Abstract
Mycobacterium tuberculosis enhances its survival in macrophages by suppressing immune responses in part through its complex cell wall structures. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ), a nuclear receptor superfamily member, is a transcriptional factor that regulates inflammation and has high expression in alternatively activated alveolar macrophages and macrophage-derived foam cells, both cell types relevant to tuberculosis pathogenesis. In this study, we show that virulent M. tuberculosis and its cell wall mannose-capped lipoarabinomannan induce PPARγ expression through a macrophage mannose receptor-dependent pathway. When activated, PPARγ promotes IL-8 and cyclooxygenase 2 expression, a process modulated by a PPARγ agonist or antagonist. Upstream, MAPK-p38 mediates cytosolic phospholipase A2 activation, which is required for PPARγ ligand production. The induced IL-8 response mediated by mannose-capped lipoarabinomannan and the mannose receptor is independent of TLR2 and NF-κB activation. In contrast, the attenuated Mycobacterium bovis bacillus Calmette-Guérin induces less PPARγ and preferentially uses the NF-κB–mediated pathway to induce IL-8 production. Finally, PPARγ knockdown in human macrophages enhances TNF production and controls the intracellular growth of M. tuberculosis. These data identify a new molecular pathway that links engagement of the mannose receptor, an important pattern recognition receptor for M. tuberculosis, with PPARγ activation, which regulates the macrophage inflammatory response, thereby playing a role in tuberculosis pathogenesis.
Tuberculosis (TB) continues to be a worldwide public-health threat with the emergence of multi- and extensively drug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains (1). Inhaled M. tuberculosis travels to the lung distal airways where it is phagocytosed by alveolar macrophages (AMs) via specific phagocytic and pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) (2, 3). M. tuberculosis infection proceeds with granuloma formation composed of multiple cell types, including foamy macrophages with lipid bodies (4).
Numerous TB animal studies have revealed an early phase of relatively unchecked growth of aerosolized M. tuberculosis within AMs. AMs are prototypic alternatively activated cells with increased expression of a subset of PRRs that enhance microbial clearance and a regulated inflammatory program with reduced proinflammatory-mediated microbial killing (5). There is increasing evidence that these uniquely regulated resident macrophages play an important role in allowing for a host-adapted intracellular pathogen like M. tuberculosis to survive and replicate for an extended period prior to complete activation of protective innate and adaptive immune responses (6–9). We have recently termed this interval to optimal macrophage activation the “switching time” within the alveolar microenvironment (8). This concept raises questions as to what the key molecular switches are in macrophages that regulate their immune response pathways (either pro- or anti-inflammatory) to M. tuberculosis and pathogenic microbes in general.
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs), members of a lipid-activated nuclear receptor superfamily, have emerged as key regulators of cellular metabolism, proliferation, differentiation, and inflammation (10). However, their role in regulating host immune responses to infectious agents is only now being recognized. These receptors act as transcription factors, forming heterodimers with the retinoid X receptor (RXR) and bind to specific PPAR response elements in the promoter region of the genes, which they regulate (11, 12). There are three types of human PPARs: PPARα, PPARγ, and PPARβ/δ, and each type is the product of a different gene (13). Natural ligands include fatty acids or fatty acid derivatives, whereas synthetic ligands include anti-diabetic thiazolidinediones, such as troglitazone (14, 15).
PPARγ is highly expressed in adipose tissue and plays a crucial role in adipocyte differentiation and glucose metabolism, but it is also expressed in a variety of tissues and cell types including macrophages (16). PPARγ serves as a negative regulator of macrophage activation; altering the expression of many inflammatory genes (17, 18), modulating macrophage differentiation and activation through transrepression of the transcription factors NF-κB, AP-1, and STAT (19), and attenuating the respiratory burst (20). These attributes have important implications for the control of M. tuberculosis infection. Of additional relevance to M. tuberculosis pathogenesis, increased PPARγ expression is seen in IL-4/IL-13–mediated alternative activation of macrophages (5), in AMs (21), and in macrophage-derived foam cells from atherosclerotic lesions (22).
Two PRRs important for the recognition of M. tuberculosis by macrophages are TLRs and the mannose receptor (MR) (CD206) (2, 3). TLRs are thought to protect against mycobacterial infection through induction of NF-κB and production of inflammatory cytokines. The MR, in contrast, may promote infection because it is highly expressed on alternatively activated macrophages (5), and ligation of this receptor is associated with an anti-inflammatory cytokine program and lack of activation of oxidative responses (23, 24). In addition, mannose-capped lipoarabinomannan (Man-LAM) and higher-order phosphatidyl-myo-inositol mannosides, major components of the M. tuberculosis cell wall, are MR ligands during phagocytosis by human macrophages and MR-mediated entry leads to limited phagosome–lysosome (P–L) fusion (25, 26).
The expression and immune functions of PPARγ in human macrophages in response to M. tuberculosis infection and the link to relevant PRRs have not been explored. In this study, we determined that infection with virulent M. tuberculosis or the addition of Man-LAM upregulates PPARγ expression and concomitantly increases IL-8 production, COX2 expression, and PGE2 production in macrophages. Furthermore, we show that PPARγ knockdown significantly reduces IL-8 release. We determined that MAPK-p38 and cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2), upstream mediators of PPARγ, are involved in IL-8 production. Surprisingly, we identified that MR ligation plays an important role in PPARγ induction in macrophages. The M. tuberculosis- or ManLAM-induced PPARγ-mediated IL-8 response was independent of NF-κB activation and TLR2 expression, suggesting that we have uncovered an MR-specific signaling pathway. In contrast, infection by the attenuated Mycobacterium bovis bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) induces less PPARγ expression and particularly PGE2 production, and IL-8 production in response to BCG was mediated by NF-κB rather than by PPARγ. Finally, we determined that PPARγ knockdown controls M. tuberculosis growth in macrophages with a concomitant increase in TNF production. Thus, we have identified a role for PPARγ as a key regulator of macrophage immune responses to M. tuberculosis and its major cell wall lipoglycan and have linked its activation to a signaling pathway initiated by ligation of the MR, an important PRR in the phagocytosis and trafficking of M. tuberculosis. These studies suggest that PPARγ functions as one important “molecular switch” in regulating macrophage immune responses to M. tuberculosis and potentially other microbial pathogens. In upregulating PPARγ activity, M. tuberculosis further drives the alternative activation state of AMs to enhance its intracellular survival.
Materials and Methods
Reagents
Dulbecco’s PBS with and without Ca2+ and Mg2+, RPMI 1640 with L-glutamine, and HEPES buffer were purchased from Invitrogen Life Technologies (Carlsbad, CA). Human serum albumin was purchased from CSL Behring (Kankakee, IL). BSA was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO) and heat-inactivated Hyclone Standard FBS from Thermo Fisher Scientific (Waltham, MA). PPARγ antagonist GW-9662, ligand 15-deoxy-Δ12,14-PGJ2 (15-d-PGJ2), PGE2 enzyme immunoassay (EIA) kit–monoclonal, and the cPLA2 inhibitor methyl arachidonyl fluorophosphonate (MAFP) were purchased from Cayman Chemical (Ann Arbor, MI). Middlebrook 7H9 broth was purchased from BD Biosciences (Mountain View, CA). 7H11 agar plates were prepared with Middlebrook 7H11 agar (BD Biosciences) to which was added oleic acid (Fisher Scientific, Pittsburgh, PA), BSA (Sigma-Aldrich), dextrose (Sigma-Aldrich), catalase (Sigma-Aldrich), and glycerol (Fisher Scientific). Pam3Cys, SB 203580, and UO126 were purchased from Calbiochem (Gibbstown, NJ).
Abs
Abs specific for phospho-p38, total p38, phospho-cPLA2, total cPLA2, and PPARγ were purchased from Cell Signaling Technology (Beverly, MA). β-Actin and anti-MR (CD 206-H300) Abs were purchased from Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Santa Cruz, CA). COX2 mAb was purchased from Cayman Chemical. Anti-CD206 mAb for confocal microscopy was purchased from BD Pharmingen (San Jose, CA). Accell PPARγ small interfering RNA (siRNA) and scramble siRNA were purchased from Thermo Scientific Dharmacon RNAi Technologies (Chicago, IL). The MR siRNA and scramble siRNA were purchased from Qiagen (Valencia, CA).
Bacterial strains and culture
Lyophilized M. tuberculosis H37Rv (ATCC 25618), M. bovis BCG (ATCC 35734), and M. smegmatis (ATCC 700084) were obtained from American Tissue Culture Collection (Manassas, VA), reconstituted, and used as described previously (27). The concentration of bacteria (1–2 × 108 bacteria/ml) and the degree of clumping (≤10%) were determined by counting in a Petroff-Hausser chamber. Bacteria prepared in this fashion are ≥90% viable by CFU assay. Killed M. tuberculosis was prepared by incubating bacteria with 4% paraformaldehyde for 30 min at room temperature, washing extensively with PBS, and resuspending in RPMI 1640 plus 10 mM HEPES plus 0.4% human serum albumin for infection.
Purification of ManLAM and lipomannan
ManLAM and lipomannan (LM) purification from M. tuberculosis H37Rv and LM purification from Mycobacterium smegmatis were performed following our laboratory protocols as reported previously (28, 29). For quality control, fractions containing pure H37Rv ManLAM, H37Rv LM, and M. smegmatis LM were analyzed by electrophoresis using 15% SDS-polyacrylamine gel, followed by periodic acid-silver staining. In addition, sample purification was further confirmed by mass spectrometry (neutral sugar and fatty acid analyses), 1H nuclear magnetic resonance, and endotoxin content determination (all samples tested had <18 pg endotoxin/mg of sample).
