Abstract
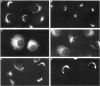
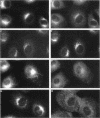
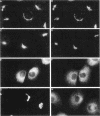
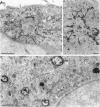
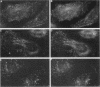
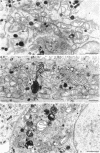
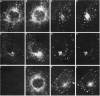
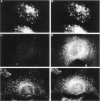
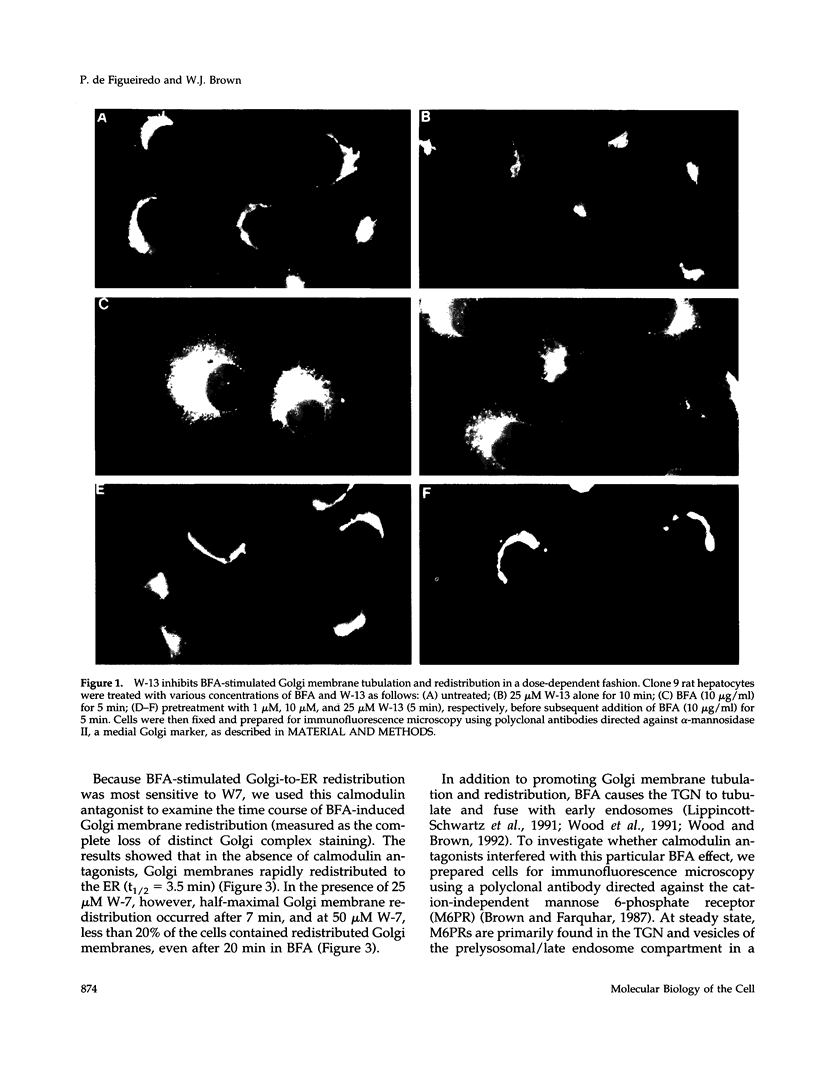
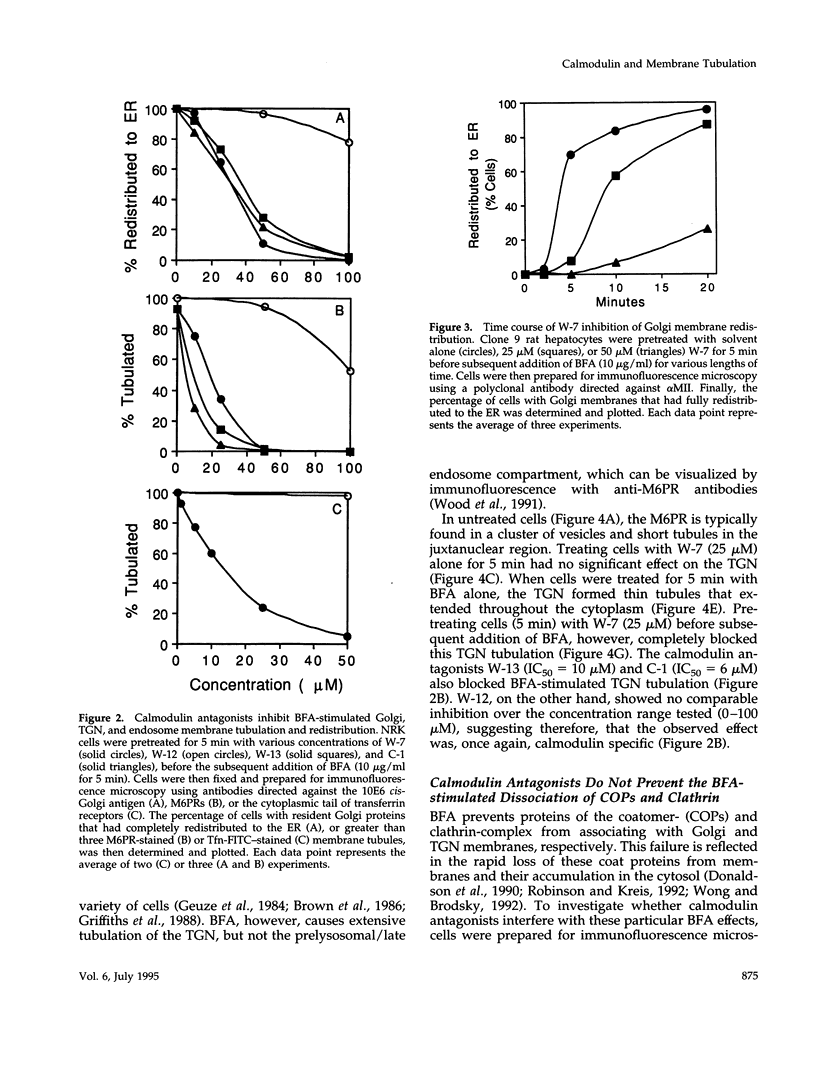
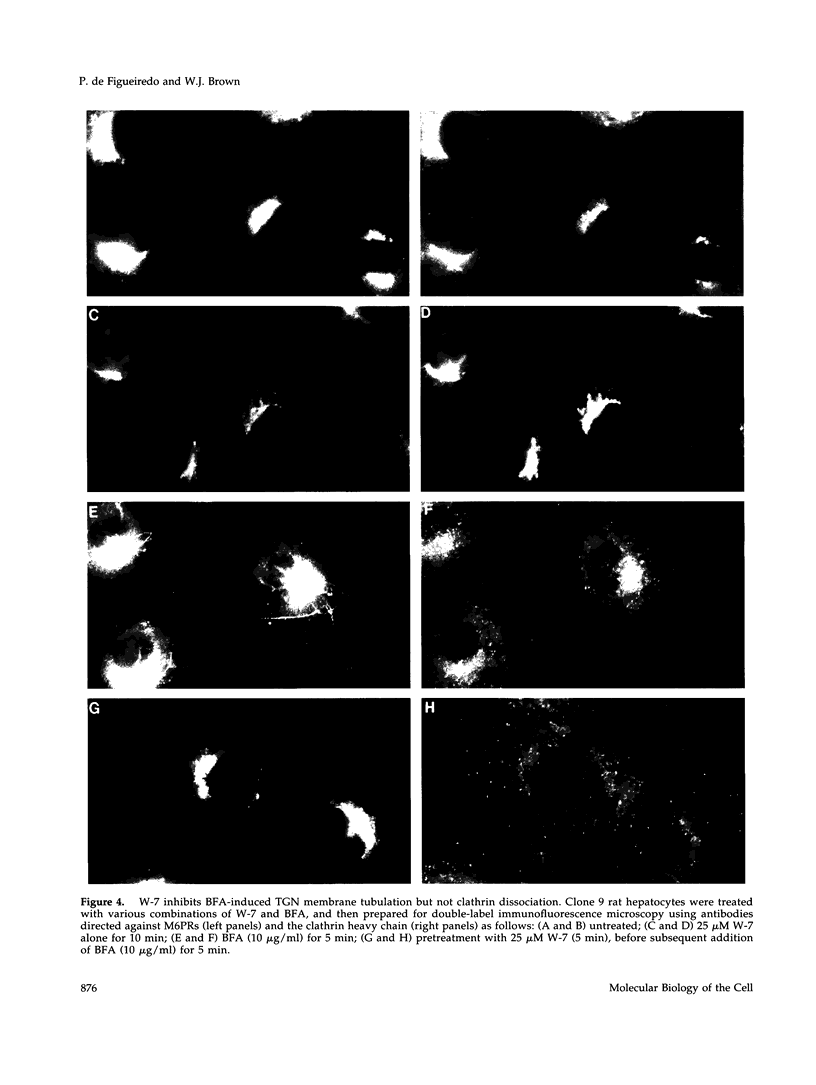
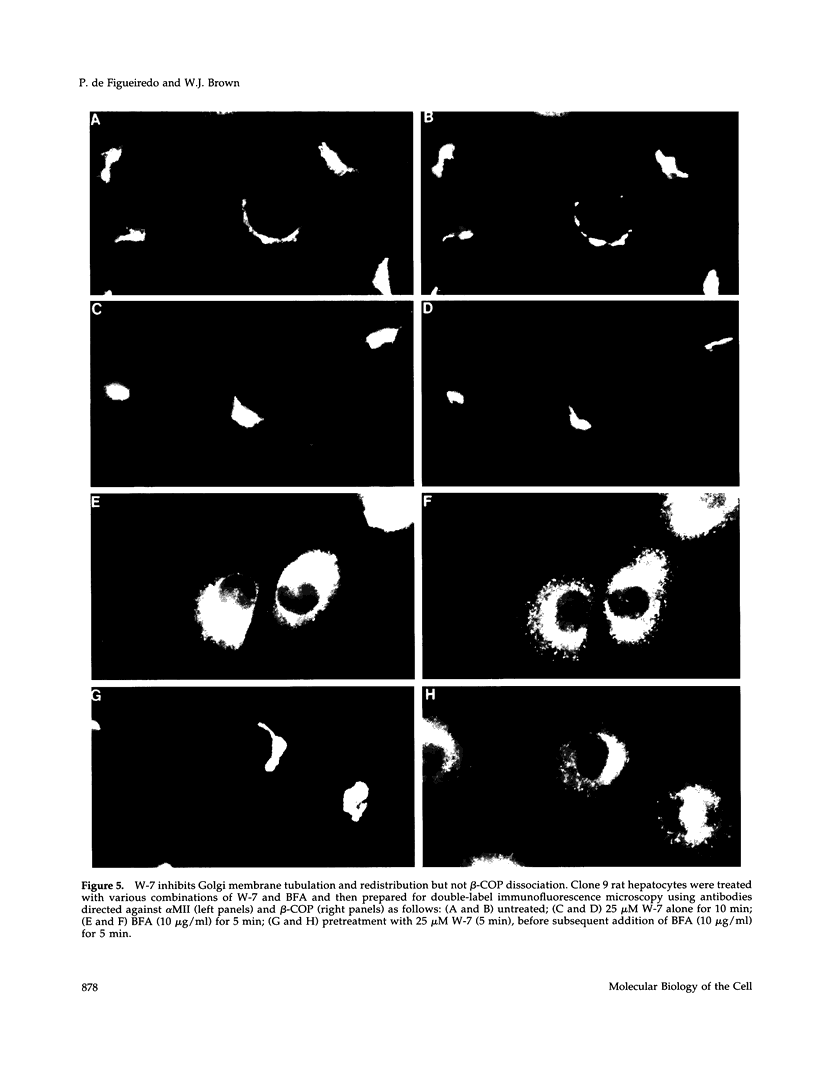
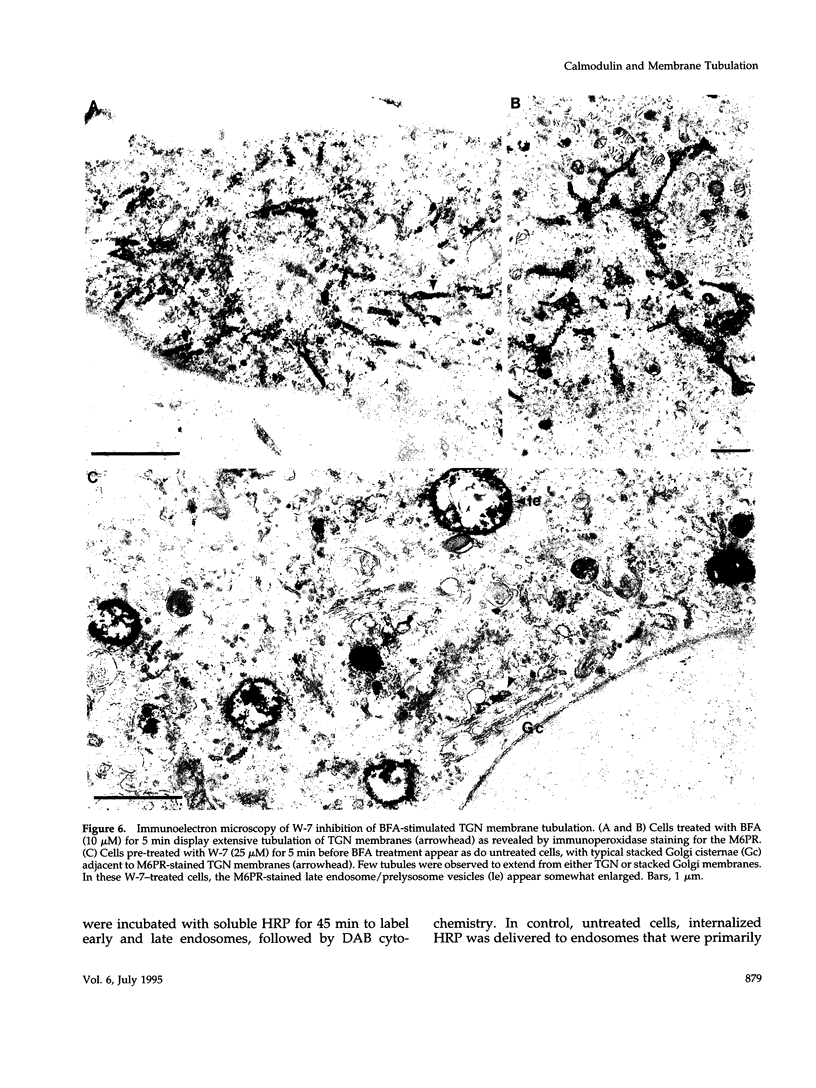
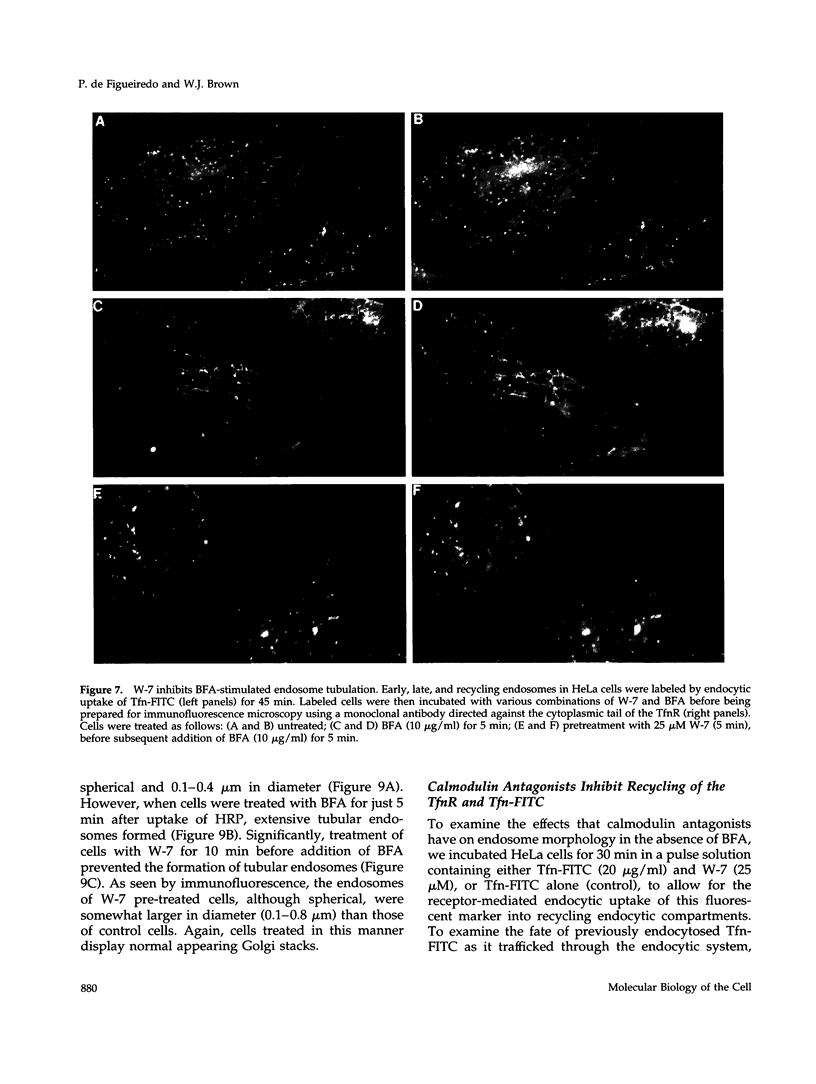
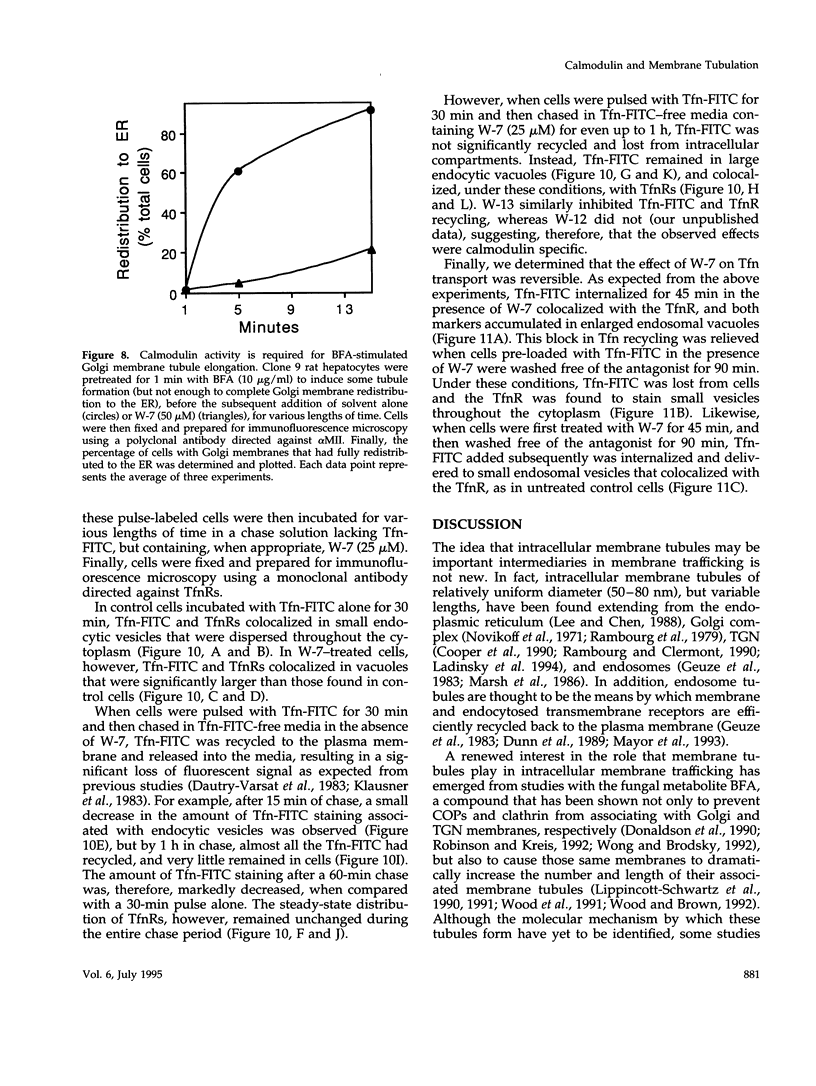
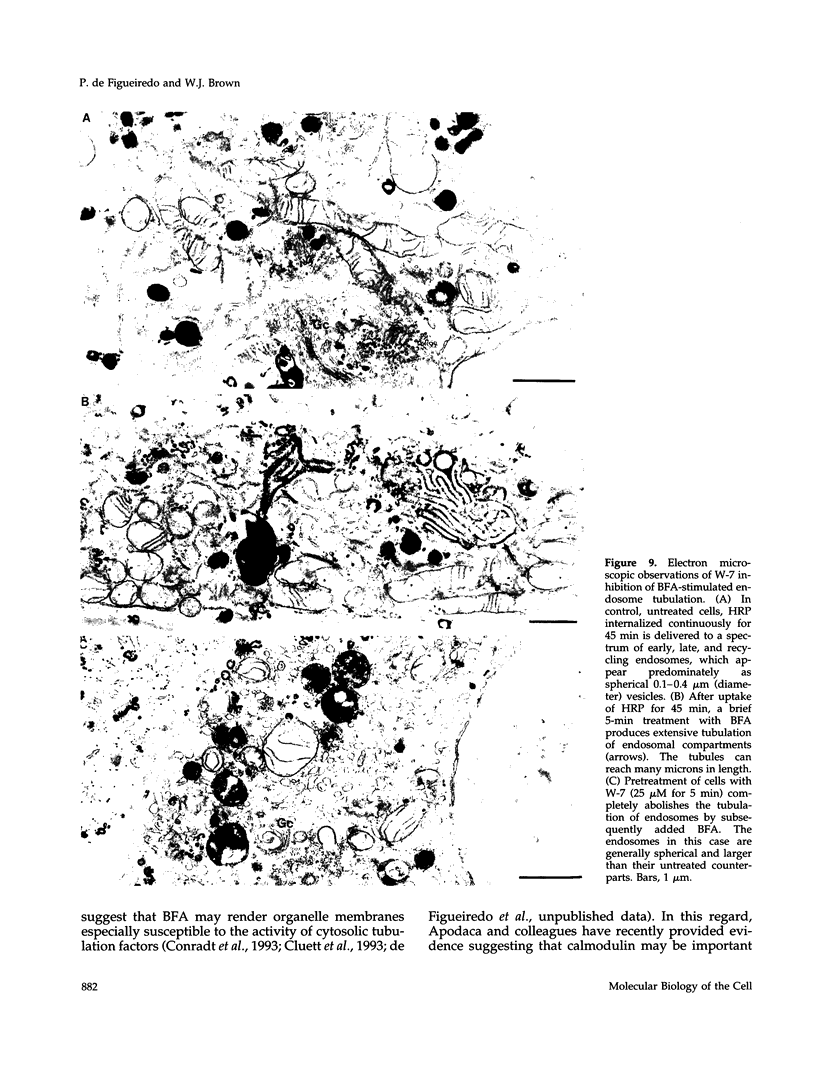
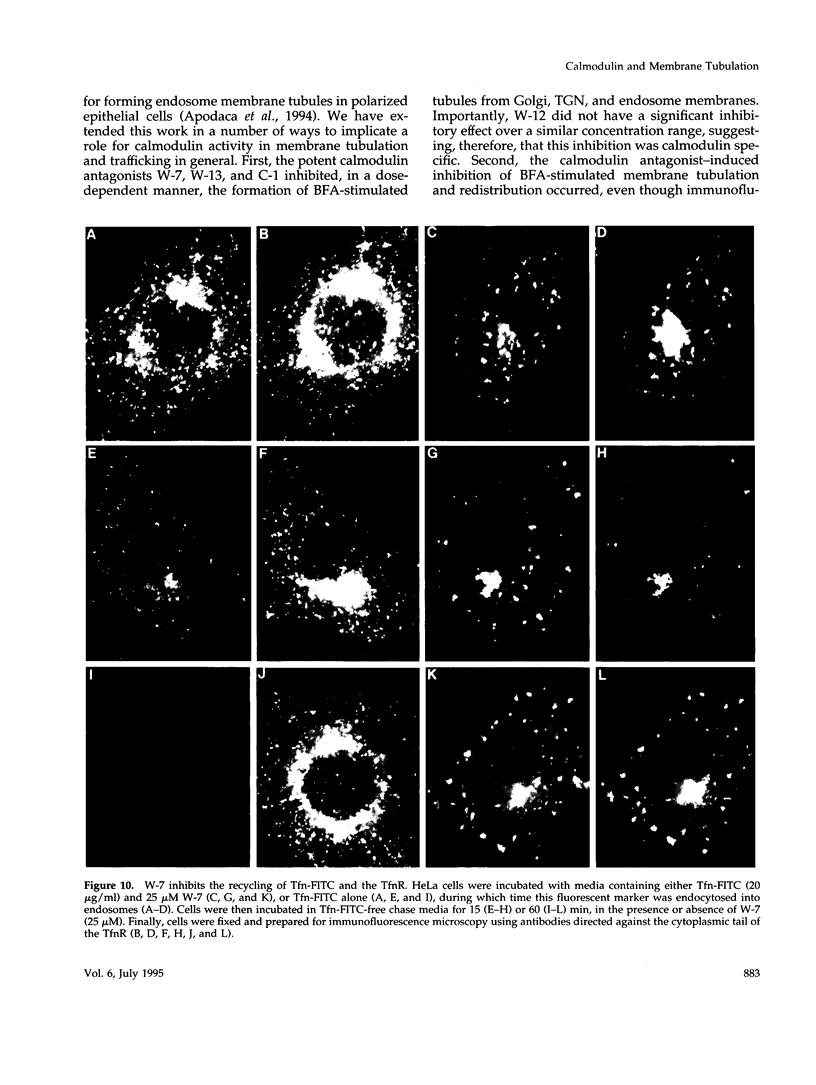
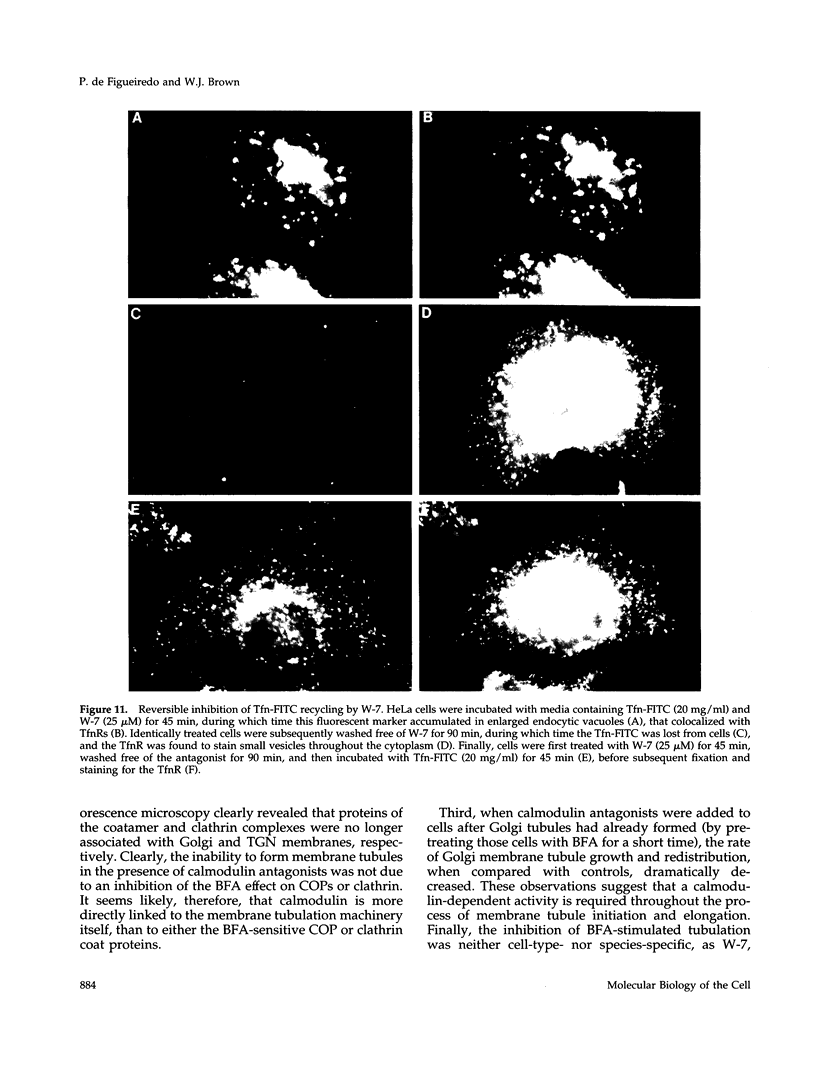
Membrane tubules of uniform diameter (60-80 nm) and variable lengths have been seen to extend from the main bodies of the Golgi complex, trans Golgi network (TGN), and endosomes. In the case of endosomes, these tubules appear to mediate membrane and receptor recycling events. Brefeldin A (BFA) is a potent drug that completely blocks coated vesicle formation from the Golgi complex and TGN, but at the same time causes the enhanced formation of membrane tubules from these same organelles. Recently, experiments have shown that calmodulin antagonists inhibit the transport of receptors out of endosomes, perhaps by inhibiting the formation of recycling tubules. Using the potent calmodulin-specific antagonists N-(6-aminohexyl)-5-chloro-1-naphthalenesulfonamide (W-7), N-(4-aminobutyl)-5-chloro-2-naphthalenesulfonamide (W-13), and N-(4-aminobutyl)-5-chloro-1-naphthalenesulfonamide (C-1), we found that the recycling of transferrin from endosomes to the cell surface was significantly inhibited, resulting in the formation of enlarged endosomal vacuoles. In addition, these same calmodulin antagonists also potently inhibited the formation of BFA-stimulated membrane tubules from the Golgi complex, TGN, and endosomes. In the case of the Golgi complex, failure to form tubules resulted in the inhibition of BFA-stimulated retrograde transport to the endoplasmic reticulum. These results suggest that calmodulin is a general regulator of membrane tubulation and is capable of influencing the morphology of several organelles.