Abstract
Glucagon activates hepatic adenylate cyclase, thereby increasing acutely the liver content of cyclic AMP (cAMP) as well as the release of cAMP into the hepatic vein. Insulin, on the other hand, antagonizes this glucagon-mediated cAMP production, thus providing a hypothetical mechanism through which insulin might correct some of the metabolic abnormalities of diabetes.
To study this hormonal interaction in man, net splanchnic cAMP production (NScAMPP) was investigated in normal and insulin-dependent diabetic men under basal conditions and in response to intravenous glucagon, 50 ng/kg/min for 2 h.
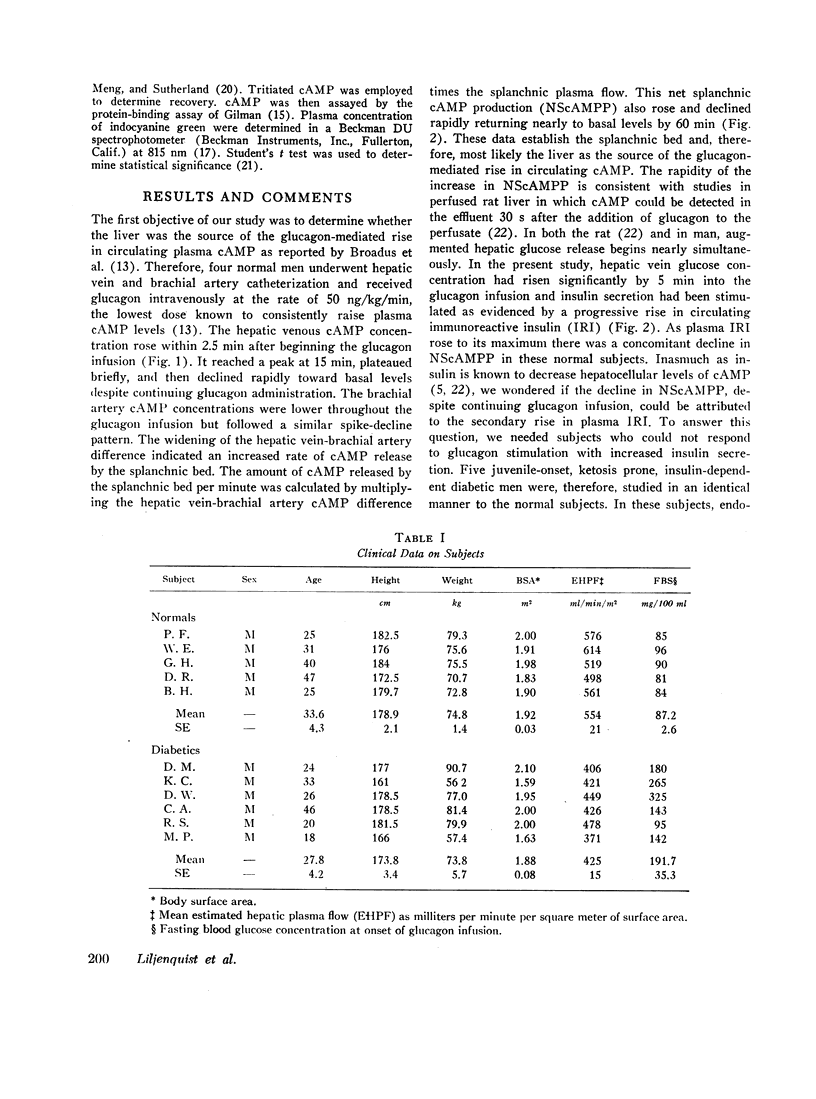
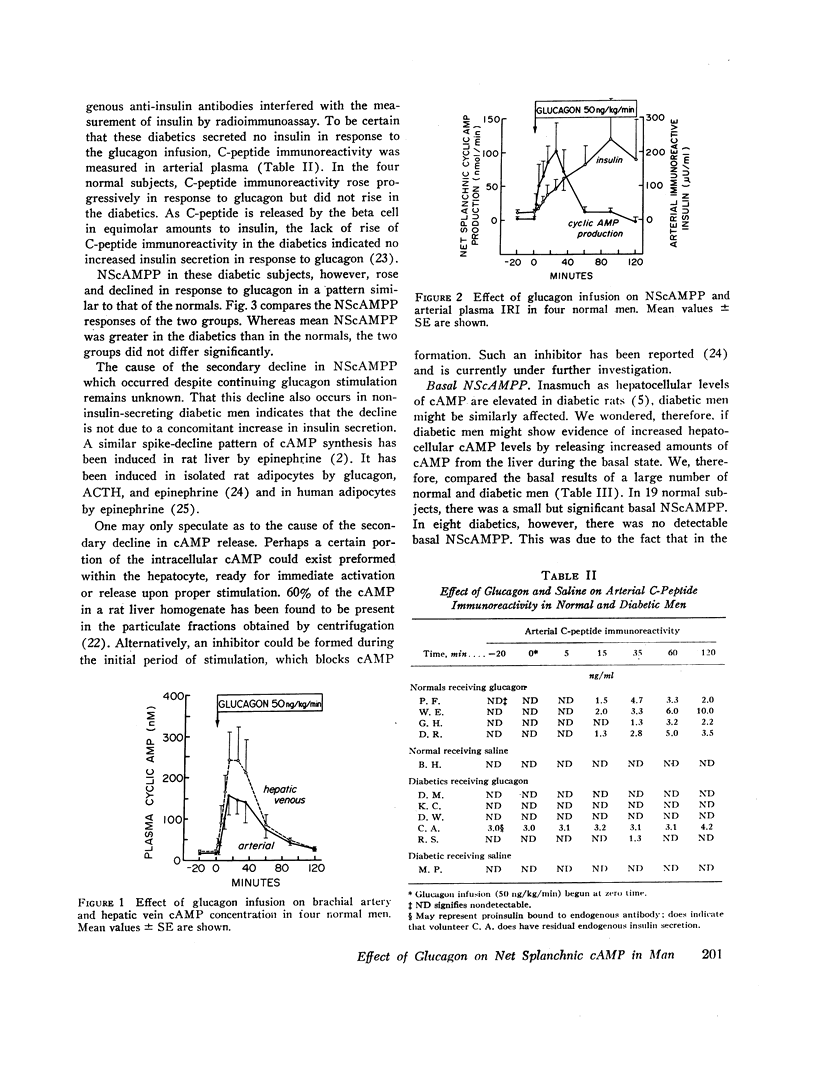
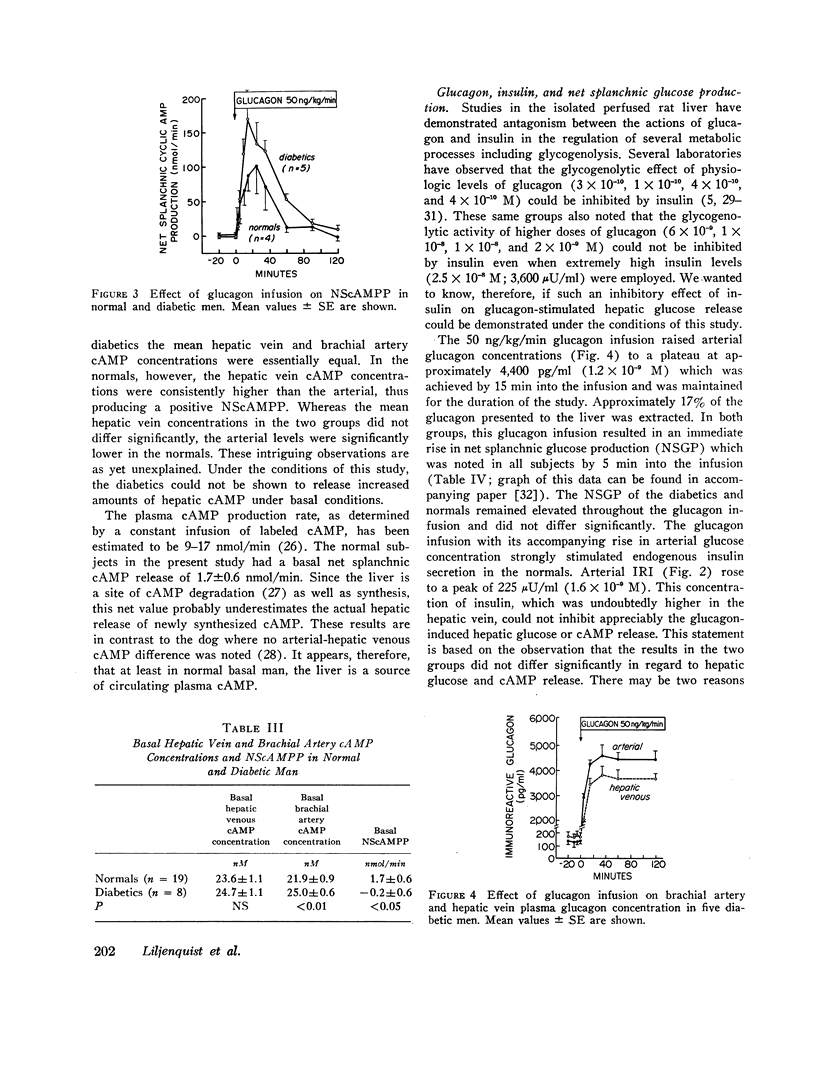
In normals (n=19), basal hepatic vein cAMP concentration was 23.6±1.1 nM and NScAMPP was 1.7±0.6 nmol/min. Glucagon stimulated NScAMPP in four normal subjects to a peak of 99.6±43 nmol/min at 25 min with a subsequent fall to 12.4±5.1 nmol/min by 90 min despite continuing glucagon infusion. Endogenous insulin secretion was stimulated as indicated by rising levels of immunoreactive insulin and C-peptide (connecting peptide) immunoreactivity, raising the