Abstract
We describe the expression of gpIRK1, an inwardly rectifying K+ channel obtained from guinea pig cardiac cDNA. gpIRK1 is a homologue of the mouse IRK1 channel identified in macrophage cells. Expression of gpIRK1 in Xenopus oocytes produces inwardly rectifying K+ current, similar to the cardiac inward rectifier current IK1. This current is blocked by external Ba2+ and Cs+. Plasmids containing the gpIRK1 coding region under the transcriptional control of constitutive (PGK) or inducible (GAL) promoters were constructed for expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Several observations suggest that gpIRK1 forms functional ion channels when expressed in yeast. gpIRK1 complements a trk1 delta trk2 delta strain, which is defective in potassium uptake. Expression of gpIRK1 in this mutant restores growth on low potassium media. Growth dependent on gpIRK1 is inhibited by external Cs+. The strain expressing gpIRK1 provides a versatile genetic system for studying the assembly and composition of inwardly rectifying K+ channels.
Full text
PDF



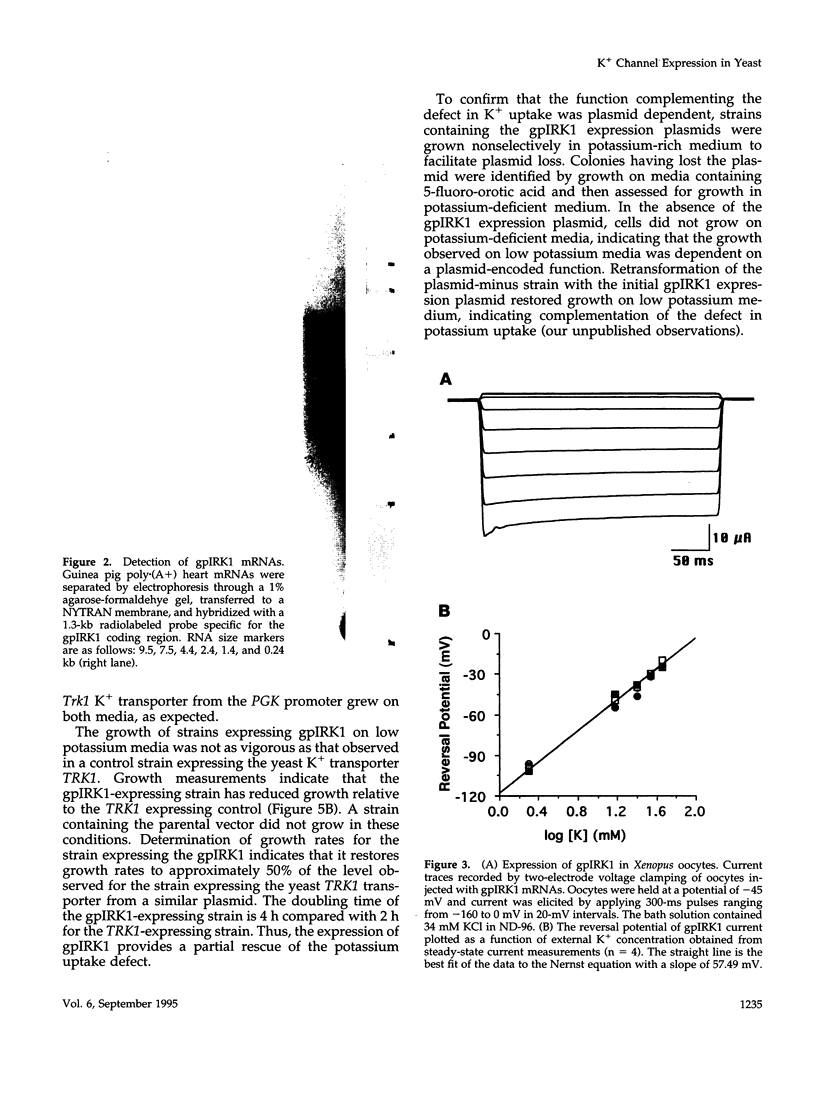
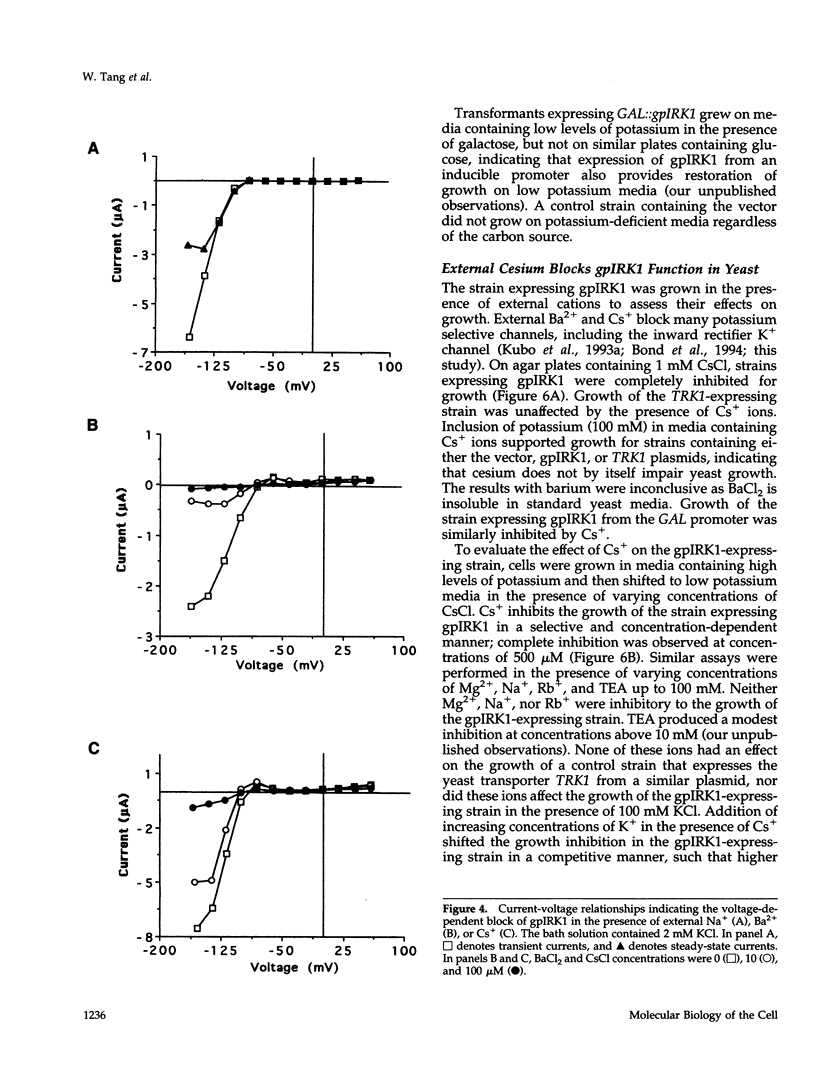
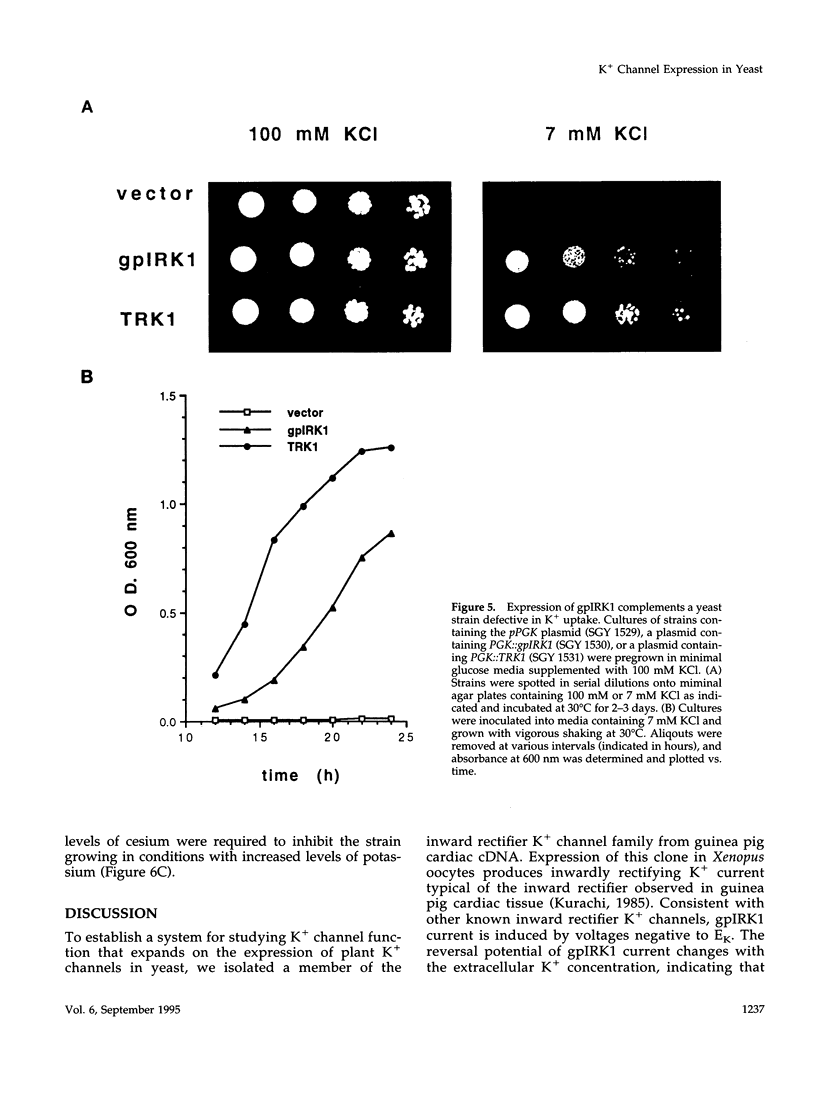


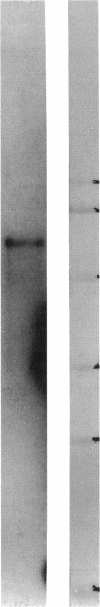
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. A., Huprikar S. S., Kochian L. V., Lucas W. J., Gaber R. F. Functional expression of a probable Arabidopsis thaliana potassium channel in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):3736–3740. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.3736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertl A., Anderson J. A., Slayman C. L., Gaber R. F. Use of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for patch-clamp analysis of heterologous membrane proteins: characterization of Kat1, an inward-rectifying K+ channel from Arabidopsis thaliana, and comparison with endogeneous yeast channels and carriers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Mar 28;92(7):2701–2705. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.7.2701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biermans G., Vereecke J., Carmeliet E. The mechanism of the inactivation of the inward-rectifying K current during hyperpolarizing steps in guinea-pig ventricular myocytes. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Dec;410(6):604–613. doi: 10.1007/BF00581320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond C. T., Pessia M., Xia X. M., Lagrutta A., Kavanaugh M. P., Adelman J. P. Cloning and expression of a family of inward rectifier potassium channels. Receptors Channels. 1994;2(3):183–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. M. Functional bases for interpreting amino acid sequences of voltage-dependent K+ channels. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1993;22:173–198. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.22.060193.001133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dascal N., Schreibmayer W., Lim N. F., Wang W., Chavkin C., DiMagno L., Labarca C., Kieffer B. L., Gaveriaux-Ruff C., Trollinger D. Atrial G protein-activated K+ channel: expression cloning and molecular properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 1;90(21):10235–10239. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.21.10235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaber R. F. Molecular genetics of yeast ion transport. Int Rev Cytol. 1992;137:299–353. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62679-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaber R. F., Styles C. A., Fink G. R. TRK1 encodes a plasma membrane protein required for high-affinity potassium transport in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;8(7):2848–2859. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.7.2848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Jaffe L. A. Electrical properties of egg cell membranes. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1979;8:385–416. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.08.060179.002125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imoto Y., Ehara T., Matsuura H. Voltage- and time-dependent block of iK1 underlying Ba2+-induced ventricular automaticity. Am J Physiol. 1987 Feb;252(2 Pt 2):H325–H333. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1987.252.2.H325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iverson L. E., Tanouye M. A., Lester H. A., Davidson N., Rudy B. A-type potassium channels expressed from Shaker locus cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5723–5727. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N. Potassium channels and their evolving gates. Nature. 1994 Sep 8;371(6493):119–122. doi: 10.1038/371119a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N. Structural elements involved in specific K+ channel functions. Annu Rev Physiol. 