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R. G. Dissecting clathrin-coated pits. Trends Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;3(6):177–179. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(93)90205-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apodaca G., Enrich C., Mostov K. E. The calmodulin antagonist, W-13, alters transcytosis, recycling, and the morphology of the endocytic pathway in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 22;269(29):19005–19013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. J., Farquhar M. G. Immunoperoxidase methods for the localization of antigens in cultured cells and tissue sections by electron microscopy. Methods Cell Biol. 1989;31:553–569. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61626-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. J., Farquhar M. G. The distribution of 215-kilodalton mannose 6-phosphate receptors within cis (heavy) and trans (light) Golgi subfractions varies in different cell types. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9001–9005. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. J., Goodhouse J., Farquhar M. G. Mannose-6-phosphate receptors for lysosomal enzymes cycle between the Golgi complex and endosomes. J Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;103(4):1235–1247. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.4.1235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chafouleas J. G., Bolton W. E., Hidaka H., Boyd A. E., 3rd, Means A. R. Calmodulin and the cell cycle: involvement in regulation of cell-cycle progression. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):41–50. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90373-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cluett E. B., Wood S. A., Banta M., Brown W. J. Tubulation of Golgi membranes in vivo and in vitro in the absence of brefeldin A. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;120(1):15–24. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.1.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conradt B., Shaw J., Vida T., Emr S., Wickner W. In vitro reactions of vacuole inheritance in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;119(6):1469–1479. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.6.1469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper M. S., Cornell-Bell A. H., Chernjavsky A., Dani J. W., Smith S. J. Tubulovesicular processes emerge from trans-Golgi cisternae, extend along microtubules, and interlink adjacent trans-golgi elements into a reticulum. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):135–145. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90221-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dautry-Varsat A., Ciechanover A., Lodish H. F. pH and the recycling of transferrin during receptor-mediated endocytosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2258–2262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson J. G., Lippincott-Schwartz J., Bloom G. S., Kreis T. E., Klausner R. D. Dissociation of a 110-kD peripheral membrane protein from the Golgi apparatus is an early event in brefeldin A action. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 1):2295–2306. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.2295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn K. W., McGraw T. E., Maxfield F. R. Iterative fractionation of recycling receptors from lysosomally destined ligands in an early sorting endosome. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 2):3303–3314. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.3303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geuze H. J., Slot J. W., Schwartz A. L. Membranes of sorting organelles display lateral heterogeneity in receptor distribution. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;104(6):1715–1723. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.6.1715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geuze H. J., Slot J. W., Strous G. J., Hasilik A., Von Figura K. Ultrastructural localization of the mannose 6-phosphate receptor in rat liver. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;98(6):2047–2054. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.6.2047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geuze H. J., Slot J. W., Strous G. J., Lodish H. F., Schwartz A. L. Intracellular site of asialoglycoprotein receptor-ligand uncoupling: double-label immunoelectron microscopy during receptor-mediated endocytosis. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):277–287. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90518-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geuze H. J., Stoorvogel W., Strous G. J., Slot J. W., Bleekemolen J. E., Mellman I. Sorting of mannose 6-phosphate receptors and lysosomal membrane proteins in endocytic vesicles. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 2):2491–2501. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grasso J. A., Bruno M., Yates A. A., Wei L. T., Epstein P. M. Calmodulin dependence of transferrin receptor recycling in rat reticulocytes. Biochem J. 1990 Feb 15;266(1):261–272. doi: 10.1042/bj2660261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths G., Hoflack B., Simons K., Mellman I., Kornfeld S. The mannose 6-phosphate receptor and the biogenesis of lysosomes. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):329–341. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauri H. P., Schweizer A. The endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;4(4):600–608. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90078-Q. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C. Effects of trifluoperazine and pimozide on stimulus-secretion coupling in pancreatic B-cells. Suggestion for a role of calmodulin? Biochem J. 1981 Jun 15;196(3):771–780. doi: 10.1042/bj1960771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Asano M., Tanaka T. Activity-structure relationship of calmodulin antagonists, Naphthalenesulfonamide derivatives. Mol Pharmacol. 1981 Nov;20(3):571–578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins C. R., Gibson A., Shipman M., Miller K. Movement of internalized ligand-receptor complexes along a continuous endosomal reticulum. Nature. 1990 Jul 26;346(6282):335–339. doi: 10.1038/346335a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins C. R., Gibson A., Shipman M., Strickland D. K., Trowbridge I. S. In migrating fibroblasts, recycling receptors are concentrated in narrow tubules in the pericentriolar area, and then routed to the plasma membrane of the leading lamella. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;125(6):1265–1274. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.6.1265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz S. B., Chia G. H., Harracksingh C., Orlow S., Pifko-Hirst S., Schneck J., Sorbara L., Speaker M., Wilk E. W., Rosen O. M. Trifluoperazine inhibits phagocytosis in a macrophagelike cultured cell line. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 1):798–802. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunziker W. The calmodulin antagonist W-7 affects transcytosis, lysosomal transport, and recycling but not endocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1994 Nov 18;269(46):29003–29009. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunziker W., Whitney J. A., Mellman I. Selective inhibition of transcytosis by brefeldin A in MDCK cells. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):617–627. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90535-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson J. D., Palade G. E. Intracellular transport of secretory proteins in the pancreatic exocrine cell. I. Role of the peripheral elements of the Golgi complex. J Cell Biol. 1967 Aug;34(2):577–596. doi: 10.1083/jcb.34.2.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausner R. D., Ashwell G., van Renswoude J., Harford J. B., Bridges K. R. Binding of apotransferrin to K562 cells: explanation of the transferrin cycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2263–2266. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausner R. D., Donaldson J. G., Lippincott-Schwartz J. Brefeldin A: insights into the control of membrane traffic and organelle structure. J Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;116(5):1071–1080. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.5.1071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladinsky M. S., Kremer J. R., Furcinitti P. S., McIntosh J. R., Howell K. E. HVEM tomography of the trans-Golgi network: structural insights and identification of a lace-like vesicle coat. J Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;127(1):29–38. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.1.29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C., Chen L. B. Dynamic behavior of endoplasmic reticulum in living cells. Cell. 1988 Jul 1;54(1):37–46. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90177-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippincott-Schwartz J., Donaldson J. G., Schweizer A., Berger E. G., Hauri H. P., Yuan L. C., Klausner R. D. Microtubule-dependent retrograde transport of proteins into the ER in the presence of brefeldin A suggests an ER recycling pathway. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):821–836. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90096-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippincott-Schwartz J., Yuan L., Tipper C., Amherdt M., Orci L., Klausner R. D. Brefeldin A's effects on endosomes, lysosomes, and the TGN suggest a general mechanism for regulating organelle structure and membrane traffic. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):601–616. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90534-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M., Griffiths G., Dean G. E., Mellman I., Helenius A. Three-dimensional structure of endosomes in BHK-21 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2899–2903. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxfield F. R., Schlessinger J., Shechter Y., Pastan I., Willingham M. C. Collection of insulin, EGF and alpha2-macroglobulin in the same patches on the surface of cultured fibroblasts and common internalization. Cell. 1978 Aug;14(4):805–810. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90336-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayor S., Presley J. F., Maxfield F. R. Sorting of membrane components from endosomes and subsequent recycling to the cell surface occurs by a bulk flow process. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;121(6):1257–1269. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.6.1257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellman I., Simons K. The Golgi complex: in vitro veritas? Cell. 1992 Mar 6;68(5):829–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90027-A. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misteli T., Warren G. COP-coated vesicles are involved in the mitotic fragmentation of Golgi stacks in a cell-free system. J Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;125(2):269–282. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.2.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikawa M., Tanaka T., Hidaka H. Ca2+-calmodulin-dependent phosphorylation and platelet secretion. Nature. 1980 Oct 30;287(5785):863–865. doi: 10.1038/287863a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novikoff P. M., Novikoff A. B., Quintana N., Hauw J. J. Golgi apparatus, GERL, and lysosomes of neurons in rat dorsal root ganglia, studied by thick section and thin section cytochemistry. J Cell Biol. 1971 Sep;50(3):859–886. doi: 10.1083/jcb.50.3.859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pryer N. K., Wuestehube L. J., Schekman R. Vesicle-mediated protein sorting. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:471–516. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.002351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rambourg A., Clermont Y., Hermo L. Three-dimensional architecture of the golgi apparatus in Sertoli cells of the rat. Am J Anat. 1979 Apr;154(4):455–476. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001540402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rambourg A., Clermont Y. Three-dimensional electron microscopy: structure of the Golgi apparatus. Eur J Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;51(2):189–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson M. S., Kreis T. E. Recruitment of coat proteins onto Golgi membranes in intact and permeabilized cells: effects of brefeldin A and G protein activators. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):129–138. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90124-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E. Mechanisms of intracellular protein transport. Nature. 1994 Nov 3;372(6501):55–63. doi: 10.1038/372055a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid S. L. Biochemical requirements for the formation of clathrin- and COP-coated transport vesicles. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;5(4):621–627. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90131-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinhardt R. A., Alderton J. M. Calmodulin confers calcium sensitivity on secretory exocytosis. Nature. 1982 Jan 14;295(5845):154–155. doi: 10.1038/295154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Ohmura T., Hidaka H. Hydrophobic interaction of the Ca2+-calmodulin complex with calmodulin antagonists. Naphthalenesulfonamide derivatives. Mol Pharmacol. 1982 Sep;22(2):403–407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tooze J., Hollinshead M. Tubular early endosomal networks in AtT20 and other cells. J Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;115(3):635–653. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.3.635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong D. H., Brodsky F. M. 100-kD proteins of Golgi- and trans-Golgi network-associated coated vesicles have related but distinct membrane binding properties. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;117(6):1171–1179. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.6.1171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood S. A., Brown W. J. The morphology but not the function of endosomes and lysosomes is altered by brefeldin A. J Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;119(2):273–285. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.2.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood S. A., Park J. E., Brown W. J. Brefeldin A causes a microtubule-mediated fusion of the trans-Golgi network and early endosomes. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):591–600. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90533-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashiro D. J., Tycko B., Fluss S. R., Maxfield F. R. Segregation of transferrin to a mildly acidic (pH 6.5) para-Golgi compartment in the recycling pathway. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):789–800. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90414-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]