Abstract
7-Chloro-5-(2-chlorophenyl)-1,5-dihydro-4,1-benzothiazepin-2(3H)-one [CGP-37157 (CGP)], a benzothiazepine derivative of clonazepam, is commonly used as a blocker of the mitochondrial Na+/Ca2+ exchanger. However, evidence suggests that CGP could also affect other targets, such as L-type Ca2+ channels and plasmalemma Na+/Ca2+ exchanger. Here, we tested the possibility of a direct modulation of ryanodine receptor channels (RyRs) and/or sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-stimulated ATPase (SERCA) by CGP. In the presence of ruthenium red (inhibitor of RyRs), CGP decreased SERCA-mediated Ca2+ uptake of cardiac and skeletal sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) microsomes (IC50 values of 6.6 and 9.9 μM, respectively). The CGP effects on SERCA activity correlated with a decreased Vmax of ATPase activity of SERCA-enriched skeletal SR fractions. CGP (≥5 μM) also increased RyR-mediated Ca2+ leak from skeletal SR microsomes. Planar bilayer studies confirmed that both cardiac and skeletal RyRs are directly activated by CGP (EC50 values of 9.4 and 12.0 μM, respectively). In summary, we found that CGP inhibits SERCA and activates RyR channels. Hence, the action of CGP on cellular Ca2+ homeostasis reported in the literature of cardiac, skeletal muscle, and other nonmuscle systems requires further analysis to take into account the contribution of all CGP-sensitive Ca2+ transporters.
Introduction
During an action potential in striated muscle, the activation of ryanodine receptor channels (RyRs) induces the global Ca2+ release from sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) Ca2+ stores triggering contraction (Sitsapesan and Williams, 1998; Bers, 2001; Fill and Copello, 2002; Fleischer, 2008). The SR Ca2+ ATPase (SERCA) rapidly sequesters the Ca2+ released into the cytosol back into the SR, leading to the relaxation of the muscle cells. The dynamics of Ca2+ release events in muscle cells is complex and still not fully understood (Fill and Copello, 2002; Stern and Cheng, 2004; Cheng and Lederer, 2008; Ríos et al., 2008). Mitochondria seem to play an intricate role in the regulation of intracellular Ca2+, which includes structural and functional interactions with the SR and plasmalemma (Rizzuto et al., 1998; Csordás and Hajnóczky, 2009; Lukyanenko et al., 2009). Among mitochondrial transporters, the 7-chloro-5-(2-chlorophenyl)-1,5-dihydro-4,1-benzothiazepin-2(3H)-one [CGP-37157 (CGP)]-sensitive Na+/Ca2+ exchanger (NCX) may mediate SR Ca2+ load and release (Szalai et al., 2000; Malli et al., 2005; Csordás and Hajnóczky, 2009). Indeed, CGP has been found to significantly affect intracellular Ca2+ signaling in smooth, cardiac, and skeletal muscle cells and in nonmuscle systems (Griffiths et al., 1997; Malli et al., 2005; Belmonte and Morad, 2008; Liu and O'Rourke, 2008; Chalmers and McCarron, 2009; Csordás and Hajnóczky, 2009).
The ability of the benzothiazepine derivative CGP to react with transporters other than the mitochondrial NCX (i.e., cross-reactivity) has not been fully explored. Reports have suggested that this compound can affect plasmalemma NCX (Czyz and Kiedrowski, 2003) and L-type Ca2+ channels (Thu et al., 2006). Various benzothiazepines with relatively different side chains, such as K201 (Kohno et al., 2003; Hunt et al., 2007) and KN-362 (Kodama et al., 1988; Tatsukawa and Arita, 1997), are known to modulate RyRs. K201 was also found to block the SERCA (Loughrey et al., 2007). As a consequence, we studied whether the effects of CGP on cellular Ca2+ homeostasis could be mediated, at least in part, by CGP's direct interaction with RyRs and SERCA. To investigate this possibility, we performed studies on isolated SR microsomes enriched in SERCA and RyRs and on RyRs reconstituted into planar lipid bilayers. Our results demonstrate that CGP can act as both a SERCA antagonist and RyR agonist.
Materials and Methods
Cardiac and Skeletal SR Microsomes.
All animal procedures were designed to minimize pain and suffering and conformed to the guidelines of the National Institutes of Health. The committee on the Use and Care of Laboratory Animals of Southern Illinois University School of Medicine reviewed and approved the protocols for animal use. R2 and R4 fractions of skeletal muscle SR microsomes (eight different preparations) were isolated from predominantly fast-twitch skeletal muscle (back and leg; adult New Zealand white rabbits), as described previously (Saito et al., 1984; Chu et al., 1988). For skeletal muscle, the R4 fraction of SR (TC microsomes) is highly enriched in terminal cisternae, which consists of both the junctional face membrane as well as the calcium pump membrane of SR. The ryanodine receptor (RyR1) is localized to the junctional face membrane, whereas the Ca2+ pump protein (SERCA 1a) is localized in the calcium pump membrane of SR (Saito et al., 1984; Fleischer, 2008). The R2 fraction of SR (LT microsomes) is referable to the longitudinal tubules of SR, which consists mainly of calcium pump membrane and is practically devoid of ryanodine receptor (Chu et al., 1988; Fleischer, 2008). The LT microsomes are used to characterize the calcium pump, whereas the TC microsomes contain both RyR1 and SERCA 1a, and therefore specific inhibitors for RyR1 and for the calcium pump must be used to sort out their response (Fleischer, 2008).