1992;54:537–555. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.54.030192.002541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamb A., Iverson L. E., Tanouye M. A. Molecular characterization of Shaker, a Drosophila gene that encodes a potassium channel. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):405–413. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90494-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ko C. H., Buckley A. M., Gaber R. F. TRK2 is required for low affinity K+ transport in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1990 Jun;125(2):305–312. doi: 10.1093/genetics/125.2.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ko C. H., Gaber R. F. TRK1 and TRK2 encode structurally related K+ transporters in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;11(8):4266–4273. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.8.4266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krapivinsky G., Gordon E. A., Wickman K., Velimirović B., Krapivinsky L., Clapham D. E. The G-protein-gated atrial K+ channel IKACh is a heteromultimer of two inwardly rectifying K(+)-channel proteins. Nature. 1995 Mar 9;374(6518):135–141. doi: 10.1038/374135a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubo Y., Baldwin T. J., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Primary structure and functional expression of a mouse inward rectifier potassium channel. Nature. 1993 Mar 11;362(6416):127–133. doi: 10.1038/362127a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubo Y., Reuveny E., Slesinger P. A., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Primary structure and functional expression of a rat G-protein-coupled muscarinic potassium channel. Nature. 1993 Aug 26;364(6440):802–806. doi: 10.1038/364802a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurachi Y. Voltage-dependent activation of the inward-rectifier potassium channel in the ventricular cell membrane of guinea-pig heart. J Physiol. 1985 Sep;366:365–385. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitra R. L., Morad M. Permeance of Cs+ and Rb+ through the inwardly rectifying K+ channel in guinea pig ventricular myocytes. J Membr Biol. 1991 May;122(1):33–42. doi: 10.1007/BF01872737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papazian D. M., Schwarz T. L., Tempel B. L., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Cloning of genomic and complementary DNA from Shaker, a putative potassium channel gene from Drosophila. Science. 