Abstract
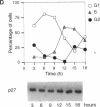
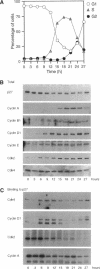
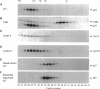
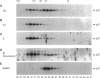
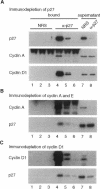
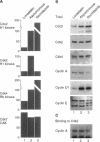
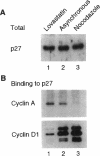
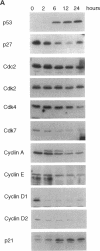
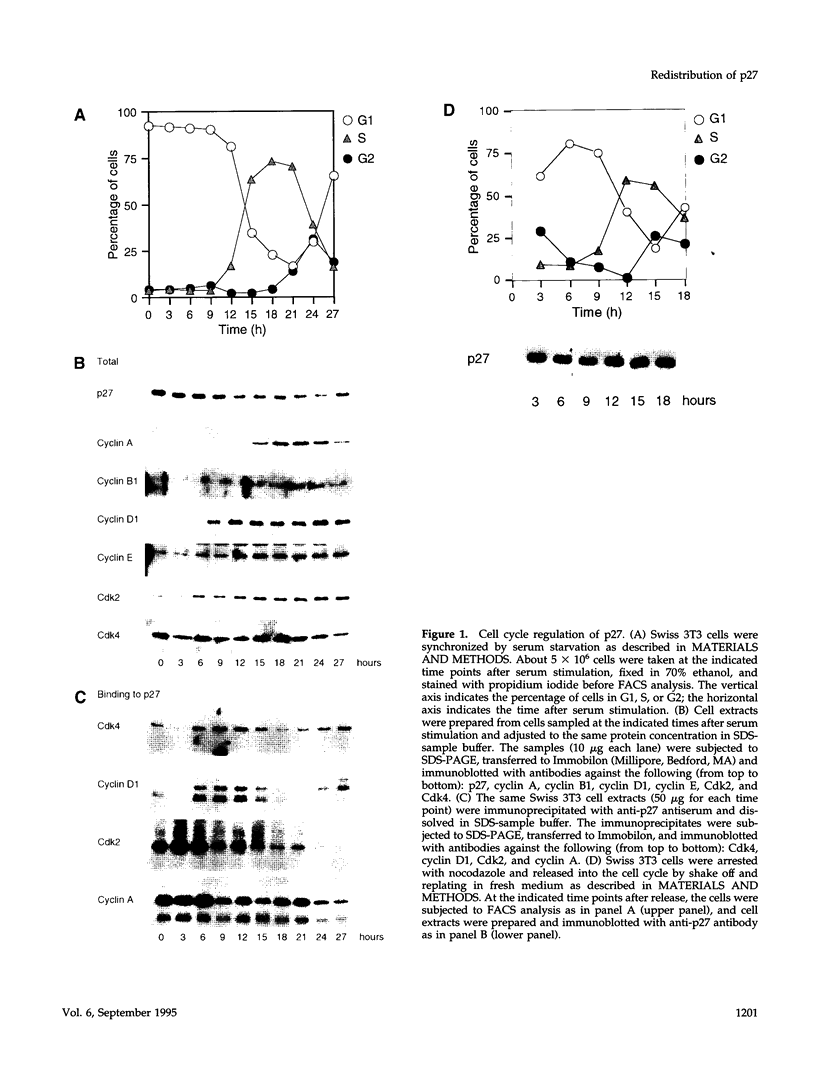
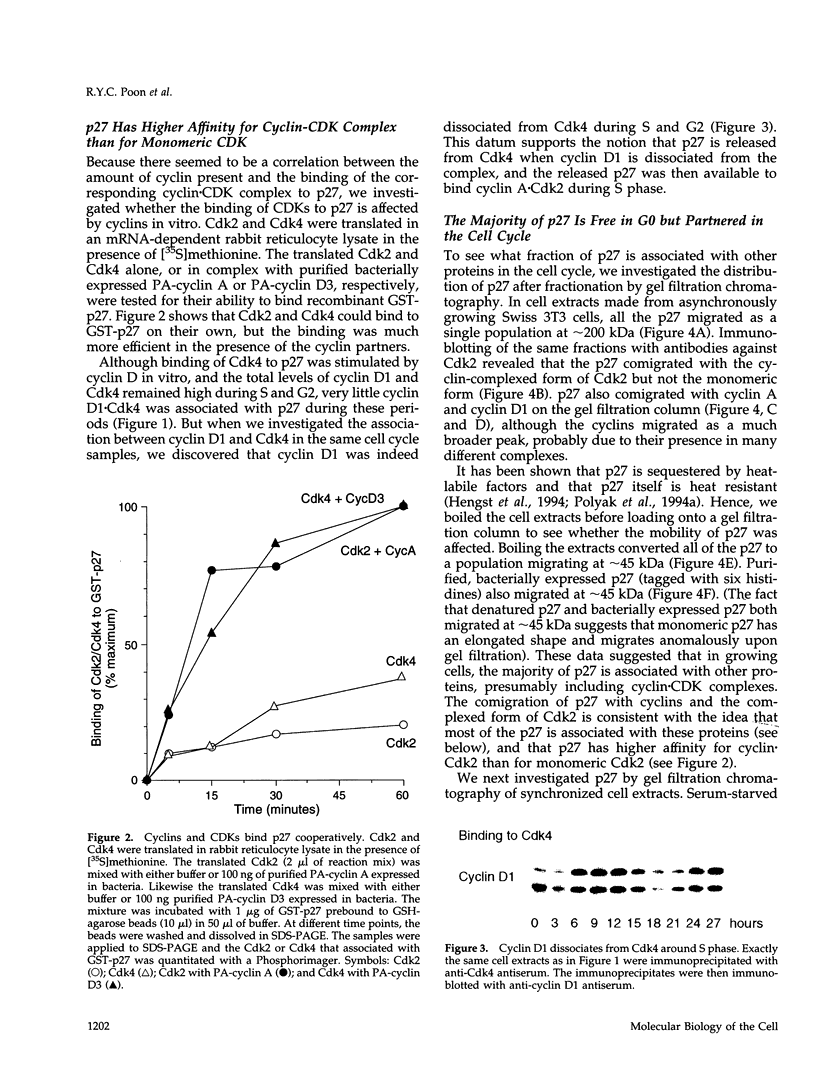
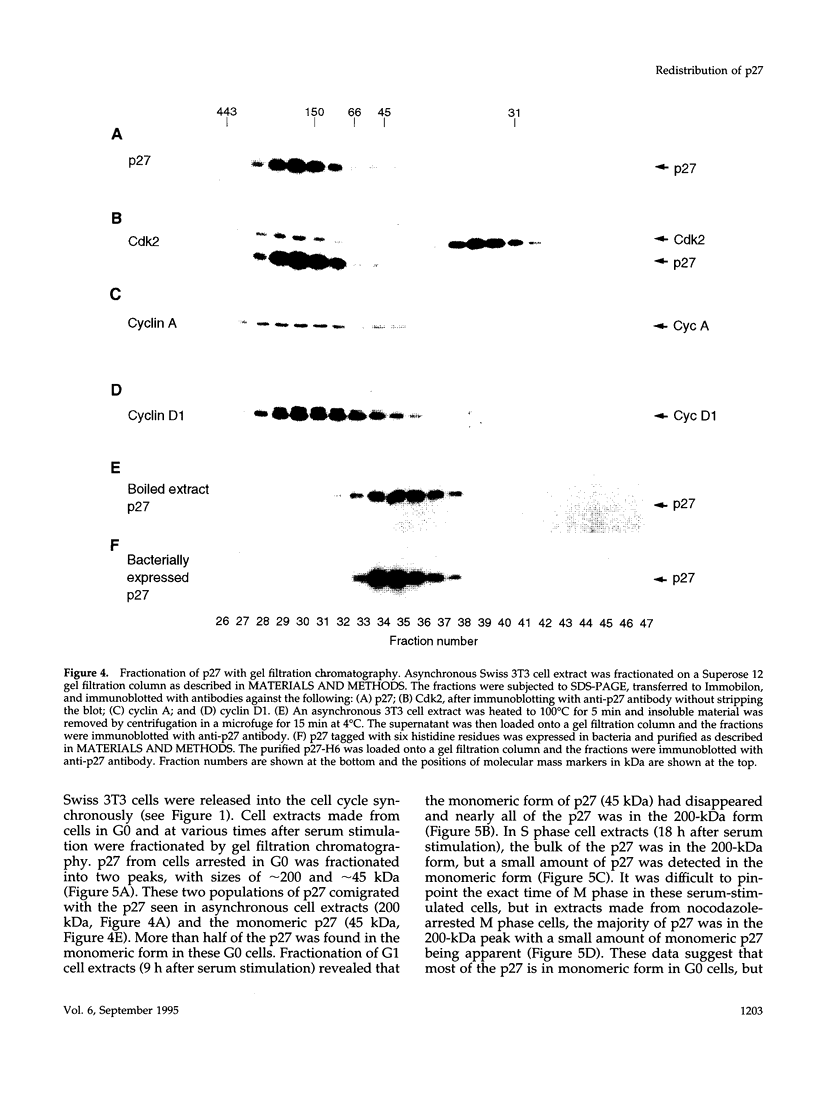
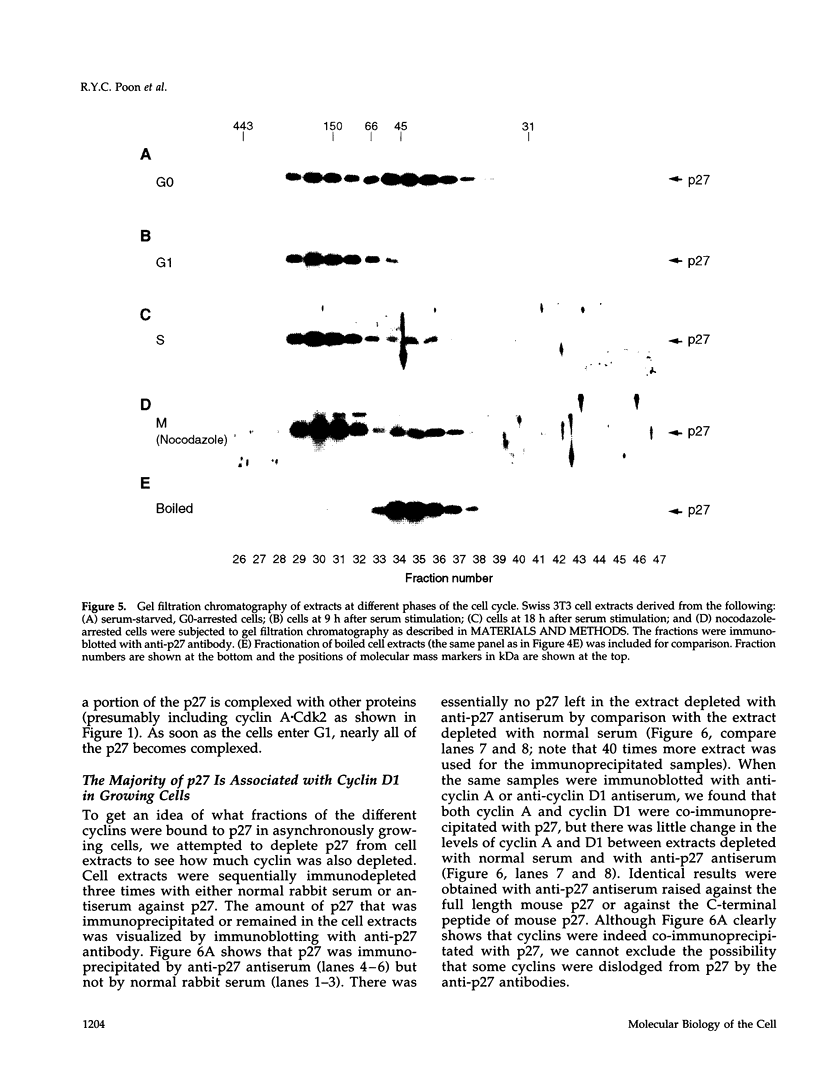
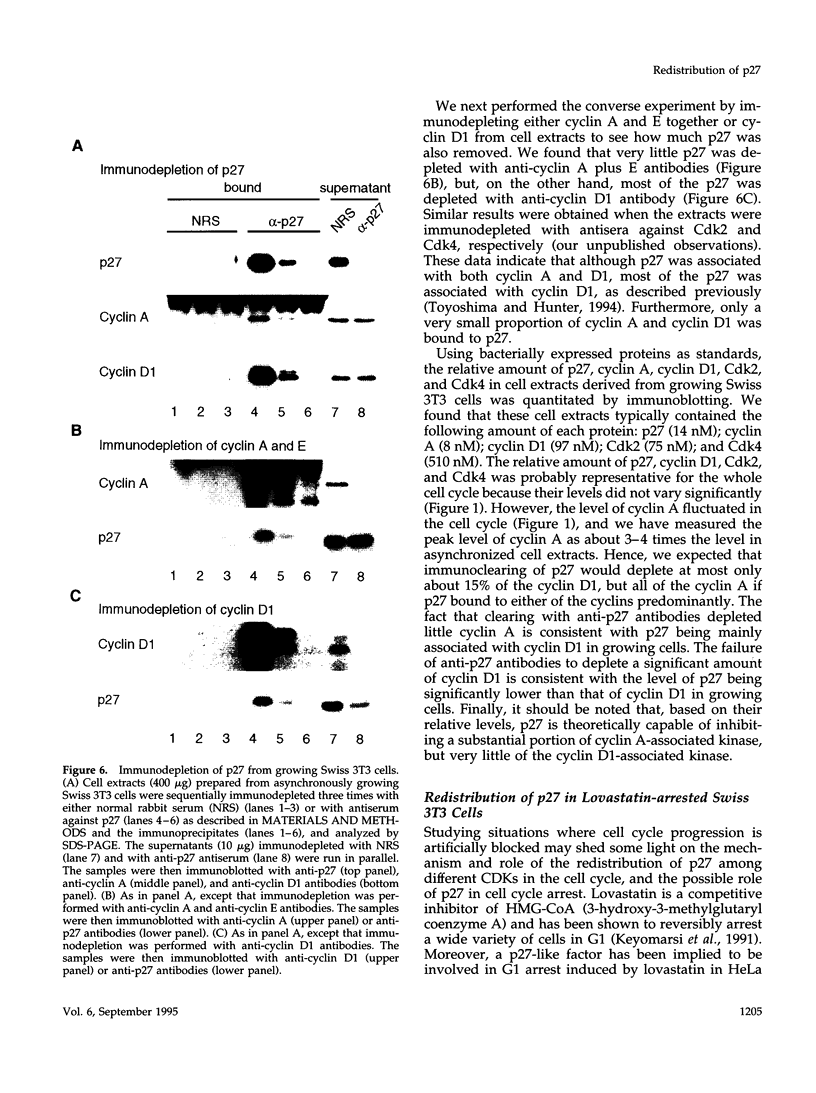
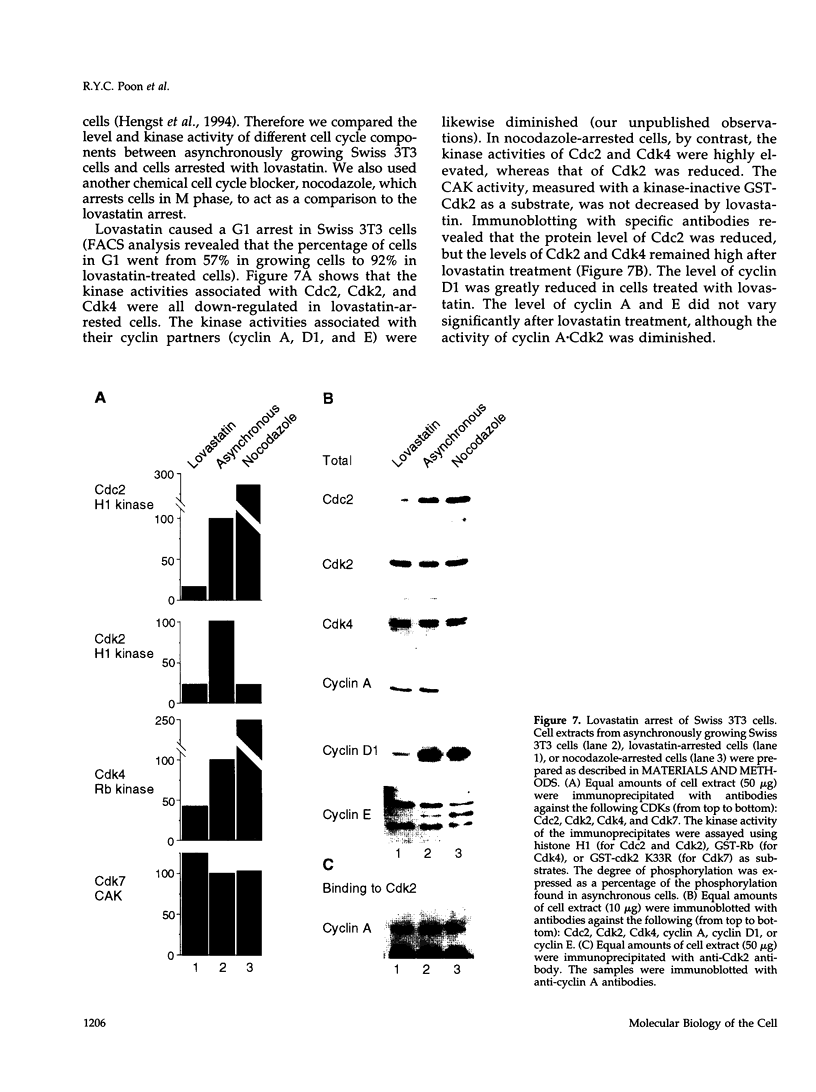
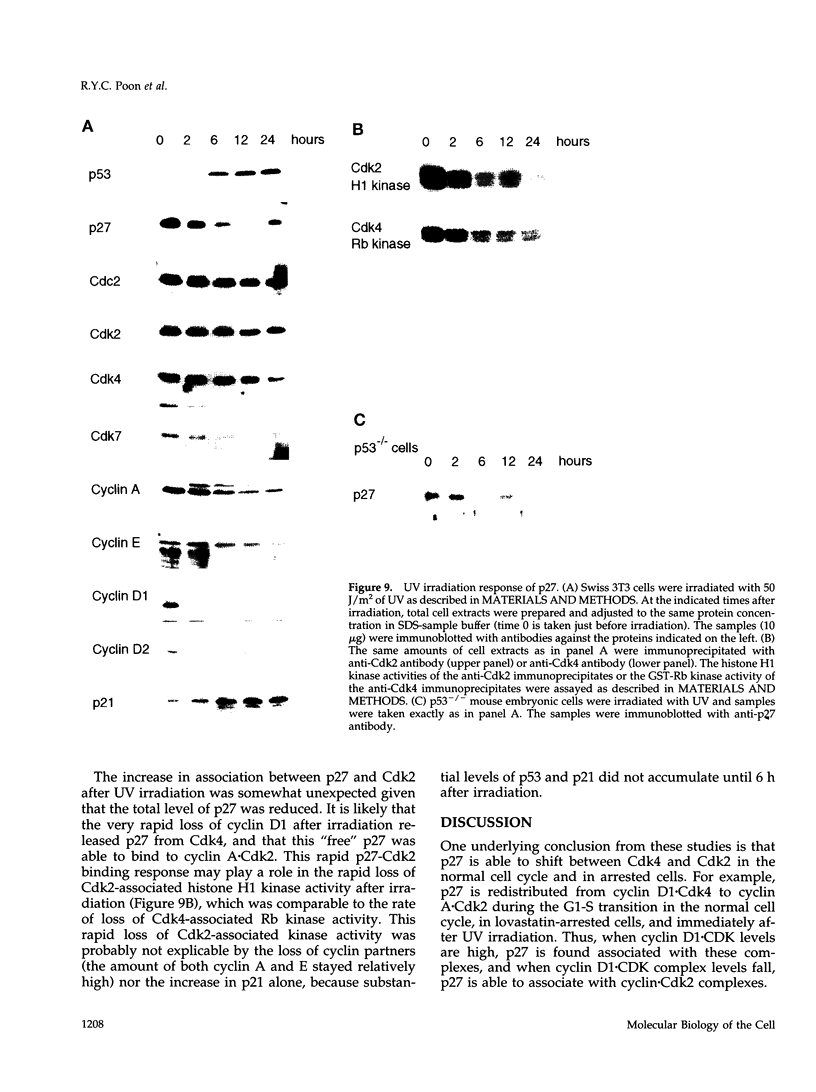
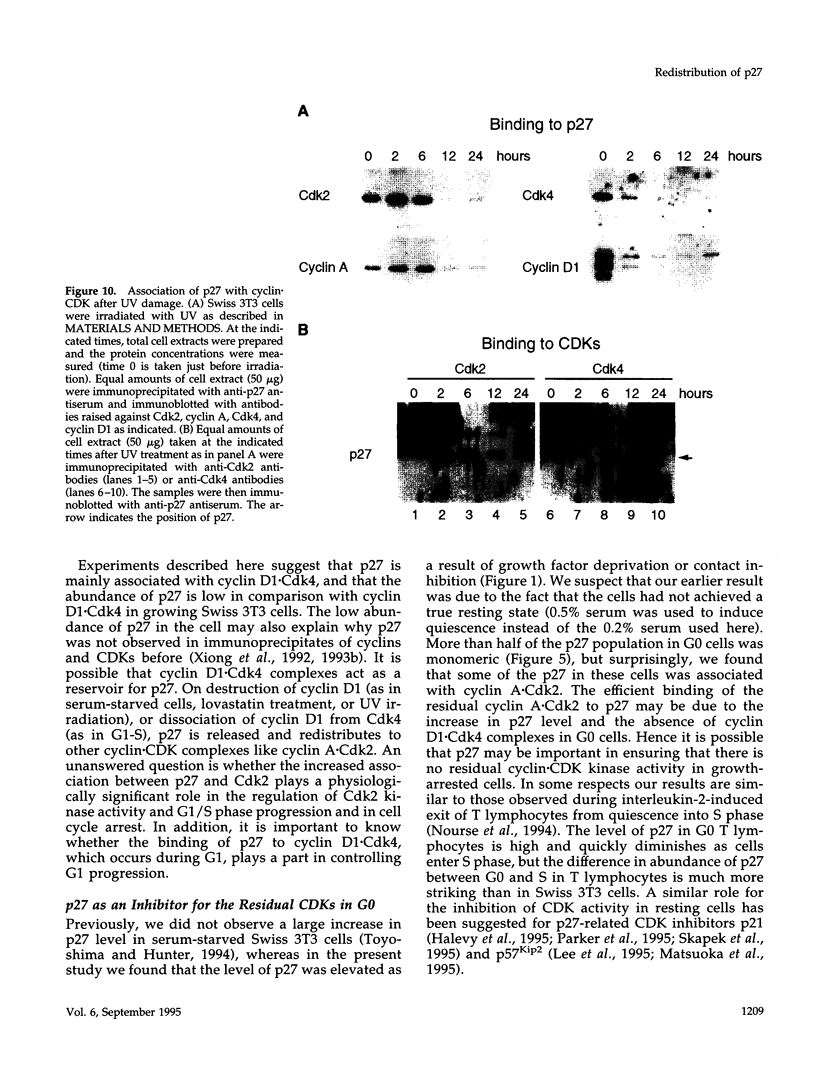
The cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) inhibitor p27 binds and inhibits the kinase activity of several CDKs. Here we report an analysis of the behavior and partners of p27 in Swiss 3T3 mouse fibroblasts during normal mitotic cell cycle progression, as well as in cells arrested at different stages in the cycle by growth factor deprivation, lovastatin treatment, or ultraviolet (UV) irradiation. We found that the level of p27 is elevated in cells arrested in G0 by growth factor deprivation or contact inhibition. In G0, p27 was predominantly monomeric, although some portion was associated with residual cyclin A.Cdk2. During G1, all of p27 was associated with cyclin D1.Cdk4 and was then redistributed to cyclin A.Cdk2 as cells entered S phase. The loss of the monomeric p27 pool as cyclins accumulate in G1 is consistent with the in vivo and in vitro data showing that p27 binds better to cyclin.CDK complexes than to monomeric CDKs. In growing cells, the majority of p27 was associated with cyclin D1 and the level of p27 was significantly lower than the level of cyclin D1. In cells arrested in G1 with lovastatin, cyclin D1 was degraded and p27 was redistributed to cyclin A.Cdk2. In contrast to p21 (which is a p27-related CDK inhibitor and is induced by UV irradiation), the level of p27 was reduced after UV irradiation, but because cyclin D1 was degraded more rapidly than p27, there was a transient increase in binding of p27 to cyclin A.Cdk2. These data suggest that cyclin D1.Cdk4 acts as a reservoir for p27, and p27 is redistributed from cyclin D1.Cdk4 to cyclin A.Cdk2 complexes during S phase, or when cells are arrested by growth factor deprivation, lovastatin treatment, or UV irradiation. It is likely that a similar principle of redistribution of p27 is used by the cell in other instances of cell cycle arrest.