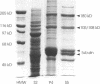
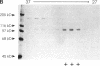
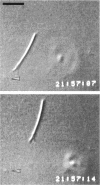
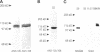Abstract
The "conventional" kinesins comprise a conserved family of molecular motors for organelle transport that have been identified in various animal species. Organelle motors from other phyla have not yet been analyzed at the molecular level. Here we report the identification, biochemical and immunological characterization, and molecular cloning of a cytoplasmic motor in a "lower" eukaryote, the Ascomycete fungus Neurospora crassa. This motor, termed Nkin (for Neurospora kinesin), exhibits several unique structural and functional features, including a high rate of microtubule transport, a lack of copurifying light chains, a second P-loop motif, and an overall sequence organization reminiscent of a kinesin-like protein. However, a greater than average sequence homology in the motor domain and the presence of a highly conserved region in the C-terminus identify Nkin as a distant relative of the family of conventional kinesins. A molecular phylogenetic analysis suggests Nkin to have diverged early in the evolution of this family of motors. The discovery of Nkin may help identify domains important for specific biological functions in conventional kinesins.
Full text
PDF



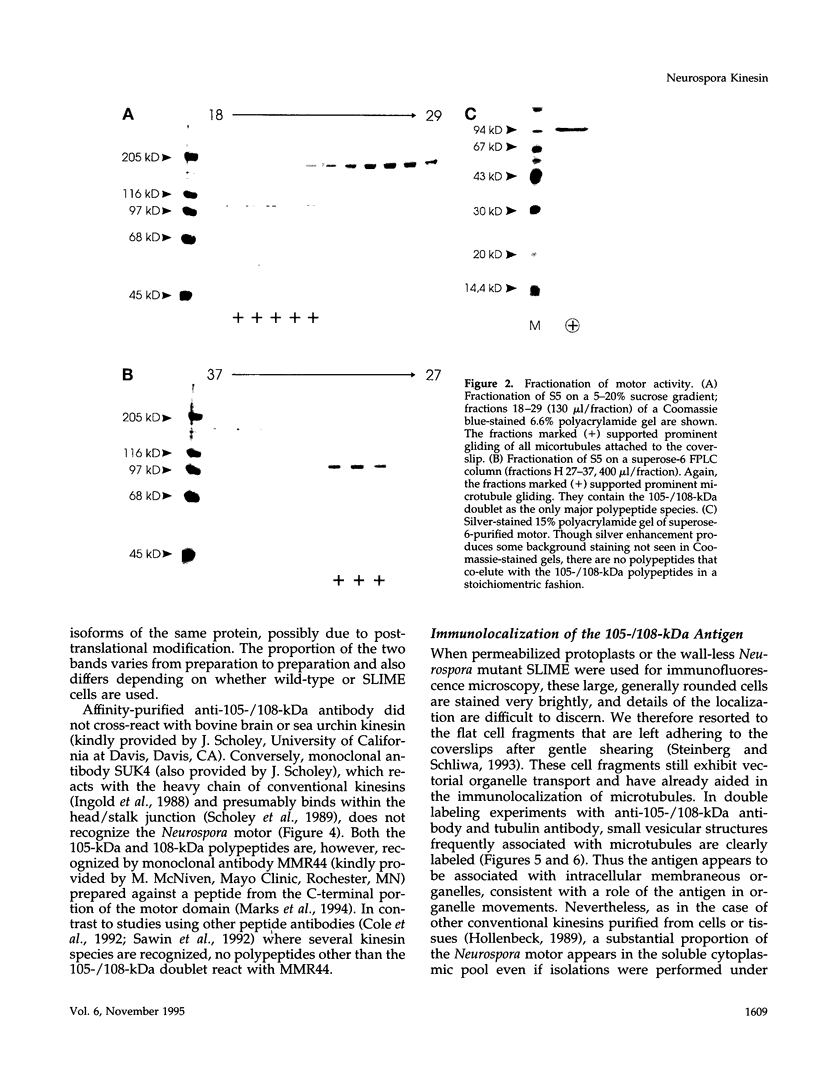
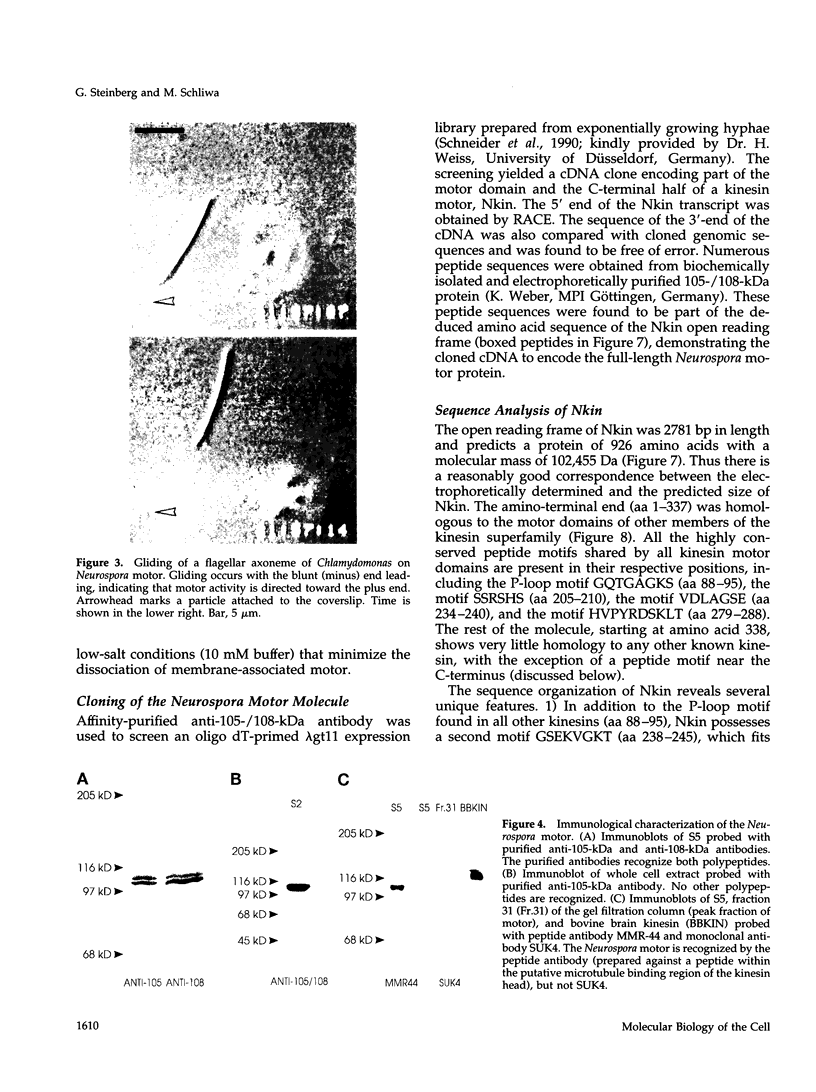




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aizawa H., Sekine Y., Takemura R., Zhang Z., Nangaku M., Hirokawa N. Kinesin family in murine central nervous system. J Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;119(5):1287–1296. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.5.1287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashkin A., Schütze K., Dziedzic J. M., Euteneuer U., Schliwa M. Force generation of organelle transport measured in vivo by an infrared laser trap. Nature. 1990 Nov 22;348(6299):346–348. doi: 10.1038/348346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldauf S. L., Palmer J. D. Animals and fungi are each other's closest relatives: congruent evidence from multiple proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 15;90(24):11558–11562. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.24.11558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beushausen S., Kladakis A., Jaffe H. Kinesin light chains: identification and characterization of a family of proteins from the optic lobe of the squid Loligo pealii. DNA Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;12(10):901–909. doi: 10.1089/dna.1993.12.901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom G. S., Endow S. A. Motor proteins. 1: kinesins. Protein Profile. 1994;1(10):1059–1116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom G. S., Wagner M. C., Pfister K. K., Brady S. T. Native structure and physical properties of bovine brain kinesin and identification of the ATP-binding subunit polypeptide. Biochemistry. 1988 May 3;27(9):3409–3416. doi: 10.1021/bi00409a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady S. T. A novel brain ATPase with properties expected for the fast axonal transport motor. Nature. 1985 Sep 5;317(6032):73–75. doi: 10.1038/317073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady S. T., Pfister K. K., Bloom G. S. A monoclonal antibody against kinesin inhibits both anterograde and retrograde fast axonal transport in squid axoplasm. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1061–1065. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn S. A., Ingold A. L., Scholey J. M. Correlation between the ATPase and microtubule translocating activities of sea urchin egg kinesin. Nature. 