possibility that endogenous insulin might be responsible for the fall in NScAMPP that followed the initial spike.
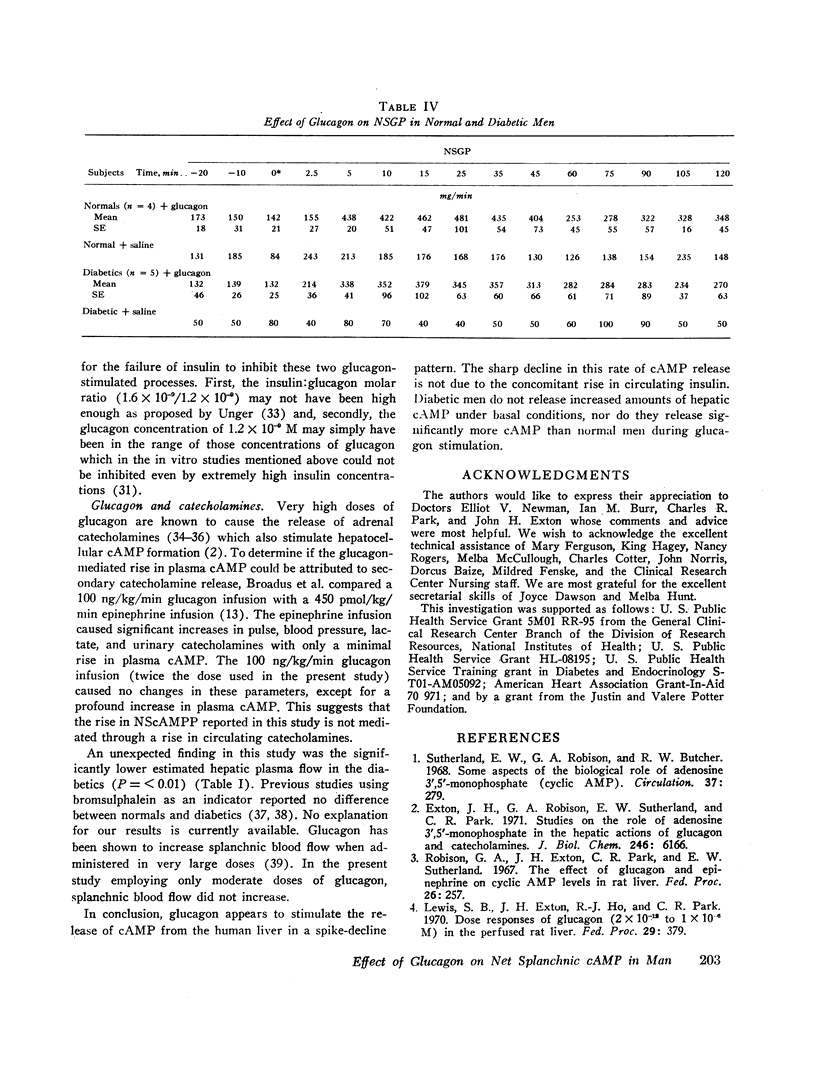
In the diabetics (n=8), basal hepatic vein cAMP concentration was 24.7±1.2 nM and NScAMPP was undetectable. Glucagon stimulated NScAMPP in five diabetics to a peak of 169.9±42.6 with a subsequent fall to 17.4±3.9 nmol/min by 90 min even though endogenous insulin secretion was not stimulated (no rise in C-peptide immunoreactivity). Although the mean increase in NScAMPP was greater in the diabetics, the two groups did not differ significantly.