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chan F. K., Zhang J., Cheng L., Shapiro D. N., Winoto A. Identification of human and mouse p19, a novel CDK4 and CDK6 inhibitor with homology to p16ink4. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 May;15(5):2682–2688. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.5.2682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman T. R., Dunphy W. G. Cdc2 regulatory factors. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994 Dec;6(6):877–882. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(94)90060-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connell-Crowley L., Solomon M. J., Wei N., Harper J. W. Phosphorylation independent activation of human cyclin-dependent kinase 2 by cyclin A in vitro. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Jan;4(1):79–92. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.1.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datto M. B., Li Y., Panus J. F., Howe D. J., Xiong Y., Wang X. F. Transforming growth factor beta induces the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21 through a p53-independent mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jun 6;92(12):5545–5549. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.12.5545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulić V., Kaufmann W. K., Wilson S. J., Tlsty T. D., Lees E., Harper J. W., Elledge S. J., Reed S. I. p53-dependent inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase activities in human fibroblasts during radiation-induced G1 arrest. Cell. 1994 Mar 25;76(6):1013–1023. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90379-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elledge S. J., Harper J. W. Cdk inhibitors: on the threshold of checkpoints and development. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994 Dec;6(6):847–852. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(94)90055-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewen M. E., Sluss H. K., Whitehouse L. L., Livingston D. M. TGF beta inhibition of Cdk4 synthesis is linked to cell cycle arrest. Cell. 1993 Sep 24;74(6):1009–1020. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90723-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. P., Morgan D. O. A novel cyclin associates with MO15/CDK7 to form the CDK-activating kinase. Cell. 1994 Aug 26;78(4):713–724. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90535-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu Y., Turck C. W., Morgan D. O. Inhibition of CDK2 activity in vivo by an associated 20K regulatory subunit. Nature. 1993 Dec 16;366(6456):707–710. doi: 10.1038/366707a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan K. L., Jenkins C. W., Li Y., Nichols M. A., Wu X., O'Keefe C. L., Matera A. G., Xiong Y. Growth suppression by p18, a p16INK4/MTS1- and p14INK4B/MTS2-related CDK6 inhibitor, correlates with wild-type pRb function. Genes Dev. 1994 Dec 15;8(24):2939–2952. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.24.2939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halevy O., Novitch B. G., Spicer D. B., Skapek S. X., Rhee J., Hannon G. J., Beach D., Lassar A. B. Correlation of terminal cell cycle arrest of skeletal muscle with induction of p21 by MyoD. Science. 1995 Feb 17;267(5200):1018–1021. doi: 10.1126/science.7863327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannon G. J., Beach D. p15INK4B is a potential effector of TGF-beta-induced cell cycle arrest. Nature. 1994 Sep 15;371(6494):257–261. doi: 10.1038/371257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J. W., Adami G. R., Wei N., Keyomarsi K., Elledge S. J. The p21 Cdk-interacting protein Cip1 is a potent inhibitor of G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):805–816. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90499-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J. W., Elledge S. J., Keyomarsi K., Dynlacht B., Tsai L. H., Zhang P., Dobrowolski S., Bai C., Connell-Crowley L., Swindell E. Inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinases by p21. Mol Biol Cell. 1995 Apr;6(4):387–400. doi: 10.1091/mbc.6.4.