Enriched porcine cardiac SR microsomes were prepared following protocols developed for dog heart SR microsomes (Chamberlain et al., 1983). All preparations were stored in liquid nitrogen. Rabbit skeletal TC or LT microsomes or porcine cardiac SR for use in experiments were separated every month in 15-μl aliquots at a concentration of 5 to 15 mg protein/ml in 5 mM imidazole chloride, 290 mM sucrose, pH ∼7, quick-frozen, and stored at −80°C. For experiments, aliquots were quickly thawed in water, kept on ice, and used within 5 h.
Measurements of Ca2+ Uptake/Leak by SR Microsomes.
Ca2+ uptake by cardiac SR microsomes or R4 fractions of skeletal TC microsomes were measured with a spectrophotometer (Cory 50; Varian, Walnut Creek, CA) using the Ca2+-sensitive dye antipyrylazo III (APIII), as described previously (Chamberlain et al., 1984; Chu et al., 1988; Diaz-Sylvester et al., 2008). In brief, Ca2+ was increased to 40 μM by adding 40 nmol CaCl2 to 1 ml of phosphate buffer [100 mM KH2PO4, 5 mM MgCl2 (free Mg2+ ∼0.3 mM), 5 mM ATP, and 0.2 mM APIII, pH 7.0] containing 40 to 100 μg of SR membranes. The rate of Ca2+ uptake by the microsomes was measured in buffer containing ruthenium red (5 μM), and the effect of CGP (0.625–20 μM; preincubated for 5 min) was measured as changes in the absorbance (710–790 nm) of APIII. Initial rate of uptake (JCa), in micromoles of Ca2+ per milligram of protein per minute was estimated from fitting the equation JCa = 40 nmol · (ΔODt/ΔOD0) · (e−k · t) · S−1 to the data. ΔOD0 is the initial optical density (OD) change produced by adding 40 μM Ca2+ to the cuvette, and ΔODt is the change in OD as function of time. S is the mass of microsomes added to the cuvette (in milligrams of protein), k is the rate of uptake (per minute) assuming a first-order process, and t is the uptake time (in minutes).
We also measured the rate of Ca2+ leak from R4 fractions of skeletal TC microsomes preloaded with Ca2+ (three pulses of 40 μM Ca2+) after the addition of cyclopiazonic acid (CPZ) (20 μM), which inhibits SERCA, plus 1 μl of DMSO (control) or 5 to 30 μM CGP in DMSO. In some leak experiments, RyR1-mediated Ca2+ release from TC microsomes was blocked with ruthenium red (5 μM).
Measurements of ATPase Activity in SR Microsomes.
The effects of CGP (10 μM) were studied at 50 μM Ca2+, which measures the effects of the drug on maximal SERCA ATPase rate (Vmax). The data allow correlating the effects of CGP on the initial rate of Ca2+ load with ATPase activity. The effects of the drug were also measured in the presence of 300 nM Ca2+. These levels are close to the half-maximal activating Ca2+ levels (Km) of SERCA pump. We followed a protocol used previously in Dr. S. Fleischer's laboratory (Chamberlain et al., 1984; Chu et al., 1988). In brief, 10 to 40 μg of R2 fractions enriched in longitudinal tubule were incubated with buffer containing 140 mM KCl, 5 mM MgCl2, 5 mM HEPES, 2 mM phosphoenolpyruvate, 8.4 U/ml pyruvate kinase, and 12 U/ml lactate dehydrogenase. The mixture also contained 150 μM Ca2+ and variable amounts of EGTA (0.1, 0.2, 0.4, and 5 mM) for free Ca2+ levels of approximately 50, 1, 0.25, and 0.01 μM. pH was adjusted to 7.0 by titration with KOH. The reaction starts by adding 1 mM ATP, which is hydrolyzed to ADP by the ATPases. ADP is regenerated to ATP by reactions that induce the oxidation of 1 molecule of NADH (to NAD+) per ATP hydrolyzed (Chu et al., 1988). The rate of ATP hydrolysis, in nanomoles of ATP per milligram of SR protein per minute was estimated from the equation ΔOD340/(Δt · ε · L · S), where ΔOD is the decrease in absorbance at 340 nm (because of NADH consumption) during the interval Δt (in minutes), ε is the NADH extinction coefficient (6.22 × 106 ml · mol−1 · cm−1), L is the cuvette length (in centimeters), and S the amount of SR protein added to the cuvette (in milligrams per milliliter).
RyR Channel Recordings and Data Analysis.
