Abstract
The genetic and molecular analysis of genes involved in the regulation of sex determination in Caenorhabditis elegans suggests that the gene fem-2 plays an important role in regulating a pathway transducing a non-cell-autonomous signal to a nuclear transcription factor. The wild-type fem-2 gene was cloned by identifying sequences from the C. elegans physical map that could restore normal Fem-2 function to homozygous mutant fem-2 transgenic animals. cDNA sequences mapping to the minimal rescuing region correspond to an open reading frame with a sequence similar to protein phosphatase 2C enzymes from systems as diverse as yeast, humans, and plants, but the alignments suggest that FEM-2 falls into a separate class of proteins than the canonical homologues. Several fem-2 mutant alleles were sequenced, and the mutations are predicted to cause protein changes consistent with their observed phenotypes, such as missense mutations in conditional alleles, and a nonsense mutation in a predicted null allele. This is the first evidence implicating phosphorylation and/or dephosphorylation as a control mechanism in C. elegans sex determination.
Full text
PDF






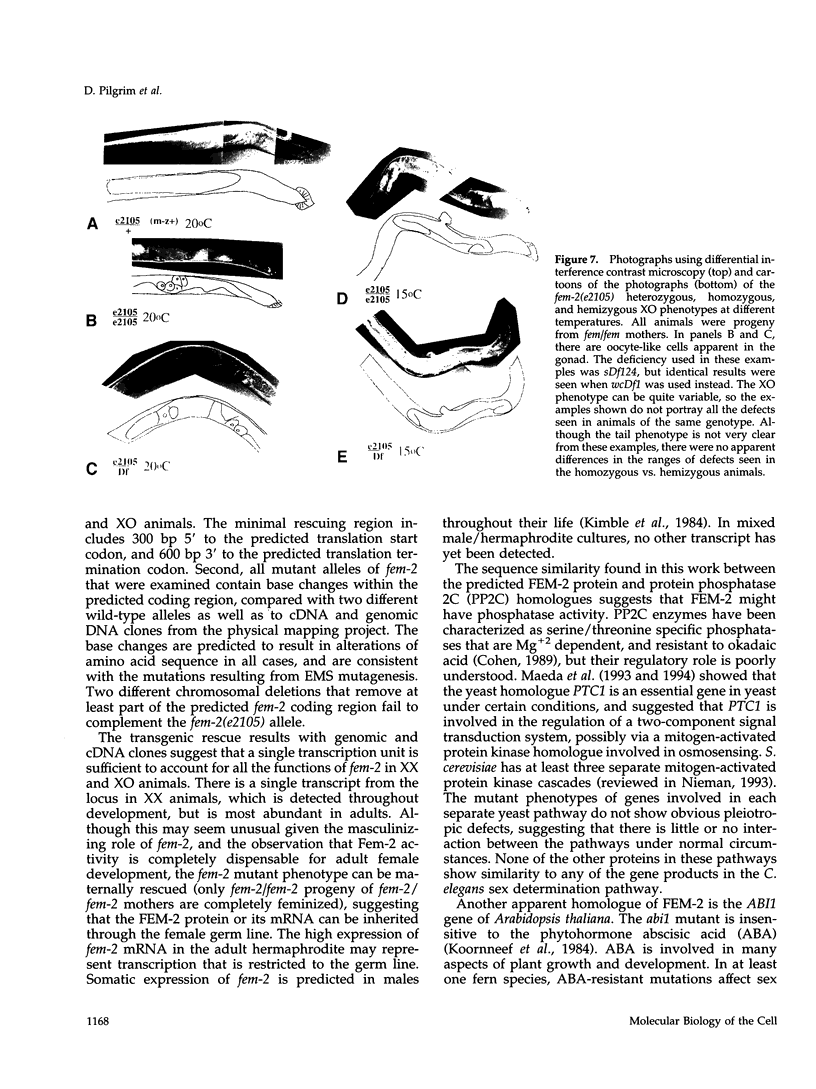



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahringer J., Kimble J. Control of the sperm-oocyte switch in Caenorhabditis elegans hermaphrodites by the fem-3 3' untranslated region. Nature. 1991 Jan 24;349(6307):346–348. doi: 10.1038/349346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahringer J., Rosenquist T. A., Lawson D. N., Kimble J. The Caenorhabditis elegans sex determining gene fem-3 is regulated post-transcriptionally. EMBO J. 1992 Jun;11(6):2303–2310. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05289.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banks J. A. Sex-determining genes in the homosporous fern Ceratopteris. Development. 1994 Jul;120(7):1949–1958. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.7.1949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barstead R. J., Waterston R. H. The basal component of the nematode dense-body is vinculin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 15;264(17):10177–10185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barton M. K., Schedl T. B., Kimble J. Gain-of-function mutations of fem-3, a sex-determination gene in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1987 Jan;115(1):107–119. doi: 10.1093/genetics/115.1.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broverman S. A., Meneely P. M. Meiotic mutants that cause a polar decrease in recombination on the X chromosome in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1994 Jan;136(1):119–127. doi: 10.1093/genetics/136.1.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The structure and regulation of protein phosphatases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:453–508. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.002321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulson A., Kozono Y., Lutterbach B., Shownkeen R., Sulston J., Waterston R. YACs and the C. elegans genome. Bioessays. 1991 Aug;13(8):413–417. doi: 10.1002/bies.950130809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulson A., Sulston J., Brenner S., Karn J. Toward a physical map of the genome of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7821–7825. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulson A., Waterston R., Kiff J., Sulston J., Kohara Y. Genome linking with yeast artificial chromosomes. Nature. 1988 Sep 8;335(6186):184–186. doi: 10.1038/335184a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLong L., Plenefisch J. D., Klein R. D., Meyer B. J. Feedback control of sex determination by dosage compensation revealed through Caenorhabditis elegans sdc-3 mutations. Genetics. 1993 Apr;133(4):875–896. doi: 10.1093/genetics/133.4.875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doniach T., Hodgkin J. A sex-determining gene, fem-1, required for both male and hermaphrodite development in Caenorhabditis elegans. Dev Biol. 1984 Nov;106(1):223–235. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90077-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman M. A., Dush M. K., Martin G. R. Rapid production of full-length cDNAs from rare transcripts: amplification using a single gene-specific oligonucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8998–9002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S., Baltimore D. Activation in vitro of NF-kappa B by phosphorylation of its inhibitor I kappa B. Nature. 1990 Apr 12;344(6267):678–682. doi: 10.1038/344678a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham P. L., Kimble J. The mog-1 gene is required for the switch from spermatogenesis to oogenesis in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1993 Apr;133(4):919–931. doi: 10.1093/genetics/133.4.919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haskill S., Beg A. A., Tompkins S. M., Morris J. S., Yurochko A. D., Sampson-Johannes A., Mondal K., Ralph P., Baldwin A. S., Jr Characterization of an immediate-early gene induced in adherent monocytes that encodes I kappa B-like activity. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1281–1289. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90022-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkin J. A., Brenner S. Mutations causing transformation of sexual phenotype in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1977 Jun;86(2 Pt 1):275–287. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
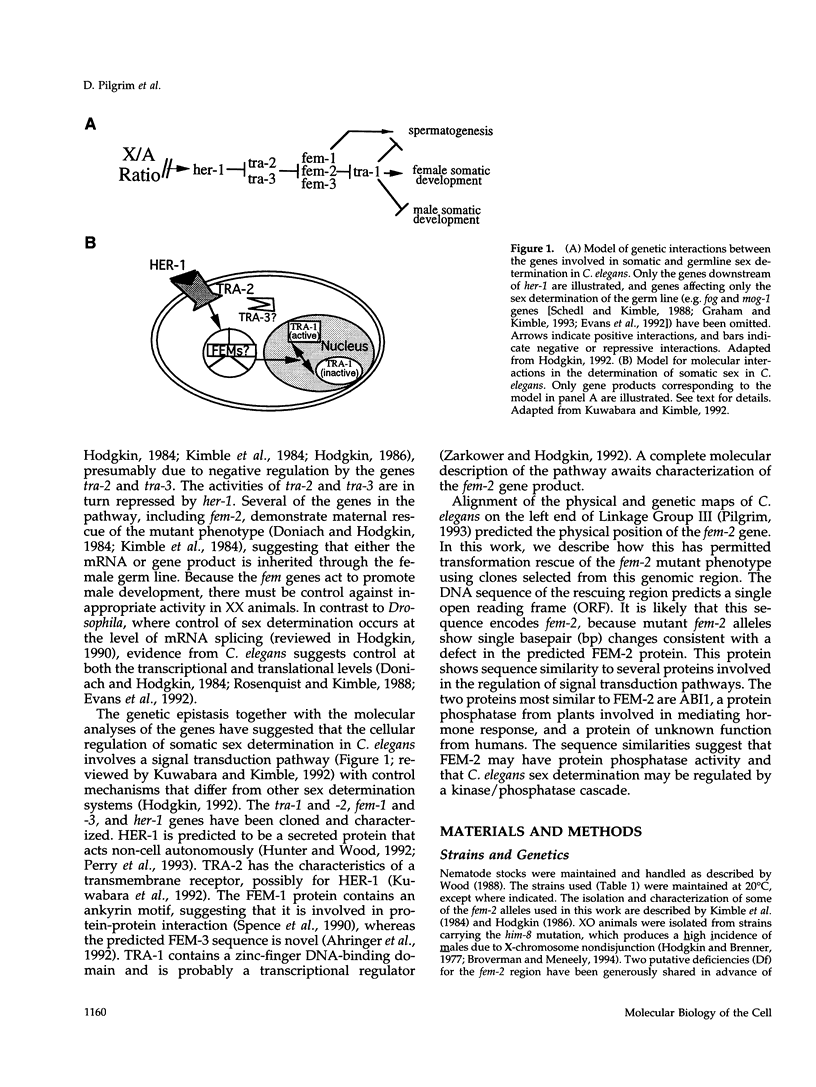
