Abstract
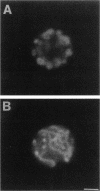
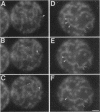
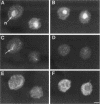
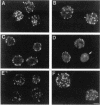
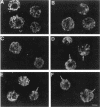
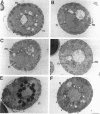
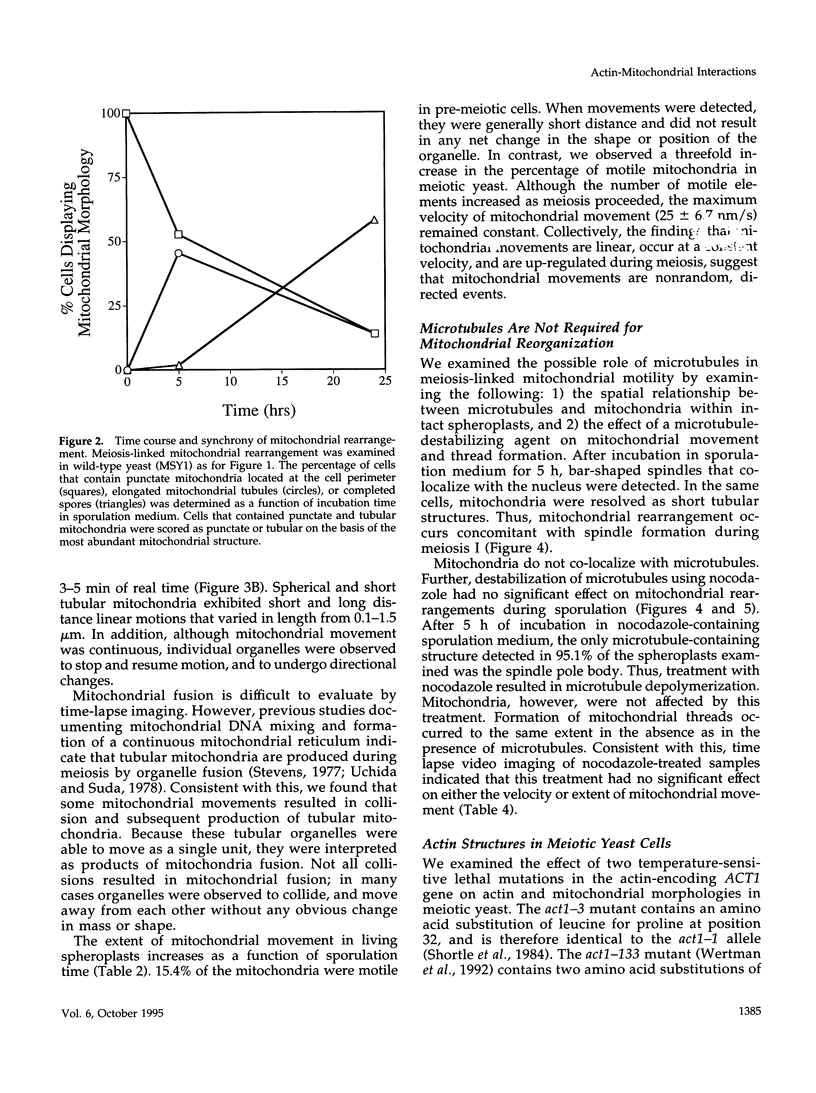
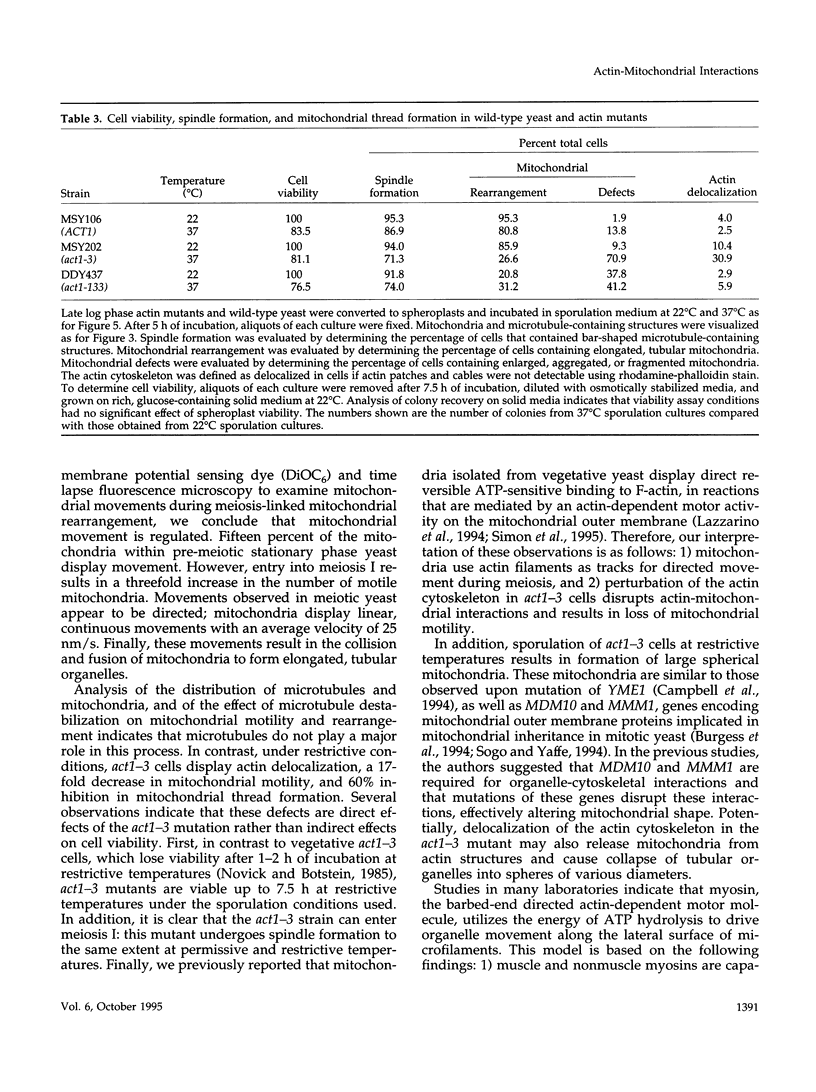
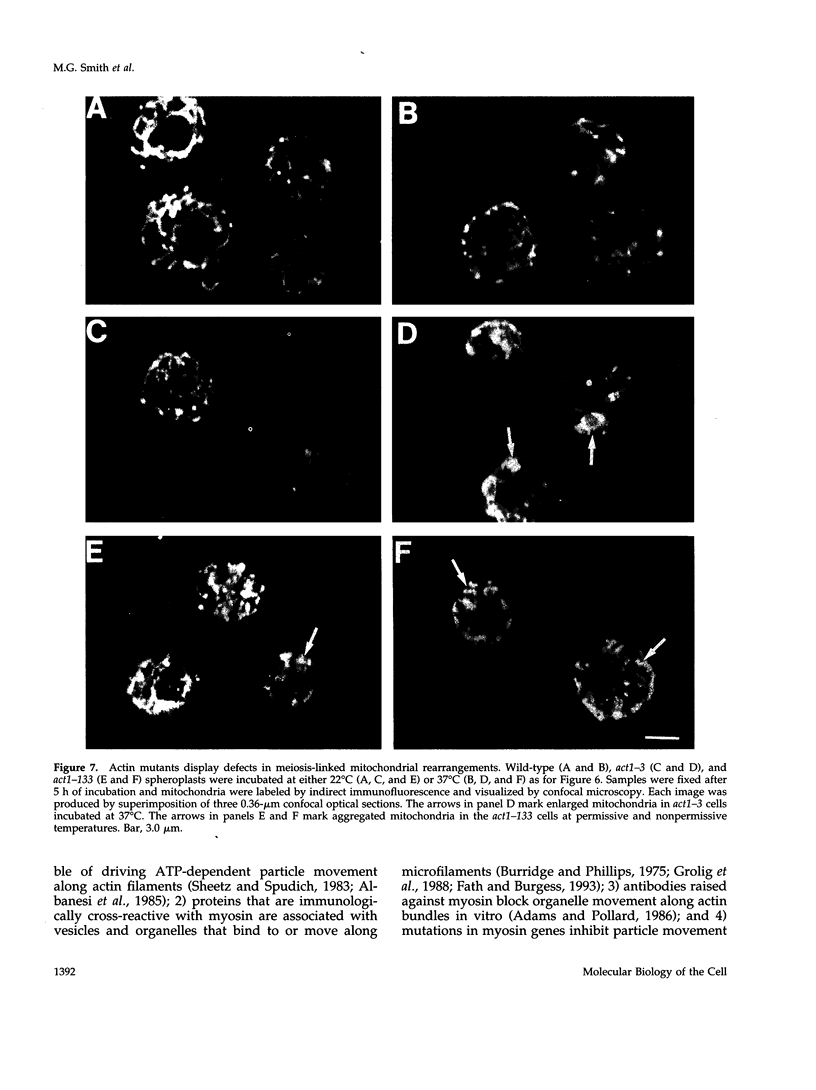
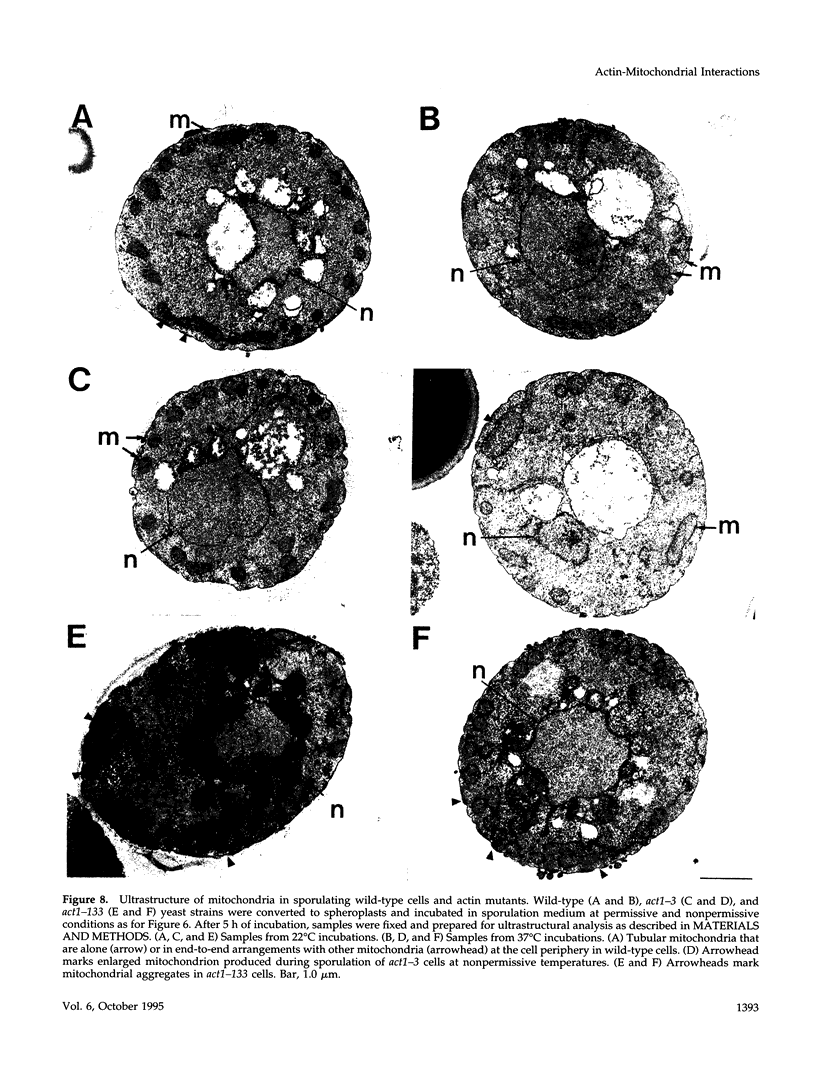
During early stages of meiosis I, yeast mitochondria fuse to form a single continuous thread. Thereafter, portions of the mitochondrial thread are equally distributed to daughter cells. Using time-lapse fluorescence microscopy and a membrane potential sensing dye, mitochondria are resolved as small particles at the cell periphery in pre-meiotic, living yeast. These organelles display low levels of movement. During meiosis I, we observed a threefold increase in mitochondrial motility. Mitochondrial movements were linear, occurred at a maximum velocity of 25 +/- 6.7 nm/s, and resulted in organelle collision and fusion to form elongated tubular structures. Mitochondria do not co-localize with microtubules. Destabilization of microtubules by nocodazole treatment has no significant effect on the rate and extent of thread formation. In contrast, yeast bearing temperature-sensitive mutations in the actin-encoding ACT1 gene (act1-3 and act1-133) exhibit abnormal mitochondrial aggregation, fragmentation, and enlargement as well as loss of mitochondrial motility. In act1-3 cells, mitochondrial defects and actin delocalization occur only at restrictive temperatures. The act1-133 mutation, which perturbs the myosin-binding site of actin without significantly affecting actin cytoskeletal structure in meiotic yeast, results in mitochondrial morphology and motility defects at restrictive and permissive temperatures. These studies support a role for the actin cytoskeleton in the control of mitochondrial position and movements in meiotic yeast.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams A. E., Botstein D., Drubin D. G. Requirement of yeast fimbrin for actin organization and morphogenesis in vivo. Nature. 1991 Dec 5;354(6352):404–408. doi: 10.1038/354404a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
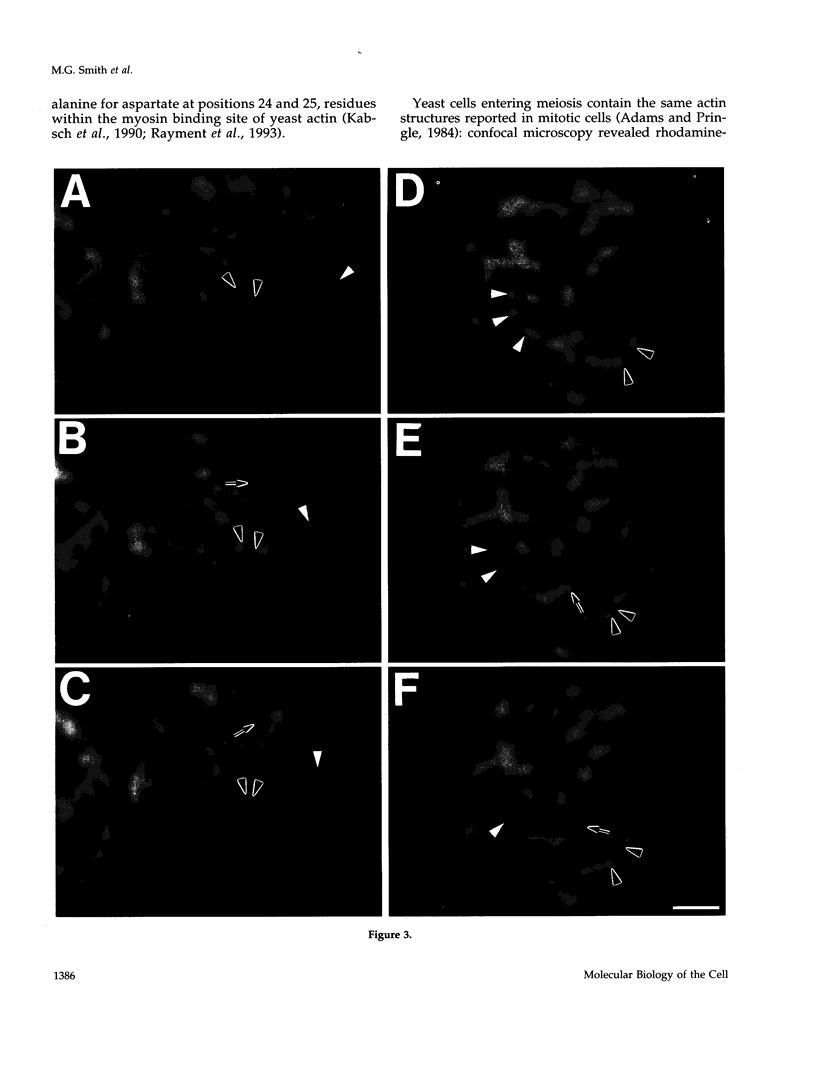
- Adams A. E., Pringle J. R. Relationship of actin and tubulin distribution to bud growth in wild-type and morphogenetic-mutant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;98(3):934–945. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.3.934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams R. J., Pollard T. D. Propulsion of organelles isolated from Acanthamoeba along actin filaments by myosin-I. Nature. 