Cardiac and skeletal RyRs were reconstituted into planar lipid bilayers formed on 80- to 120-μm diameter circular holes in Teflon septa, separating two 1.2-ml compartments as described previously (Copello et al., 1997). The trans compartment contained a HEPES-Ca2+ solution [250 mM HEPES and 50 mM Ca(OH)2, pH 7.4] and clamped at 0 mV with an Axopatch 200B patch-clamp amplifier (Molecular Devices, Sunnyvale, CA). The cis compartment (ground) was filled with HEPES-Tris solution (250 mM HEPES and 120 mM Tris, pH 7.4). Fusion of SR vesicles was promoted by subsequently adding, while stirring, 500 to 1000 mM CsCl, 1 mM CaCl2, and SR microsomes (5–15 μg) to the cis solution (Copello et al., 1997). This manipulation allows for reconstitution of RyRs with their cytosolic surface facing the cis chamber. Excess CsCl and Ca2+ were removed by perfusing the cis chamber for 5 min at 4 ml/min with HEPES-Tris solution. A mixture of BAPTA (1 mM) and dibromo-BAPTA (1 mM) was used to buffer free [Ca2+] on the cytosolic surface of the channel ([Ca2+]cyt) (Copello et al., 1997). Free [Mg2+] in mixtures of Mg2+ and ATP was estimated using Winmaxc2.5 by Chris Patton (Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA) (http://www.stanford.edu/∼cpatton/maxc.html).
Drug and Chemicals.
CaCl2 standard for calibration was from World Precision Instruments Inc. (Sarasota, FL). Phospholipids (phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylserine, and phosphatidylcholine) were obtained from Avanti Polar Lipids (Alabaster, AL). CGP-37157 was from Tocris Bioscience (Ellisville, MO). All other drugs and chemicals were from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO).
Statistical Analysis.
Data are presented as means ± S.E.M. of n measurements. Statistical comparisons between groups were performed with a paired t test. Differences were considered statistically significant at p < 0.05, and figures indicate p values.
Results
CGP Inhibits SERCA-Mediated Ca2+ Loading and ATPase Activity in Cardiac and Skeletal SR Microsomes.
We measured Ca2+ uptake by cardiac SR microsomes and from skeletal TC microsomes. The net Ca2+ uptake is the difference between the active SR Ca2+ influx (which depends on SERCA activity) and the passive efflux of Ca2+ from the SR microsomes (which depends mainly on RyRs activity). The experiments were carried out in the presence of ruthenium red (5 μM), which inhibited the efflux from RyRs. Therefore, under these conditions, changes in the net Ca2+ uptake by the cardiac and skeletal microsomes closely correlate with the SERCA pumping rate.
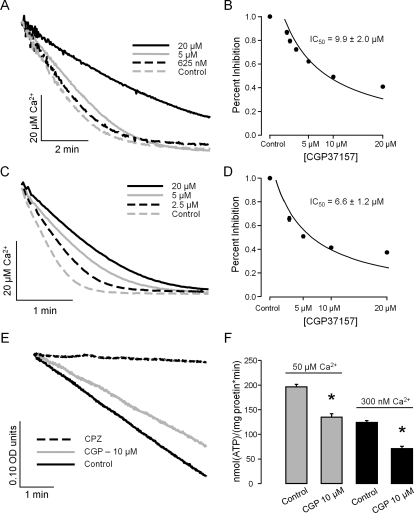
Figure 1A illustrates an example of how CGP inhibited the process of Ca2+ uptake by cardiac SR microsomes. The dose-response curve (Fig. 1B) suggests that CGP produced a half-maximal inhibition (IC50) at 9.9 ± 2.0 μM (n = 4 paired experiments). Likewise, Fig. 1, C and D, suggests that in skeletal muscle TC microsomes, CGP also inhibited the rate of loading with an IC50 of 6.6 ± 1.2 μM (n = 4 paired experiments).
Fig. 1.
CGP inhibits SR Ca2+ uptake and SERCA-mediated ATPase activity. SR microsomes were incubated in phosphate buffer containing ATP/Mg with 2 μl of CGP in DMSO (final CGP levels from 0.625 to 20 μM) or with 2 μl of DMSO (control). SR Ca2+ loading was started by increasing Ca2+ in the cuvette to 40 micromolar. A, example of Ca2+ uptake by porcine cardiac SR microsomes measured under control conditions and in the presence of various doses of CGP (0.625–20 μM). B, percentage of inhibition of the rate of SR Ca2+ loading by porcine cardiac SR microsomes versus CGP concentrations. Experimental data as in A were fitted by a single exponential function from which the initial rate of Ca2+ uptake was derived (see Materials and Methods). The average rate of uptake decreased by 60.2 ± 4.6% at 20 μM CGP (n = 3). From the data in A, a half-maximal inhibitory concentration of 9.9 ± 2.0 μM was estimated. C, example of CGP-induced inhibition of Ca2+ uptake by rabbit skeletal muscle TC microsomes. D, the drug decreased the rate of uptake by skeletal TC microsomes by 62.7 ± 7.0% with 20 μM CGP, IC50 = 6.6 ± 1.2 μM (n = 4). E, decrease in NADH absorption versus time (indicative of ATPase activity) by skeletal LT microsomes enriched in SERCA. As shown, CGP (10 μM) partially inhibited the decrease of NADH levels, whereas CPZ (20 μM) completely stopped the reaction. F, CGP-induced inhibition of ATPase activity of skeletal LT microsomes incubated with free [Ca2+] of either 50 or 300 nM. The inhibitory action at the two free [Ca2+] was comparable, 31.3 ± 5.3 and 42.7 ± 6.4% respectively (n = 4).