Conclusions. In normal resting man the liver is a significant source of circulating cAMP. Diabetics do not release abnormally large amounts of hepatic cAMP under basal conditions. Glucagon markedly enhances hepatic cAMP release with a spike-decline pattern in both normal and diabetic men. The decline in hepatic cAMP release despite continuing glucagon stimulation is due to factors other than a stimulation of insulin secretion.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aguilar-Parada E., Eisentraut A. M., Unger R. H. Pancreatic glucagon secretion in normal and diabetic subjects. Am J Med Sci. 1969 Jun;257(6):415–419. doi: 10.1097/00000441-196906000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block M. B., Mako M. E., Steiner D. F., Rubenstein A. H. Circulating C-peptide immunoreactivity. Studies in normals and diabetic patients. Diabetes. 1972 Oct;21(10):1013–1026. doi: 10.2337/diab.21.10.1013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broadus A. E., Kaminsky N. I., Hardman J. G., Sutherland E. W., Liddle G. W. Kinetic parameters and renal clearances of plasma adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate and guanosine 3',5'-monophosphate in man. J Clin Invest. 1970 Dec;49(12):2222–2236. doi: 10.1172/JCI106441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broadus A. E., Kaminsky N. I., Northcutt R. C., Hardman J. G., Sutherland E. W., Liddle G. W. Effects of glucagon on adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate and guanosine 3',5'-monophosphate in human plasma and urine. J Clin Invest. 1970 Dec;49(12):2237–2245. doi: 10.1172/JCI106442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns T. W., Langley P. E., Robison G. A. Adrenergic receptors and cyclic AMP in the regulation of human adipose tissue lipolysis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Dec 30;185:115–128. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb45242.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butcher R. W., Ho R. J., Meng H. C., Sutherland E. W. Adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate in biological materials. II. The measurement of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate in tissues and the role of the cyclic nucleotide in the lipolytic response of fat to epinephrine. J Biol Chem. 1965 Nov;240(11):4515–4523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exton J. H., Robison G. A., Sutherland E. W., Park C. R. Studies on the role of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate in the hepatic actions of glucagon and catecholamines. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 25;246(20):6166–6177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floyd J. C., Jr, Fajans S. S., Conn J. W., Knopf R. F., Rull J. Insulin secretion in response to protein ingestion. J Clin Invest. 1966 Sep;45(9):1479–1486. doi: 10.1172/JCI105455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. A protein binding assay for adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):305–312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glinsmann W. H., Mortimore G. E. Influence of glucagon and 3', 5'-AMP on insulin responsiveness of the perfused rat liver. Am J Physiol. 1968 Sep;215(3):553–559. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.215.3.553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho R. J., Sutherland E. W. Formation and release of a hormone antagonist by rat adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1971 Nov 25;246(22):6822–6827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferson L. S., Exton J. H., Butcher R. W., Sutherland E. W., Park C. R. Role of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate in the effects of insulin and anti-insulin serum on liver metabolism. J Biol Chem. 1968 Mar 10;243(5):1031–1038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEEVY C. M., BENDER J. PHYSIOLOGY OF DYE EXTRACTION BY THE LIVER: COMPARATIVE STUDIES OF SULFOBROMOPHTHALEIN AND INDOCYANINE GREEN. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1963 Dec 30;111:161–176. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1963.tb36956.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEEVY C. M., MENDENHALL C. L., LESKO W., HOWARD M. M. Estimation of hepatic blood flow with indocyanine green. J Clin Invest. 