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heichman K. A., Roberts J. M. Rules to replicate by. Cell. 1994 Nov 18;79(4):557–562. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90541-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hengst L., Dulic V., Slingerland J. M., Lees E., Reed S. I. A cell cycle-regulated inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 7;91(12):5291–5295. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.12.5291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai H., Roussel M. F., Kato J. Y., Ashmun R. A., Sherr C. J. Novel INK4 proteins, p19 and p18, are specific inhibitors of the cyclin D-dependent kinases CDK4 and CDK6. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 May;15(5):2672–2681. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.5.2672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Pines J. Cyclins and cancer. II: Cyclin D and CDK inhibitors come of age. Cell. 1994 Nov 18;79(4):573–582. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90543-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato J. Y., Matsuoka M., Polyak K., Massagué J., Sherr C. J. Cyclic AMP-induced G1 phase arrest mediated by an inhibitor (p27Kip1) of cyclin-dependent kinase 4 activation. Cell. 1994 Nov 4;79(3):487–496. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90257-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keyomarsi K., Sandoval L., Band V., Pardee A. B. Synchronization of tumor and normal cells from G1 to multiple cell cycles by lovastatin. Cancer Res. 1991 Jul 1;51(13):3602–3609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King R. W., Jackson P. K., Kirschner M. W. Mitosis in transition. Cell. 1994 Nov 18;79(4):563–571. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90542-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ko T. C., Sheng H. M., Reisman D., Thompson E. A., Beauchamp R. D. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 inhibits cyclin D1 expression in intestinal epithelial cells. Oncogene. 