The effects of CGP (10 μM) on SERCA were also assayed in skeletal muscle LT microsomes with an ATPase assay at two Ca2+ concentrations. The first set was performed at a Ca2+ concentration of 50 μM, where SERCA reaches maximal activity (Vmax) and the second set was carried out with a Ca2+ concentration of 300 nM, which is near the SERCA's half-maximal activity (Km) for Ca2+ (Bers, 2001). Figure 1E shows that with 50 μM Ca2+, approximately 95% of the ATPase of LT microsomes was blocked by 20 μM CPZ, which inhibits SERCA. We also found that decreasing Ca2+ to 5 nM fully inhibited the ATPase activity (data not shown). Thus, SERCA seems to mediate most of the ATPase activity in these skeletal LT microsomes, which are highly enriched in longitudinal tubule. As shown in Fig. 1, E and F, 10 μM CGP decreased Vmax (at 50 μM Ca2+) by 31.3 ± 5.3%. When the ATPase activity was measured at 300 nM Ca2+ (which is near the Km of SERCA for Ca2+ activation), we also found a comparable inhibition of 42.7 ± 6.4%.
CGP Activates Skeletal and Cardiac RyRs.
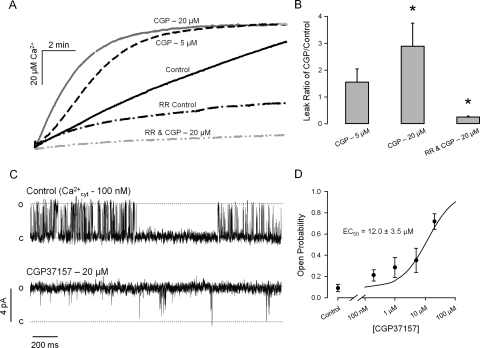
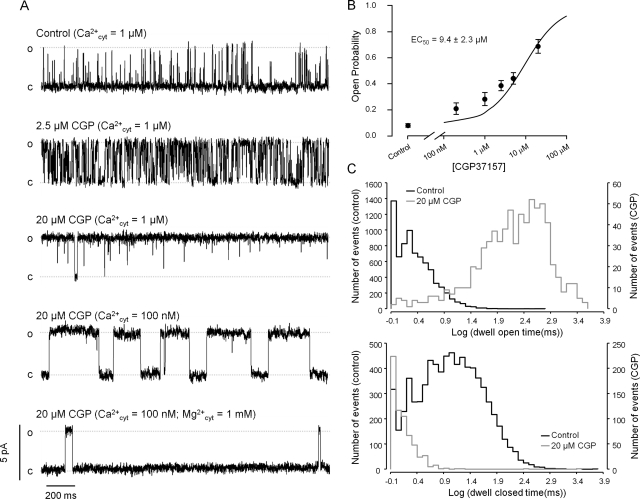
In another set of experiments, we loaded skeletal muscle TC microsomes with Ca2+ in the absence or presence of ruthenium red. Thereafter, the SERCA pump was inhibited by CPZ, and the rate of Ca2+ leak was measured in the absence or presence of ruthenium red. In the absence of ruthenium red, where most of the Ca2+ efflux from the vesicles is via RyR1, CGP (5 and 20 μM) significantly increases the rate of Ca2+ leak from the TC microsomes. In contrast, the residual leak in the presence of ruthenium red (which inhibit RyR1) was decreased by CGP (20 μM) (Fig. 2, A and B). These results suggest that the increased Ca2+ leak observed in the absence of ruthenium red resulted from the activation of RyR1. The inhibition of the remaining leak in the presence of ruthenium red may represent a secondary Ca2+-permeable path found in microsomes or inhibition of the reverse mode of SERCA. The activating effect of CGP on RyR1 was confirmed by reconstituting the channels into artificial lipid bilayers. Figure 2C shows single-channel recordings of a RyR1 under control condition and after the addition of 20 μM CGP to the cytosolic solution. The effect of CGP was observed 5 to 10 s after the addition, reached a plateau in ∼2 min, and remained stable during the experiments (up to 1 h in duration). CGP was cumulatively added to the cytosolic solution of RyR1 in the planar lipid bilayer to determine a half-maximal effective concentration (EC50) of 12.0 ± 3.5 μM (n = 6 paired experiments; Fig. 2D). The effects of CGP were also studied on porcine cardiac RyR channels (RyR2). Figure 3A shows one RyR2 incubated with 1 μM cytosolic Ca2+ (control). In this condition, the channel opened with moderate activity (Po = 0.16, estimated from 8-min recording). As shown in the figure, 2.5 μM CGP significantly activated the channel (Po = 0.49). With higher doses (20 μM), the channels were further activated (Po = 0.74). Figure 3B shows a dose response to cumulative doses of CGP to the cytosolic solution of RyR2 with a EC50 of 9.4 ± 2.3 μM (n = 6 paired experiments). As suggested by the recordings, CGP changed the RyR2 kinetics. Dwell-time distributions show that the duration of openings significantly increased, and the duration of closures greatly decreased (Fig. 3C). As shown in the example of Fig. 3A, we found that the RyR2 remained active when [Ca2+]cis was decreased to 100 nM and that this effect was partially counteracted by the addition of 1 mM Mg2+. In absence of CGP, we found that the open probability of RyR2 at 100 nM is less than 5% (absence of Mg2+) or less than 1% (presence of Mg2+), as reported previously (Copello et al., 1997). The effect of CGP on the channels was reversed after its removal from the cytosolic solution through superfusion.
Fig. 2.
