Abstract
To identify proteins that interact in vivo with muscle components we have used a genetic approach based on the isolation of suppressors of mutant alleles of known muscle components. We have applied this system to the case of troponin I (TnI) in Drosophila and its mutant allele heldup2 (hdp2). This mutation causes an alanine to valine substitution at position 116 after a single nucleotide change in a constitutive exon. Among the isolated suppressors, one of them results from a second site mutation at the TnI gene itself. Muscles endowed with TnI mutated at both sites support nearly normal myofibrillar structure, perform notably well in wing beating and flight tests, and isolated muscle fibers produce active force. We show that the structural and functional recovery in this suppressor does not result from a change in the stoichiometric ratio of TnI isoforms. The second site suppression is due to a leucine to phenylalanine change within a heptameric leucine string motif adjacent to the actin binding domain of TnI. These data evidence a structural and functional role for the heptameric leucine string that is most noticeable, if not specific, in the indirect flight muscle.
Full text
PDF



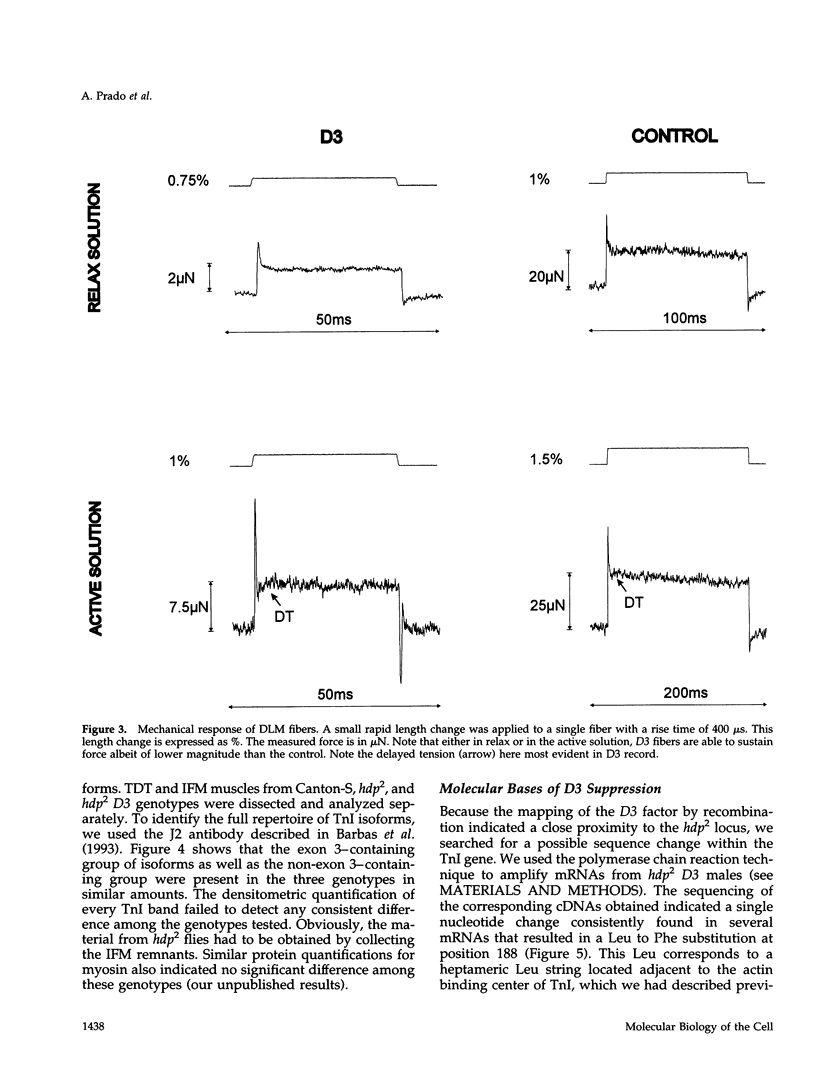



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbas J. A., Galceran J., Krah-Jentgens I., de la Pompa J. L., Canal I., Pongs O., Ferrús A. Troponin I is encoded in the haplolethal region of the Shaker gene complex of Drosophila. Genes Dev. 1991 Jan;5(1):132–140. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.1.132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbas J. A., Galceran J., Torroja L., Prado A., Ferrús A. Abnormal muscle development in the heldup3 mutant of Drosophila melanogaster is caused by a splicing defect affecting selected troponin I isoforms. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1433–1439. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beall C. J., Fyrberg E. Muscle abnormalities in Drosophila melanogaster heldup mutants are caused by missing or aberrant troponin-I isoforms. J Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;114(5):941–951. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.5.941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein S. I., O'Donnell P. T., Cripps R. M. Molecular genetic analysis of muscle development, structure, and function in Drosophila. Int Rev Cytol. 1993;143:63–152. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61874-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond D. R., Hennessey E. S., Sparrow J. C. Characterisation of missense mutations in the Act88F gene of Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Apr;226(1-2):70–80. doi: 10.1007/BF00273589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farah C. S., Miyamoto C. A., Ramos C. H., da Silva A. C., Quaggio R. B., Fujimori K., Smillie L. B., Reinach F. C. Structural and regulatory functions of the NH2- and COOH-terminal regions of skeletal muscle troponin I. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 18;269(7):5230–5240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita S. C., Inoue H., Yoshioka T., Hotta Y. Quantitative tissue isolation from Drosophila freeze-dried in acetone. Biochem J. 1987 Apr 1;243(1):97–104. doi: 10.1042/bj2430097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo X., Wattanapermpool J., Palmiter K. A., Murphy A. M., Solaro R. J. Mutagenesis of cardiac troponin I. Role of the unique NH2-terminal peptide in myofilament activation. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 27;269(21):15210–15216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz J., Bullard B., Mercola D. Interaction of troponin subunits. The interaction between the inhibitory and tropomyosin-binding subunits. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jan 25;254(2):350–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi T., Tao T., Gergely J., Collins J. H. Structure of the troponin complex. Implications of photocross-linking of troponin I to troponin C thiol mutants. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 25;269(8):5725–5729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai-Fook J. The structure of developing muscle insertions in insects. J Morphol. 1967 Dec;123(4):503–527. doi: 10.1002/jmor.1051230411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lan J., Albaugh S., Steiner R. F. Interactions of troponin I and its inhibitory fragment (residues 104-115) with troponin C and calmodulin. Biochemistry. 1989 Sep 5;28(18):7380–7385. doi: 10.1021/bi00444a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leszyk J., Grabarek Z., Gergely J., Collins J. H. Characterization of zero-length cross-links between rabbit skeletal muscle troponin C and troponin I: evidence for direct interaction between the inhibitory region of troponin I and the NH2-terminal, regulatory domain of troponin C. Biochemistry. 1990 Jan 9;29(1):299–304. doi: 10.1021/bi00453a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki M. Resonance energy transfer between points in a reconstituted skeletal muscle thin filament. A conformational change of the thin filament in response to a change in Ca2+ concentration. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Jan 12;187(1):155–162. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15289.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peckham M., Molloy J. E., Sparrow J. C., White D. C. Physiological properties of the dorsal longitudinal flight muscle and the tergal depressor of the trochanter muscle of Drosophila melanogaster. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1990 Jun;11(3):203–215. doi: 10.1007/BF01843574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringle J. W. The contractile mechanism of insect fibrillar muscle. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1967;17:1–60. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(67)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reedy M. C., Beall C. Ultrastructure of developing flight muscle in Drosophila. I. Assembly of myofibrils. Dev Biol. 1993 Dec;160(2):443–465. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1993.1320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reedy M. C., Beall C. Ultrastructure of developing flight muscle in Drosophila. II. Formation of the myotendon junction. Dev Biol. 1993 Dec;160(2):466–479. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1993.1321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spurr A. R. A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1969 Jan;26(1):31–43. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(69)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao T., Gong B. J., Leavis P. C. Calcium-induced movement of troponin-I relative to actin in skeletal muscle thin filaments. Science. 1990 Mar 16;247(4948):1339–1341. doi: 10.1126/science.2138356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Z. Y., Sarkar S., Gergely J., Tao T. Ca2(+)-dependent interactions between the C-helix of troponin-C and troponin-I. Photocross-linking and fluorescence studies using a recombinant troponin-C. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 25;265(9):4953–4957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]