1987 Jul 9;328(6126):160–163. doi: 10.1038/328160a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole D. G., Cande W. Z., Baskin R. J., Skoufias D. A., Hogan C. J., Scholey J. M. Isolation of a sea urchin egg kinesin-related protein using peptide antibodies. J Cell Sci. 1992 Feb;101(Pt 2):291–301. doi: 10.1242/jcs.101.2.291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole D. G., Chinn S. W., Wedaman K. P., Hall K., Vuong T., Scholey J. M. Novel heterotrimeric kinesin-related protein purified from sea urchin eggs. Nature. 1993 Nov 18;366(6452):268–270. doi: 10.1038/366268a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole D. G., Saxton W. M., Sheehan K. B., Scholey J. M. A "slow" homotetrameric kinesin-related motor protein purified from Drosophila embryos. J Biol Chem. 1994 Sep 16;269(37):22913–22916. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cyr J. L., Pfister K. K., Bloom G. S., Slaughter C. A., Brady S. T. Molecular genetics of kinesin light chains: generation of isoforms by alternative splicing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10114–10118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabora S. L., Sheetz M. P. The microtubule-dependent formation of a tubulovesicular network with characteristics of the ER from cultured cell extracts. Cell. 1988 Jul 1;54(1):27–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90176-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endow S. A., Hatsumi M. A multimember kinesin gene family in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4424–4427. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endow S. A., Kang S. J., Satterwhite L. L., Rose M. D., Skeen V. P., Salmon E. D. Yeast Kar3 is a minus-end microtubule motor protein that destabilizes microtubules preferentially at the minus ends. EMBO J. 1994 Jun 1;13(11):2708–2713. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06561.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ersfeld K., Wehland J., Plessmann U., Dodemont H., Gerke V., Weber K. Characterization of the tubulin-tyrosine ligase. J Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;120(3):725–732. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.3.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Euteneuer U., Koonce M. P., Pfister K. K., Schliwa M. An ATPase with properties expected for the organelle motor of the giant amoeba, Reticulomyxa. Nature. 1988 Mar 10;332(6160):176–178. doi: 10.1038/332176a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman M. A., Dush M. K., Martin G. R. Rapid production of full-length cDNAs from rare transcripts: amplification using a single gene-specific oligonucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8998–9002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauger A. K., Goldstein L. S. The Drosophila kinesin light chain. Primary structure and interaction with kinesin heavy chain. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 25;268(18):13657–13666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons I. R., Gibbons B. H., Mocz G., Asai D. J. Multiple nucleotide-binding sites in the sequence of dynein beta heavy chain. Nature. 1991 Aug 15;352(6336):640–643. doi: 10.1038/352640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein L. S. With apologies to scheherazade: tails of 1001 kinesin motors. Annu Rev Genet. 1993;27:319–351. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.27.120193.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
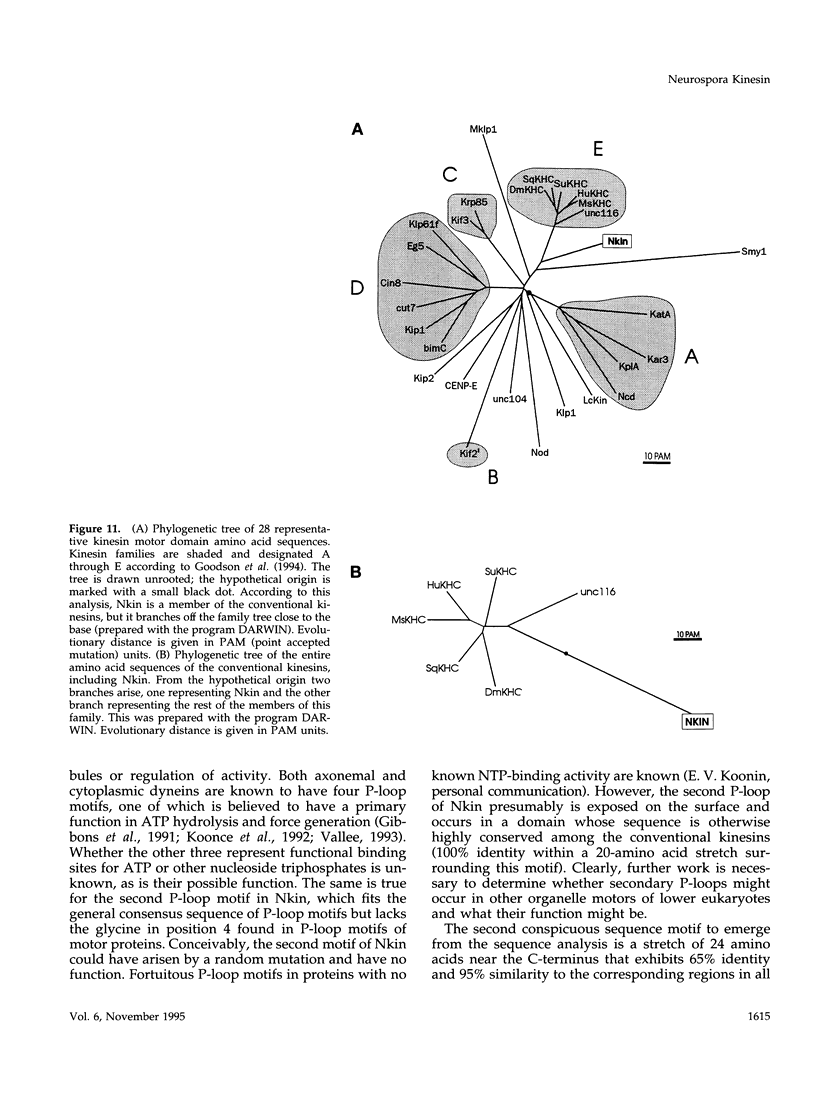