Isolation and culture of human monocyte-derived macrophages
Monocyte-derived macrophage (MDM) monolayers were prepared from healthy, purified protein derivative-negative human volunteers using an approved The Ohio State University Institutional Review Board protocol as described previously (30). Briefly, PBMCs were isolated from heparinized blood on a Ficoll cushion and then cultured in Teflon wells (Savillex, Minnetonka, MN) for 5 d in the presence of 20% autologous serum. The wells were then placed on ice for 30 min, and the PBMCs were removed by washing. MDMs in the cultured PBMCs were adhered to 12- or 24-well tissue culture plates (Falcon; BD Biosciences Labware, Franklin Lakes, NJ) for 2–3 h at 37°C/5% CO2 in 10% autologous serum. Lymphocytes were then washed away, and MDM monolayers were repleted with RPMI 1640 containing 10% autologous serum and incubated overnight. For ManLAM and LM stimulation experiments or infection with M. tuberculosis H37Rv, BCG or M. smegmatis, the MDM monolayers in tissue culture plates were washed with warm RPMI 1640 and repleted with 1 ml RPMI 1640 plus 10 mM HEPES plus 0.4% human serum albumin, and 5 μg/ml ManLAM, 5 μg/ml LM, or mycobacteria at the indicated multiplicity of infection (MOI) was subsequently added. The conditions for MDM transfection experiments and confocal microscopy studies are detailed below.
Mycobacterial infection of macrophages, macrophage lysis, and Western blotting
Following the addition of mycobacteria, MDM monolayers in tissue culture plates were placed on a platform shaker for 30 min at 37°C/5% CO2 for effective dispersion of bacteria and then left stationary for an additional 90 min (30). The cells were then washed three times with warm RPMI 1640 to remove extracellular bacteria and incubated in 2% autologous serum in RPMI 1640 for different time periods. The infected and uninfected MDMs as well as ManLAM-stimulated MDMs were rinsed with warm PBS and lysed in TN1 buffer (50 mM Tris [pH 8.0], 10 mM EDTA, 10 mM Na4P2O7, 10 mM NaF, 1% Triton X-100, 125 mM NaCl, 10 mM Na3VO4, and 10 μg/ml each of aprotinin and leupeptin), incubated on ice for 10 min, and then centrifuged at 17,949 × g at 4°C to pellet the cell debris. Protein concentrations of the cleared cell lysates were measured using the Pierce BCA-protein assay kit (Thermo Scientific, Rockford, IL). Cell lysates were separated by SDS-PAGE under reduced and denaturing conditions and analyzed by Western blot by probing with the Ab of interest and development using ECL (Amersham Biosciences, Pittsburg, PA).
Band densitometry was measured using Scion image software (Scion, Frederick, MD). To quantify the band in each sample, we first subtracted the background, normalized the signal to the amount of β-actin in the lysate, and plotted the values as band intensities.
Transfection of MDMs
MDMs were transfected with scramble siRNA, PPARγ siRNA (target sequence 5′-GAUUGAAGCUUAUCUAUGA-3′) (200 nM), MR siRNA (target sequence 5′-GUGGUACGCAGAUUGCACGTT-3′) (400 nM) and TLR2 siRNA (sense sequence 5′-CUGGUAGUUGUGGGUUGAAGCdTdT-3′, and antisense sequence 5′-GCUUCAACCCACAACUACCAGdTdT-3′) (200 nM) using the Amaxa Nucleofector (Amaxa Biosystems, Gaithersburg, MD). Briefly, day 5 PBMCs (1 × 107) were resuspended in 100 μl nucleofector solution, followed by the addition of scramble siRNA or target-specific siRNA, incubated at room temperature for 5 min, and nucleofected according to the manufacturer’s instructions. PBMCs were then seeded on 12-well tissue culture plates (except for confocal microscopy studies below) with 1.0 ml RPMI 1640 supplemented with 10% autologous serum and incubated for 2 h at 37°C/5% CO2. After 2 h, adhered transfected cells (MDMs) were washed and repleted with warm RPMI 1640 containing 20% autologous serum for 16 h (PPARγ) or 48 h (MR and TLR2). Transfected cells were used for subsequent experiments, such as CFU and cytokine assays, Western blots, and confocal microscopy. The transfection efficiency was analyzed by transfecting a GFP-expressing plasmid pmaxGFP into day 5 PBMCs, and the number of GFP expressing cells was counted (200 consecutive cells in triplicate wells) by using inverted fluorescence microscopy. The transfection efficiency was >95%.
Cytokine and PGE2 assays
MDMs (3 × 105) in monolayer culture were incubated with M. tuberculosis H37Rv or BCG or exposed to ManLAM for different time periods. Cytokines (TNF, IL-6, IL-12p40, IL-8, and IL-10) in cell supernatants were analyzed by ELISA (R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN). For PGE2 measurements, MDMs (3 × 105) in monolayer culture were incubated with M. tuberculosis H37Rv or BCG for different time periods. The amount of PGE2 present in the cell supernatants was measured according to the manufacturer’s instruction by using a PGE2 EIA kit.
Macrophage colocalization studies of PPARγ and the nucleus by confocal microscopy
MDMs were transfected with scramble siRNA, PPARγ siRNA, or MR siRNA by the Amaxa nucleofector system and plated onto Chromerge-cleaned glass coverslips in 24-well tissue culture plates for 2 h at 37°C (1 × 105 MDM/coverslip). The MDM monolayers were washed with warm RPMI 1640 and repleted with RPMI 1640 containing 20% autologous serum, incubated at 37°C for an additional 16 h, and left untreated or treated with ManLAM (5 μg/ml) for different time periods. MDM monolayers on coverslips were washed with PBS, fixed with 2% paraformaldehyde, and permeabilized (cells were not permeabilized for MR surface expression experiments) with 100% methanol for 5 min at room temperature (31). The cells were blocked overnight at 4°C in blocking buffer (Dulbecco’s PBS plus 5 mg/ml BSA plus 10% heat-inactivated FBS), incubated with Abs against PPARγ and CD206, followed by incubation with the secondary Abs conjugated with rabbit Alexa Fluor 594 and Mouse Alexa Fluor 488, respectively. For isotype control, the permeablized or nonpermeablized MDMs were incubated with rabbit IgG or mouse IgG. MDM nuclei were labeled with 0.1 μg/ml of the DNA stain DAPI (Molecular Probes, Carlsbad, CA) in PBS for 5 min at room temperature. After extensive washing in blocking buffer, the coverslips were dried and mounted on glass slides. PPARγ and MR protein expression levels and the colocalization of PPARγ with the nucleus were examined by confocal microscopy (LSM 510; Carl Zeiss MicroImaging, Thornwood, NY).
M. tuberculosis intracellular growth assays in macrophages
Intracellular growth assays using CFU were performed as described previously (32). Briefly, scramble siRNA- or PPARγ siRNA-transfected MDM monolayers were incubated with M. tuberculosis H37Rv (MOI 1:1, triplicate samples in each test group) for 2 h (30 min on a platform shaker and 90 min stationary as noted earlier). The MDM monolayers were then washed three times with warm RPMI 1640 and either lysed or repleted with RPMI 1640 containing 2% human autologous serum and incubated for 24 h. The supernatants and MDM monolayers were then plated, the number of colonies counted after 4 wk, and CFUs were enumerated.
Statistics
For M. tuberculosis- or ManLAM-mediated cytokine responses and PPARγ and COX2 expression analyses in MDMs, the magnitude of the response from each independent experiment varied among the donors; however, the pattern of experimental results was the same from donor to donor. To account for this variability, we normalized the data to an internal control in each experiment. A ratio of experimental results to control was obtained, and the mean ratio was then tested for a significant difference from one using t statistics. Statistical significance was defined as p < 0.05.
Results
M. tuberculosis H37Rv infection or ManLAM stimulation upregulates PPARγ expression in human macrophages
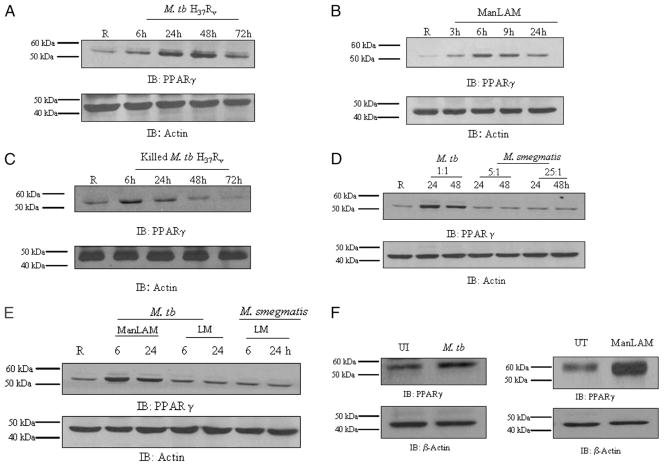
Human AMs are reported to have high levels of PPARγ expression compared with other tissue macrophages (3, 19, 21). We began our studies by determining the level of PPARγ expression using an established human MDM model (30). As shown in Fig. 1A and 1B, the basal expression level of PPARγ was low as measured in cell lysates by Western blot analysis. To assess whether M. tuberculosis and ManLAM induce PPARγ expression, MDMs were infected with live virulent M. tuberculosis H37Rv or stimulated with Man-LAM from M. tuberculosis H37Rv, and PPARγ expression was assessed. We found that PPARγ expression was significantly increased in M. tuberculosis-infected MDMs for up to 72 h (Fig. 1A). A similar response was observed in ManLAM-stimulated MDMs (Fig. 1B), although the response followed a shorter time course. To determine whether the viability of bacteria was required for PPARγ expression, MDMs were incubated with killed M. tuberculosis for different time points. Our results indicate that PPARγ expression is enhanced under this condition; however, the time course is shorter than that seen with live bacteria, more closely resembling the time course seen with ManLAM treatment (Fig. 1C). To examine the specificity of the response, we next examined PPARγ expression in MDMs incubated with the avirulent M. smegmatis at different MOIs (5:1 and 25:1) and observed that M. smegmatis did not upregulate PPARγ expression (Fig. 1D). We extended our studies on PPARγ expression using LM, another major mycobacterial cell wall component (Fig. 1E). LM from M. tuberculosis H37Rv and M. smegmatis failed to induce PPARγ expression. Finally, we verified that human AMs have a higher basal level of PPARγ expression and that M. tuberculosis infection or ManLAM stimulation further increased this level (Fig. 1F). Taken together, these results provide evidence that M. tuberculosis infection but not infection with the avirulent M. smegmatis upregulates PPARγ expression in human macrophages and that ManLAM is one contributing cell wall component to this response.