CGP activates skeletal muscle RyR1. A, Ca2+ leak from TC microsomes (R4 fractions) was induced by blocking the SERCA pump with 20 μM CPZ. Measurements were performed under control conditions and upon addition of 5 or 20 μM CGP. Ca2+ leak was also measured in presence of 5 μM ruthenium red (which inhibits RyR1). B, ratio of Ca2+ leak rate in presence of CGP versus control. Leak rate significantly increased from control values by 281 ± 20% in presence of CGP. Ruthenium red significantly decreased the rate of leak, in which the addition of CGP decreased the leak rate further by 74.4 ± 38.0%. C, CGP (20 μM) activated skeletal RyRs reconstituted into planar lipid bilayers from TC microsomes. Recordings were carried out at 0 mV transmembrane voltage with 100 nM cytosolic free Ca2+ concentration (for details, see Materials and Methods). Openings are shown as discrete upward deflections. D, dose-response of cumulative doses of CGP to RyR1 in planar lipid bilayers with an EC50 of 12.0 ± 3.5 μM. Values are means ± S.E.M. *, p < 0.05 compared with absence of CGP (n = 4–6 paired experiments).
Fig. 3.
CGP activates cardiac RyR2. A, single-channel recordings of a RyR2 reconstituted into bilayer from porcine cardiac SR microsomes. All recordings were performed at holding voltage (Vm) = 0 mV. Lumenal (trans) Ca2+ (50 mM) was the current carrier. Channel openings are observed as positive deflections of the current (o, open state; c, baseline). The top trace shows a 2-s segment representative of a 4-min recording of a channel under control conditions (cytosolic Ca2+ = 1 μM). The second and third traces are recordings of the same channel after the addition of increasing concentrations of CGP to the cytosolic solution (2.5 and 20 μM, respectively). The fourth trace was recorded after subsequent addition of BAPTA to lower the cytosolic Ca2+ concentration down to 100 nM. The bottom trace shows the activity of the same channel after the addition of 1 mM MgCl2 to the cytosolic chamber. B, dose-response of cumulative doses of CGP to RyR2 in planar lipid bilayers with an EC50 of 9.4 ± 2.3 μM (n = 6 experiments). Values are means ± S.E.M. C, examples of representative dwell-time distributions of channel events. Histograms for open and closed times (top and bottom charts, respectively) were obtained from recordings of channels under control conditions (black outlines) and in the presence of 20 μM CGP (gray outlines). Fitting two exponential components to the data produce, under control conditions, dwell open times τo1 = 1.17 ± 0.01 ms (70 ± 0.6%) and τo2 = 3.82 ± 0.07 ms (30 ± 0.7%). Closed times were τc1 = 2.34 ± 0.04 ms (28 ± 0.3%) and τc2 = 19.18 ± 0.25 ms (72 ± 0.4%). For 25 μM CGP, dwell open times were much longer: τo1 = 96 ± 5 ms (18 ± 0.5%) and τo2 = 633 ± 6 ms (82 ± 0.8%). In contrast, dwell closed times were shorter and distributed with a single τc1 = 1.16 ± 0.12 ms.
Discussion
Our results show that cytosolic CGP has differential direct effects on SERCA pump and RyRs of striated muscle. CGP inhibited both cardiac and skeletal SERCA (putatively SERCA 1a and SERCA 2a), which would decrease SR load. In addition, CGP significantly activated both RyR1 and RyR2, which would increase SR leak. Our results suggest that these direct effects of CGP on SERCA and RyRs may have relevance in explaining the SR depletion observed in myocytes in situ.
Comparison with Other Benzothiazepines.
This is the first report on CGP direct modulation of RyRs. In this study, we found that CGP increased the activity of RyRs by stabilizing long-lasting opening events (EC50 ∼10–12.0 μM). In addition, CGP was also found to inhibit SERCA Vmax both in skeletal and cardiac muscle (IC50 ∼6.6 and 9.9 μM, respectively), without an apparent modification of the Km for Ca2+. Only one report tested CGP action on SERCA and found the drug at 10 μM was without significant action on ATP-ase activity of SR microsomes (Cox et al., 1993).
Previous studies have shown that CGP, a clonazepam derivative, is an effective (IC50 ∼500 nM) and specific inhibitor of the mitochondrial NCX (Gunter and Pfeiffer, 1990; Cox et al., 1993). Yet, it was reported that CGP inhibits NCX in the plasmalemma (IC50 ∼13 μM) and blocks the L-type Ca2+ channels (IC50 ∼0.27 μM) (Czyz and Kiedrowski, 2003; Thu et al., 2006). Inhibition of plasmalemma NCX, L-type channels, and SERCA has also been reported for clonazepam, the parent compound (Gershon, 1992; Cox et al., 1993; Griffiths et al., 1997). Moreover, clonazepam is a well-known agonist of GABA-induced chloride currents (Yakushiji et al., 1989), but effects on RyRs have not been reported.