1962 May;41:1169–1179. doi: 10.1172/JCI104570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine R. A., Lewis S. E., Shulman J., Washington A. Metabolism of cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-8-14C by isolated, perfused rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 10;244(15):4017–4022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljenquist J. E., Bomboy J. D., Lewis S. B., Sinclair-Smith B. C., Felts P. W., Lacy W. W., Crofford O. B., Liddle G. W. Effects of glucagon on lipolysis and ketogenesis in normal and diabetic men. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jan;53(1):190–197. doi: 10.1172/JCI107537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luyckx A. S., Lefebvre P. J. Arguments for a regulation of pancreatic glucagon secretion by circulating plasma free fatty acids. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Feb;133(2):524–528. doi: 10.3181/00379727-133-34511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MYERS J. D. Net splanchnic glucose production in normal man and in various disease states. J Clin Invest. 1950 Nov;29(11):1421–1429. doi: 10.1172/JCI102380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackrell D. J., Sokal J. E. Antagonism between the effects of insulin and glucagon on the isolated liver. Diabetes. 1969 Nov;18(11):724–732. doi: 10.2337/diab.18.11.724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madden J. J., Jr, Ludewig R. M., Wangensteen S. L. Effects of glucagon on the splanchnic and the systemic circulation. Am J Surg. 1971 Jul;122(1):85–90. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(71)90355-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melani F., Rubenstein A. H., Oyer P. E., Steiner D. F. Identification of proinsulin and C-peptide in human serum by a specific immunoassay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):148–155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porte D., Jr, Graber A. L., Kuzuya T., Williams R. H. The effect of epinephrine on immunoreactive insulin levels in man. J Clin Invest. 1966 Feb;45(2):228–236. doi: 10.1172/JCI105335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson R. P., Porte D., Jr Adrenergic modulation of basal insulin secretion in man. Diabetes. 1973 Jan;22(1):1–8. doi: 10.2337/diab.22.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAMOLS E., MARRI G., MARKS V. PROMOTION OF INSULIN SECRETION BY GLUCAGON. Lancet. 1965 Aug 28;2(7409):415–416. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(65)90761-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SARCIONE E. J., BACK N., SOKAL J. E., MEHLMAN B., KNOBLOCK E. Elevation of plasma epinephrine levels produced by glucagon in vivo. Endocrinology. 1963 Apr;72:523–526. doi: 10.1210/endo-72-4-523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCIAN L. F., WESTERMANN C. D., VERDESCA A. S., HILTON J. G. Adrenocortical and medullary effects of glucagon. Am J Physiol. 1960 Nov;199:867–870. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1960.199.5.867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheps S. G., Maher F. T. Histamine and glucagon tests in diagnosis of pheochromocytoma. JAMA. 1968 Sep 23;205(13):895–899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standardization of the oral glucose tolerance test. Report of the Committee on Statistics of the American Diabetes Association June 14, 1968. Diabetes. 1969 May;18(5):299–307. doi: 10.2337/diab.18.5.299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger R. H. Glucagon and the insulin: glucagon ratio in diabetes and other catabolic illnesses. Diabetes. 1971 Dec;20(12):834–838. doi: 10.2337/diab.20.12.834. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger R. H., Ketterer H., Dupré J., Eisentraut A. M. The effects of secretin, pancreozymin, and gastrin on insulin and glucagon secretion in anesthetized dogs. J Clin Invest. 1967 Apr;46(4):630–645. doi: 10.1172/JCI105565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger R. H., Ohneda A., Aguilar-Parada E., Eisentraut A. M. The role of aminogenic glucagon secretion in blood glucose homeostasis. J Clin Invest. 1969 May;48(5):810–822. doi: 10.1172/JCI106039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



