Abstract
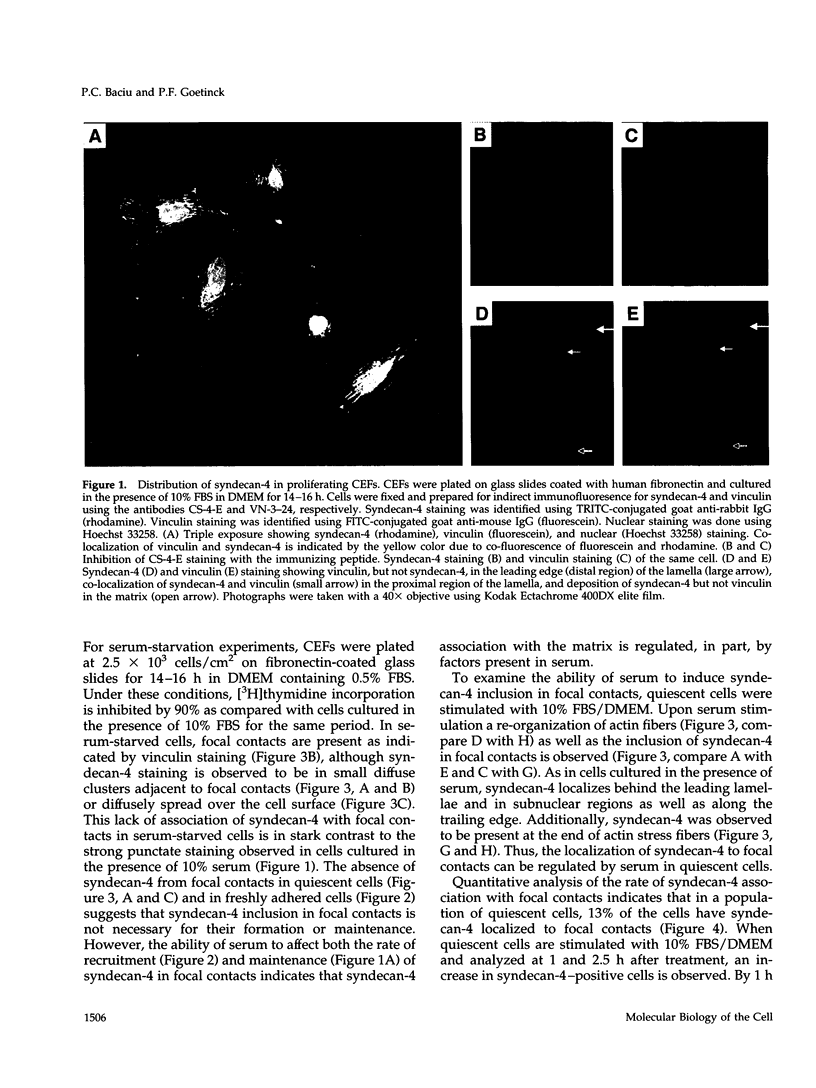
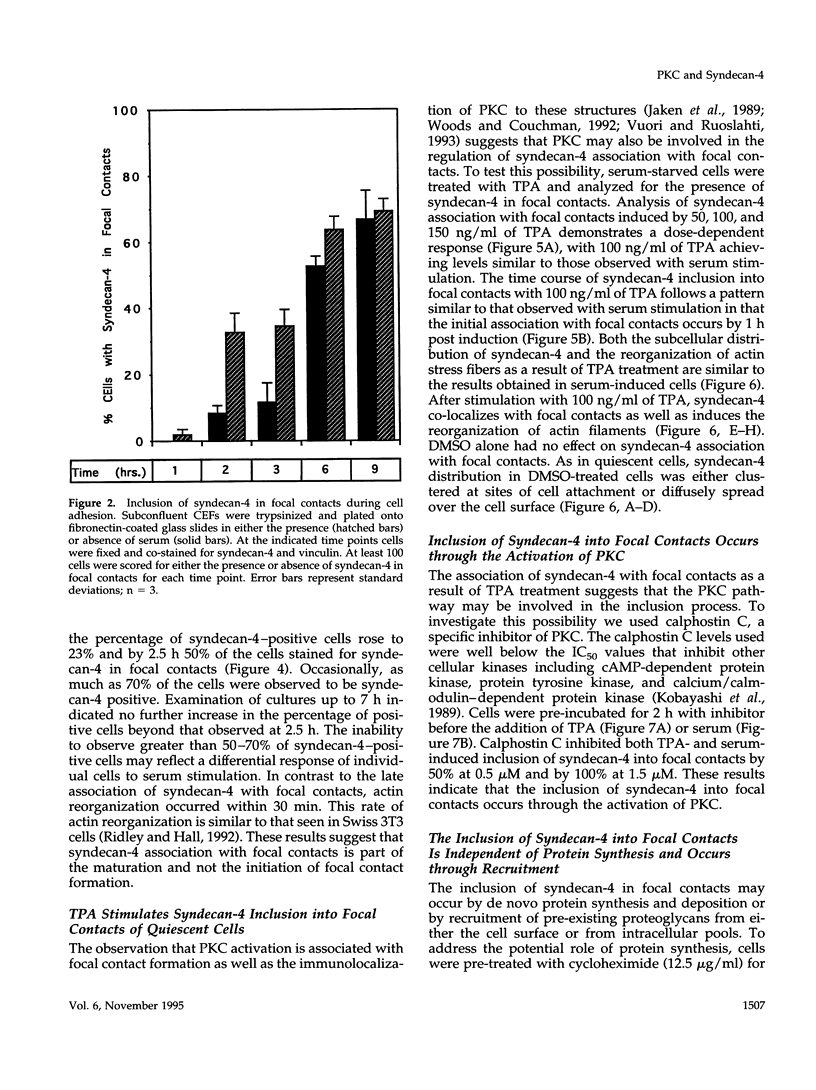
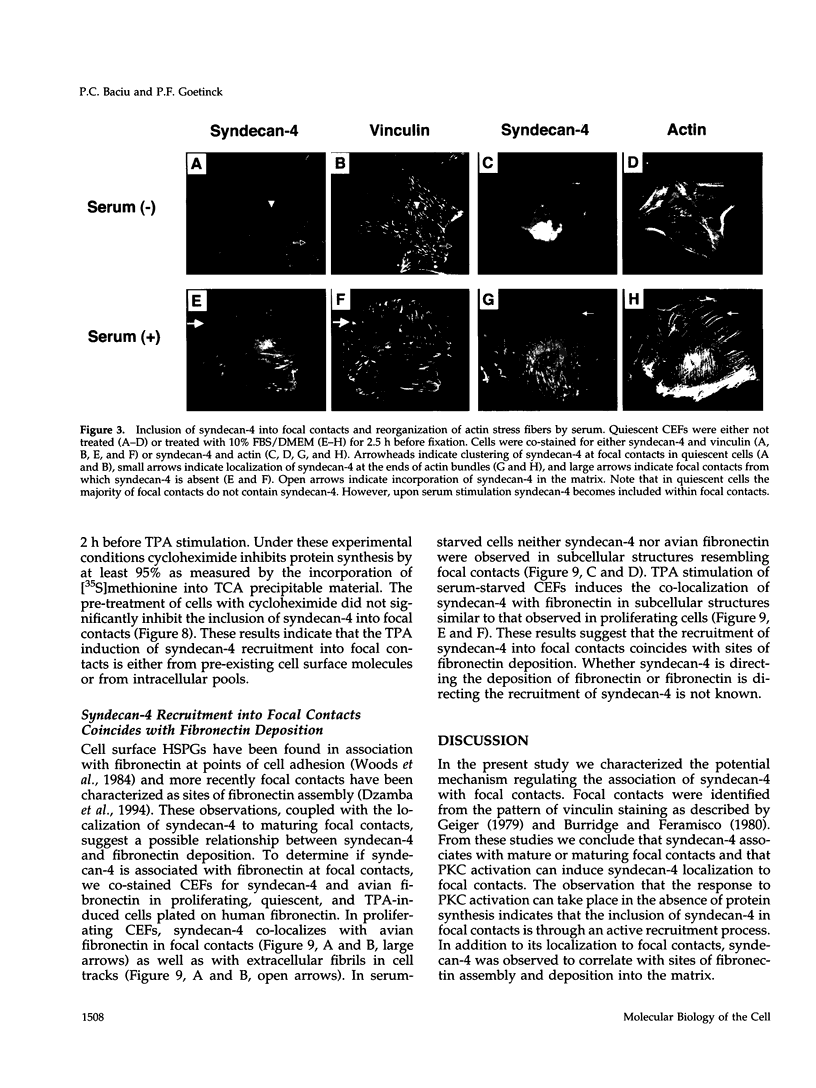
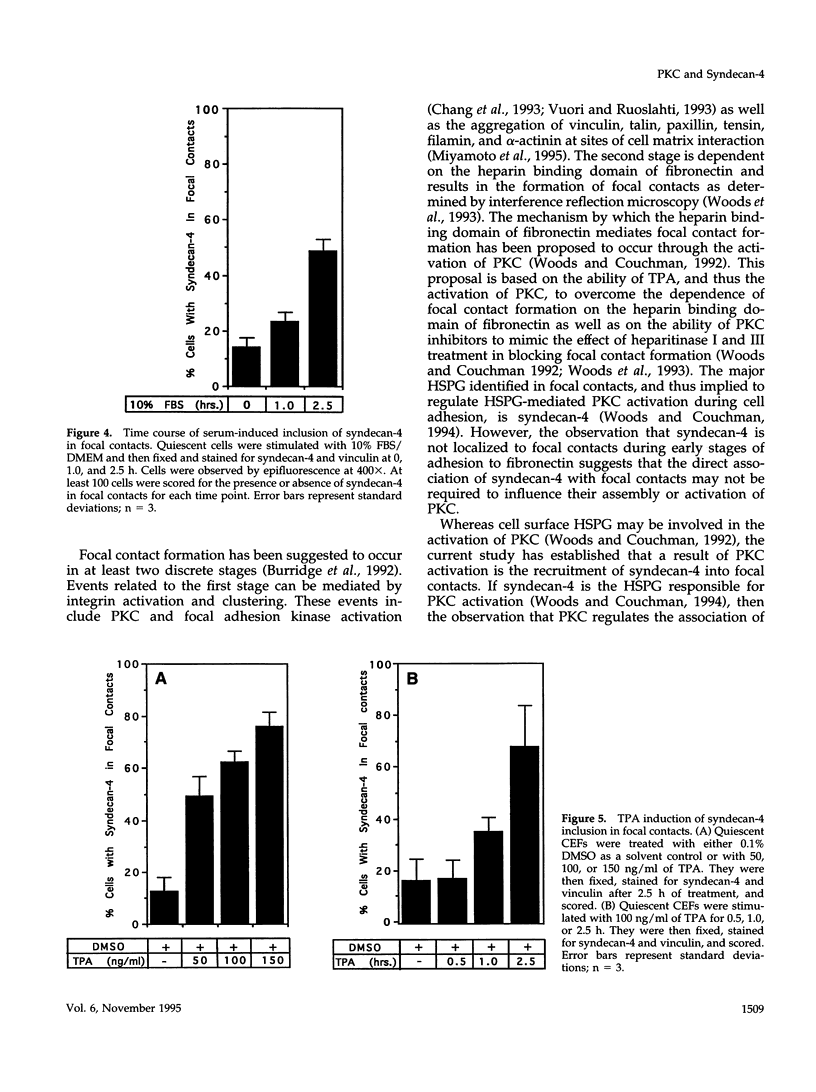
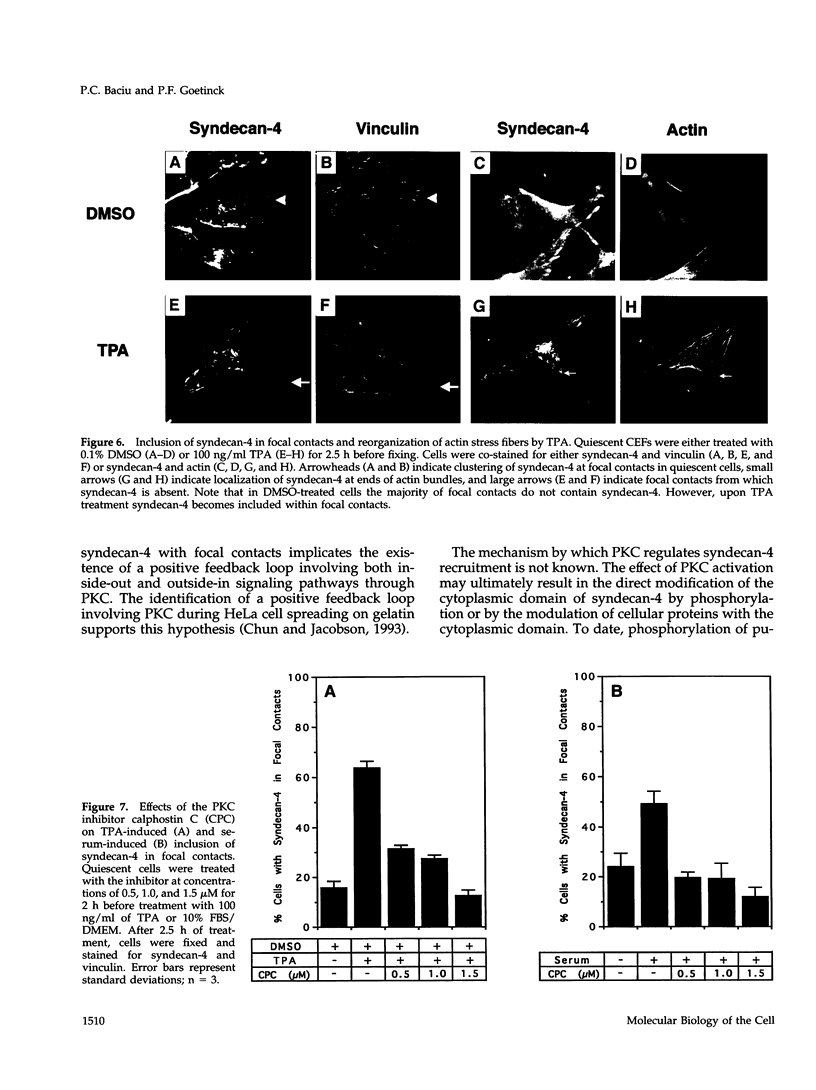
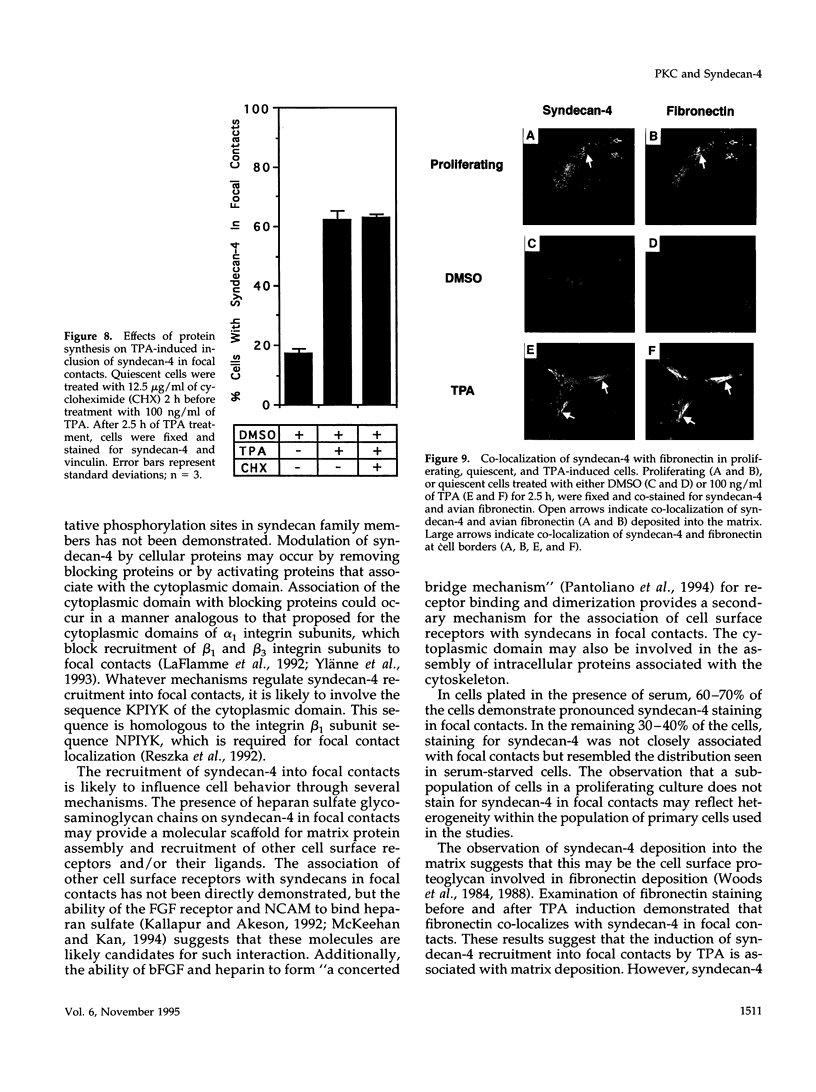
Cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans have been implicated as co-receptors facilitating cell adhesion and growth factor binding. Recent studies on the role of a family of transmembrane heparan sulfate proteoglycans, syndecans, in cell adhesion has identified one member, syndecan-4, to be present within focal contacts. The current study investigates the mechanisms regulating the association of syndecan-4 with focal contacts based upon its immunolocalization with vinculin in quiescent, serum-stimulated, and 12-0-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate (TPA)-induced cultures. In quiescent cells, syndecan-4 did not localize to focal contacts. However, activation of protein kinase C by TPA or serum induces the active recruitment of syndecan-4 into focal contacts. This induction preferentially localizes syndecan-4 to focal contacts behind the leading lamella, the subnuclear region, and along the trailing edge of migratory cells. Focal contacts in either freshly adhered cells or in the leading lamellae of migrating cells did not stain for syndecan-4. In addition to the observed subcellular distribution and recruitment, syndecan-4 was observed to co-localize with endogenously synthesized fibronectin fibrils within focal contacts as well as with fibrils present in the matrix. These findings suggest that protein kinase C activation results in syndecan-4 recruitment to focal contacts and its association with sites of matrix deposition.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviezer D., Hecht D., Safran M., Eisinger M., David G., Yayon A. Perlecan, basal lamina proteoglycan, promotes basic fibroblast growth factor-receptor binding, mitogenesis, and angiogenesis. Cell. 1994 Dec 16;79(6):1005–1013. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90031-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baciu P. C., Acaster C., Goetinck P. F. Molecular cloning and genomic organization of chicken syndecan-4. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 7;269(1):696–703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernfield M., Kokenyesi R., Kato M., Hinkes M. T., Spring J., Gallo R. L., Lose E. J. Biology of the syndecans: a family of transmembrane heparan sulfate proteoglycans. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:365–393. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.002053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burridge K., Feramisco J. R. Microinjection and localization of a 130K protein in living fibroblasts: a relationship to actin and fibronectin. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):587–595. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80035-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burridge K., Turner C. E., Romer L. H. Tyrosine phosphorylation of paxillin and pp125FAK accompanies cell adhesion to extracellular matrix: a role in cytoskeletal assembly. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(4):893–903. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.4.893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey D. J., Stahl R. C., Cizmeci-Smith G., Asundi V. K. Syndecan-1 expressed in Schwann cells causes morphological transformation and cytoskeletal reorganization and associates with actin during cell spreading. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;124(1-2):161–170. doi: 10.1083/jcb.124.1.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey D. J., Stahl R. C., Tucker B., Bendt K. A., Cizmeci-Smith G. Aggregation-induced association of syndecan-1 with microfilaments mediated by the cytoplasmic domain. Exp Cell Res. 1994 Sep;214(1):12–21. doi: 10.1006/excr.1994.1228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Z. L., Beezhold D. H., Personius C. D., Shen Z. L. Fibronectin cell-binding domain triggered transmembrane signal transduction in human monocytes. J Leukoc Biol. 1993 Jan;53(1):79–85. doi: 10.1002/jlb.53.1.79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chun J. S., Jacobson B. S. Requirement for diacylglycerol and protein kinase C in HeLa cell-substratum adhesion and their feedback amplification of arachidonic acid production for optimum cell spreading. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Mar;4(3):271–281. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.3.271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couchman J. R., Austria R., Woods A., Hughes R. C. Adhesion defective BHK cell mutant has cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycan of altered properties. J Cell Physiol. 1988 Aug;136(2):226–236. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041360204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dzamba B. J., Bultmann H., Akiyama S. K., Peters D. M. Substrate-specific binding of the amino terminus of fibronectin to an integrin complex in focal adhesions. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 29;269(30):19646–19652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elenius K., Jalkanen M. Function of the syndecans--a family of cell surface proteoglycans. J Cell Sci. 1994 Nov;107(Pt 11):2975–2982. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.11.2975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiger B. A 130K protein from chicken gizzard: its localization at the termini of microfilament bundles in cultured chicken cells. Cell. 1979 Sep;18(1):193–205. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90368-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guimond S., Maccarana M., Olwin B. B., Lindahl U., Rapraeger A. C. Activating and inhibitory heparin sequences for FGF-2 (basic FGF). Distinct requirements for FGF-1, FGF-2, and FGF-4. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 15;268(32):23906–23914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen L. K., Mooney D. J., Vacanti J. P., Ingber D. E. Integrin binding and cell spreading on extracellular matrix act at different points in the cell cycle to promote hepatocyte growth. Mol Biol Cell. 1994 Sep;5(9):967–975. doi: 10.1091/mbc.5.9.967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaken S., Leach K., Klauck T. Association of type 3 protein kinase C with focal contacts in rat embryo fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;109(2):697–704. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. R., Wong L. Heparan sulfate is essential to amphiregulin-induced mitogenic signaling by the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 28;269(43):27149–27154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallapur S. G., Akeson R. A. The neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM) heparin binding domain binds to cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans. J Neurosci Res. 1992 Dec;33(4):538–548. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490330406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi E., Nakano H., Morimoto M., Tamaoki T. Calphostin C (UCN-1028C), a novel microbial compound, is a highly potent and specific inhibitor of protein kinase C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Mar 15;159(2):548–553. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)90028-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaFlamme S. E., Akiyama S. K., Yamada K. M. Regulation of fibronectin receptor distribution. J Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;117(2):437–447. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.2.437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBaron R. G., Esko J. D., Woods A., Johansson S., Hök M. Adhesion of glycosaminoglycan-deficient chinese hamster ovary cell mutants to fibronectin substrata. J Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;106(3):945–952. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.3.945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebersbach B. F., Sanderson R. D. Expression of syndecan-1 inhibits cell invasion into type I collagen. J Biol Chem. 1994 Aug 5;269(31):20013–20019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeehan W. L., Kan M. Heparan sulfate fibroblast growth factor receptor complex: structure-function relationships. Mol Reprod Dev. 1994 Sep;39(1):69–82. doi: 10.1002/mrd.1080390112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto S., Akiyama S. K., Yamada K. M. Synergistic roles for receptor occupancy and aggregation in integrin transmembrane function. Science. 1995 Feb 10;267(5199):883–885. doi: 10.1126/science.7846531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olwin B. B., Rapraeger A. Repression of myogenic differentiation by aFGF, bFGF, and K-FGF is dependent on cellular heparan sulfate. J Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;118(3):631–639. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.3.631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pantoliano M. W., Horlick R. A., Springer B. A., Van Dyk D. E., Tobery T., Wetmore D. R., Lear J. D., Nahapetian A. T., Bradley J. D., Sisk W. P. Multivalent ligand-receptor binding interactions in the fibroblast growth factor system produce a cooperative growth factor and heparin mechanism for receptor dimerization. Biochemistry. 1994 Aug 30;33(34):10229–10248. doi: 10.1021/bi00200a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reszka A. A., Hayashi Y., Horwitz A. F. Identification of amino acid sequences in the integrin beta 1 cytoplasmic domain implicated in cytoskeletal association. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;117(6):1321–1330. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.6.1321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley A. J., Hall A. The small GTP-binding protein rho regulates the assembly of focal adhesions and actin stress fibers in response to growth factors. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):389–399. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90163-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson R. D., Sneed T. B., Young L. A., Sullivan G. L., Lander A. D. Adhesion of B lymphoid (MPC-11) cells to type I collagen is mediated by integral membrane proteoglycan, syndecan. J Immunol. 1992 Jun 15;148(12):3902–3911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thom D., Powell A. J., Rees D. A. Mechanisms of cellular adhesion. IV. Role of serum glycoproteins in fibroblast spreading on glass. J Cell Sci. 1979 Feb;35:281–305. doi: 10.1242/jcs.35.1.281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vuori K., Ruoslahti E. Activation of protein kinase C precedes alpha 5 beta 1 integrin-mediated cell spreading on fibronectin. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 15;268(29):21459–21462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods A., Couchman J. R., Johansson S., Hök M. Adhesion and cytoskeletal organisation of fibroblasts in response to fibronectin fragments. EMBO J. 1986 Apr;5(4):665–670. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04265.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods A., Couchman J. R. Protein kinase C involvement in focal adhesion formation. J Cell Sci. 1992 Feb;101(Pt 2):277–290. doi: 10.1242/jcs.101.2.277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods A., Couchman J. R. Syndecan 4 heparan sulfate proteoglycan is a selectively enriched and widespread focal adhesion component. Mol Biol Cell. 1994 Feb;5(2):183–192. doi: 10.1091/mbc.5.2.183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods A., Hök M., Kjellén L., Smith C. G., Rees D. A. Relationship of heparan sulfate proteoglycans to the cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix of cultured fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;99(5):1743–1753. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.5.1743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods A., Johansson S., Hök M. Fibronectin fibril formation involves cell interactions with two fibronectin domains. Exp Cell Res. 1988 Aug;177(2):272–283. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(88)90461-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods A., McCarthy J. B., Furcht L. T., Couchman J. R. A synthetic peptide from the COOH-terminal heparin-binding domain of fibronectin promotes focal adhesion formation. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Jun;4(6):605–613. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.6.605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamagata M., Saga S., Kato M., Bernfield M., Kimata K. Selective distributions of proteoglycans and their ligands in pericellular matrix of cultured fibroblasts. Implications for their roles in cell-substratum adhesion. J Cell Sci. 1993 Sep;106(Pt 1):55–65. doi: 10.1242/jcs.106.1.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ylänne J., Chen Y., O'Toole T. E., Loftus J. C., Takada Y., Ginsberg M. H. Distinct functions of integrin alpha and beta subunit cytoplasmic domains in cell spreading and formation of focal adhesions. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;122(1):223–233. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.1.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoneda J., Saiki I., Igarashi Y., Kobayashi H., Fujii H., Ishizaki Y., Kimizuka F., Kato I., Azuma I. Role of the heparin-binding domain of chimeric peptides derived from fibronectin in cell spreading and motility. Exp Cell Res. 1995 Mar;217(1):169–179. doi: 10.1006/excr.1995.1076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]