Various other benzothiazepines have been reported to affect intracellular Ca2+ signaling in striated muscle. Some agents, such as diltiazem, more specifically target L-type channels and only affect SERCA and RyRs at much higher doses (Chamberlain et al., 1984). Other compounds of this class, such as 5-[3[2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)ethylamino]-1-oxopropyl]-2,3,4,5- tetrahydro-1,5-benzothiazepine fumarate (KT-362), were termed “intracellular Ca2+ channel antagonists” because they more specifically impair intracellular Ca2+ release in vascular smooth muscle (Shibata et al., 1987; Ueyama et al., 1996). Yet, for many of these compounds, the mechanism of action remains unclear. Two reports found that 4-[-3{1-(4-benzyl) piperidinyl} propionyl]-7-methoxy-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1, 4-benzothiazepine (K201), also known as JTV519, inhibited RyRs, but they differ on the requirement of hexadecahydro-5,19-dihydroxy-3-[2-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxycyclohexyl)-1-methylethenyl]-14,16-dimethoxy-4,10,12,18-tetramethyl-8-(2-propenyl)-15,19-epoxy-3H-pyrido[2,1-c][1,4]oxaazacyclotricosine-1,7,20,21(4H,23H)-tetrone (FK-506) binding protein for inhibition (Wehrens et al., 2005; Hunt et al., 2007). However, an early study suggested that K201 could increase [3H]ryanodine binding (Kohno et al., 2003). In addition, others reported a noticeable inhibitory action of K201 on ventricular myocytes whole-cell Na+, Ca2+, and K+ currents and on SERCA (Kimura et al., 1999; James, 2007).
In summary, CGP displays, as do various other benzothiazepines, a complex pattern of interference with transporters involved in Ca2+ signaling (RyRs, SERCA, L-type Ca2+ channels, plasmalemma, and mitochondrial NCXs). These results are quite interesting because CGP acts as a RyR channel agonist and seems to be opposite to K201 or KT-362. This suggests that RyRs may have a domain that binds these compounds and could be targeted for positive/negative modulation of RyR function through drug design.
CGP Seems to Modulate Multiple Molecular Targets in Cells.
Evidence suggests that mitochondria modulate intracellular Ca2+ signaling by acting both as a Ca2+ sink when cytosolic levels are high and as a Ca2+ source for repletion of the intracellular Ca2+ stores (Bers, 2001). The process of mitochondrial Ca2+ release that feeds the SR seems to be mediated by various transporters, including the mitochondrial NCX (Szalai et al., 2000; Malli et al., 2005; Csordás and Hajnóczky, 2009). Reports have suggested that inhibition of the mitochondrial NCX by CGP results in significant depletion of SR Ca2+ load (Rizzuto et al., 1998; Malli et al., 2005; Csordás and Hajnóczky, 2009). Yet, in those studies in which SR depletion was manifest, micromolar levels (ranging from 1 to 20 μM) of CGP were used.
Overall, this and previous studies demonstrate that micromolar levels of CGP would not only inhibit its most sensitive target (the mitochondrial NCX) but would also affect various other transporters known to significantly modulate intracellular Ca2+ signaling and SR Ca2+ content. From the inhibition of the SERCA pump activity and activation of RyRs, SR depletion and weakened excitation-contraction coupling would be expected (Bers, 2001). Inhibition of L-type Ca2+ currents by CGP (Thu et al., 2006) may also be responsible for the SR Ca2+ depletion, a process that has been observed with other L-type Ca2+ channel blockers (Hussain and Orchard, 1997). Inhibition of the plasmalemma NCX by CGP (Czyz and Kiedrowski, 2003) would increase the SR Ca2+ content under normal conditions, because this inhibition would increase the fraction of Ca2+ that is sequestered into SR by SERCA. However, NCX blockers are known to produce the opposite effect during reperfusion after ischemia, because the NCX works in a reverse mode (Ca2+ influx), and inhibition would prevent hypercontracture and arrhythmia (Bers 2001). Thus, the effects of CGP are complex because there are various alternatives to explain its action on SR intracellular Ca2+ levels and potential cardioprotective action.
Reports in the literature suggest that mitochondrial Ca2+ efflux may play a deleterious role during cardiac ischemia, which can be prevented by CGP or clonazepam (Liu and O'Rourke, 2008; Csordás and Hajnóczky, 2009; Bonazzola and Takara, 2010). A cardioprotective action has been reported for benzothiazepine derivatives (Farber and Gross, 1989; Wehrens et al., 2005) and for many other drug classes and processes such as preconditioning (Downey and Cohen, 2009). Although there is large heterogeneity in the mechanisms of action for cardioprotective agents, many of them seem to produce, directly or indirectly, a decrease in the use of Ca2+ sources/sinks (mitochondria, SR stores, and/or plasmalemma) during excitation-contraction coupling. This may lead to a significant decrease in the energy expenditure of cells that may be beneficial under pathological conditions, such as ischemia (Bonazzola and Takara, 2010).
In summary, the literature is replete with studies suggesting that a mitochondrial NCX block by CGP results in intracellular Ca2+ store depletion in various cell systems (Griffiths et al., 1997; Malli et al., 2005; Belmonte and Morad, 2008). In this study, the nature of CGP interactions with SR transporters was explored, and we found that there is direct CGP action on SERCA and RyRs. This report adds to a body of evidence that CGP targets other membrane transporters that play a key role in Ca2+ homeostasis. The significant cross-reactivity of CGP with such a variety of molecular targets confounds the simple interpretation that the action of CGP, in intact cell Ca2+ homeostasis, is due to block of the mitochondrial NCX.
Acknowledgments
We thank R. Herndon, Research Administrator, and J. Bryan, Office System Specialist (Southern Illinois University School of Medicine), for proofreading the manuscript. We also thank C. G. Copello for laboratory assistance with experiments of Ca2+ loading and ATPase activity.