1995 Jan 5;10(1):177–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi H., Golsteyn R., Poon R., Stewart E., Gannon J., Minshull J., Smith R., Hunt T. Cyclins and their partners during Xenopus oocyte maturation. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1991;56:437–447. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1991.056.01.051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornbluth S., Sebastian B., Hunter T., Newport J. Membrane localization of the kinase which phosphorylates p34cdc2 on threonine 14. Mol Biol Cell. 1994 Mar;5(3):273–282. doi: 10.1091/mbc.5.3.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li R., Waga S., Hannon G. J., Beach D., Stillman B. Differential effects by the p21 CDK inhibitor on PCNA-dependent DNA replication and repair. Nature. 1994 Oct 6;371(6497):534–537. doi: 10.1038/371534a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Jenkins C. W., Nichols M. A., Xiong Y. Cell cycle expression and p53 regulation of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21. Oncogene. 1994 Aug;9(8):2261–2268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuoka M., Kato J. Y., Fisher R. P., Morgan D. O., Sherr C. J. Activation of cyclin-dependent kinase 4 (cdk4) by mouse MO15-associated kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Nov;14(11):7265–7275. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.11.7265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuoka S., Edwards M. C., Bai C., Parker S., Zhang P., Baldini A., Harper J. W., Elledge S. J. p57KIP2, a structurally distinct member of the p21CIP1 Cdk inhibitor family, is a candidate tumor suppressor gene. Genes Dev. 1995 Mar 15;9(6):650–662. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.6.650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. O. Principles of CDK regulation. Nature. 1995 Mar 9;374(6518):131–134. doi: 10.1038/374131a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäkelä T. P., Tassan J. P., Nigg E. A., Frutiger S., Hughes G. J., Weinberg R. A. A cyclin associated with the CDK-activating kinase MO15. Nature. 