FIGURE 1.
M. tuberculosis H37Rv and its cell wall component ManLAM upregulate PPARγ expression in human macrophages. MDM monolayers were incubated with M. tuberculosis H37Rv (MOI 5:1) (A) for 2 h; cells were washed and incubated in 2% autologous serum for different times (6, 24, 48, and 72 h) and ManLAM (5 μg/ml) (B) or killed M. tuberculosis H37Rv (MOI 5:1) (C) for different times (3, 6, 9, and 24 h) following 2 h and washed. MDM monolayers were incubated with M. tuberculosis H37Rv (MOI 5:1) or M. smegmatis (MOI 5:1; 25:1) (D) or with M. tuberculosis LM (5 μg/ml) or M. smegmatis LM (5 μg/ml) (E) for different time points (6 and 24 h). F, Human AMs were incubated with or without M. tuberculosis H37Rv (MOI 5:1) for 24 h or ManLAM (5 μg/ml) for 6 h. Cell lysates were analyzed for PPARγ expression by Western blotting using PPARγ Ab and for β-actin as a loading control. Shown are representative blots from three independent experiments (three donors), except C and F, which are representative blots from two independent experiments (two donors).
M. tuberculosis H37Rv infection or ManLAM stimulation enhances IL-8 production and COX2 expression in human macrophages
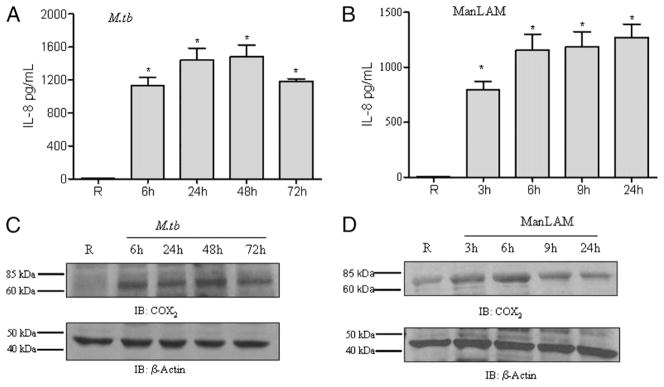
We next investigated whether the M. tuberculosis- or ManLAM-mediated induction of PPARγ leads to altered downstream immune functions in human macrophages. Activated PPARγ heterodimerizes with RXR and binds to PPAR response element in the promoter region of IL-8 and COX2 genes to enhance their expression (33). MDMs were incubated with M. tuberculosis H37Rv for different time periods, and cell culture supernatants were analyzed for IL-8 secretion by ELISA, and cell lysates were analyzed for COX2 expression by Western blot. Our results demonstrate that M. tuberculosis infection induces IL-8 release (Fig. 2A) and COX2 expression (Fig. 2C). Similarly, ManLAM-stimulated MDMs exhibited increased IL-8 production (Fig. 2B) and COX2 expression (Fig. 2D). Interestingly, MDMs and the monocytic cell line THP-1 stimulated with ManLAM did not induce other proinflammatory cytokines, such as TNF, IL-6, and IL-12p40 (data not shown). Thus, these results suggested that the observed PPARγ upregulation is specifically involved in IL-8 production and COX2 expression in M. tuberculosis-infected or ManLAM-stimulated macrophages.
FIGURE 2.
M. tuberculosis H37Rv infection or ManLAM stimulation enhances IL-8 production and COX2 expression in human macrophages. The cell culture media and cell lysates of MDMs incubated with M. tuberculosis H37Rv or stimulated with ManLAM were analyzed for IL-8 production by ELISA and COX2 expression by Western blot, respectively. The time points were the same as in Fig. 1. The media of uninfected macrophages showed undetectable levels of IL-8. In contrast, the media of M. tuberculosis-infected cells (A) or ManLAM-stimulated cells (B) showed significantly increased levels of IL-8. Shown are cumulative results of three independent experiments performed in triplicate in A and five independent experiments performed in triplicate in B (mean ± SEM). *p < 0.0001. Cell lysates from M. tuberculosis-infected cells showed increased COX2 expression relative to uninfected cells (C). MDMs stimulated with ManLAM showed increased expression of COX2; the expression peaked at 6 h and was sustained until 9 h (D). The Western blots shown are representative of three independent experiments. Immunostaining for β-actin was used as a loading control.
PPARγ knockdown in human macrophages inhibits ManLAM-mediated IL-8 release
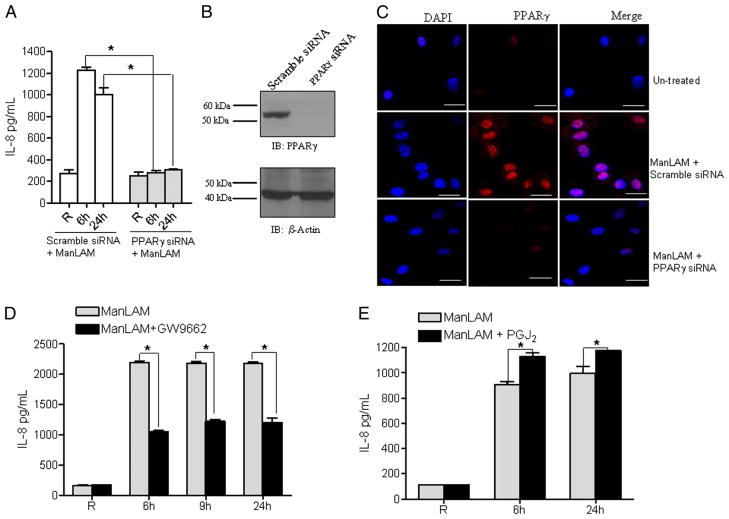
To confirm the direct involvement of PPARγ in the ManLAM-mediated IL-8 response from macrophages, we used siRNA targeted to PPARγ to knock down its expression in MDMs and subsequently stimulated the cells with ManLAM. Cell culture supernatants were used to measure IL-8 production. In control scramble siRNA-transfected MDMs, IL-8 production in response to ManLAM was increased; in contrast, there was no increase in IL-8 production from PPARγ siRNA-transfected cells compared with unstimulated cells (Fig. 3A). This result provided strong evidence that PPARγ is an important regulator of ManLAM-mediated IL-8 production in MDMs. In parallel, cell lysates were analyzed for PPARγ expression. Results in Fig. 3B show that PPARγ siRNA transfection nearly abolished PPARγ expression. Simultaneously, we assessed the expression and colocalization of PPARγ within the nucleus by confocal microscopy. Scramble or PPARγ siRNA-transfected MDM monolayers were stimulated with or without ManLAM. The cells were fixed, permeabilized, and stained with an isotype control or PPARγ Ab and DAPI. Untreated control cells showed very low levels of PPARγ expression (Fig. 3C, upper panel). Consistent with our Western blot results, PPARγ expression was dramatically increased by ManLAM stimulation following scramble siRNA transfection (Fig. 3C, middle panel) as indicated by its translocation and colocalization within the nucleus. In contrast, ManLAM-stimulated PPARγ siRNA-transfected cells showed a marked decrease in PPARγ expression (Fig. 3C, lower panel). There was no staining of PPARγ following incubation with the isotype control Ab (data not shown). Taken together, these data demonstrate that ManLAM-induced PPARγ expression is involved in the induction of IL-8 in human macrophages.
FIGURE 3.
PPARγ knockdown and modulation of activity alter ManLAM-mediated IL-8 release. MDMs were transfected with scramble siRNA (control) or PPARγ siRNA by nucleofection. After 16 h, cells were stimulated with ManLAM (5 μg/ml) for 6 and 24 h. Supernatants and cell lysates were analyzed for IL-8 production by ELISA (A) and PPARγ expression by Western blot (B). The results in A are the mean ± SD from a representative experiment performed in triplicate (n = 3) and in B from the same experiment (representative of blots that were performed in each experiment with immunostaining for β-actin as a loading control). In parallel experiments, scramble siRNA- or PPARγ siRNA-transfected MDMs on coverslips were stimulated with or without ManLAM (5 μg/ml) for 6 h. The MDMs were fixed with paraformaldehyde, permeabilized, stained with anti-PPARγ Ab (red) and DAPI (blue) for nuclear localization, and examined by confocal microscopy (magnification ×630) (C). The upper panel shows untreated cells, the middle panel shows scramble siRNA-transfected ManLAM-stimulated cells, and the lower panel shows PPARγ siRNA-transfected ManLAM-stimulated cells (from two independent experiments). Scale (white line) represents 20 μm. MDMs were pretreated with the PPARγ antagonist, GW9662 (100 nM) (D), the PPARγ ligand 15-d-PGJ2 (PGJ2) (2 μM) (E), or DMSO for 30 min and subsequently stimulated with ManLAM (5 μg/ml). Supernatants were collected and analyzed for IL-8 production by ELISA. The results in D and E are the mean ± SD from a representative experiment performed in triplicate (n = 3). *p < 0.0398; **p < 0.0025; and ***p < 0.0001 for the control versus inhibitor group.
Modulation of PPARγ activity alters IL-8 production in human macrophages
To further validate the involvement of PPARγ in IL-8 production in human macrophages, we treated MDMs with the PPARγ antagonist GW9662 (34) and subsequently stimulated them with ManLAM. Cell culture supernatants were analyzed for IL-8 production. Our results show that treatment with the PPARγ antagonist significantly decreased IL-8 production (Fig. 3D). We next tested whether PPARγ activity was further enhanced by its natural ligand 15-d-PGJ2. MDMs were treated with exogenous 15-d-PGJ2 and then with ManLAM. PPARγ ligand increased IL-8 production following ManLAM stimulation compared with ManLAM stimulation alone (Fig. 3E). MDMs treated with 15-d-PGJ2 alone without ManLAM stimulation did not increase IL-8 production when compared with resting cells (data not shown). Thus, consistent with our previous PPARγ knockdown results, IL-8 production is regulated by PPARγ levels in ManLAM-stimulated human macrophages.