- Hodgkin J. Genetic sex determination mechanisms and evolution. Bioessays. 1992 Apr;14(4):253–261. doi: 10.1002/bies.950140409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkin J. More sex-determination mutants of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1980 Nov;96(3):649–664. doi: 10.1093/genetics/96.3.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkin J. Primary sex determination in the nematode C. elegans. Development. 1987;101 (Suppl):5–16. doi: 10.1242/dev.101.Supplement.5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkin J. Sex determination compared in Drosophila and Caenorhabditis. Nature. 1990 Apr 19;344(6268):721–728. doi: 10.1038/344721a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkin J. Sex determination in the nematode C. elegans: analysis of tra-3 suppressors and characterization of fem genes. Genetics. 1986 Sep;114(1):15–52. doi: 10.1093/genetics/114.1.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope I. A. PES-1 is expressed during early embryogenesis in Caenorhabditis elegans and has homology to the fork head family of transcription factors. Development. 1994 Mar;120(3):505–514. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.3.505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter C. P., Wood W. B. Evidence from mosaic analysis of the masculinizing gene her-1 for cell interactions in C. elegans sex determination. Nature. 1992 Feb 6;355(6360):551–555. doi: 10.1038/355551a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Karin M. The regulation of transcription by phosphorylation. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):375–387. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90162-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimble J., Edgar L., Hirsh D. Specification of male development in Caenorhabditis elegans: the fem genes. Dev Biol. 1984 Sep;105(1):234–239. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90279-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause M., Hirsh D. A trans-spliced leader sequence on actin mRNA in C. elegans. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):753–761. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90613-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwabara P. E., Kimble J. Molecular genetics of sex determination in C. elegans. Trends Genet. 1992 May;8(5):164–168. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(92)90218-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwabara P. E., Okkema P. G., Kimble J. tra-2 encodes a membrane protein and may mediate cell communication in the Caenorhabditis elegans sex determination pathway. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Apr;3(4):461–473. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.4.461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung J., Bouvier-Durand M., Morris P. C., Guerrier D., Chefdor F., Giraudat J. Arabidopsis ABA response gene ABI1: features of a calcium-modulated protein phosphatase. Science. 