1994 Sep 15;371(6494):254–257. doi: 10.1038/371254a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda A., Ning Y., Venable S. F., Pereira-Smith O. M., Smith J. R. Cloning of senescent cell-derived inhibitors of DNA synthesis using an expression screen. Exp Cell Res. 1994 Mar;211(1):90–98. doi: 10.1006/excr.1994.1063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nourse J., Firpo E., Flanagan W. M., Coats S., Polyak K., Lee M. H., Massague J., Crabtree G. R., Roberts J. M. Interleukin-2-mediated elimination of the p27Kip1 cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor prevented by rapamycin. Nature. 1994 Dec 8;372(6506):570–573. doi: 10.1038/372570a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagano M., Theodoras A. M., Tam S. W., Draetta G. F. Cyclin D1-mediated inhibition of repair and replicative DNA synthesis in human fibroblasts. Genes Dev. 1994 Jul 15;8(14):1627–1639. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.14.1627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker S. B., Eichele G., Zhang P., Rawls A., Sands A. T., Bradley A., Olson E. N., Harper J. W., Elledge S. J. p53-independent expression of p21Cip1 in muscle and other terminally differentiating cells. Science. 1995 Feb 17;267(5200):1024–1027. doi: 10.1126/science.7863329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parry D., Bates S., Mann D. J., Peters G. Lack of cyclin D-Cdk complexes in Rb-negative cells correlates with high levels of p16INK4/MTS1 tumour suppressor gene product. EMBO J. 1995 Feb 1;14(3):503–511. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07026.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polyak K., Kato J. Y., Solomon M. J., Sherr C. J., Massague J., Roberts J. M., Koff A. p27Kip1, a cyclin-Cdk inhibitor, links transforming growth factor-beta and contact inhibition to cell cycle arrest. Genes Dev. 1994 Jan;8(1):9–22. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.1.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polyak K., Lee M. H., Erdjument-Bromage H., Koff A., Roberts J. M., Tempst P., Massagué J. Cloning of p27Kip1, a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor and a potential mediator of extracellular antimitogenic signals. Cell. 1994 Jul 15;78(1):59–66. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90572-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poon R. Y., Hunt T. Reversible immunoprecipitation using histidine- or glutathione S-transferase-tagged staphylococcal protein A. Anal Biochem. 