Abstract
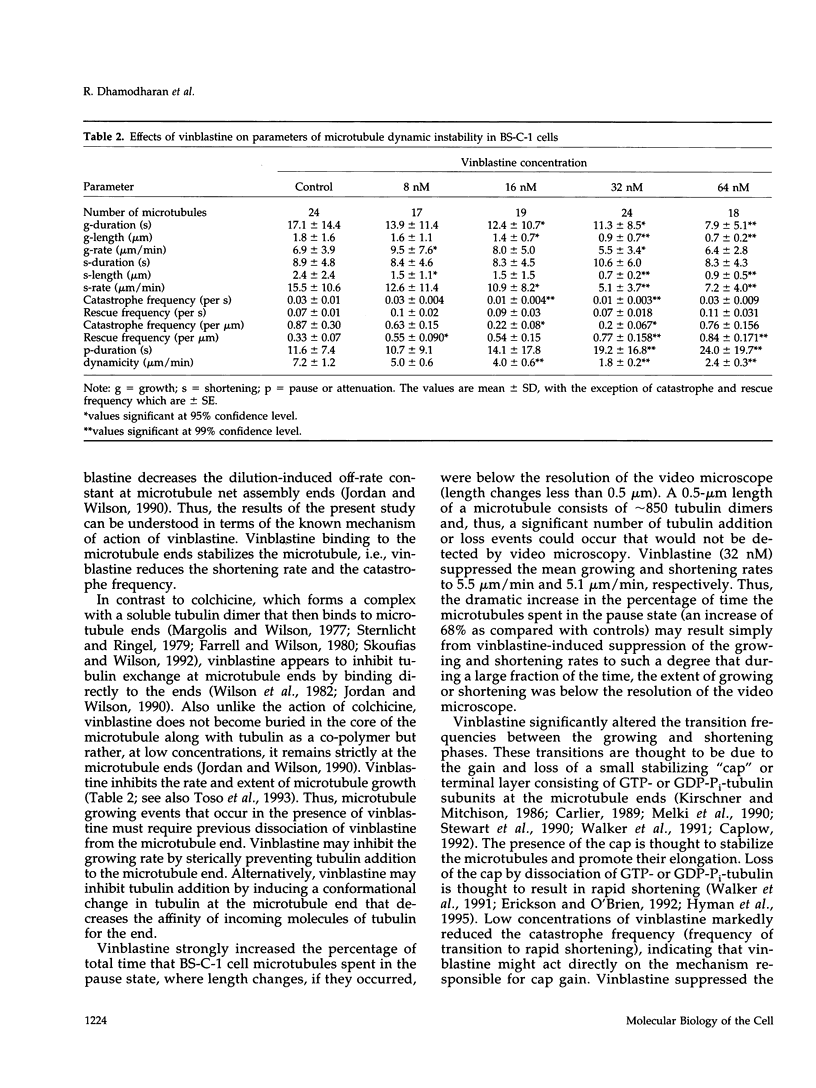
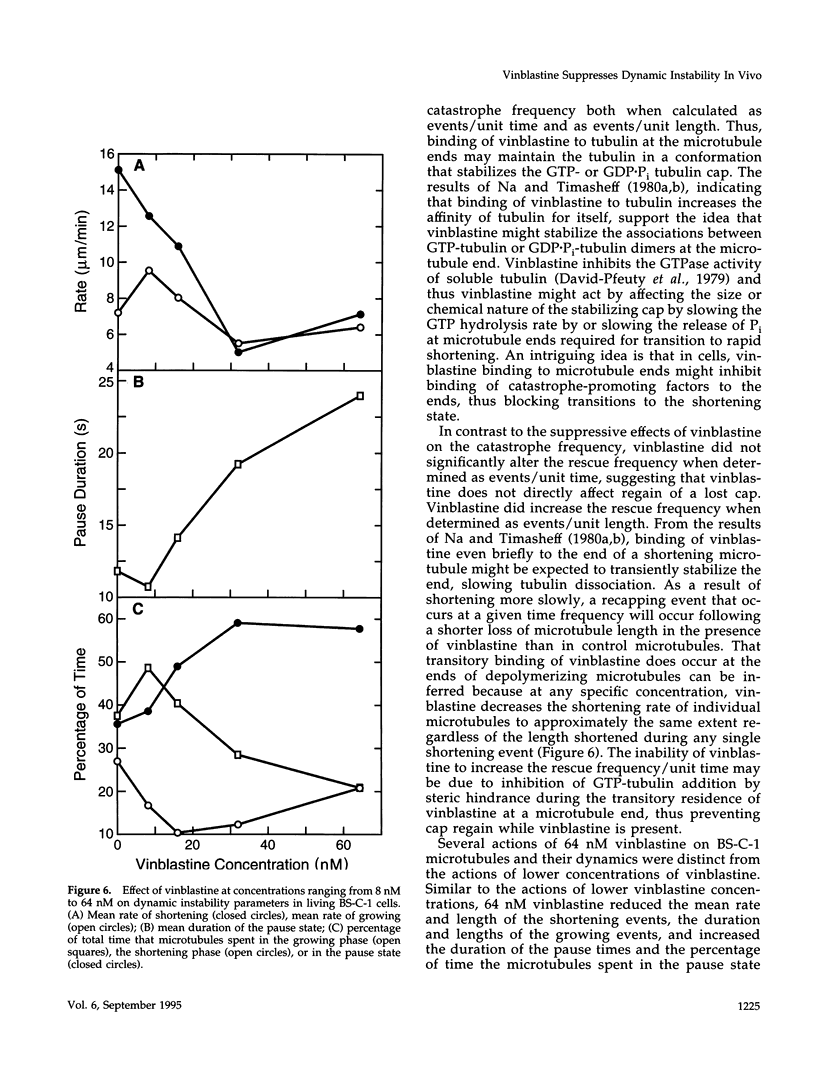
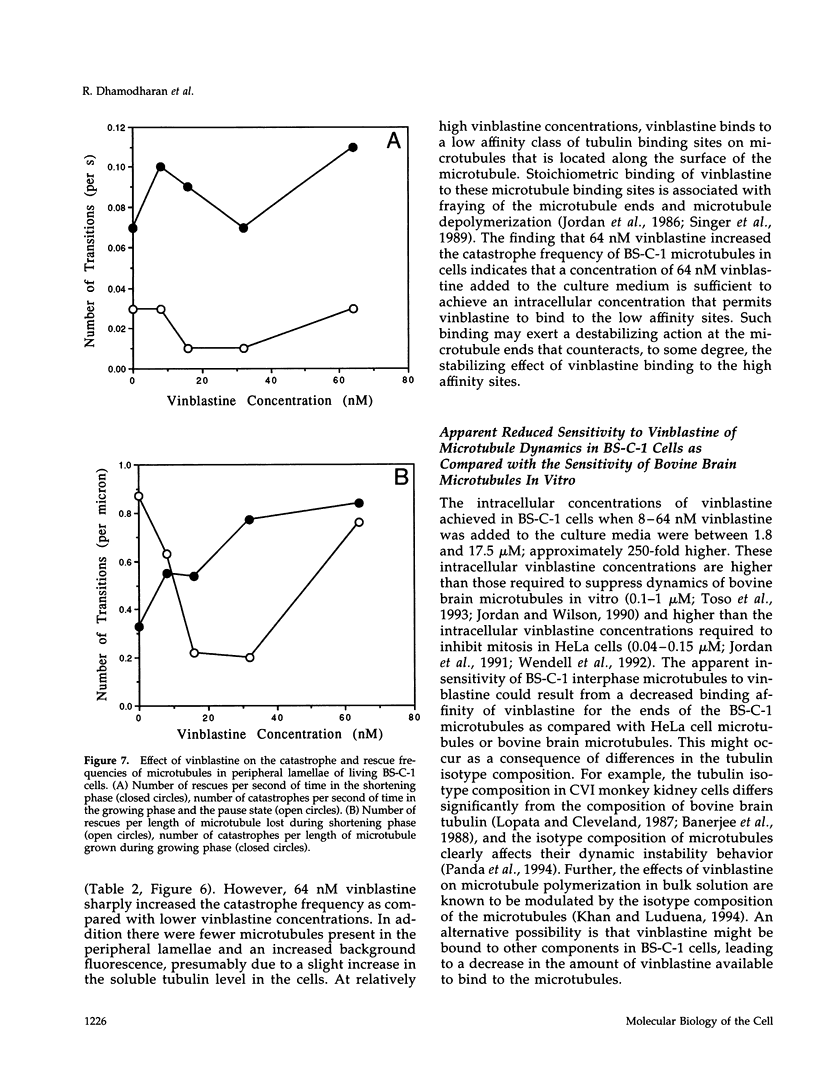
We have characterized the effects of vinblastine on the dynamic instability behavior of individual microtubules in living BS-C-1 cells microinjected with rhodamine-labeled tubulin and have found that at low concentrations (3-64 nM), vinblastine potently suppresses dynamic instability without causing net microtubule depolymerization. Vinblastine suppressed the rates of microtubule growth and shortening, and decreased the frequency of transitions from growth or pause to shortening, also called catastrophe. In vinblastine-treated cells, both the average duration of a pause (a state of attenuated dynamics where neither growth nor shortening could be detected) and the percentage of total time spent in pause were significantly increased. Vinblastine potently decreased dynamicity, a measure of the overall dynamic activity of microtubules, reducing this parameter by 75% at 32 nM. The present work, consistent with earlier in vitro studies, demonstrates that vinblastine kinetically caps the ends of microtubules in living cells and supports the hypothesis that the potent chemotherapeutic action of vinblastine as an antitumor drug is suppression of mitotic spindle microtubule dynamics. Further, the results indicate that molecules that bind to microtubule ends can regulate microtubule dynamic behavior in living cells and suggest that endogenous regulators of microtubule dynamics that work by similar mechanisms may exist in living cells.
Full text
PDF



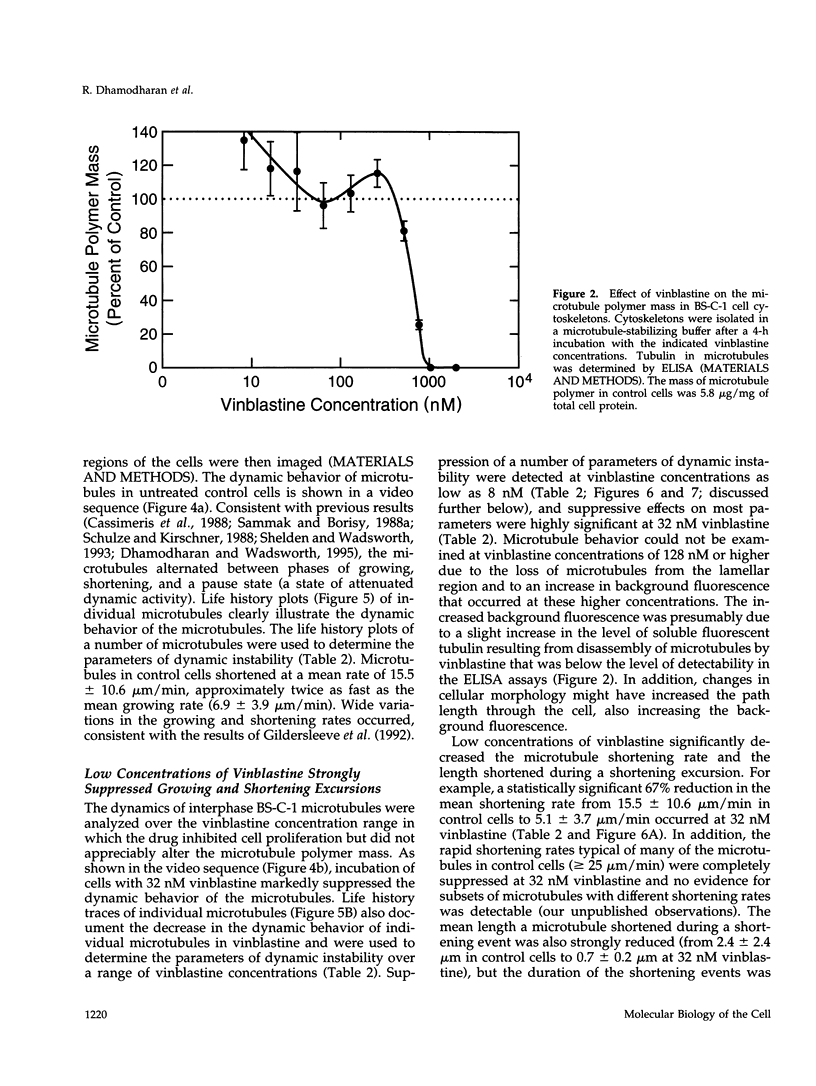
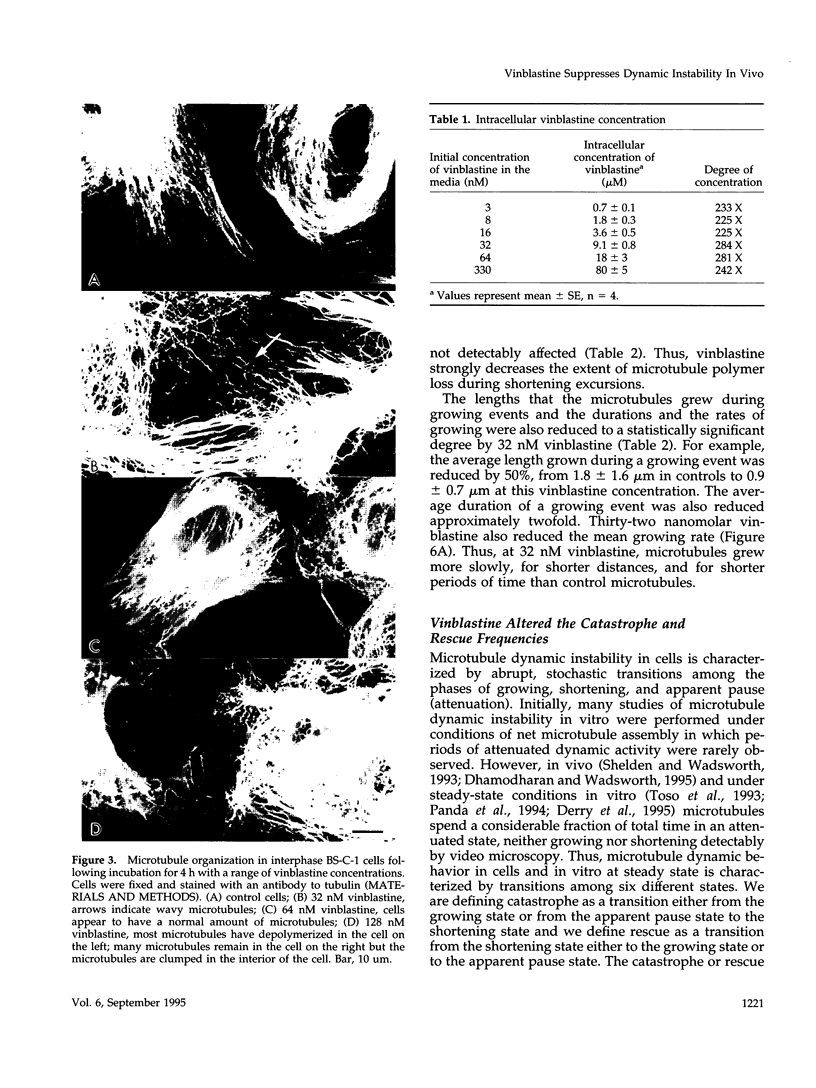
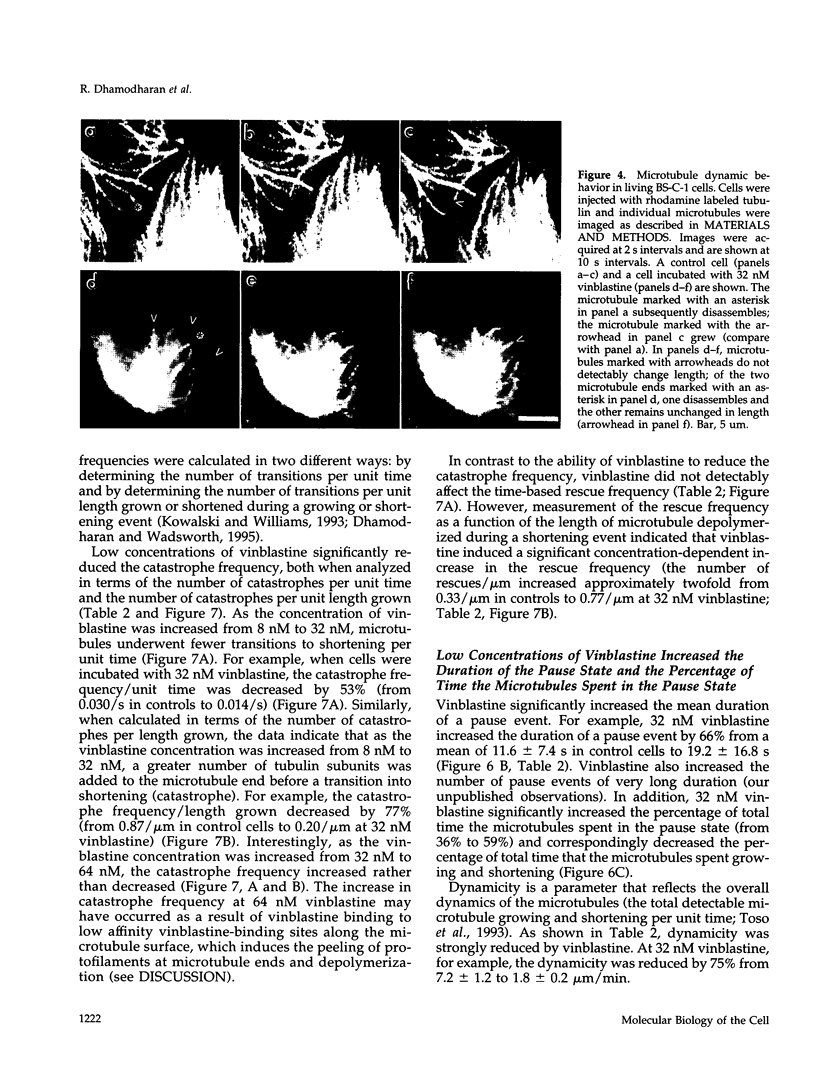
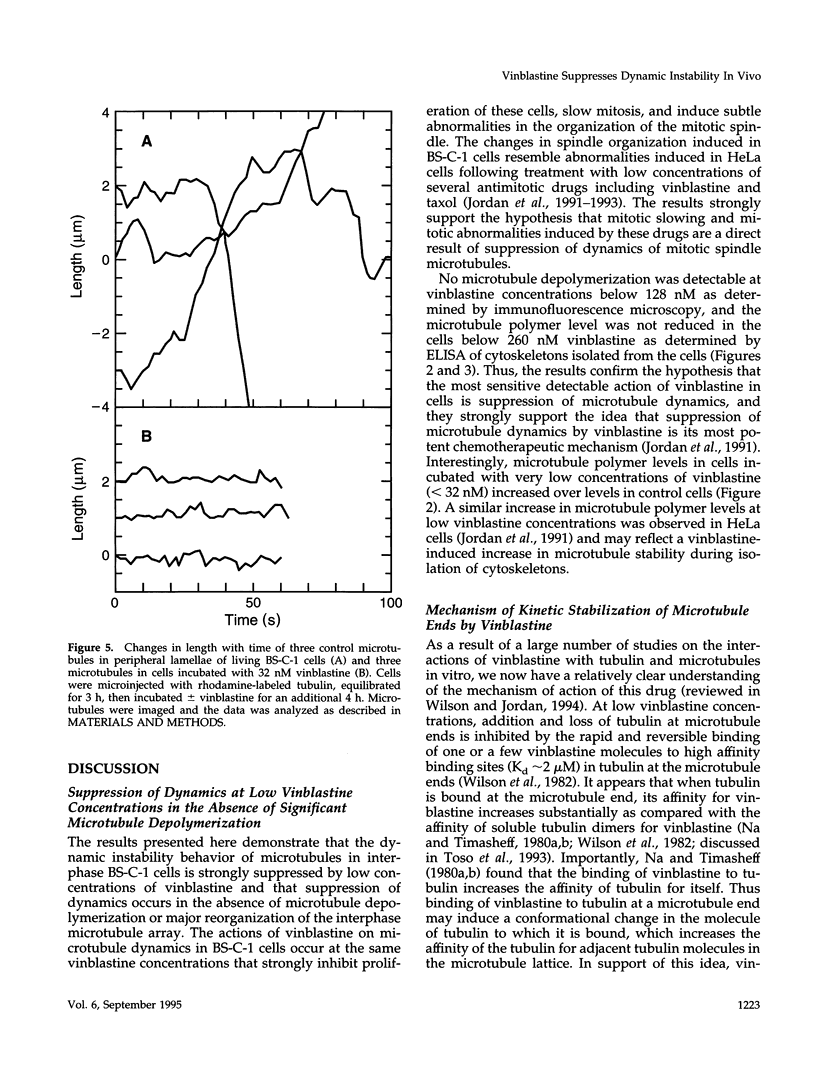



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baas P. W., Ahmad F. J. The transport properties of axonal microtubules establish their polarity orientation. J Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;120(6):1427–1437. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.6.1427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee A., Roach M. C., Wall K. A., Lopata M. A., Cleveland D. W., Ludueña R. F. A monoclonal antibody against the type II isotype of beta-tubulin. Preparation of isotypically altered tubulin. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):3029–3034. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belmont L. D., Hyman A. A., Sawin K. E., Mitchison T. J. Real-time visualization of cell cycle-dependent changes in microtubule dynamics in cytoplasmic extracts. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):579–589. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90022-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caplow M. Microtubule dynamics. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;4(1):58–65. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90059-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlier M. F. Role of nucleotide hydrolysis in the dynamics of actin filaments and microtubules. Int Rev Cytol. 1989;115:139–170. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60629-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassimeris L., Pryer N. K., Salmon E. D. Real-time observations of microtubule dynamic instability in living cells. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 1):2223–2231. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassimeris L. Regulation of microtubule dynamic instability. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1993;26(4):275–281. doi: 10.1002/cm.970260402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David-Pfeuty T., Simon C., Pantaloni D. Effect of antimitotic drugs on tubulin GTPase activity and self-assembly. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 25;254(22):11696–11702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derry W. B., Wilson L., Jordan M. A. Substoichiometric binding of taxol suppresses microtubule dynamics. Biochemistry. 1995 Feb 21;34(7):2203–2211. doi: 10.1021/bi00007a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhamodharan R., Wadsworth P. Modulation of microtubule dynamic instability in vivo by brain microtubule associated proteins. J Cell Sci. 1995 Apr;108(Pt 4):1679–1689. doi: 10.1242/jcs.108.4.1679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donoso J. A., Himes R. H. The action of two Vinca alkaloids on B16 melanoma in vitro. Cancer Biochem Biophys. 