The macrophage MR regulates PPARγ expression in response to ManLAM
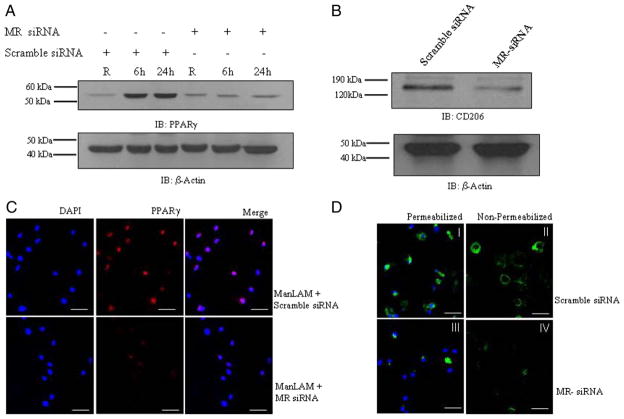
Engagement of the MR by ManLAM through its mannose caps during phagocytosis directs M. tuberculosis to its initial phagosomal niche in human macrophages by limiting P–L fusion (25, 35). Because ManLAM preferentially binds to the MR, we hypothesized that the MR plays a role in increasing PPARγ expression in macrophages following ManLAM stimulation. To test this hypothesis, MDMs were transfected with scramble siRNA or MR siRNA and then stimulated with ManLAM. Cell lysates were analyzed for PPARγ expression by Western blot analysis. The results demonstrate that MR knockdown in MDMs significantly reduces PPARγ expression (Fig. 4A). In parallel, the same cell lysates were analyzed for MR protein expression to determine the efficiency of siRNA-mediated knockdown. Transfection of MR siRNA in MDMs decreased the MR protein level ~75% when compared with scramble siRNA-transfected cells (Fig. 4B). The results were further confirmed by confocal microscopy. MR siRNA-transfected MDM monolayers were stimulated with Man-LAM, fixed and immunostained for PPARγ. The results in Fig. 4C show that MR knockdown suppresses PPARγ expression and colocalization with the nucleus. In addition, both surface and intracellular levels of MR were markedly reduced in MR siRNA transfected macrophages (Fig. 4D). The confocal microscopy results were consistent with Western blot results and provide evidence that the MR is involved in ManLAM-mediated upregulation of PPARγ expression in human macrophages.
FIGURE 4.
The macrophage MR regulates PPARγ expression in response to ManLAM. MDMs were transfected with MR siRNA or scramble siRNA by nucleofection and plated in RPMI 1640 containing 20% autologous serum. After 48 h, the cells were washed and stimulated with ManLAM (5 μg/ml) for 6, 9, and 24 h. Cell lysates were examined for PPARγ and β-actin expression (A) by Western blot analysis. B, MR knockdown was confirmed by Western blot using a MR Ab. The Western blots shown are representative of greater than or equal to three independent experiments. In parallel, MR siRNA or scramble siRNA-transfected MDMs were treated with ManLAM for 6 h. The cells were fixed, permeabilized, stained with anti-PPARγ Ab (red) and DAPI (blue) for nuclear localization, and then examined by confocal microscopy (C; n = 2) (magnification ×400). MR expression in MR siRNA-transfected cells was analyzed by confocal microscopy (D; n = 2) (magnification ×400). Both permeabilized (I and III) and nonpermeabilized (II and IV) cells (scramble siRNA or MR siRNA) were stained with anti-MR Ab (green) and DAPI (blue) for the nucleus. Scale (white line) represents 20 μm.
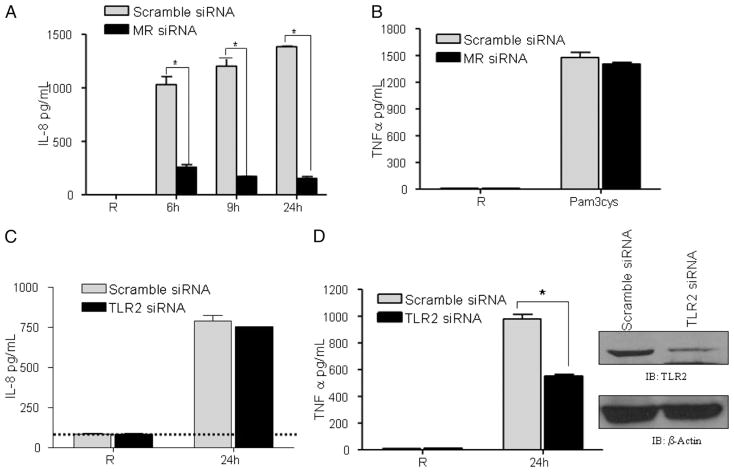
ManLAM-mediated IL-8 response in human macrophages is dependent on the MR but not on TLR2
To further link involvement of the MR with increased PPARγ expression in response to ManLAM, we measured the IL-8 response from MR knockdown macrophages. Scramble siRNA- or MR siRNA-transfected cells were stimulated with ManLAM for different time periods, and cell culture supernatants were analyzed for IL-8 production. MR knockdown in MDMs significantly reduced IL-8 production (Fig. 5A), providing evidence for the MR in regulating PPARγ expression and downstream IL-8 production in macrophages. In parallel, we examined whether MR knockdown influences activity of another PRR that has been associated with the MR (i.e., TLR2) (36). MR siRNA-transfected macrophages were stimulated with the TLR2 ligand Pam3Cys for 24 h, and the cell culture supernatants were analyzed for TNF production. The results in Fig. 5B show that MR knockdown does not influence TLR2 function.
FIGURE 5.
The MR modulates the macrophage IL-8 response to ManLAM without involvement of TLR2. MDMs were transfected with scramble siRNA, MR siRNA, or TLR2 siRNA as described in Fig. 4. A, ManLAM-stimulated IL-8 production was analyzed in MDMs transfected with MR siRNA or scramble siRNA by ELISA. B, MR siRNA-transfected MDMs were stimulated with the TLR2 ligand Pam3Cys (100 ng/ml) for 24 h, and culture supernatants were analyzed for TNF production by ELISA. C, TLR2 siRNA or scramble siRNA-transfected MDMs were stimulated with ManLAM for 24 h. The cell culture supernatants were analyzed for IL-8 production by ELISA. The dotted line represents the level of IL-8 production in resting cells. For a positive control (D), the TLR2-mediated cytokine response was analyzed by stimulating transfected cells with Pam3Cys (100 ng/ml) and measuring the amount of TNF produced by ELISA. TLR2 knockdown was confirmed by Western blot using a TLR2 Ab. The Western blots shown are representative of more than or equal to three independent experiments. Results in A–D are representative experiments (mean ± SD of triplicate samples in each test group) of three independent experiments for each condition. *p < 0.0003.
Recent reports have demonstrated that coexpression of the MR and TLR2 is required for Pnemocystis carinii-mediated IL-8 release (36). Thus, we asked whether TLR2 is required for the ManLAM-mediated IL-8 response. MDMs were transfected with scramble siRNA or TLR2 siRNA and subsequently stimulated with Man-LAM. We found no change in IL-8 production between control and TLR2 knockdown macrophages (Fig. 5C). In parallel, TLR2 knockdown was confirmed by Western blot analysis and by stimulating the transfected cells with Pam3Cys and measuring TNF production. The results show that TLR2 knockdown significantly reduces TNF production and TLR2 protein (Fig. 5D). Taken together, these results provide evidence that TLR2 is not involved in IL-8 production in MDMs stimulated with ManLAM.
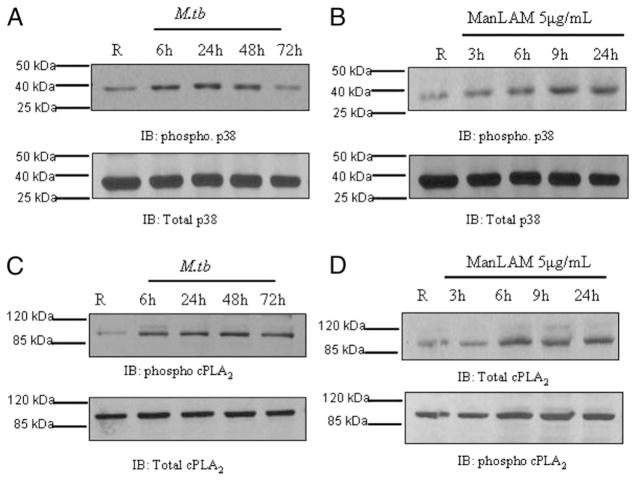
M. tuberculosis infection or ManLAM stimulation activates MAPK-p38 and cPLA2 in human macrophages
M. tuberculosis infection or stimulation with different cell wall components activates MAPKs, especially p38 (37). MAPK-p38 catalyzes the activation of cPLA2 by phosphorylating the serine 505 and 727 residues (38). Activation of cPLA2 then catalyzes the release of arachidonic acids (AAs) from membrane phosholipids (33, 39), which are hydrolyzed and further processed by lipooxygenase and cyclooxygenases (COX1 and COX2) to generate leukotrienes and PGH2, respectively (40). PG synthase converts PGH2 to PGD2, which is further converted to 15-d-PGJ2, which serves as a ligand for PPARγ. Therefore, we examined whether M. tuberculosis infection or ManLAM stimulation of MDMs leads to activation of MAPK-p38 and cPLA2. Our results show that M. tuberculosis infection or ManLAM stimulation enhances the phosphorylation of MAPK-p38 and cPLA2 (Fig. 6). Thus, M. tuberculosis or ManLAM stimulation leads to the activation of MAPK-p38 and cPLA2 which is critical for AA cleavage.
FIGURE 6.