1987 Aug 14;237(4816):749–753. doi: 10.1126/science.2441470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peña A., Pardo J. P., Ramírez J. Early metabolic effects and mechanism of ammonium transport in yeast. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 Mar;253(2):431–438. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90196-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Navarro A., Ramos J. Dual system for potassium transport in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1984 Sep;159(3):940–945. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.3.940-945.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. J. One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:202–211. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachtman D. P., Schroeder J. I., Lucas W. J., Anderson J. A., Gaber R. F. Expression of an inward-rectifying potassium channel by the Arabidopsis KAT1 cDNA. Science. 1992 Dec 4;258(5088):1654–1658. doi: 10.1126/science.8966547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachtman D. P., Schroeder J. I. Structure and transport mechanism of a high-affinity potassium uptake transporter from higher plants. Nature. 1994 Aug 25;370(6491):655–658. doi: 10.1038/370655a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sentenac H., Bonneaud N., Minet M., Lacroute F., Salmon J. M., Gaymard F., Grignon C. Cloning and expression in yeast of a plant potassium ion transport system. Science. 1992 May 1;256(5057):663–665. doi: 10.1126/science.1585180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Boeke J. D. In vitro mutagenesis and plasmid shuffling: from cloned gene to mutant yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:302–318. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang W., Yang X. C. Cloning a novel human brain inward rectifier potassium channel and its functional expression in Xenopus oocytes. FEBS Lett. 1994 Jul 18;348(3):239–243. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)00612-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timpe L. C., Schwarz T. L., Tempel B. L., Papazian D. M., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Expression of functional potassium channels from Shaker cDNA in Xenopus oocytes. Nature. 1988 Jan 14;331(6152):143–145. doi: 10.1038/331143a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]