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health National Institute of General Medical Sciences [Grant R01-GM078665].
Article, publication date, and citation information can be found at http://molpharm.aspetjournals.org.
doi:10.1124/mol.110.067165.
- RyR
- ryanodine receptor channel
- SR
- sarcoplasmic reticulum
- SERCA
- sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase
- CGP
- CGP-37157, 7-chloro-5-(2-chlorophenyl)-1,5-dihydro-4,1-benzothiazepin-2(3H)-one
- NCX
- Na+/Ca2+ exchanger
- APIII
- antipyrylazo III
- RyR1
- skeletal ryanodine receptor channel
- RyR2
- cardiac ryanodine receptor channel
- CPZ
- cyclopiazonic acid
- TC
- terminal cisternae
- LT
- longitudinal tubule
- DMSO
- dimethyl sulfoxide
- BAPTA
- 1,2-bis(2-aminophenoxy)ethane-N,N,N′,N′-tetraacetic acid
- KT-362
- 5-[3[2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)ethylamino]-1-oxopropyl]-2,3,4,5- tetrahydro-1,5-benzothiazepine fumarate
- K201
- JTV519, 4-[-3{1-(4-benzyl) piperidinyl}propionyl]-7-methoxy-2, 3, 4, 5-tetrahydro-1,4-benzothiazepine
- FK-506
- hexadecahydro-5,19-dihydroxy-3-[2-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxycyclohexyl)-1-methylethenyl]-14,16-dimethoxy-4,10,12,18-tetramethyl-8-(2-propenyl)-15,19-epoxy-3H-pyrido[2,1-c][1,4]oxaazacyclotricosine-1,7,20,21(4H,23H)-tetrone.
Authorship Contributions
Participated in research design: Neumann, Diaz-Sylvester, and Copello.
Conducted experiments: Neumann, Diaz-Sylvester, and Copello.
Contributed new reagents or analytic tools: Fleischer and Copello.
Performed data analysis: Neumann, Diaz-Sylvester, and Copello.
Wrote or contributed to the writing of the manuscript: Neumann, Diaz-Sylvester, Fleischer, and Copello.
References
- Belmonte S, Morad M. (2008) ‘Pressure-flow’-triggered intracellular Ca2+ transients in rat cardiac myocytes: possible mechanisms and role of mitochondria. J Physiol 586:1379–1397 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bers DM. (2001) Excitation-Contraction Coupling and Cardiac Contractile Force, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston [Google Scholar]
- Bonazzola P, Takara D. (2010) Cardiac basal metabolism: energetic cost of calcium withdrawal in the adult rat heart. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 199:293–304 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalmers S, McCarron JG. (2009) Inhibition of mitochondrial calcium uptake rather than efflux impedes calcium release by inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate-sensitive receptors. Cell Calcium 46:107–113 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain BK, Levitsky DO, Fleischer S. (1983) Isolation and characterization of canine cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum with improved Ca2+ transport properties. J Biol Chem 258:6602–6609 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain BK, Volpe P, Fleischer S. (1984) Inhibition of calcium-induced calcium release from purified cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles. J Biol Chem 259:7547–7553 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng H, Lederer WJ. (2008) Calcium sparks. Physiol Rev 88:1491–1545 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu A, Dixon MC, Saito A, Seiler S, Fleischer S. (1988) Isolation of sarcoplasmic reticulum fractions referable to longitudinal tubules and junctional terminal cisternae from rabbit skeletal muscle. Methods Enzymol 157:36–46 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copello JA, Barg S, Onoue H, Fleischer S. (1997) Heterogeneity of Ca2+ gating of skeletal muscle and cardiac ryanodine receptors. Biophys J 73:141–156 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox DA, Conforti L, Sperelakis N, Matlib MA. (1993) Selectivity of inhibition of Na+-Ca2+ exchange of heart mitochondria by benzothiazepine CGP-37157. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 21:595–599 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csordás G, Hajnóczky G. (2009) SR/ER-mitochondrial local communication: calcium and ROS. Biochim Biophys Acta 1787:1352–1362 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czyz A, Kiedrowski L. (2003) Inhibition of plasmalemmal Na+/Ca2+ exchange by mitochondrial Na+/Ca2+ exchange inhibitor 7-chloro-5-(2-chlorophenyl)-1,5-dihydro-4,1-benzothiazepin-2(3H)-one (CGP-37157) in cerebellar granule cells. Biochem Pharmacol 66:2409–2411 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz-Sylvester PL, Porta M, Copello JA. (2008) Halothane modulation of skeletal muscle ryanodine receptors: dependence on Ca2+, Mg2+, and ATP. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 294:C1103–C1112 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downey JM, Cohen MV. (2009) Why do we still not have cardioprotective drugs? Circ J 73:1171–1177 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farber NE, Gross GJ. (1989) Cardioprotective effects of a new vascular intracellular calcium antagonist, KT-362, in the stunned myocardium. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 248:39–43 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fill M, Copello JA. (2002) Ryanodine receptor calcium release channels. Physiol Rev 82:893–922 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer S. (2008) Personal recollections on the discovery of the ryanodine receptors of muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 369:195–207 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershon E. (1992) Effect of benzodiazepine ligands on Ca2+ channel currents in Xenopus oocytes injected with rat heart RNA. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol 3:81–97 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths EJ, Wei SK, Haigney MC, Ocampo CJ, Stern MD, Silverman HS. (1997) Inhibition of mitochondrial calcium efflux by clonazepam in intact single rat cardiomyocytes and effects on NADH production. Cell Calcium 21:321–329 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunter TE, Pfeiffer DR. (1990) Mechanisms by which mitochondria transport calcium. Am J Physiol 258:C755–C786 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt DJ, Jones PP, Wang R, Chen W, Bolstad J, Chen K, Shimoni Y, Chen SR. (2007) K201 (JTV519) suppresses spontaneous Ca2+ release and [3H]ryanodine binding to RyR2 irrespective of FKBP12.6 association. Biochem J 404:431–438 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hussain M, Orchard CH. (1997) Sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ content, L-type Ca2+ current and the Ca2+ transient in rat myocytes during beta-adrenergic stimulation. J Physiol 505:385–402 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James AF. (2007) Inhibition of SR Ca2+ uptake: a novel action of the RyR2-FKBP12.6 antagonist K201. Cardiovasc Res 76:199–201 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura J, Kawahara M, Sakai E, Yatabe J, Nakanishi H. (1999) Effects of a novel cardioprotective drug, JTV-519, on membrane currents of guinea pig ventricular myocytes. Jpn J Pharmacol 79:275–281 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodama I, Wakabayashi S, Toyama J, Shibata S, Yamada K. (1988) Electrophysiological effects of KT-362, a new antiarrhythmic agent with vasodilating action, on isolated guinea pig ventricular muscle. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 11:687–693 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohno M, Yano M, Kobayashi S, Doi M, Oda T, Tokuhisa T, Okuda S, Ohkusa T, Kohno M, Matsuzaki M. (2003) A new cardioprotective agent, JTV519, improves defective channel gating of ryanodine receptor in heart failure. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 284:H1035–H1042 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu T, O'Rourke B. (2008) Enhancing mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake in myocytes from failing hearts restores energy supply and demand matching. Circ Res 103:279–288 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loughrey CM, Otani N, Seidler T, Craig MA, Matsuda R, Kaneko N, Smith GL. (2007) K201 modulates excitation-contraction coupling and spontaneous Ca2+ release in normal adult rabbit ventricular cardiomyocytes. Cardiovasc Res 76:236–246 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukyanenko V, Chikando A, Lederer WJ. (2009) Mitochondria in cardiomyocyte Ca2+ signaling. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 41:1957–1971 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malli R, Frieden M, Trenker M, Graier WF. (2005) The role of mitochondria for Ca2+ refilling of the endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem 280:12114–12122 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ríos E, Zhou J, Brum G, Launikonis BS, Stern MD. (2008) Calcium-dependent inactivation terminates calcium release in skeletal muscle of amphibians. J Gen Physiol 131:335–348 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizzuto R, Pinton P, Carrington W, Fay FS, Fogarty KE, Lifshitz LM, Tuft RA, Pozzan T. (1998) Close contacts with the endoplasmic reticulum as determinants of mitochondrial Ca2+ responses. Science 280:1763–1766 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito A, Seiler S, Chu A, Fleischer S. (1984) Preparation and morphology of sarcoplasmic reticulum terminal cisternae from rabbit skeletal muscle. J Cell Biol 99:875–885 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata S, Wakabayashi S, Satake N, Hester RK, Ueda S, Tomiyama A. (1987) Mode of vasorelaxing action of 5-[3-[[2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-ethyl]amino]-1-oxopropyl]-2,3,4,5- tetrahydro-1,5-benzothiazepine fumarate (KT-362), a new intracellular calcium antagonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 240:16–22 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitsapesan R, Williams AJ. (1998) The Structure and Function of Ryanodine Receptors, Imperial College Press, London [Google Scholar]
- Stern MD, Cheng H. (2004) Putting out the fire: what terminates calcium-induced calcium release in cardiac muscle? Cell Calcium 35:591–601 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szalai G, Csordás G, Hantash BM, Thomas AP, Hajnóczky G. (2000) Calcium signal transmission between ryanodine receptors and mitochondria. J Biol Chem 275:15305–15313 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatsukawa Y, Arita M. (1997) Effects of KT-362, a sarcolemmal and intracellular calcium antagonist, on calcium transients of cultured neonatal rat ventricular cells: a comparison with gallopamil and ryanodine. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 10:667–675 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thu le T, Ahn JR, Woo SH. (2006) Inhibition of L-type Ca2+ channel by mitochondrial Na+-Ca2+ exchange inhibitor CGP-37157 in rat atrial myocytes. Eur J Pharmacol 552:15–19 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueyama N, Wakabayashi S, Tomiyama T. (1996) New intracellular calcium antagonists. I. Synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of 2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1,5-benzothiazepine analogs. Yakugaku Zasshi 116:106–124 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wehrens XH, Lehnart SE, Reiken S, van der Nagel R, Morales R, Sun J, Cheng Z, Deng SX, de Windt LJ, Landry DW, et al. (2005) Enhancing calstabin binding to ryanodine receptors improves cardiac and skeletal muscle function in heart failure. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:9607–9612 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yakushiji T, Fukuda T, Oyama Y, Akaike N. (1989) Effects of benzodiazepines and non-benzodiazepine compounds on the GABA-induced response in frog isolated sensory neurones. Br J Pharmacol 98:735–740 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]