M. tuberculosis infection or ManLAM stimulation activates MAPK-p38 and cPLA2 in human macrophages. MDMs were infected with M. tuberculosis H37Rv (MOI 5:1) for 2 h (A) or left uninfected. Cells were washed and incubated in 2% autologous serum for different times (6, 24, 48, and 72 h). B, MDMs were stimulated with ManLAM (5 μg/ml) for 3, 6, 9, and 24 h. Cell lysates from M. tuberculosis-infected or Man-LAM-stimulated cells were analyzed for the activation of MAPK-p38 (A, B) or cPLA2 (C, D) by Western blot using anti–phospho-specific Abs and reprobed for total p38 and total cPLA2, respectively. The Western blots shown are representative blots of three independent experiments.
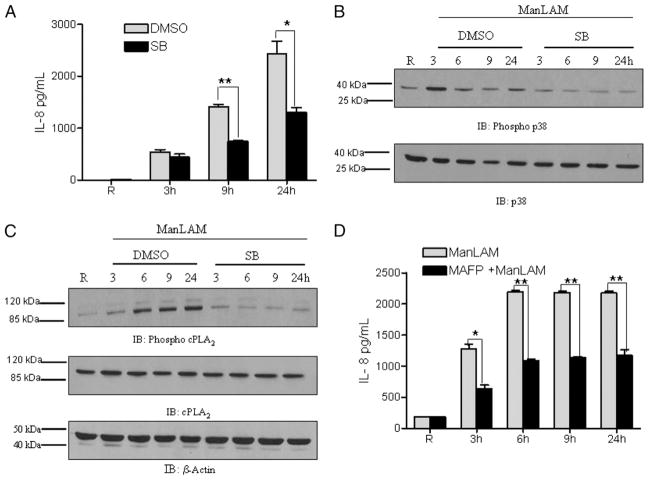
ManLAM activation of MAPK-p38 regulates the PPARγ-mediated IL-8 response through the activation of cPLA2 in human macrophages
We next hypothesized that MAPK-p38 activation and p38-mediated cPLA2 phosphorylation were involved in the observed PPARγ-mediated IL-8 response. To test this, MDMs were pre-treated with the MAPK-p38 inhibitor SB-203580 (5 μM) and subsequently stimulated with ManLAM. IL-8 was measured in cell culture supernatants, and cell lysates were analyzed for MAPK-p38 activation. We found that inhibition of MAPK-p38 significantly reduces IL-8 production in response to ManLAM (Fig. 7A). The Western blot results confirmed that SB-203580 efficiently suppresses the phosphorylation of p38 in response to ManLAM (Fig. 7B). Inhibition of p38 activation also reduced activation of the downstream signaling molecule cPLA2 in response to ManLAM (Fig. 7C). In contrast to the results with MAPK-p38, we found that ManLAM stimulation does not activate MAPK-Erk and also that inhibition of MAPK-Erk by the pharmacological inhibitor UO-126 (2.5 μM) does not affect the activation of cPLA2 in response to ManLAM (data not shown). Thus, our results indicate that MAPK-p38 is directly involved in the regulation of cPLA2 activation in this pathway.
FIGURE 7.
ManLAM activation of MAPK-p38 regulates the PPARγ-mediated IL-8 response through activation of cPLA2 in macrophages. MDMs were pretreated with the p38 inhibitor SB-203580 (5 μM) or DMSO for 30 min and subsequently stimulated with ManLAM (5 μg/ml) or left unstimulated for 3, 6, 9, and 24 h. Cell culture supernatants were analyzed for IL-8 production by ELISA (A); a representative experiment is shown. Mean ± SD of triplicate samples. n = 3. *p < 0.013; **p < 0.0003. Cell lysates were used to analyze the activation of p38 (B) and cPLA2 (C) by Western blotting using phospho-specific Abs and reprobed for total p38 and cPLA2 or actin. The Western blots shown are representative of three independent experiments. D, MDMs were pretreated with the cPLA2 inhibitor MAFP (2.5 nM) for 30 min and subsequently stimulated with ManLAM (5 μg/ml) for the indicated times. Cell culture supernatants were analyzed for IL-8 production by ELISA; a representative experiment is shown. Mean ± SD of triplicate samples. n = 3. *p < 0.0024; **p < 0.0003.
To determine more directly whether cPLA2 is critical for the ManLAM-mediated IL-8 response, we examined the effect of a cPLA2 inhibitor on IL-8 production. MDMs were pretreated with 2.5 nM MAFP or vehicle control and stimulated with Man-LAM, and culture supernatants were analyzed for IL-8 production. Our results confirmed that inhibition of cPLA2 significantly reduced the production of IL-8 (Fig. 7D). Taken together, these results provide evidence that activation of MAPKp38 and cPLA2 is required for the PPARγ-mediated IL-8 response in macrophages. This effect is likely due to the cPLA2-mediated release of AAs and generation of the PPARγ ligand 15-d-PGJ2 during ManLAM stimulation (also see Fig. 3E).
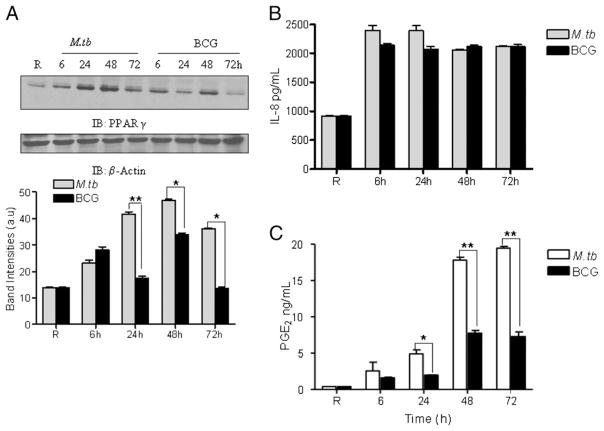
M. bovis BCG infection of macrophages induces IL-8 production despite low expression of PPARγ
On the basis of a recent report that the attenuated M. bovis BCG induces PPARγ expression in murine macrophages (41), we directly compared MDMs infected with virulent M. tuberculosis H37Rv or the attenuated M. bovis BCG for PPARγ expression by Western blot analysis of cell lysates. The results indicate that BCG infection leads to a more limited expression profile of PPARγ than M. tuberculosis (Fig. 8A). Although PPARγ expression levels were similar between M. tuberculosis and BCG at the 6-h time point, PPARγ expression in M. tuberculosis-infected MDMs was greater at 24, 48, and 72 h. We next determined whether the difference in PPARγ expression observed between M. tuberculosis- and BCG-infected MDMs led to a difference in IL-8 production. Unexpectedly, there was no difference in IL-8 production between the two mycobacterial species (Fig. 8B). This result suggested that BCG activates other signaling pathways for IL-8 production, which are not activated or may be inhibited by M. tuberculosis. To further assess the role of PPARγ during M. tuberculosis and BCG infection, we elected to measure the production of PGE2, one of the key downstream products of PG biosynthesis and an indicator of natural PPARγ ligand biosynthesis from PGD2 in MDMs (42). The results show that M. tuberculosis H37Rv infection significantly increases PGE2 production relative to BCG infection (Fig. 8C). In the experiments that directly compared M. tuberculosis- and BCG-induced production of IL-8 and PGE2 by MDMs, the levels of M. tuberculosis and BCG cell association were equivalent as assessed by fluorescence microscopy (data not shown). Taken together, these results provide evidence that although BCG infection leads to the induction of PPARγ to a more limited extent, it is not involved in the production of IL-8. Thus, BCG may activate an alternative pathway for induced IL-8 production.
FIGURE 8.
M. bovis BCG infection induces limited PPARγ expression in macrophages. A, MDMs were infected with M. tuberculosis H37Rv or BCG at an MOI of 5:1. After 2 h, the cells were washed and incubated in 2% autologous serum for 6, 24, 48, and 72 h. Cell lysates were examined for PPARγ expression by Western blot analysis (upper panel). The band intensities (lower panel) were measured in each experiment by densitometry, and the bar graphs shown represent the mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. *p < 0.0043; **p < 0.0001. B, The cell culture supernatants were harvested from M. tuberculosis and BCG-infected MDMs and analyzed for IL-8 production by ELISA; PGE2 production was analyzed by an EIA kit (C). Shown is a representative experiment. Mean ± SD of triplicate samples. n = 3. *p = 0.0030; **p < 0.0001.
NF-κB mediates IL-8 production following BCG infection of human macrophages, whereas PPARγ mediates IL-8 production following M. tuberculosis H37Rv infection or ManLAM stimulation
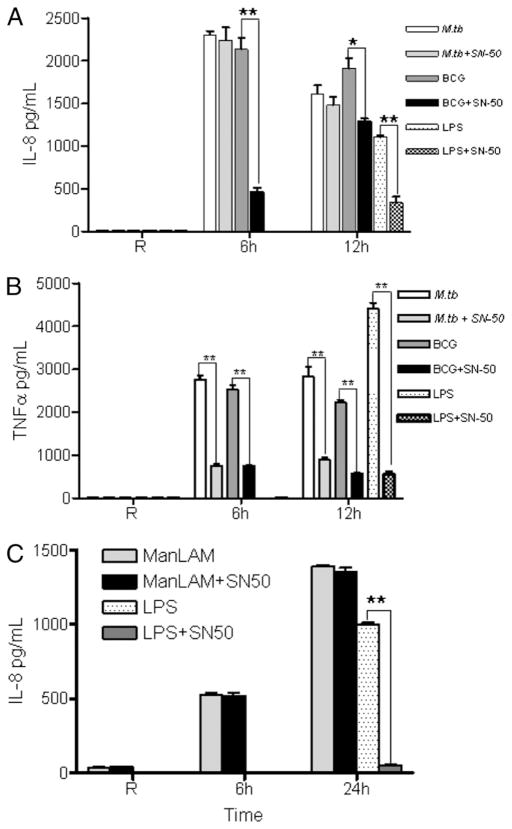
Following exposure to pathogens and endotoxins, NF-κB activation in macrophages induces proinflammatory cytokine production including IL-8. To delineate the roles of NF-κB and PPARγ in mediating IL-8 production following infection of macrophages with M. tuberculosis or BCG, MDMs were pretreated with the NF-κB inhibitor SN-50 (75 μg/ml) and subsequently infected with M. tuberculosis H37Rv or BCG or stimulated with ManLAM. As a positive control, MDMs were stimulated with LPS (100 ng/ml). Cell culture supernatants were analyzed for IL-8 and TNF secretion. The results show that IL-8 secretion was significantly decreased (~5-fold) in SN-50–treated BCG-infected cells at 6 h, whereas in M.tb-infected cells, the NF-κB inhibitor did not influence IL-8 production (Fig. 9A). In contrast, inhibition of NF-κB significantly reduced TNF production in both M. tuberculosis- and BCG-infected MDMs (Fig. 9B). Thus, these results indicate that PPARγ rather than NF-κB is the major transcription factor for inducing IL-8 production during M. tuberculosis but not BCG infection, despite BCG being able to induce low levels of PPARγ. Instead, BCG uses NF-κB as a transcription factor for IL-8 production. In addition, the NF-κB inhibitor did not affect the production of IL-8 during ManLAM stimulation (Fig. 9C). ManLAM stimulation also did not induce the production of other NF-κB–mediated proinflammatory cytokines, such as TNF, IL-6, and IL 12-p40 (data not shown).