1994 Jun 3;264(5164):1448–1452. doi: 10.1126/science.7910981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda T., Tsai A. Y., Saito H. Mutations in a protein tyrosine phosphatase gene (PTP2) and a protein serine/threonine phosphatase gene (PTC1) cause a synthetic growth defect in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;13(9):5408–5417. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.9.5408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda T., Wurgler-Murphy S. M., Saito H. A two-component system that regulates an osmosensing MAP kinase cascade in yeast. Nature. 1994 May 19;369(6477):242–245. doi: 10.1038/369242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mello C. C., Kramer J. M., Stinchcomb D., Ambros V. Efficient gene transfer in C.elegans: extrachromosomal maintenance and integration of transforming sequences. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3959–3970. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04966.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer K., Leube M. P., Grill E. A protein phosphatase 2C involved in ABA signal transduction in Arabidopsis thaliana. Science. 1994 Jun 3;264(5164):1452–1455. doi: 10.1126/science.8197457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. M., Plenefisch J. D., Casson L. P., Meyer B. J. xol-1: a gene that controls the male modes of both sex determination and X chromosome dosage compensation in C. elegans. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):167–183. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90019-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neiman A. M. Conservation and reiteration of a kinase cascade. Trends Genet. 1993 Nov;9(11):390–394. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(93)90139-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nusbaum C., Meyer B. J. The Caenorhabditis elegans gene sdc-2 controls sex determination and dosage compensation in XX animals. Genetics. 1989 Jul;122(3):579–593. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.3.579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry M. D., Li W., Trent C., Robertson B., Fire A., Hageman J. M., Wood W. B. Molecular characterization of the her-1 gene suggests a direct role in cell signaling during Caenorhabditis elegans sex determination. Genes Dev. 1993 Feb;7(2):216–228. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.2.216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilgrim D. B., Bell J. B. Expression of a Drosophila melanogaster amber suppressor tRNA(Ser) in Caenorhabditis elegans. Mol Gen Genet. 1993 Oct;241(1-2):26–32. doi: 10.1007/BF00280197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
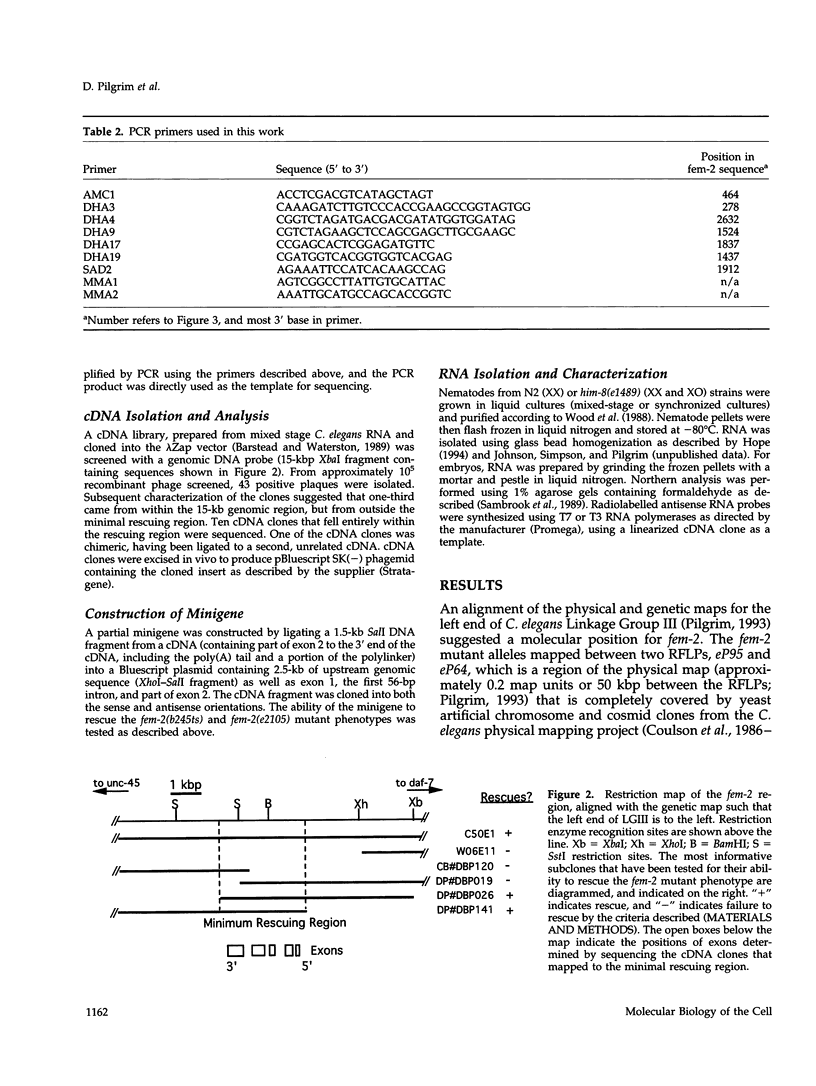