1994 Apr;218(1):26–33. doi: 10.1006/abio.1994.1137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poon R. Y., Yamashita K., Adamczewski J. P., Hunt T., Shuttleworth J. The cdc2-related protein p40MO15 is the catalytic subunit of a protein kinase that can activate p33cdk2 and p34cdc2. EMBO J. 1993 Aug;12(8):3123–3132. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05981.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poon R. Y., Yamashita K., Howell M., Ershler M. A., Belyavsky A., Hunt T. Cell cycle regulation of the p34cdc2/p33cdk2-activating kinase p40MO15. J Cell Sci. 1994 Oct;107(Pt 10):2789–2799. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.10.2789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serrano M., Hannon G. J., Beach D. A new regulatory motif in cell-cycle control causing specific inhibition of cyclin D/CDK4. Nature. 1993 Dec 16;366(6456):704–707. doi: 10.1038/366704a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherr C. J. G1 phase progression: cycling on cue. Cell. 1994 Nov 18;79(4):551–555. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90540-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skapek S. X., Rhee J., Spicer D. B., Lassar A. B. Inhibition of myogenic differentiation in proliferating myoblasts by cyclin D1-dependent kinase. Science. 1995 Feb 17;267(5200):1022–1024. doi: 10.1126/science.7863328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slingerland J. M., Hengst L., Pan C. H., Alexander D., Stampfer M. R., Reed S. I. A novel inhibitor of cyclin-Cdk activity detected in transforming growth factor beta-arrested epithelial cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;14(6):3683–3694. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.6.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon M. J., Harper J. W., Shuttleworth J. CAK, the p34cdc2 activating kinase, contains a protein identical or closely related to p40MO15. EMBO J. 1993 Aug;12(8):3133–3142. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05982.