1984 Jun;7(2):133–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson H. P., O'Brien E. T. Microtubule dynamic instability and GTP hydrolysis. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1992;21:145–166. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.21.060192.001045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell K. W., Wilson L. Proposed mechanism for colchicine poisoning of microtubules reassembled in vitro from Strongylocentrotus purpuratus sperm tail outer doublet tubulin. Biochemistry. 1980 Jun 24;19(13):3048–3054. doi: 10.1021/bi00554a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gildersleeve R. F., Cross A. R., Cullen K. E., Fagen A. P., Williams R. C., Jr Microtubules grow and shorten at intrinsically variable rates. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 25;267(12):7995–8006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gliksman N. R., Parsons S. F., Salmon E. D. Okadaic acid induces interphase to mitotic-like microtubule dynamic instability by inactivating rescue. J Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;119(5):1271–1276. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.5.1271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamel E., Lin C. M. Glutamate-induced polymerization of tubulin: characteristics of the reaction and application to the large-scale purification of tubulin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Jun;209(1):29–40. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90253-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horio T., Hotani H. Visualization of the dynamic instability of individual microtubules by dark-field microscopy. Nature. 1986 Jun 5;321(6070):605–607. doi: 10.1038/321605a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman A. A., Chrétien D., Arnal I., Wade R. H. Structural changes accompanying GTP hydrolysis in microtubules: information from a slowly hydrolyzable analogue guanylyl-(alpha,beta)-methylene-diphosphonate. J Cell Biol. 1995 Jan;128(1-2):117–125. doi: 10.1083/jcb.128.1.