1986 Aug 21;322(6081):754–756. doi: 10.1038/322754a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albanesi J. P., Fujisaki H., Hammer J. A., 3rd, Korn E. D., Jones R., Sheetz M. P. Monomeric Acanthamoeba myosins I support movement in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 25;260(15):8649–8652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen R. D., Metuzals J., Tasaki I., Brady S. T., Gilbert S. P. Fast axonal transport in squid giant axon. Science. 1982 Dec 10;218(4577):1127–1129. doi: 10.1126/science.6183744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amatruda J. F., Cooper J. A. Purification, characterization, and immunofluorescence localization of Saccharomyces cerevisiae capping protein. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;117(5):1067–1076. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.5.1067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady S. T., Lasek R. J., Allen R. D. Fast axonal transport in extruded axoplasm from squid giant axon. Science. 1982 Dec 10;218(4577):1129–1131. doi: 10.1126/science.6183745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridgman P. C., Kachar B., Reese T. S. The structure of cytoplasm in directly frozen cultured cells. II. Cytoplasmic domains associated with organelle movements. J Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;102(4):1510–1521. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.4.1510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess S. M., Delannoy M., Jensen R. E. MMM1 encodes a mitochondrial outer membrane protein essential for establishing and maintaining the structure of yeast mitochondria. J Cell Biol. 1994 Sep;126(6):1375–1391. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.6.1375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burridge K., Phillips J. H. Association of actin and myosin with secretory granule membranes. Nature. 1975 Apr 10;254(5500):526–529. doi: 10.1038/254526a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell C. L., Tanaka N., White K. H., Thorsness P. E. Mitochondrial morphological and functional defects in yeast caused by yme1 are suppressed by mutation of a 26S protease subunit homologue. Mol Biol Cell. 1994 Aug;5(8):899–905. doi: 10.1091/mbc.5.8.899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury S., Smith K. W., Gustin M. C. Osmotic stress and the yeast cytoskeleton: phenotype-specific suppression of an actin mutation. J Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;118(3):561–571. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.3.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A. Effects of cytochalasin and phalloidin on actin. J Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;105(4):1473–1478. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.4.1473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drubin D. G., Jones H. D., Wertman K. F. Actin structure and function: roles in mitochondrial organization and morphogenesis in budding yeast and identification of the phalloidin-binding site. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Dec;4(12):1277–1294. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.12.1277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drubin D. G., Miller K. G., Botstein D. Yeast actin-binding proteins: evidence for a role in morphogenesis. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 2):2551–2561. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fath K. R., Burgess D. R. Golgi-derived vesicles from developing epithelial cells bind actin filaments and possess myosin-I as a cytoplasmically oriented peripheral membrane protein. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;120(1):117–127. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.1.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govindan B., Bowser R., Novick P. The role of Myo2, a yeast class V myosin, in vesicular transport. J Cell Biol. 1995 Mar;128(6):1055–1068. doi: 10.1083/jcb.128.6.1055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grolig F., Williamson R. E., Parke J., Miller C., Anderton B. H. Myosin and Ca2+-sensitive streaming in the alga Chara: detection of two polypeptides reacting with a monoclonal anti-myosin and their localization in the streaming endoplasm. Eur J Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;47(1):22–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guthrie B. A., Wickner W. Yeast vacuoles fragment when microtubules are disrupted. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;107(1):115–120. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.1.115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayden J. H., Allen R. D. Detection of single microtubules in living cells: particle transport can occur in both directions along the same microtubule. J Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;99(5):1785–1793. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.5.1785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegmann T. E., Lin J. L., Lin J. J. Probing the role of nonmuscle tropomyosin isoforms in intracellular granule movement by microinjection of monoclonal antibodies. J Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;109(3):1141–1152. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.3.1141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegmann T. E., Schulte D. L., Lin J. L., Lin J. J. Inhibition of intracellular granule movement by microinjection of monoclonal antibodies against caldesmon. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1991;20(2):109–120. doi: 10.1002/cm.970200204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs C. W., Adams A. E., Szaniszlo P. J., Pringle J. R. Functions of microtubules in the Saccharomyces cerevisiae cell cycle. J Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;107(4):1409–1426. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.4.1409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johara M., Toyoshima Y. Y., Ishijima A., Kojima H., Yanagida T., Sutoh K. Charge-reversion mutagenesis of Dictyostelium actin to map the surface recognized by myosin during ATP-driven sliding motion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2127–2131. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston G. C., Prendergast J. A., Singer R. A. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae MYO2 gene encodes an essential myosin for vectorial transport of vesicles. J Cell Biol. 1991 May;113(3):539–551. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.3.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabsch W., Mannherz H. G., Suck D., Pai E. F., Holmes K. C. Atomic structure of the actin:DNase I complex. Nature. 1990 Sep 6;347(6288):37–44. doi: 10.1038/347037a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kachar B. Direct visualization of organelle movement along actin filaments dissociated from characean algae. Science. 1985 Mar 15;227(4692):1355–1357. doi: 10.1126/science.4038817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kachar B., Reese T. S. The mechanism of cytoplasmic streaming in characean algal cells: sliding of endoplasmic reticulum along actin filaments. J Cell Biol. 1988 May;106(5):1545–1552. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.5.1545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilmartin J. V., Adams A. E. Structural rearrangements of tubulin and actin during the cell cycle of the yeast Saccharomyces. J Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;98(3):922–933. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.3.922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohno T., Shimmen T. Accelerated sliding of pollen tube organelles along Characeae actin bundles regulated by Ca2+. J Cell Biol. 1988 May;106(5):1539–1543. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.5.1539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koning A. J., Lum P. Y., Williams J. M., Wright R. DiOC6 staining reveals organelle structure and dynamics in living yeast cells. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1993;25(2):111–128. doi: 10.1002/cm.970250202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koonce M. P., Schliwa M. Bidirectional organelle transport can occur in cell processes that contain single microtubules. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;100(1):322–326. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.1.322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kron S. J., Drubin D. G., Botstein D., Spudich J. A. Yeast actin filaments display ATP-dependent sliding movement over surfaces coated with rabbit muscle myosin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4466–4470. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuznetsov S. A., Langford G. M., Weiss D. G. Actin-dependent organelle movement in squid axoplasm. Nature. 1992 Apr 23;356(6371):722–725. doi: 10.1038/356722a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kübler E., Riezman H. Actin and fimbrin are required for the internalization step of endocytosis in yeast. EMBO J. 1993 Jul;12(7):2855–2862. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05947.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazzarino D. A., Boldogh I., Smith M. G., Rosand J., Pon L. A. Yeast mitochondria contain ATP-sensitive, reversible actin-binding activity. Mol Biol Cell. 1994 Jul;5(7):807–818. doi: 10.1091/mbc.5.7.807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu H., Bretscher A. Characterization of TPM1 disrupted yeast cells indicates an involvement of tropomyosin in directed vesicular transport. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;118(2):285–299. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.2.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menzel D., Schliwa M. Motility in the siphonous green alga Bryopsis. I. Spatial organization of the cytoskeleton and organelle movements. Eur J Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;40(2):275–285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyakawa I., Aoi H., Sando N., Kuroiwa T. Fluorescence microscopic studies of mitochondrial nucleoids during meiosis and sporulation in the yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Sci. 1984 Mar;66:21–38. doi: 10.1242/jcs.66.1.21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moens P. B., Rapport E. Spindles, spindle plaques, and meiosis in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Hansen). J Cell Biol. 1971 Aug;50(2):344–361. doi: 10.1083/jcb.50.2.344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon A. L., Janmey P. A., Louie K. A., Drubin D. G. Cofilin is an essential component of the yeast cortical cytoskeleton. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;120(2):421–435. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.2.421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulholland J., Preuss D., Moon A., Wong A., Drubin D., Botstein D. Ultrastructure of the yeast actin cytoskeleton and its association with the plasma membrane. J Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;125(2):381–391. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.2.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick P., Botstein D. Phenotypic analysis of temperature-sensitive yeast actin mutants. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):405–416. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90154-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. E., Sullivan D. S., Huffaker T., Koshland D. Role of astral microtubules and actin in spindle orientation and migration in the budding yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(3):583–593. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.3.583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D., Doberstein S. K., Zot H. G. Myosin-I. Annu Rev Physiol. 1991;53:653–681. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.53.030191.003253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringle J. R., Preston R. A., Adams A. E., Stearns T., Drubin D. G., Haarer B. K., Jones E. W. Fluorescence microscopy methods for yeast. Methods Cell Biol. 1989;31:357–435. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61620-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayment I., Holden H. M., Whittaker M., Yohn C. B., Lorenz M., Holmes K. C., Milligan R. A. Structure of the actin-myosin complex and its implications for muscle contraction. Science. 1993 Jul 2;261(5117):58–65. doi: 10.1126/science.8316858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read E. B., Okamura H. H., Drubin D. G. Actin- and tubulin-dependent functions during Saccharomyces cerevisiae mating projection formation. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Apr;3(4):429–444. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.4.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riezman H., Hay R., Gasser S., Daum G., Schneider G., Witte C., Schatz G. The outer membrane of yeast mitochondria: isolation of outside-out sealed vesicles. EMBO J. 1983;2(7):1105–1111. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01553.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. D., Fink G. R. KAR1, a gene required for function of both intranuclear and extranuclear microtubules in yeast. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):1047–1060. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90712-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroer T. A., Sheetz M. P. Functions of microtubule-based motors. Annu Rev Physiol. 1991;53:629–652. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.53.030191.003213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheetz M. P., Spudich J. A. Movement of myosin-coated fluorescent beads on actin cables in vitro. Nature. 1983 May 5;303(5912):31–35. doi: 10.1038/303031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shortle D., Novick P., Botstein D. Construction and genetic characterization of temperature-sensitive mutant alleles of the yeast actin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4889–4893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon V. R., Swayne T. C., Pon L. A. Actin-dependent mitochondrial motility in mitotic yeast and cell-free systems: identification of a motor activity on the mitochondrial surface. J Cell Biol. 1995 Jul;130(2):345–354. doi: 10.1083/jcb.130.2.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogo L. F., Yaffe M. P. Regulation of mitochondrial morphology and inheritance by Mdm10p, a protein of the mitochondrial outer membrane. J Cell Biol. 1994 Sep;126(6):1361–1373. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.6.1361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titus M. A. Myosins. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;5(1):77–81. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(05)80011-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida A. Distribution of mitochondrially inherited drug-resistance genes to tetrads from young zygotes in yeast. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Oct 4;165(2):191–197. doi: 10.1007/BF00269906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wertman K. F., Drubin D. G., Botstein D. Systematic mutational analysis of the yeast ACT1 gene. Genetics. 1992 Oct;132(2):337–350. doi: 10.1093/genetics/132.2.337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessels D., Schroeder N. A., Voss E., Hall A. L., Condeelis J., Soll D. R. cAMP-mediated inhibition of intracellular particle movement and actin reorganization in Dictyostelium. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):2841–2851. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.2841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessels D., Soll D. R. Myosin II heavy chain null mutant of Dictyostelium exhibits defective intracellular particle movement. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):1137–1148. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.1137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson D. H., Fennell D. J. The use of fluorescent DNA-binding agent for detecting and separating yeast mitochondrial DNA. Methods Cell Biol. 1975;12:335–351. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60963-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]