- Goodson H. V., Kang S. J., Endow S. A. Molecular phylogeny of the kinesin family of microtubule motor proteins. J Cell Sci. 1994 Jul;107(Pt 7):1875–1884. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.7.1875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackney D. D., Levitt J. D., Suhan J. Kinesin undergoes a 9 S to 6 S conformational transition. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 25;267(12):8696–8701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackney D. D., Levitt J. D., Wagner D. D. Characterization of alpha 2 beta 2 and alpha 2 forms of kinesin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Jan 31;174(2):810–815. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91490-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins D. G., Bleasby A. J., Fuchs R. CLUSTAL V: improved software for multiple sequence alignment. Comput Appl Biosci. 1992 Apr;8(2):189–191. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/8.2.189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirokawa N., Pfister K. K., Yorifuji H., Wagner M. C., Brady S. T., Bloom G. S. Submolecular domains of bovine brain kinesin identified by electron microscopy and monoclonal antibody decoration. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):867–878. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90691-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirokawa N., Sato-Yoshitake R., Kobayashi N., Pfister K. K., Bloom G. S., Brady S. T. Kinesin associates with anterogradely transported membranous organelles in vivo. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;114(2):295–302. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.2.295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenbeck P. J., Swanson J. A. Radial extension of macrophage tubular lysosomes supported by kinesin. Nature. 1990 Aug 30;346(6287):864–866. doi: 10.1038/346864a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenbeck P. J. The distribution, abundance and subcellular localization of kinesin. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;108(6):2335–2342. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.6.2335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyt M. A., He L., Loo K. K., Saunders W. S. Two Saccharomyces cerevisiae kinesin-related gene products required for mitotic spindle assembly. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;118(1):109–120. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.1.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingold A. L., Cohn S. A., Scholey J. M. Inhibition of kinesin-driven microtubule motility by monoclonal antibodies to kinesin heavy chains. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 2):2657–2667. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kachar B., Albanesi J. P., Fujisaki H., Korn E. D. Extensive purification from Acanthamoeba castellanii of a microtubule-dependent translocator with microtubule-activated Mg2+-ATPase activity. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 25;262(33):16180–16185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King S. M., Otter T., Witman G. B. Purification and characterization of Chlamydomonas flagellar dyneins. Methods Enzymol. 1986;134:291–306. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)34097-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koonce M. P., Grissom P. M., McIntosh J. R. Dynein from Dictyostelium: primary structure comparisons between a cytoplasmic motor enzyme and flagellar dynein. J Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;119(6):1597–1604. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.6.1597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuznetsov S. A., Gelfand V. I. Bovine brain kinesin is a microtubule-activated ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8530–8534. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuznetsov S. A., Vaisberg E. A., Shanina N. A., Magretova N. N., Chernyak V. Y., Gelfand V. I. The quaternary structure of bovine brain kinesin. EMBO J. 1988 Feb;7(2):353–356. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02820.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuznetsov S. A., Vaisberg Y. A., Rothwell S. W., Murphy D. B., Gelfand V. I. Isolation of a 45-kDa fragment from the kinesin heavy chain with enhanced ATPase and microtubule-binding activities. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):589–595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leopold P. L., McDowall A. W., Pfister K. K., Bloom G. S., Brady S. T. Association of kinesin with characterized membrane-bounded organelles. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1992;23(1):19–33. doi: 10.1002/cm.970230104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lill R., Dowhan W., Wickner W. The ATPase activity of SecA is regulated by acidic phospholipids, SecY, and the leader and mature domains of precursor proteins. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):271–280. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90742-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lupas A., Van Dyke M., Stock J. Predicting coiled coils from protein sequences. Science. 1991 May 24;252(5009):1162–1164. doi: 10.1126/science.252.5009.1162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandelkow E. M., Herrmann M., Rühl U. Tubulin domains probed by limited proteolysis and subunit-specific antibodies. J Mol Biol. 1985 Sep 20;185(2):311–327. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90406-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks D. L., Larkin J. M., McNiven M. A. Association of kinesin with the Golgi apparatus in rat hepatocytes. J Cell Sci. 1994 Sep;107(Pt 9):2417–2426. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.9.2417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCaffrey G., Vale R. D. Identification of a kinesin-like microtubule-based motor protein in Dictyostelium discoideum. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3229–3234. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08482.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murofushi H., Ikai A., Okuhara K., Kotani S., Aizawa H., Kumakura K., Sakai H. Purification and characterization of kinesin from bovine adrenal medulla. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12744–12750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nangaku M., Sato-Yoshitake R., Okada Y., Noda Y., Takemura R., Yamazaki H., Hirokawa N. KIF1B, a novel microtubule plus end-directed monomeric motor protein for transport of mitochondria. Cell. 1994 Dec 30;79(7):1209–1220. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connell M. J., Meluh P. B., Rose M. D., Morris N. R. Suppression of the bimC4 mitotic spindle defect by deletion of klpA, a gene encoding a KAR3-related kinesin-like protein in Aspergillus nidulans. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;120(1):153–162. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.1.153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmsted J. B. Analysis of cytoskeletal structures using blot-purified monospecific antibodies. Methods Enzymol. 1986;134:467–472. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)34112-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paschal B. M., Shpetner H. S., Vallee R. B. MAP 1C is a microtubule-activated ATPase which translocates microtubules in vitro and has dynein-like properties. J Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;105(3):1273–1282. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.3.1273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paschal B. M., Vallee R. B. Microtubule and axoneme gliding assays for force production by microtubule motor proteins. Methods Cell Biol. 1993;39:65–74. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60161-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfister K. K., Wagner M. C., Stenoien D. L., Brady S. T., Bloom G. S. Monoclonal antibodies to kinesin heavy and light chains stain vesicle-like structures, but not microtubules, in cultured cells. J Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;108(4):1453–1463. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.4.1453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodionov V. I., Gyoeva F. K., Gelfand V. I. Kinesin is responsible for centrifugal movement of pigment granules in melanophores. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4956–4960. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saraste M., Sibbald P. R., Wittinghofer A. The P-loop--a common motif in ATP- and GTP-binding proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Nov;15(11):430–434. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90281-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawin K. E., Mitchison T. J., Wordeman L. G. Evidence for kinesin-related proteins in the mitotic apparatus using peptide antibodies. J Cell Sci. 1992 Feb;101(Pt 2):303–313. doi: 10.1242/jcs.101.2.303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxton W. M., Porter M. E., Cohn S. A., Scholey J. M., Raff E. C., McIntosh J. R. Drosophila kinesin: characterization of microtubule motility and ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1109–1113. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schliwa M., van Blerkom J. Structural interaction of cytoskeletal components. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jul;90(1):222–235. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.1.222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider H., Arretz M., Wachter E., Neupert W. Matrix processing peptidase of mitochondria. Structure-function relationships. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 15;265(17):9881–9887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholey J. M., Heuser J., Yang J. T., Goldstein L. S. Identification of globular mechanochemical heads of kinesin. Nature. 1989 Mar 23;338(6213):355–357. doi: 10.1038/338355a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholey J. M., Porter M. E., Grissom P. M., McIntosh J. R. Identification of kinesin in sea urchin eggs, and evidence for its localization in the mitotic spindle. Nature. 1985 Dec 5;318(6045):483–486. doi: 10.1038/318483a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroer T. A., Schnapp B. J., Reese T. S., Sheetz M. P. The role of kinesin and other soluble factors in organelle movement along microtubules. J Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;107(5):1785–1792. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.5.1785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sebald W., Neupert W., Weiss H. Preparation of Neurospora crassa mitochondria. Methods Enzymol. 1979;55:144–148. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)55020-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skoufias D. A., Cole D. G., Wedaman K. P., Scholey J. M. The carboxyl-terminal domain of kinesin heavy chain is important for membrane binding. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 14;269(2):1477–1485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R., Scarborough G. A. Large-scale isolation of the Neurospora plasma membrane H+-ATPase. Anal Biochem. 