Abstract
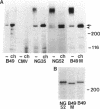
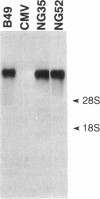
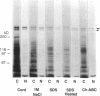
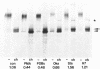
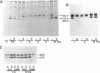
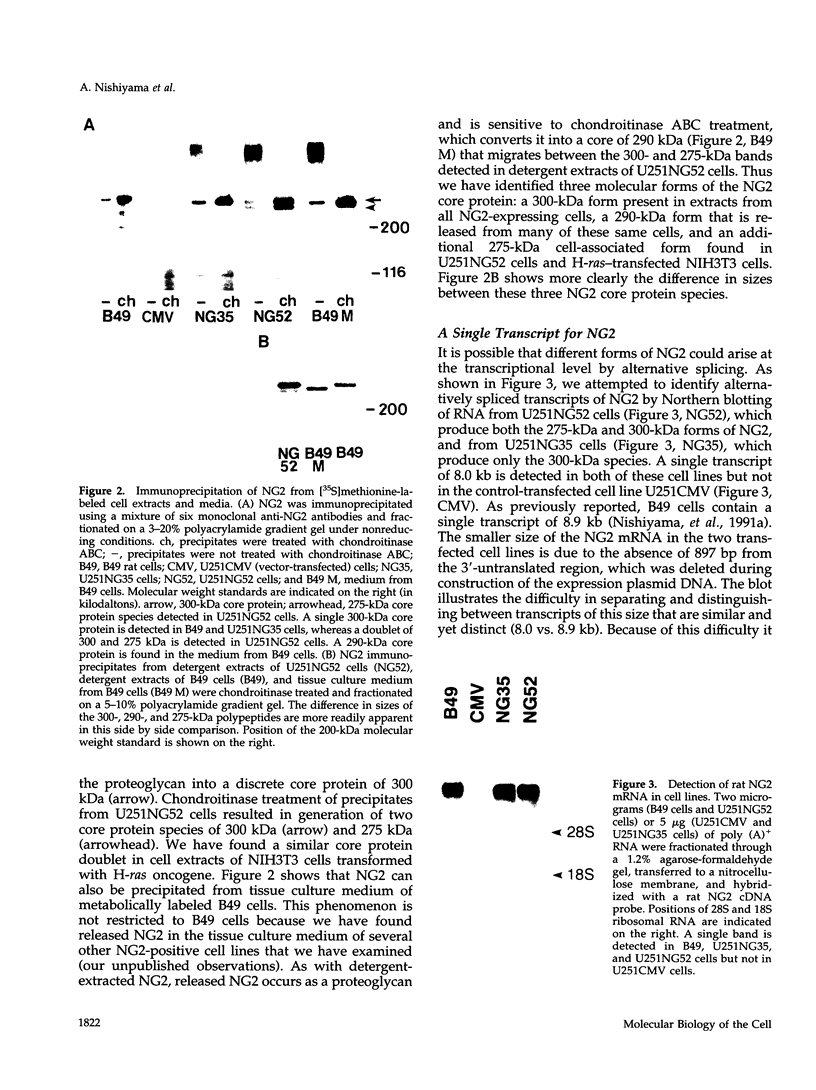
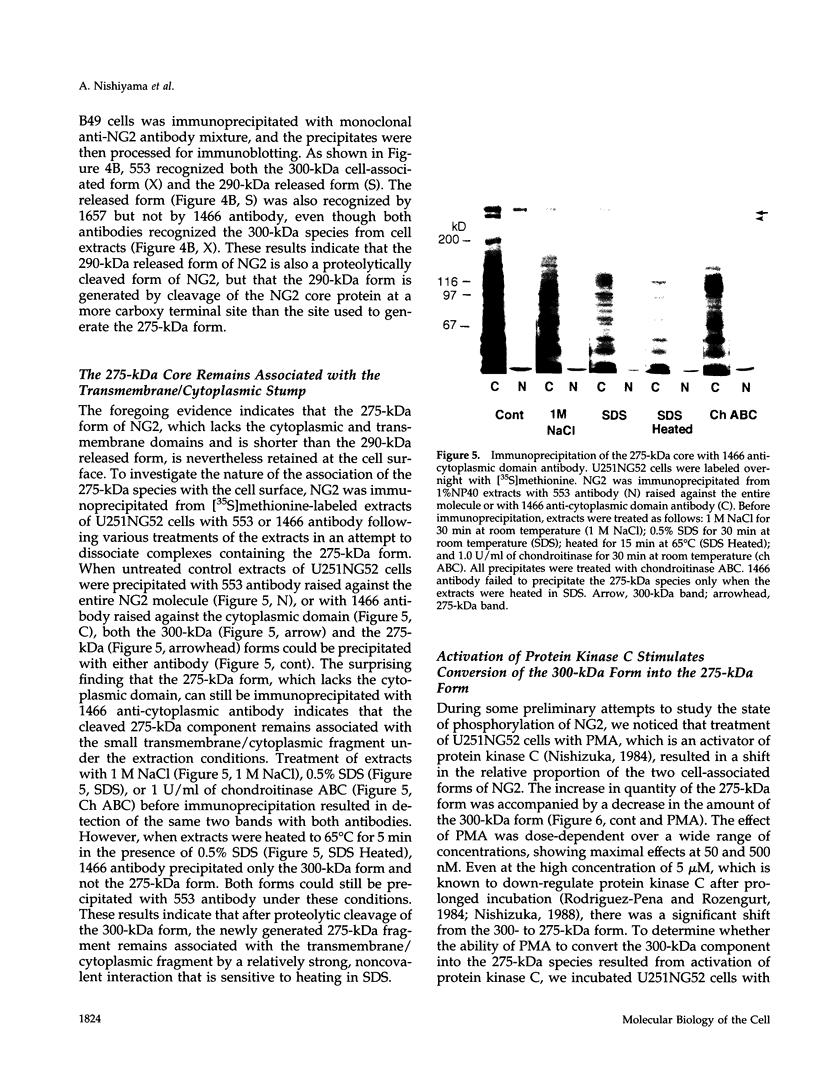
NG2 is a chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan that is expressed on dividing progenitor cells of several lineages including glia, muscle, and cartilage. It is an integral membrane proteoglycan with a core glycoprotein of 300 kDa. In the present study we have characterized three molecular forms of the NG2 core protein expressed by different cell lines. Many cell lines that express the full length 300-kDa NG2 core protein also release a 290-kDa form into the medium. This species lacks the cytoplasmic domain but contains almost the entire ectodomain. Two core protein species, the intact 300-kDa form and a truncated 275-kDa form, are expressed at the surface of an NG2-transfected cell line U251NG52. The 275-kDa species lacks the cytoplasmic domain and at least 64 amino acids of the ectodomain. Mild trypsinization of B49 cells also generates the 275-kDa species, suggesting that this component is produced by proteolysis of the 300-kDa form. Conversion of the 300-kDa species to the 275-kDa form in U251NG52 cells is stimulated by reagents such as phorbol esters, which activate protein kinase C. Phorbol esters are also known to induce expression of metalloproteinases such as collagenase and stromelysin, which could be responsible for cleavage of the 300-kDa core protein. Although B49 cells do not spontaneously produce the truncated 275-kDa species, use of monoclonal antibodies against NG2 to block the interaction between NG2 and type VI collagen results in the appearance of the 275-kDa component in these cells. Thus the interaction between NG2 and type VI collagen, which contains a Kunitz-type proteinase inhibitor sequence in the alpha 3 chain, may protect the proteoglycan against proteolysis. This is consistent with the observed deficiency of U251NG52 cells in anchoring type VI collagen at the surface.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angel P., Baumann I., Stein B., Delius H., Rahmsdorf H. J., Herrlich P. 12-O-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate induction of the human collagenase gene is mediated by an inducible enhancer element located in the 5'-flanking region. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2256–2266. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballin M., Gomez D. E., Sinha C. C., Thorgeirsson U. P. Ras oncogene mediated induction of a 92 kDa metalloproteinase; strong correlation with the malignant phenotype. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Aug 15;154(3):832–838. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90215-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernfield M., Kokenyesi R., Kato M., Hinkes M. T., Spring J., Gallo R. L., Lose E. J. Biology of the syndecans: a family of transmembrane heparan sulfate proteoglycans. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:365–393. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.002053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bialojan C., Takai A. Inhibitory effect of a marine-sponge toxin, okadaic acid, on protein phosphatases. Specificity and kinetics. Biochem J. 1988 Nov 15;256(1):283–290. doi: 10.1042/bj2560283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonaldo P., Colombatti A. The carboxyl terminus of the chicken alpha 3 chain of collagen VI is a unique mosaic structure with glycoprotein Ib-like, fibronectin type III, and Kunitz modules. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 5;264(34):20235–20239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley R. S., Brown A. M. The proto-oncogene int-1 encodes a secreted protein associated with the extracellular matrix. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1569–1575. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08276.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buxbaum J. D., Gandy S. E., Cicchetti P., Ehrlich M. E., Czernik A. J., Fracasso R. P., Ramabhadran T. V., Unterbeck A. J., Greengard P. Processing of Alzheimer beta/A4 amyloid precursor protein: modulation by agents that regulate protein phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):6003–6006. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.6003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis S., Aldrich T. H., Ip N. Y., Stahl N., Scherer S., Farruggella T., DiStefano P. S., Curtis R., Panayotatos N., Gascan H. Released form of CNTF receptor alpha component as a soluble mediator of CNTF responses. Science. 1993 Mar 19;259(5102):1736–1739. doi: 10.1126/science.7681218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiStefano P. S., Chelsea D. M., Schick C. M., McKelvy J. F. Involvement of a metalloprotease in low-affinity nerve growth factor receptor truncation: inhibition of truncation in vitro and in vivo. J Neurosci. 1993 Jun;13(6):2405–2414. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-06-02405.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downing J. R., Roussel M. F., Sherr C. J. Ligand and protein kinase C downmodulate the colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor by independent mechanisms. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):2890–2896. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.2890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehlers M. R., Riordan J. F. Membrane proteins with soluble counterparts: role of proteolysis in the release of transmembrane proteins. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 22;30(42):10065–10074. doi: 10.1021/bi00106a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flannery C. R., Lark M. W., Sandy J. D. Identification of a stromelysin cleavage site within the interglobular domain of human aggrecan. Evidence for proteolysis at this site in vivo in human articular cartilage. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):1008–1014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisch S. M., Clark E. J., Werb Z. Coordinate regulation of stromelysin and collagenase genes determined with cDNA probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2600–2604. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grako K. A., Stallcup W. B. Participation of the NG2 proteoglycan in rat aortic smooth muscle cell responses to platelet-derived growth factor. Exp Cell Res. 1995 Nov;221(1):231–240. doi: 10.1006/excr.1995.1371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Inagaki M., Kawamoto S., Sasaki Y. Isoquinolinesulfonamides, novel and potent inhibitors of cyclic nucleotide dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 9;23(21):5036–5041. doi: 10.1021/bi00316a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard A. L., Cohn Z. A. The enzymatic iodination of the red cell membrane. J Cell Biol. 1972 Nov;55(2):390–405. doi: 10.1083/jcb.55.2.390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayyem J. F., Roman J. M., de la Rosa E. J., Schwarz U., Dreyer W. J. Bravo/Nr-CAM is closely related to the cell adhesion molecules L1 and Ng-CAM and has a similar heterodimer structure. J Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;118(5):1259–1270. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.5.1259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lantz M., Gullberg U., Nilsson E., Olsson I. Characterization in vitro of a human tumor necrosis factor-binding protein. A soluble form of a tumor necrosis factor receptor. J Clin Invest. 1990 Nov;86(5):1396–1402. doi: 10.1172/JCI114853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. H., Bell R. M. The lipid binding, regulatory domain of protein kinase C. A 32-kDa fragment contains the calcium- and phosphatidylserine-dependent phorbol diester binding activity. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 15;261(32):14867–14870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine J. M. Increased expression of the NG2 chondroitin-sulfate proteoglycan after brain injury. J Neurosci. 1994 Aug;14(8):4716–4730. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-08-04716.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine J. M., Stallcup W. B. Plasticity of developing cerebellar cells in vitro studied with antibodies against the NG2 antigen. J Neurosci. 1987 Sep;7(9):2721–2731. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-09-02721.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matrisian L. M. Metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in matrix remodeling. Trends Genet. 1990 Apr;6(4):121–125. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90126-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauviel A. Cytokine regulation of metalloproteinase gene expression. J Cell Biochem. 1993 Dec;53(4):288–295. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240530404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer U., Pöschl E., Nischt R., Specks U., Pan T. C., Chu M. L., Timpl R. Recombinant expression and properties of the Kunitz-type protease-inhibitor module from human type VI collagen alpha 3(VI) chain. Eur J Biochem. 1994 Oct 15;225(2):573–580. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.00573.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosley B., Beckmann M. P., March C. J., Idzerda R. L., Gimpel S. D., VandenBos T., Friend D., Alpert A., Anderson D., Jackson J. The murine interleukin-4 receptor: molecular cloning and characterization of secreted and membrane bound forms. Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):335–348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90295-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishiyama A., Dahlin K. J., Prince J. T., Johnstone S. R., Stallcup W. B. The primary structure of NG2, a novel membrane-spanning proteoglycan. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;114(2):359–371. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.2.359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishiyama A., Dahlin K. J., Stallcup W. B. The expression of NG2 proteoglycan in the developing rat limb. Development. 1991 Apr;111(4):933–944. doi: 10.1242/dev.111.4.933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishiyama A., Stallcup W. B. Expression of NG2 proteoglycan causes retention of type VI collagen on the cell surface. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Nov;4(11):1097–1108. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.11.1097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The molecular heterogeneity of protein kinase C and its implications for cellular regulation. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):661–665. doi: 10.1038/334661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandiella A., Massagué J. Cleavage of the membrane precursor for transforming growth factor alpha is a regulated process. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1726–1730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papkoff J., Schryver B. Secreted int-1 protein is associated with the cell surface. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2723–2730. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pontén J., Westermark B. Properties of human malignant glioma cells in vitro. Med Biol. 1978 Aug;56(4):184–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince J. T., Milona N., Stallcup W. B. Characterization of a partial cDNA clone for the NILE glycoprotein and identification of the encoded polypeptide domain. J Neurosci. 1989 May;9(5):1825–1834. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-05-01825.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Pena A., Rozengurt E. Disappearance of Ca2+-sensitive, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase activity in phorbol ester-treated 3T3 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 May 16;120(3):1053–1059. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80213-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassone-Corsi P., Der C. J., Verma I. M. ras-induced neuronal differentiation of PC12 cells: possible involvement of fos and jun. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3174–3183. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrappe M., Klier F. G., Spiro R. C., Waltz T. A., Reisfeld R. A., Gladson C. L. Correlation of chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan expression on proliferating brain capillary endothelial cells with the malignant phenotype of astroglial cells. Cancer Res. 1991 Sep 15;51(18):4986–4993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert D., Heinemann S., Carlisle W., Tarikas H., Kimes B., Patrick J., Steinbach J. H., Culp W., Brandt B. L. Clonal cell lines from the rat central nervous system. Nature. 1974 May 17;249(454):224–227. doi: 10.1038/249224a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprecher C. A., Kisiel W., Mathewes S., Foster D. C. Molecular cloning, expression, and partial characterization of a second human tissue-factor-pathway inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 12;91(8):3353–3357. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.8.3353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stallcup W. B., Beasley L. Bipotential glial precursor cells of the optic nerve express the NG2 proteoglycan. J Neurosci. 1987 Sep;7(9):2737–2744. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-09-02737.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stallcup W. B., Beasley L., Levine J. Cell-surface molecules that characterize different stages in the development of cerebellar interneurons. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;48(Pt 2):761–774. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.048.01.078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stallcup W. B., Dahlin K., Healy P. Interaction of the NG2 chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan with type VI collagen. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 2):3177–3188. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.3177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaoki T., Nomoto H., Takahashi I., Kato Y., Morimoto M., Tomita F. Staurosporine, a potent inhibitor of phospholipid/Ca++dependent protein kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Mar 13;135(2):397–402. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson S. S., Baetge E. E., Stallcup W. B. Antisera specific for cell lines with mixed neuronal and glial properties. Dev Biol. 1981 Apr 15;83(1):146–153. doi: 10.1016/s0012-1606(81)80017-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]