- Pilgrim D. The genetic and RFLP characterization of the left end of linkage group III in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genome. 1993 Aug;36(4):712–724. doi: 10.1139/g93-096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenquist T. A., Kimble J. Molecular cloning and transcript analysis of fem-3, a sex-determination gene in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genes Dev. 1988 May;2(5):606–616. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.5.606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schedl T., Kimble J. fog-2, a germ-line-specific sex determination gene required for hermaphrodite spermatogenesis in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1988 May;119(1):43–61. doi: 10.1093/genetics/119.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spence A. M., Coulson A., Hodgkin J. The product of fem-1, a nematode sex-determining gene, contains a motif found in cell cycle control proteins and receptors for cell-cell interactions. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):981–990. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90346-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone J. M., Collinge M. A., Smith R. D., Horn M. A., Walker J. C. Interaction of a protein phosphatase with an Arabidopsis serine-threonine receptor kinase. Science. 1994 Nov 4;266(5186):793–795. doi: 10.1126/science.7973632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulston J., Du Z., Thomas K., Wilson R., Hillier L., Staden R., Halloran N., Green P., Thierry-Mieg J., Qiu L. The C. elegans genome sequencing project: a beginning. Nature. 1992 Mar 5;356(6364):37–41. doi: 10.1038/356037a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villeneuve A. M., Meyer B. J. sdc-1: a link between sex determination and dosage compensation in C. elegans. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):25–37. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90352-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenk J., Trompeter H. I., Pettrich K. G., Cohen P. T., Campbell D. G., Mieskes G. Molecular cloning and primary structure of a protein phosphatase 2C isoform. FEBS Lett. 1992 Feb 3;297(1-2):135–138. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80344-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B. D., Schrank B., Huynh C., Shownkeen R., Waterston R. H. A genetic mapping system in Caenorhabditis elegans based on polymorphic sequence-tagged sites. Genetics. 1992 Jul;131(3):609–624. doi: 10.1093/genetics/131.3.609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R., Ainscough R., Anderson K., Baynes C., Berks M., Bonfield J., Burton J., Connell M., Copsey T., Cooper J. 2.2 Mb of contiguous nucleotide sequence from chromosome III of C. elegans. Nature. 1994 Mar 3;368(6466):32–38. doi: 10.1038/368032a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarkower D., Hodgkin J. Molecular analysis of the C. elegans sex-determining gene tra-1: a gene encoding two zinc finger proteins. Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):237–249. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90099-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]