1984 Apr;138(1):156–163. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90784-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg G., Schliwa M. Organelle movements in the wild type and wall-less fz;sg;os-1 mutants of Neurospora crassa are mediated by cytoplasmic microtubules. J Cell Sci. 1993 Oct;106(Pt 2):555–564. doi: 10.1242/jcs.106.2.555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoshima I., Yu H., Steuer E. R., Sheetz M. P. Kinectin, a major kinesin-binding protein on ER. J Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;118(5):1121–1131. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.5.1121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vale R. D., Reese T. S., Sheetz M. P. Identification of a novel force-generating protein, kinesin, involved in microtubule-based motility. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):39–50. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80099-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallee R. Molecular analysis of the microtubule motor dynein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 1;90(19):8769–8772. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.19.8769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner M. C., Pfister K. K., Bloom G. S., Brady S. T. Copurification of kinesin polypeptides with microtubule-stimulated Mg-ATPase activity and kinetic analysis of enzymatic properties. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1989;12(4):195–215. doi: 10.1002/cm.970120403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner M. C., Pfister K. K., Brady S. T., Bloom G. S. Purification of kinesin from bovine brain and assay of microtubule-stimulated ATPase activity. Methods Enzymol. 1991;196:157–175. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)96016-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wainright P. O., Hinkle G., Sogin M. L., Stickel S. K. Monophyletic origins of the metazoa: an evolutionary link with fungi. Science. 1993 Apr 16;260(5106):340–342. doi: 10.1126/science.8469985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wainright P. O., Patterson D. J., Sogin M. L. Monophyletic origin of animals: a shared ancestry with the fungi. Soc Gen Physiol Ser. 1994;49:39–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker R. A., Salmon E. D., Endow S. A. The Drosophila claret segregation protein is a minus-end directed motor molecule. Nature. 1990 Oct 25;347(6295):780–782. doi: 10.1038/347780a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witman G. B. Isolation of Chlamydomonas flagella and flagellar axonemes. Methods Enzymol. 1986;134:280–290. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)34096-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright B. D., Henson J. H., Wedaman K. P., Willy P. J., Morand J. N., Scholey J. M. Subcellular localization and sequence of sea urchin kinesin heavy chain: evidence for its association with membranes in the mitotic apparatus and interphase cytoplasm. J Cell Biol. 1991 May;113(4):817–833. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.4.817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J. T., Laymon R. A., Goldstein L. S. A three-domain structure of kinesin heavy chain revealed by DNA sequence and microtubule binding analyses. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):879–889. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90692-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J. T., Saxton W. M., Goldstein L. S. Isolation and characterization of the gene encoding the heavy chain of Drosophila kinesin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1864–1868. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]