FIGURE 9.
NF-κB mediates IL-8 production following BCG but not M. tuberculosis infection of human macrophages. MDMs were pretreated with the NF-κB inhibitor SN-50 (75 μg/ml) for 30 min and subsequently infected with M. tuberculosis H37Rv or BCG at an MOI of 5:1 or stimulated with LPS (100 ng/ml). The cell culture supernatants were analyzed for IL-8 (A) and TNF-α (B) production by ELISA. A and B are representative experiments (mean ± SD of triplicate samples; n = 3; *p < 0.0080; **p < 0.0006). C, In parallel, NF-κB inhibitor-treated cells were stimulated with ManLAM (5 μg/ml) for 6 and 24 h or with LPS (100 ng/ml) for 24 h. Cell culture supernatants were used to measure IL-8 production by ELISA. Shown is a representative experiment (mean ± SD of triplicate samples; n = 3; **p < 0.0006).
PPARγ knockdown in human macrophages controls M. tuberculosis H37Rv infection
PPARγ has been shown to be a marker of alternative activation in macrophages, and several reports indicate that PPARγ activation efficiently transrepresses NF-κB activity within the nucleus that blocks the expression of many proinflammatory cytokines, such as TNF and IL-6, as well as oxidant generation. These inflammatory mediators play a crucial role in pathogen clearance. In addition, there is increasing recognition of the importance of alternatively activated macrophages in the survival of M. tuberculosis (6–9). Therefore, we sought to determine whether PPARγ knockdown in MDMs alters the control of M. tuberculosis H37Rv intracellular survival along with the production of proinflammatory cytokines. MDMs were transfected with scramble or PPARγ siRNA and subsequently infected with M. tuberculosis. The results show that M. tuberculosis intracellular growth is significantly decreased in PPARγ knockdown MDMs compared with control cells (Fig. 10A, cumulative data showed a 35 ± 4% decrease, mean ± SEM, n = 7; p < 0.0001). Cell culture supernatants from these survival experiments contained significantly increased amounts of TNF in infected PPARγ siRNA-transfected MDMs (Fig. 10B). Thus, these data provide evidence that M. tuberculosis-induced PPARγ is an important mediator in controlling M. tuberculosis growth in human macrophages at least in part through transcriptional regulation of inflammatory cytokines.
FIGURE 10.
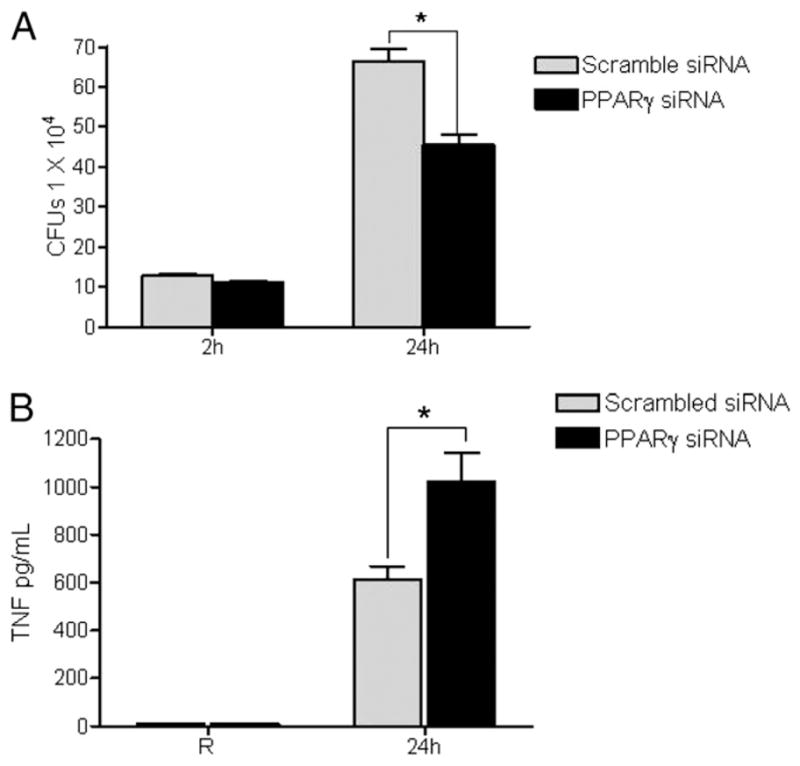
PPARγ knockdown leads to decreased growth of M. tuberculosis in human macrophages and increased TNF production. A, MDMs were transfected with scrambled siRNA or PPARγ siRNA by nucleofection. After 24 h, the cells were incubated with M. tuberculosis H37Rv at an MOI of 1:1 for 2 h, washed, and either lysed or incubated in 2% autologous serum for another 24 h before lysing. CFUs were obtained from the cell lysates by serial dilution and plating on 7H11 agar in triplicate. The colonies were counted after 30 d. The graph shows the mean ± SD of triplicate wells from a representative experiment (n = 7; *p < 0.034). B, Culture supernatants were used to measure TNF production by ELISA. Shown is a representative experiment (mean ± SD of triplicate samples; n = 3; *p < 0.037).
Discussion
Modulation of the host immune response is an essential component of mycobacterial pathogenesis. AMs play a critical role in clearing inhaled particles and pathogens and function to inhibit the amplification of signaling, which leads to a vigorous proinflammatory response (5). These prototypic alternatively activated cells are endowed with unique immune properties and are increasingly recognized as playing an important role in TB pathogenesis. We are interested in identifying the key molecular signaling pathways, intracellular “switches,” and inflammatory mediators that regulate the biology of macrophages in general and in response to M. tuberculosis in particular. PPARγ is a prime candidate for an intracellular molecular switch based on its central role in controlling macrophage inflammatory responses (43) and lipid metabolism, including foam cell generation (44). AMs express high levels of PPARγ (19), and elevated PPARγ in human macrophages is one of the biological markers of IL-4/IL-13–mediated alternative activation. Foamy appearing macrophages are being recognized as playing an important role in TB pathogenesis, particularly within granulomas (4, 45). Finally, PPARγ has been implicated in the downregulation of proinflammatory responses. For these reasons, we explored the role of PPARγ in regulating the immune response of human macrophages to virulent M. tuberculosis and its major cell wall immune regulatory lipoglycan, ManLAM.
Although PPARγ has been extensively investigated for its role in other diseases (10), its immunoregulatory role(s) in infectious diseases is just now being recognized (46–49). There are two recent reports for altered PPARγ levels during mycobacterial infection in humans, both involving the attenuated BCG. BCG infection has been found to induce PPARγ expression in bladder cancer cells (50), whereas transcriptional profiling of PBMCs from BCG-vaccinated infants stimulated ex vivo has revealed a downregulation of PPARγ (51). The role of PPARγ during infection with virulent M. tuberculosis and human macrophages has not been explored previously.
In this study, we identify PPARγ as an important contributor to regulation of the macrophage immune response to M. tuberculosis infection. Expression and activity of PPARγ in human macrophages were enhanced by both M. tuberculosis and ManLAM. As reported, we found that AMs express a high basal level of PPARγ, which is further increased by M. tuberculosis and ManLAM. Because PPARγ knockdown in macrophages led to reduced intracellular growth of M. tuberculosis, PPARγ activation appears to correlate with a more susceptible host cell phenotype for this bacterium. Thus, our findings indicate that M. tuberculosis infection alters AM function further toward an alternative activation state, which is advantageous for this host-adapted intracellular pathogen within the lung microenvironment particularly during primary infection.
We observed an increase in IL-8 and COX2 following PPARγ induction in MDMs by M. tuberculosis infection and/or ManLAM stimulation. IL-8 has been implicated as a chemoattractant in the lung in a variety of lung diseases (52, 53). A previous study in AMs showed that infection with M. tuberculosis or stimulation with its cell wall components significantly enhances IL-8 production, which serves to attract both neutrophils and T cells (54) to the site of infection. IL-8 may also play a role in granuloma formation and necrotic changes in granuloma (55). A recent study demonstrated that IL-8 and COX2 expression was induced by cPLA2 in human lung cells (33). Although previous studies had established that COX2 expression is induced by MAPK-p38 and NF-κB–dependent pathways in human lung epithelial cells for another respiratory pathogen (56), the M. tuberculosis- and/or ManLAM-mediated biochemical signaling pathway(s) involved in macrophages was not known. Our results provide evidence that COX2 expression in response to M. tuberculosis infection or ManLAM stimulation involves the upregulation and activation of PPARγ in MDMs. PPARγ knockdown in MDMs blocked the release of IL-8 during ManLAM stimulation. This was further confirmed by blocking or enhancing the transcriptional activity of PPARγ in ManLAM-stimulated macrophages. Last, the induction of PGE2 by M. tuberculosis is also consistent with a role for PPARγ in mediating COX2 expression because it is a key intermediate in PG biosynthesis.