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman A., Drechsel D., Kellogg D., Salser S., Sawin K., Steffen P., Wordeman L., Mitchison T. Preparation of modified tubulins. Methods Enzymol. 1991;196:478–485. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)96041-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan M. A., Margolis R. L., Himes R. H., Wilson L. Identification of a distinct class of vinblastine binding sites on microtubules. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jan 5;187(1):61–73. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90406-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan M. A., Thrower D., Wilson L. Effects of vinblastine, podophyllotoxin and nocodazole on mitotic spindles. Implications for the role of microtubule dynamics in mitosis. J Cell Sci. 1992 Jul;102(Pt 3):401–416. doi: 10.1242/jcs.102.3.401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan M. A., Thrower D., Wilson L. Mechanism of inhibition of cell proliferation by Vinca alkaloids. Cancer Res. 1991 Apr 15;51(8):2212–2222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan M. A., Toso R. J., Thrower D., Wilson L. Mechanism of mitotic block and inhibition of cell proliferation by taxol at low concentrations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 15;90(20):9552–9556. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.20.9552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan M. A., Wilson L. Kinetic analysis of tubulin exchange at microtubule ends at low vinblastine concentrations. Biochemistry. 1990 Mar 20;29(11):2730–2739. doi: 10.1021/bi00463a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschner M., Mitchison T. Beyond self-assembly: from microtubules to morphogenesis. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):329–342. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90318-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalski R. J., Williams R. C., Jr Microtubule-associated protein 2 alters the dynamic properties of microtubule assembly and disassembly. