Abstract
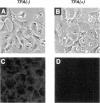
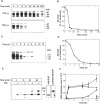
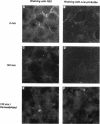
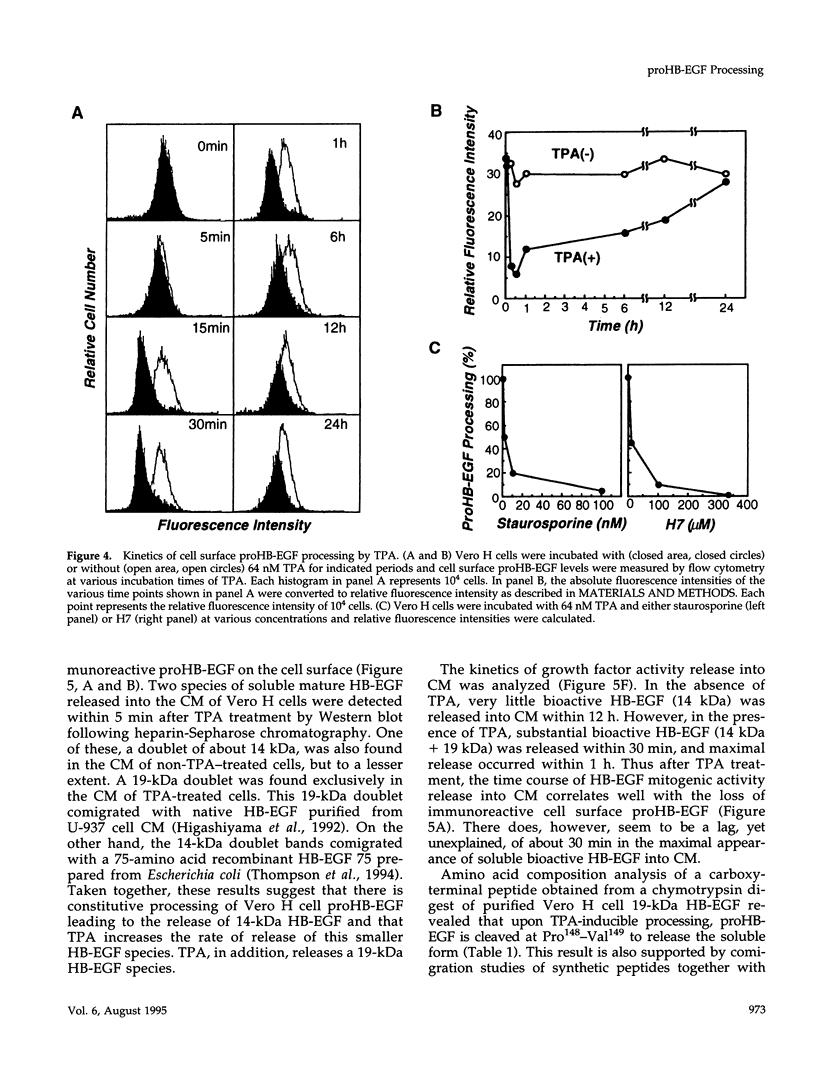
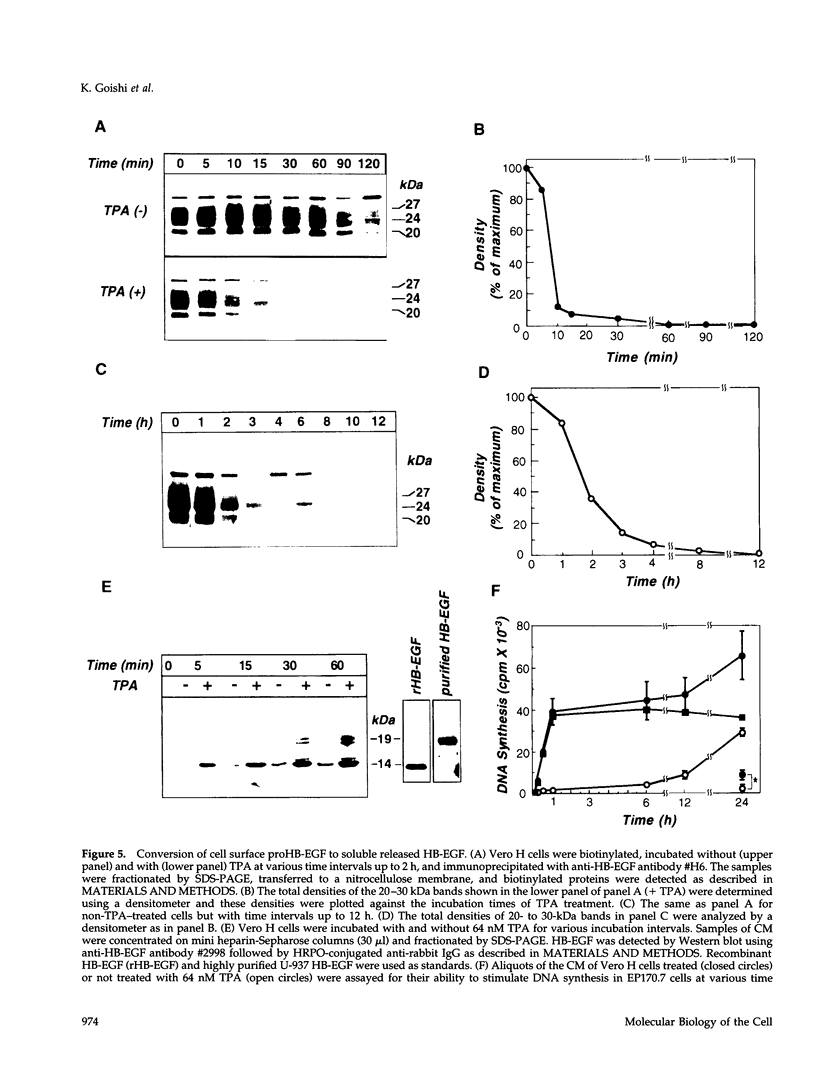
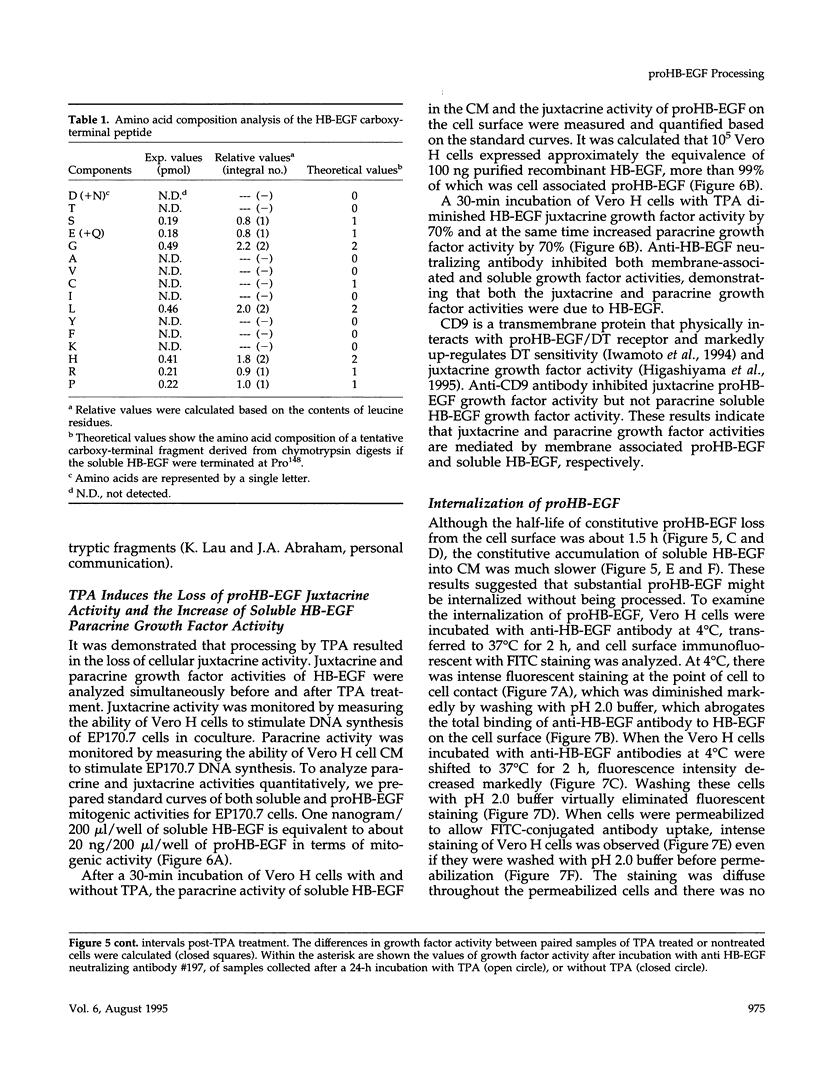
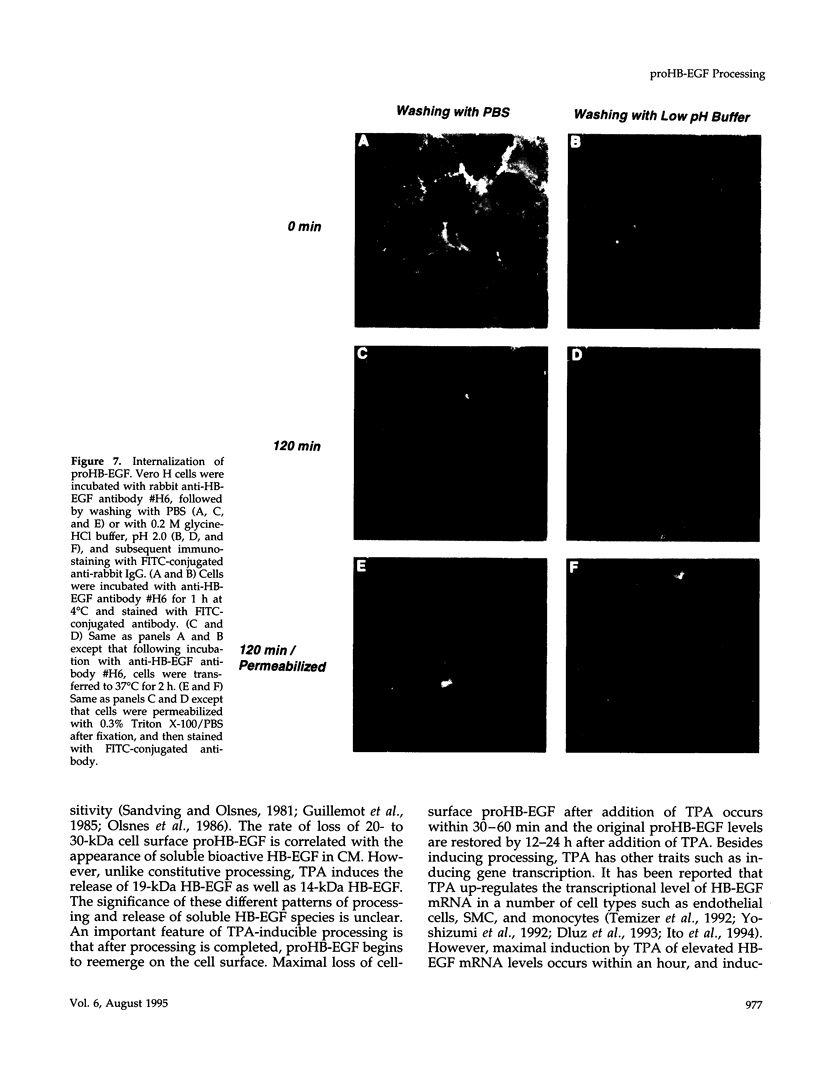
Vero cell heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor (HB-EGF) is synthesized as a 20- to 30-kDa membrane-anchored HB-EGF precursor (proHB-EGF). Localization and processing of proHB-EGF, both constitutive and 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate (TPA)-inducible, was examined in Vero cells overexpressing recombinant HB-EGF (Vero H cells). Flow cytometry and fluorescence immunostaining demonstrated that Vero cell proHB-EGF is cell surface-associated and localized at the interface of cell to cell contact. Cell surface biotinylation and immunoprecipitation detected a 20- to 30-kDa heterogeneous proHB-EGF species. Vero H cell surface proHB-EGF turned over constitutively with a half-life of 1.5 h. Some of the 20- to 30-kDa cell surface-associated proHB-EGF was processed and a 14-kDa species of bioactive HB-EGF was released slowly, but most of the proHB-EGF was internalized, displaying a diffuse immunofluorescent staining pattern and accumulation of proHB-EGF in endosomes. Addition of TPA induced a rapid processing of proHB-EGF at a Pro148-Val149 site with a half-life of 7min. The TPA effect was abrogated by the protein kinase C inhibitors, staurosporine and H7. Kinetic analysis showed that loss of cell surface proHB-EGF is maximal at 30 min after addition of TPA and that proHB-EGF is resynthesized and the initial cell surface levels are regained within 12-24 h. Loss of cell surface proHB-EGF was concomitant with appearance of 14- and 19-kDa soluble HB-EGF species in conditioned medium. Vero H cell-associated proHB-EGF is a juxtacrine growth factor for EP170.7 cells in coculture. Processing of proHB-EGF resulted in loss of juxtacrine activity and a simultaneous increase in soluble HB-EGF paracrine mitogenic activity. It was concluded that processing regulates HB-EGF bioactivity by converting it from a cell-surface juxtacrine growth factor to a processed, released soluble paracrine growth factor.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almond B. D., Eidels L. The cytoplasmic domain of the diphtheria toxin receptor (HB-EGF precursor) is not required for receptor-mediated endocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 28;269(43):26635–26641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besner G., Higashiyama S., Klagsbrun M. Isolation and characterization of a macrophage-derived heparin-binding growth factor. Cell Regul. 1990 Oct;1(11):811–819. doi: 10.1091/mbc.1.11.811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosenberg M. W., Pandiella A., Massagué J. Activated release of membrane-anchored TGF-alpha in the absence of cytosol. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;122(1):95–101. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. A., Okayama H. Calcium phosphate-mediated gene transfer: a highly efficient transfection system for stably transforming cells with plasmid DNA. Biotechniques. 1988 Jul-Aug;6(7):632–638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das S. K., Wang X. N., Paria B. C., Damm D., Abraham J. A., Klagsbrun M., Andrews G. K., Dey S. K. Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor gene is induced in the mouse uterus temporally by the blastocyst solely at the site of its apposition: a possible ligand for interaction with blastocyst EGF-receptor in implantation. Development. 1994 May;120(5):1071–1083. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.5.1071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derynck R., Roberts A. B., Winkler M. E., Chen E. Y., Goeddel D. V. Human transforming growth factor-alpha: precursor structure and expression in E. coli. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):287–297. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90550-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dluz S. M., Higashiyama S., Damm D., Abraham J. A., Klagsbrun M. Heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor expression in cultured fetal human vascular smooth muscle cells. Induction of mRNA levels and secretion of active mitogen. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 25;268(24):18330–18334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan J. G., Chan D. C., Leder P. Transmembrane form of the kit ligand growth factor is determined by alternative splicing and is missing in the Sld mutant. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):1025–1035. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90326-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillemot J. C., Sundan A., Olsnes S., Sandvig K. Entry of diphtheria toxin linked to concanavalin A into primate and murine cells. J Cell Physiol. 1985 Feb;122(2):193–199. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041220205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto K., Higashiyama S., Asada H., Hashimura E., Kobayashi T., Sudo K., Nakagawa T., Damm D., Yoshikawa K., Taniguchi N. Heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor is an autocrine growth factor for human keratinocytes. J Biol Chem. 1994 Aug 5;269(31):20060–20066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashiyama S., Abraham J. A., Klagsbrun M. Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor stimulation of smooth muscle cell migration: dependence on interactions with cell surface heparan sulfate. J Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;122(4):933–940. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.4.933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashiyama S., Abraham J. A., Miller J., Fiddes J. C., Klagsbrun M. A heparin-binding growth factor secreted by macrophage-like cells that is related to EGF. Science. 