Previous reports using murine and human macrophages have shown that mycobacterial infection or ManLAM stimulation leads to activation of the MAPK pathway and subsequent proinflammatory cytokine production in infected cells (37, 57, 58). Consistent with these earlier findings, our results demonstrate that virulent M. tuberculosis infection or ManLAM stimulation activates MAPK-p38 in MDMs (59). There is also evidence that MAPK-p38 activation is necessary for the phosphorylation of Ser505 and Ser727 in cPLA2, which leads to an increase in its enzymatic activity (38, 60). Our study shows that cPLA2 phosphorylation is induced by M. tuberculosis and/or ManLAM in MDMs. Inhibition of MAPK-p38 activation by a pharmacological inhibitor significantly decreased IL-8 production and also the phosphorylation of cPLA2 in MDMs. In human lung epithelial cells, cPLA2 activation induces the production of IL-8 and COX2 gene expression through PPARγ, and this induction was significantly reduced by cPLA2 inhibitor MAFP (61). Our results demonstrate that suppression of cPLA2 activation also leads to reduced IL-8 release in response to ManLAM in human macrophages.
An important discovery in the current study is the identification of a pathway that links engagement of the MR with increased expression and activation of PPARγ. The MR plays an important role in the phagocytosis and trafficking of virulent M. tuberculosis by human macrophages by binding ManLAM and higher-order phosphatidyl-myo-inositol mannosides (30, 62) and regulating the intracellular trafficking of M. tuberculosis following phagocytosis resulting in limited P–L fusion (25). MR ligation leads to an anti-inflammatory program (23), suppresses proinflammatory cytokine release (63), and bypasses oxidative responses (24). The MR is highly expressed on AMs as a marker of alternative activation (5). For these reasons, its role in regulating the early host response to M. tuberculosis infection in the lung is likely to be important. In this context, it is important that the biological consequences of MR ligation are generally in concert with the activity of PPARγ as a negative regulator of macrophage activation (64). PPARγ down-regulates proinflammatory gene expression by antagonizing the activity of several transcription factors (19), downregulates IFN-γ–stimulated iNOS production in murine macrophages (65), and attenuates the respiratory burst (20). PPARγ depletion in AMs leads to a Th1 pulmonary inflammatory response (66). Further supporting this concept, PPARγ as well as PGE2 production have been shown to increase MR expression and activity on macrophages (67, 68).
Specific biochemical signaling pathways triggered by MR ligation have been elusive. It has a short cytoplasmic tail and lacks an intracellular ITIM. The lack of discernable signaling motifs has led some to question its role in phagocytosis and signaling (69). Despite this, recent studies continue to implicate the MR in signaling cascades, most often in conjunction with other PRRs like TLR2 and CD14 (36, 63, 70, 71). Thus, another important finding in the current study is the identification of a new pathway activated by MR ligation that leads to enhanced expression and activity of PPARγ and excludes TLR2 and the NF-κB pathway. Our results show that the ManLAM/MR pathway-mediated IL-8 response is independent of TLR2. This result together with earlier findings that ManLAM does not induce other proinflammatory cytokines in macrophages identifies a key branch point in IL-8 production, and potentially in the production of other inflammatory cytokines, that differentiates the known NF-κB–mediated pathway from the PPARγ-mediated pathway. Importantly, activation of the latter pathway can block NF-κB–mediated gene expression and thereby augment an immunosuppressive program in the cells (18). Our results identify the MR as a key PRR in initiating this pathway, and these results place us in an excellent position to further explore upstream biochemical signaling mediators.
Our studies show differential PPARγ expression following infection with virulent M. tuberculosis and the attenuated BCG, but this difference in expression did not lead to a difference in IL-8 production. In addition, infection with virulent M. tuberculosis led to a significantly greater release of PGE2 when compared with BCG. Similarly, previous studies reported that heat-killed BCG did not induce expression of COX2 and the production of PGE2 in macrophages (72). Production of PGE2 is important in that it dampens the Th1 response (73) and cell-mediated immunity in part through enhanced activity of regulatory T cells (74). We found that inhibition of NF-κB translocation significantly reduced the IL-8 response from BCG-infected MDMs; however, inhibition of NF-κB did not affect the IL-8 release from M. tuberculosis-infected MDMs. In contrast, NF-κB–mediated TNF production was inhibited in both M. tuberculosis- and BCG-infected macrophages, and similar results were observed in ManLAM-stimulated cells. It has recently been reported that BCG induces PPARγ expression in murine macrophages (41). However, in contrast to our findings, PPARγ expression and PGE2 production were dependent on TLR2 in that study. The potential difference(s) between human and mouse macrophages in the PPARγ pathway leading to PGE2 production is not clear at present. One possibility is that there are differences between species in the involvement of the MR or in the signaling response downstream of MR engagement. Another possibility is that there are differences in MR expression and/or receptor partners for the MR between human and mouse macrophages. For example, most unstimulated human macrophages (including the MDMs used in the current study) do not express dendritic cell-specific intercellular adhesion molecule-3-grabbing nonintegrin (SIGN), whereas murine macrophages express various related SIGN receptors (75). Because SIGN receptors can bind the same carbohydrate motifs as the MR, it is possible that signaling in murine macrophages involves coligation of the MR and SIGN receptors or other lectin PRRs, such as Dectin-1 (69).
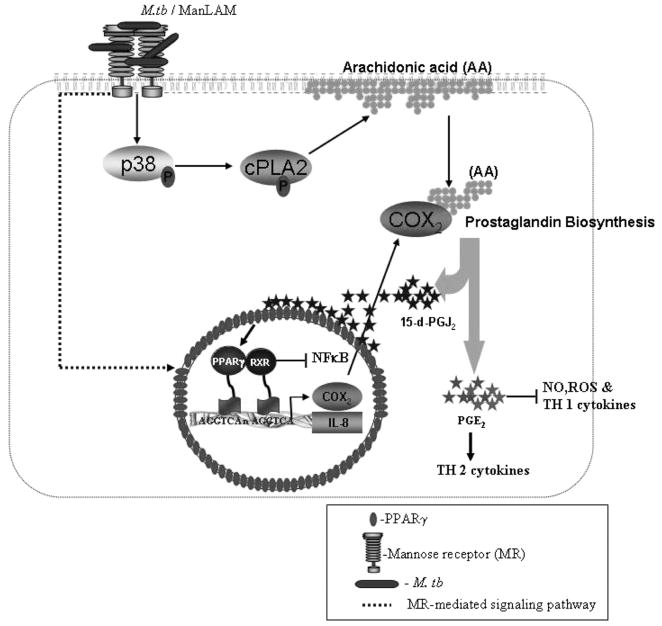
On the basis of our results, we propose a model (Fig. 11) whereby virulent M. tuberculosis or ManLAM upregulates PPARγ expression through an MR-mediated signaling pathway and simultaneously activates the MAPK-p38 pathway, leading to activation of downstream cPLA2 and release of AAs from membrane phosholipids. Hydrolyzed AAs are further processed by lipooxygenase and COXs (COX1 and COX2) to generate leukotrienes (76, 76) and PGH2 (40), respectively, which play diverse roles in apoptosis, inflammation, and lipid metabolism (77). PGH2 is acted upon by PG synthase to generate PGs, including 15-d-PGJ2, which serves as a PPARγ ligand enabling the initiation of transcription. PPARγ activation results in blockade of NF-κB–mediated gene transcription and upregulation of COX2, IL-8, and MR expression.
FIGURE 11.
Model of the PPARγ signaling pathway in human macrophages in response to virulent M. tuberculosis or ManLAM. Shown is a schematic based on our results along with those in the literature of how virulent M. tuberculosis infection or ManLAM stimulation induces PPARγ-mediated immunosuppression in macrophages. M. tuberculosis or ManLAM binds to the MR, which leads to upregulation of PPARγ expression through an MR-dependent signaling pathway and, simultaneously, to activation of MAPK-p38-mediated cPLA2, which leads to the release and hydrolysis of AA from the plasma membrane to generate the ligand for PPARγ (15-d-PGJ2). Activated PPARγ heterodimerizes with RXR, and they bind to PPREs in the IL-8 and COX2 promoters, thereby inducing their expression as well as expression of the MR. Activation of PPARγ leads to transrepression of NF-κB activity but promotes the generation of Th2 cytokines through PGE2 production.
In summary, we demonstrate that virulent M. tuberculosis and ManLAM induce the expression of nuclear receptor/transcriptional factor PPARγ in human macrophages and that upregulation of PPARγ expression is mediated by the MR, a major PRR in macrophage recognition and response to M. tuberculosis. M. tuberculosis and ManLAM activate MAPK-p38 and cPLA2, which lead to increased IL-8 production and COX2 expression. Virulent M. tuberculosis is a more potent inducer of PPARγ compared with the attenuated BCG, and the M. tuberculosis-mediated IL-8 response is dependent on PPARγ and not on TLR2 or NF-κB. Downregulation of PPARγ in macrophages controls M. tuberculosis growth and enhances the inflammatory cytokine response. Given its central role in cellular metabolism, differentiation, inflammation, and lipid metabolism, our findings support a role for PPARγ as a key intracellular molecular switch in regulating the nature of the inflammatory response to M. tuberculosis infection and a potential target for immunotherapy as has been suggested for other diseases (44).
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Mark Wewers for performing bronchoscopies. We also acknowledge the support of the Campus Microscopy and Imaging Facility at The Ohio State University (Columbus, OH).
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health Grants AI059639 and AI052458 (to L.S.S.).
