kindle K., Merchant S. The plastocyanin-deficient phenotype of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii Ac-208 results from a frame-shift mutation in the nuclear gene encoding preapoplastocyanin. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 15;268(11):7832–7841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranum L. P., Thompson M. D., Schloss J. A., Lefebvre P. A., Silflow C. D. Mapping flagellar genes in Chlamydomonas using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Genetics. 1988 Sep;120(1):109–122. doi: 10.1093/genetics/120.1.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
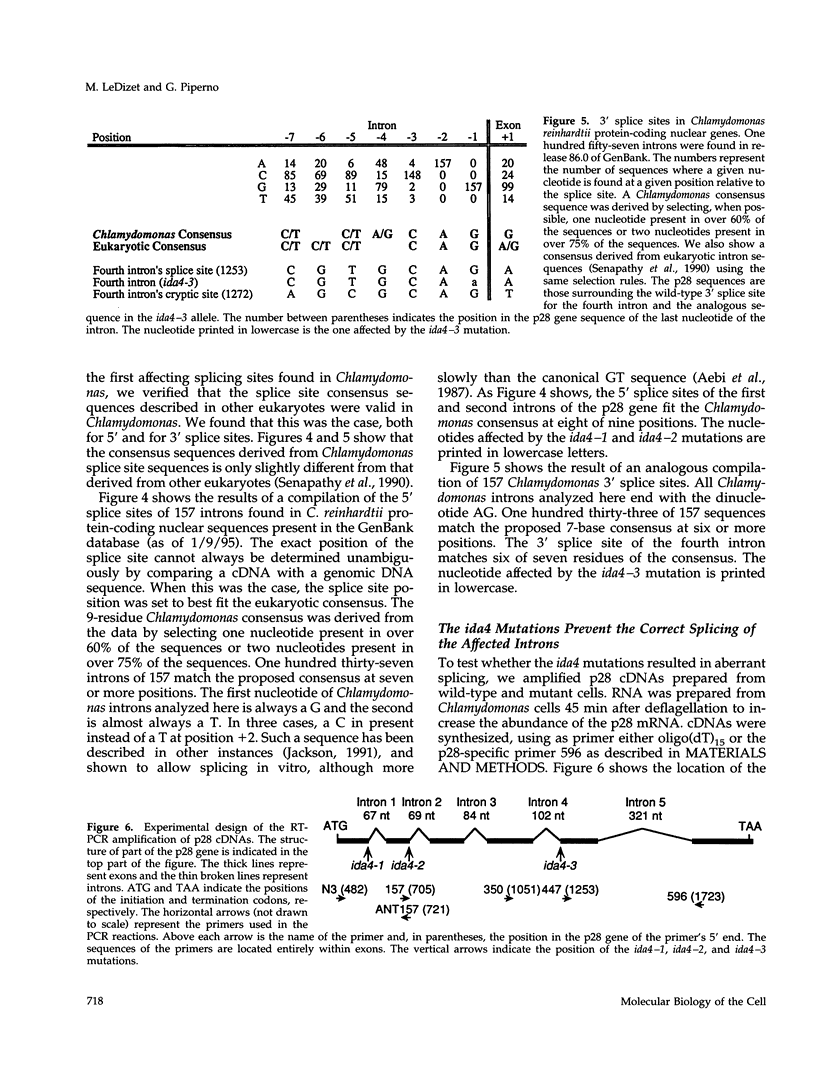
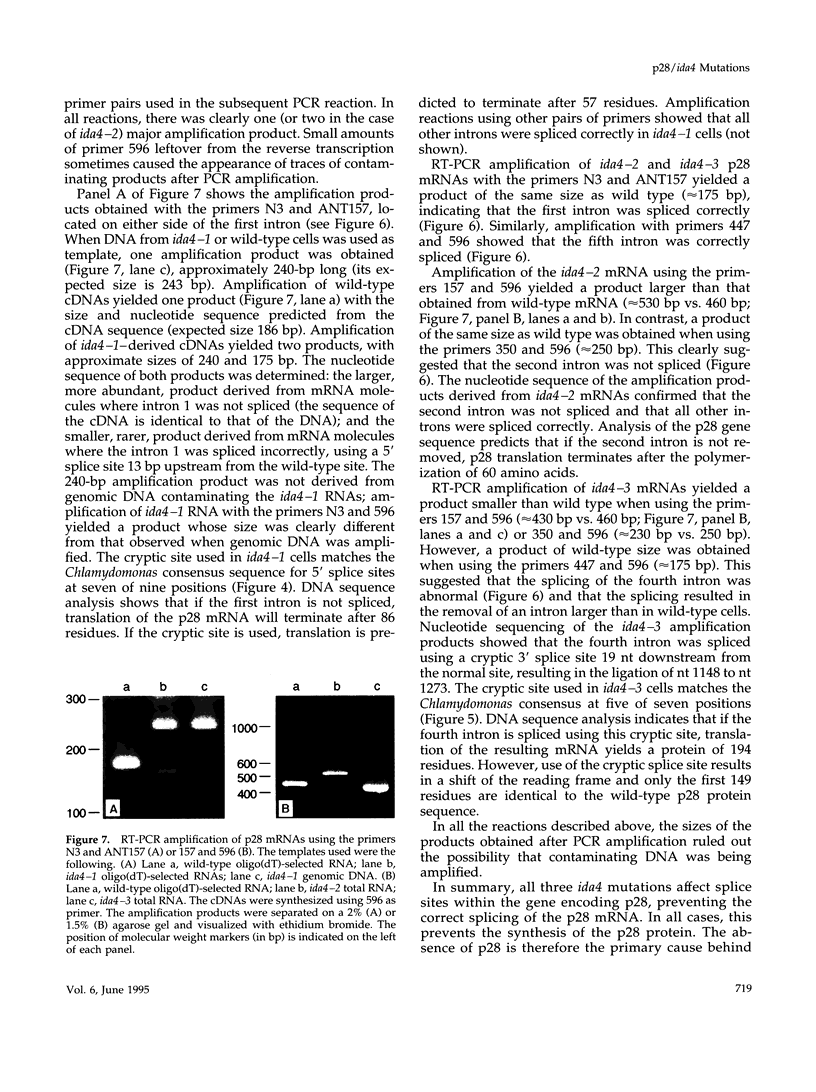
- Senapathy P., Shapiro M. B., Harris N. L. Splice junctions, branch point sites, and exons: sequence statistics, identification, and applications to genome project. Methods Enzymol. 1990;183:252–278. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)83018-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taillon B. E., Adler S. A., Suhan J. P., Jarvik J. W. Mutational analysis of centrin: an EF-hand protein associated with three distinct contractile fibers in the basal body apparatus of Chlamydomonas. J Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;119(6):1613–1624. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.6.1613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urlaub G., Mitchell P. J., Ciudad C. J., Chasin L. A. Nonsense mutations in the dihydrofolate reductase gene affect RNA processing. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):2868–2880. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.2868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walther Z., Vashishtha M., Hall J. L. The Chlamydomonas FLA10 gene encodes a novel kinesin-homologous protein. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;126(1):175–188. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.1.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkerson C. G., King S. M., Witman G. B. Molecular analysis of the gamma heavy chain of Chlamydomonas flagellar outer-arm dynein. J Cell Sci. 1994 Mar;107(Pt 3):497–506. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.3.497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B. D., Velleca M. A., Curry A. M., Rosenbaum J. L. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of the Chlamydomonas gene coding for radial spoke protein 3: flagellar mutation pf-14 is an ochre allele. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;109(1):235–245. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.1.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]