1991 Feb 22;251(4996):936–939. doi: 10.1126/science.1840698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashiyama S., Iwamoto R., Goishi K., Raab G., Taniguchi N., Klagsbrun M., Mekada E. The membrane protein CD9/DRAP 27 potentiates the juxtacrine growth factor activity of the membrane-anchored heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor. J Cell Biol. 1995 Mar;128(5):929–938. doi: 10.1083/jcb.128.5.929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashiyama S., Lau K., Besner G. E., Abraham J. A., Klagsbrun M. Structure of heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor. Multiple forms, primary structure, and glycosylation of the mature protein. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):6205–6212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang E. J., Nocka K. H., Buck J., Besmer P. Differential expression and processing of two cell associated forms of the kit-ligand: KL-1 and KL-2. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Mar;3(3):349–362. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.3.349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito N., Kawata S., Tamura S., Kiso S., Tsushima H., Damm D., Abraham J. A., Higashiyama S., Taniguchi N., Matsuzawa Y. Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor is a potent mitogen for rat hepatocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Jan 14;198(1):25–31. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwamoto R., Higashiyama S., Mitamura T., Taniguchi N., Klagsbrun M., Mekada E. Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor, which acts as the diphtheria toxin receptor, forms a complex with membrane protein DRAP27/CD9, which up-regulates functional receptors and diphtheria toxin sensitivity. EMBO J. 1994 May 15;13(10):2322–2330. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06516.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn J., Ingraham R. H., Shirley F., Migaki G. I., Kishimoto T. K. Membrane proximal cleavage of L-selectin: identification of the cleavage site and a 6-kD transmembrane peptide fragment of L-selectin. J Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;125(2):461–470. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.2.461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerbiriou D. M., Griffin J. H. Human high molecular weight kininogen. Studies of structure-function relationships and of proteolysis of the molecule occurring during contact activation of plasma. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 10;254(23):12020–12027. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee D. C., Rose T. M., Webb N. R., Todaro G. J. Cloning and sequence analysis of a cDNA for rat transforming growth factor-alpha. Nature. 1985 Feb 7;313(6002):489–491. doi: 10.1038/313489a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marikovsky M., Breuing K., Liu P. Y., Eriksson E., Higashiyama S., Farber P., Abraham J., Klagsbrun M. Appearance of heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor in wound fluid as a response to injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):3889–3893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.3889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J., Pandiella A. Membrane-anchored growth factors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:515–541. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.002503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekada E., Uchida T. Binding properties of diphtheria toxin to cells are altered by mutation in the fragment A domain. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):12148–12153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitamura T., Higashiyama S., Taniguchi N., Klagsbrun M., Mekada E. Diphtheria toxin binds to the epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like domain of human heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor/diphtheria toxin receptor and inhibits specifically its mitogenic activity. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jan 20;270(3):1015–1019. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.3.1015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyagawa J., Higashiyama S., Kawata S., Inui Y., Tamura S., Yamamoto K., Nishida M., Nakamura T., Yamashita S., Matsuzawa Y. Localization of heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor in the smooth muscle cells and macrophages of human atherosclerotic plaques. J Clin Invest. 1995 Jan;95(1):404–411. doi: 10.1172/JCI117669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscatelli D. High and low affinity binding sites for basic fibroblast growth factor on cultured cells: absence of a role for low affinity binding in the stimulation of plasminogen activator production by bovine capillary endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 1987 Apr;131(1):123–130. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041310118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naglich J. G., Metherall J. E., Russell D. W., Eidels L. Expression cloning of a diphtheria toxin receptor: identity with a heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor precursor. Cell. 1992 Jun 12;69(6):1051–1061. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90623-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsnes S., Carvajal E., Sandvig K. Interactions between diphtheria toxin entry and anion transport in vero cells. III. Effect on toxin binding and anion transport of tumor-promoting phorbol esters, vanadate, fluoride, and salicylate. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 5;261(4):1562–1569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandiella A., Massagué J. Cleavage of the membrane precursor for transforming growth factor alpha is a regulated process. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1726–1730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandiella A., Massagué J. Multiple signals activate cleavage of the membrane transforming growth factor-alpha precursor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 25;266(9):5769–5773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce J. H., Ruggiero M., Fleming T. P., Di Fiore P. P., Greenberger J. S., Varticovski L., Schlessinger J., Rovera G., Aaronson S. A. Signal transduction through the EGF receptor transfected in IL-3-dependent hematopoietic cells. Science. 