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoshima H., Hunter T. p27, a novel inhibitor of G1 cyclin-Cdk protein kinase activity, is related to p21. Cell. 1994 Jul 15;78(1):67–74. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90573-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waga S., Hannon G. J., Beach D., Stillman B. The p21 inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinases controls DNA replication by interaction with PCNA. Nature. 1994 Jun 16;369(6481):574–578. doi: 10.1038/369574a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong Y., Hannon G. J., Zhang H., Casso D., Kobayashi R., Beach D. p21 is a universal inhibitor of cyclin kinases. Nature. 1993 Dec 16;366(6456):701–704. doi: 10.1038/366701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong Y., Zhang H., Beach D. D type cyclins associate with multiple protein kinases and the DNA replication and repair factor PCNA. Cell. 1992 Oct 30;71(3):505–514. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90518-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong Y., Zhang H., Beach D. Subunit rearrangement of the cyclin-dependent kinases is associated with cellular transformation. Genes Dev. 1993 Aug;7(8):1572–1583. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.8.1572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang H., Hannon G. J., Beach D. p21-containing cyclin kinases exist in both active and inactive states. Genes Dev. 1994 Aug 1;8(15):1750–1758. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.15.1750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Deiry W. S., Harper J. W., O'Connor P. M., Velculescu V. E., Canman C. E., Jackman J., Pietenpol J. A., Burrell M., Hill D. E., Wang Y. WAF1/CIP1 is induced in p53-mediated G1 arrest and apoptosis. Cancer Res. 1994 Mar 1;54(5):1169–1174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Deiry W. S., Tokino T., Velculescu V. E., Levy D. B., Parsons R., Trent J. M., Lin D., Mercer W. E., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. WAF1, a potential mediator of p53 tumor suppression. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):817–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90500-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]