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 5;268(13):9847–9855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopata M. A., Cleveland D. W. In vivo microtubules are copolymers of available beta-tubulin isotypes: localization of each of six vertebrate beta-tubulin isotypes using polyclonal antibodies elicited by synthetic peptide antigens. J Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;105(4):1707–1720. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.4.1707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis R. L., Wilson L. Addition of colchicine--tubulin complex to microtubule ends: the mechanism of substoichiometric colchicine poisoning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3466–3470. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melki R., Carlier M. F., Pantaloni D. Direct evidence for GTP and GDP-Pi intermediates in microtubule assembly. Biochemistry. 1990 Sep 25;29(38):8921–8932. doi: 10.1021/bi00490a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchison T., Kirschner M. Dynamic instability of microtubule growth. Nature. 1984 Nov 15;312(5991):237–242. doi: 10.1038/312237a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchison T., Kirschner M. Microtubule assembly nucleated by isolated centrosomes. Nature. 1984 Nov 15;312(5991):232–237. doi: 10.1038/312232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Na G. C., Timasheff S. N. In vitro vinblastine-induced tubulin paracrystals. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10387–10391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Na G. C., Timasheff S. N. Stoichiometry of the vinblastine-induced self-association of calf brain tubulin. Biochemistry. 1980 Apr 1;19(7):1347–1354. doi: 10.1021/bi00548a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Na G. C., Timasheff S. N. Thermodynamic linkage between tubulin self-association and the binding of vinblastine. Biochemistry. 1980 Apr 1;19(7):1355–1365. doi: 10.1021/bi00548a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ookata K., Hisanaga S., Bulinski J. C., Murofushi H., Aizawa H., Itoh T. J., Hotani H., Okumura E., Tachibana K., Kishimoto T. Cyclin B interaction with microtubule-associated protein 4 (MAP4) targets p34cdc2 kinase to microtubules and is a potential regulator of M-phase microtubule dynamics. J Cell Biol. 1995 Mar;128(5):849–862. doi: 10.1083/jcb.128.5.849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panda D., Miller H. P., Banerjee A., Ludueña R. F., Wilson L. Microtubule dynamics in vitro are regulated by the tubulin isotype composition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Nov 22;91(24):11358–11362. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.24.11358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pryer N. K., Walker R. A., Skeen V. P., Bourns B. D., Soboeiro M. F., Salmon E. D. Brain microtubule-associated proteins modulate microtubule dynamic instability in vitro. Real-time observations using video microscopy. J Cell Sci. 1992 Dec;103(Pt 4):965–976. doi: 10.1242/jcs.103.4.965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSE G. G., POMERAT C. M., SHINDLER T. O., TRUNNELL J. B. A cellophane-strip technique for culturing tissue in multipurpose culture chambers. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 Nov 25;4(6):761–764. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.6.761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sammak P. J., Borisy G. G. Direct observation of microtubule dynamics in living cells. Nature. 1988 Apr 21;332(6166):724–726. doi: 10.1038/332724a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxton W. M., Stemple D. L., Leslie R. J., Salmon E. D., Zavortink M., McIntosh J. R. Tubulin dynamics in cultured mammalian cells. J Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;99(6):2175–2186. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.6.2175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze E., Kirschner M. New features of microtubule behaviour observed in vivo. Nature. 1988 Jul 28;334(6180):356–359. doi: 10.1038/334356a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelden E., Wadsworth P. Microinjection of biotin-tubulin into anaphase cells induces transient elongation of kinetochore microtubules and reversal of chromosome-to-pole motion. J Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;116(6):1409–1420. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.6.1409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelden E., Wadsworth P. Observation and quantification of individual microtubule behavior in vivo: microtubule dynamics are cell-type specific. J Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;120(4):935–945. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.4.935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer W. D., Jordan M. A., Wilson L., Himes R. H. Binding of vinblastine to stabilized microtubules. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Sep;36(3):366–370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skoufias D. A., Wilson L. Mechanism of inhibition of microtubule polymerization by colchicine: inhibitory potencies of unliganded colchicine and tubulin-colchicine complexes. Biochemistry. 1992 Jan 28;31(3):738–746. doi: 10.1021/bi00118a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternlicht H., Ringel I. Colchicine inhibition of microtubule assembly via copolymer formation. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):10540–10550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart R. J., Farrell K. W., Wilson L. Role of GTP hydrolysis in microtubule polymerization: evidence for a coupled hydrolysis mechanism. Biochemistry. 1990 Jul 10;29(27):6489–6498. doi: 10.1021/bi00479a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka E., Ho T., Kirschner M. W. The role of microtubule dynamics in growth cone motility and axonal growth. J Cell Biol. 1995 Jan;128(1-2):139–155. doi: 10.1083/jcb.128.1.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thrower D., Jordan M. A., Wilson L. A quantitative solid-phase binding assay for tubulin. Methods Cell Biol. 1993;37:129–145. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60248-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thrower D., Jordan M. A., Wilson L. Quantitation of cellular tubulin in microtubules and tubulin pools by a competitive ELISA. J Immunol Methods. 1991 Jan 24;136(1):45–51. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(91)90248-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toso R. J., Jordan M. A., Farrell K. W., Matsumoto B., Wilson L. Kinetic stabilization of microtubule dynamic instability in vitro by vinblastine. Biochemistry. 