1988 Feb 5;239(4840):628–631. doi: 10.1126/science.3257584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K., Olsnes S. Effects of retinoids and phorbol esters on the sensitivity of different cell lines to the polypeptide toxins modeccin, abrin, ricin and diphtheria toxin. Biochem J. 1981 Mar 15;194(3):821–827. doi: 10.1042/bj1940821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein J., Rettenmier C. W. Proteolytic processing of a plasma membrane-bound precursor to human macrophage colony-stimulating factor (CSF-1) is accelerated by phorbol ester. Oncogene. 1991 Apr;6(4):601–605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teixido J., Wong S. T., Lee D. C., Massagué J. Generation of transforming growth factor-alpha from the cell surface by an O-glycosylation-independent multistep process. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 15;265(11):6410–6415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temizer D. H., Yoshizumi M., Perrella M. A., Susanni E. E., Quertermous T., Lee M. E. Induction of heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor mRNA by phorbol ester and angiotensin II in rat aortic smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 5;267(34):24892–24896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S. A., Higashiyama S., Wood K., Pollitt N. S., Damm D., McEnroe G., Garrick B., Ashton N., Lau K., Hancock N. Characterization of sequences within heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor that mediate interaction with heparin. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 28;269(4):2541–2549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida T., Pappenheimer A. M., Jr, Greany R. Diphtheria toxin and related proteins. I. Isolation and properties of mutant proteins serologically related to diphtheria toxin. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 10;248(11):3838–3844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umata T., Moriyama Y., Futai M., Mekada E. The cytotoxic action of diphtheria toxin and its degradation in intact Vero cells are inhibited by bafilomycin A1, a specific inhibitor of vacuolar-type H(+)-ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 15;265(35):21940–21945. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshizumi M., Kourembanas S., Temizer D. H., Cambria R. P., Quertermous T., Lee M. E. Tumor necrosis factor increases transcription of the heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor gene in vascular endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 15;267(14):9467–9469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- no M., Raab G., Lau K., Abraham J. A., Klagsbrun M. Purification and characterization of transmembrane forms of heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 9;269(49):31315–31321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]