1993 Feb 9;32(5):1285–1293. doi: 10.1021/bi00056a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasquez R. J., Gard D. L., Cassimeris L. XMAP from Xenopus eggs promotes rapid plus end assembly of microtubules and rapid microtubule polymer turnover. J Cell Biol. 1994 Nov;127(4):985–993. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.4.985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigers G. P., Coue M., McIntosh J. R. Fluorescent microtubules break up under illumination. J Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;107(3):1011–1024. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.3.1011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadsworth P., McGrail M. Interphase microtubule dynamics are cell type-specific. J Cell Sci. 1990 Jan;95(Pt 1):23–32. doi: 10.1242/jcs.95.1.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker R. A., O'Brien E. T., Pryer N. K., Soboeiro M. F., Voter W. A., Erickson H. P., Salmon E. D. Dynamic instability of individual microtubules analyzed by video light microscopy: rate constants and transition frequencies. J Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;107(4):1437–1448. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.4.1437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker R. A., Pryer N. K., Salmon E. D. Dilution of individual microtubules observed in real time in vitro: evidence that cap size is small and independent of elongation rate. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;114(1):73–81. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.1.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wendell K. L., Wilson L., Jordan M. A. Mitotic block in HeLa cells by vinblastine: ultrastructural changes in kinetochore-microtubule attachment and in centrosomes. J Cell Sci. 1993 Feb;104(Pt 2):261–274. doi: 10.1242/jcs.104.2.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson L., Jordan M. A., Morse A., Margolis R. L. Interaction of vinblastine with steady-state microtubules in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jul 25;159(1):125–149. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90035-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]