Abbreviations used in this paper
- 15-d-PGJ2
15-deoxy-Δ12,14 PGJ2
- AA
arachidonic acid
- AM
alveolar macrophage
- BCG
bacillus Calmette-Guérin
- cPLA2
cytosolic phospholipase A2
- EIA
enzyme immunoassay
- LM
lipomannan
- MAFP
methyl arachidonyl fluorophosphonate
- ManLAM
mannose-capped lipoarabinomannan
- MDM
monocyte-derived macrophage
- MOI
multiplicity of infection
- MR
mannose receptor
- P–L
phagosome–lysosome
- PPAR
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
- PRR
pattern recognition receptor
- SIGN
specific intercellular adhesion molecule-3-grabbing nonintegrin
- siRNA
small interfering RNA
- TB
tuberculosis
Footnotes
Disclosures
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
References
- 1.Shah NS, Wright A, Bai GH, Barrera L, Boulahbal F, Martín-Casabona N, Drobniewski F, Gilpin C, Havelková M, Lepe R, et al. Worldwide emergence of extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis. Emerg Infect Dis. 2007;13:380–387. doi: 10.3201/eid1303.061400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Schlesinger LS. Phagocytosis and Toll-like receptors in tuberculosis. In: Rom WN, Garay SM, editors. Tuberculosis. Lippincott, Williams, and Wilkins; Philadelphia: 2004. pp. 203–214. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Jo EK, Yang CS, Choi CH, Harding CV. Intracellular signalling cascades regulating innate immune responses to Mycobacteria: branching out from Toll-like receptors. Cell Microbiol. 2007;9:1087–1098. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2007.00914.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ordway D, Henao-Tamayo M, Orme IM, Gonzalez-Juarrero M. Foamy macrophages within lung granulomas of mice infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis express molecules characteristic of dendritic cells and antiapoptotic markers of the TNF receptor-associated factor family. J Immunol. 2005;175:3873–3881. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.175.6.3873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Gordon S. Alternative activation of macrophages. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003;3:23–35. doi: 10.1038/nri978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Schreiber T, Ehlers S, Heitmann L, Rausch A, Mages J, Murray PJ, Lang R, Hölscher C. Autocrine IL-10 induces hallmarks of alternative activation in macrophages and suppresses antituberculosis effector mechanisms without compromising T cell immunity. J Immunol. 2009;183:1301–1312. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0803567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kahnert A, Seiler P, Stein M, Bandermann S, Hahnke K, Mollenkopf H, Kaufmann SHE. Alternative activation deprives macrophages of a coordinated defense program to Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Eur J Immunol. 2006;36:631–647. doi: 10.1002/eji.200535496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Day J, Friedman A, Schlesinger LS. Modeling the immune rheostat of macrophages in the lung in response to infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106:11246–11251. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0904846106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Verreck FA, de Boer T, Langenberg DM, Hoeve MA, Kramer M, Vaisberg E, Kastelein R, Kolk A, de Waal-Malefyt R, Ottenhoff THM. Human IL-23–producing type 1 macrophages promote but IL-10–producing type 2 macrophages subvert immunity to (myco)bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:4560–4565. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0400983101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Moraes LA, Piqueras L, Bishop-Bailey D. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors and inflammation. Pharmacol Ther. 2006;110:371–385. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2005.08.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kota BP, Huang TH, Roufogalis BD. An overview on biological mechanisms of PPARs. Pharmacol Res. 2005;51:85–94. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2004.07.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kliewer SA, Umesono K, Noonan DJ, Heyman RA, Evans RM. Convergence of 9-cis retinoic acid and peroxisome proliferator signalling pathways through heterodimer formation of their receptors. Nature. 1992;358:771–774. doi: 10.1038/358771a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Braissant O, Foufelle F, Scotto C, Dauça M, Wahli W. Differential expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs): tissue distribution of PPAR-α, -β, and -γ in the adult rat. Endocrinology. 1996;137:354–366. doi: 10.1210/endo.137.1.8536636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Reddy RC, V, Narala R, Keshamouni VG, Milam JE, Newstead MW, Standiford TJ. Sepsis-induced inhibition of neutrophil chemotaxis is mediated by activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ. Blood. 2008;112:4250–4258. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-12-128967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Gervois P, Fruchart JC, Staels B. Inflammation, dyslipidaemia, diabetes and PPars: pharmacological interest of dual PPARα and PPARγ agonists. Int J Clin Pract Suppl. 2004;143:22–29. doi: 10.1111/j.1368-504x.2004.00376.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Rigamonti E, Fontaine C, Lefebvre B, Duhem C, Lefebvre P, Marx N, Staels B, Chinetti-Gbaguidi G. Induction of CXCR2 receptor by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ in human macrophages. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2008;28:932–939. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.107.161679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Jiang C, Ting AT, Seed B. PPAR-γ agonists inhibit production of monocyte inflammatory cytokines. Nature. 1998;391:82–86. doi: 10.1038/34184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Ricote M, Huang JT, Welch JS, Glass CK. The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor(PPARγ) as a regulator of monocyte/macrophage-function. J Leukoc Biol. 1999;66:733–739. doi: 10.1002/jlb.66.5.733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ricote M, Li AC, Willson TM, Kelly CJ, Glass CK. The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ is a negative regulator of macrophage activation. Nature. 1998;391:79–82. doi: 10.1038/34178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Von Knethen A, Brüne B. Activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ by nitric oxide in monocytes/macrophages down-regulates p47phox and attenuates the respiratory burst. J Immunol. 2002;169:2619–2626. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.169.5.2619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Standiford TJ, V, Keshamouni G, Reddy RC. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ as a regulator of lung inflammation and repair. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2005;2:226–231. doi: 10.1513/pats.200501-010AC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ricote M, Huang J, Fajas L, Li A, Welch J, Najib J, Witztum JL, Auwerx J, Palinski W, Glass CK. Expression of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) in human atherosclerosis and regulation in macrophages by colony stimulating factors and oxidized low density lipoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998;95:7614–7619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.13.7614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Chieppa M, Bianchi G, Doni A, Del Prete A, Sironi M, Laskarin G, Monti P, Piemonti L, Biondi A, Mantovani A, et al. Cross-linking of the mannose receptor on monocyte-derived dendritic cells activates an anti-inflammatory immunosuppressive program. J Immunol. 2003;171:4552–4560. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.171.9.4552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Astarie-Dequeker C, N’Diaye EN, Le Cabec V, Rittig MG, Prandi J, Maridonneau-Parini I. The mannose receptor mediates uptake of pathogenic and nonpathogenic mycobacteria and bypasses bactericidal responses in human macrophages. Infect Immun. 1999;67:469–477. doi: 10.1128/iai.67.2.469-477.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Kang PB, Azad AK, Torrelles JB, Kaufman TM, Beharka AA, Tibesar E, DesJardin LE, Schlesinger LS. The human macrophage mannose receptor directs Mycobacterium tuberculosis lipoarabinomannan-mediated phagosome biogenesis. J Exp Med. 2005;202:987–999. doi: 10.1084/jem.20051239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Torrelles JB, Azad AK, Schlesinger LS. Fine discrimination in the recognition of individual species of phosphatidyl-myo-inositol mannosides from Mycobacterium tuberculosis by C-type lectin pattern recognition receptors. J Immunol. 2006;177:1805–1816. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.177.3.1805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Schlesinger LS, Bellinger-Kawahara CG, Payne NR, Horwitz MA. Phagocytosis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis is mediated by human monocyte complement receptors and complement component C3. J Immunol. 1990;144:2771–2780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Torrelles JB, Khoo KH, Sieling PA, Modlin RL, Zhang N, Marques AM, Treumann A, Rithner CD, Brennan PJ, Chatterjee D. Truncated structural variants of lipoarabinomannan in Mycobacterium leprae and an ethambutol-resistant strain of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:41227–41239. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M405180200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Torrelles JB, Knaup R, Kolareth A, Slepushkina T, Kaufman TM, Kang PB, Hill PJ, Brennan PJ, Chatterjee D, Belisle JT, et al. Identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis clinical isolates with altered phagocytosis by human macrophages due to a truncated lipoarabinomannan. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:31417–31428. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M806350200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Schlesinger LS. Macrophage phagocytosis of virulent but not attenuated strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis is mediated by mannose receptors in addition to complement receptors. J Immunol. 1993;150:2920–2930. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Henning LN, Azad AK, Parsa KV, Crowther JE, Tridandapani S, Schlesinger LS. Pulmonary surfactant protein A regulates TLR expression and activity in human macrophages. J Immunol. 2008;180:7847–7858. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.180.12.7847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Olakanmi O, Britigan BE, Schlesinger LS. Gallium disrupts iron metabolism of mycobacteria residing within human macrophages. Infect Immun. 2000;68:5619–5627. doi: 10.1128/iai.68.10.5619-5627.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Pawliczak R, Han C, Huang XL, Demetris AJ, Shelhamer JH, Wu T. 85-kDa cytosolic phospholipase A2 mediates peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ activation in human lung epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:33153–33163. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M200246200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Davies SS, Pontsler AV, Marathe GK, Harrison KA, Murphy RC, Hinshaw JC, Prestwich GD, Hilaire AS, Prescott SM, Zimmerman GA, McIntyre TM. Oxidized alkyl phospholipids are specific, high affinity peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ ligands and agonists. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:16015–16023. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M100878200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Schlesinger LS, Hull SR, Kaufman TM. Binding of the terminal mannosyl units of lipoarabinomannan from a virulent strain of Mycobacterium tuberculosis to human macrophages. J Immunol. 1994;152:4070–4079. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Tachado SD, Zhang J, Zhu J, Patel N, Cushion M, Koziel H. Pneumocystis-mediated IL-8 release by macrophages requires coexpression of mannose receptors and TLR2. J Leukoc Biol. 2007;81:205–211. doi: 10.1189/jlb.1005580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Briken V, Porcelli SA, Besra GS, Kremer L. Mycobacterial lipoarabinomannan and related lipoglycans: from biogenesis to modulation of the immune response. Mol Microbiol. 2004;53:391–403. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.04183.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Lin LL, Wartmann M, Lin AY, Knopf JL, Seth A, Davis RJ. cPLA2 is phosphorylated and activated by MAP kinase. Cell. 1993;72:269–278. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90666-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Seeds MC, Bass DA. Regulation and metabolism of arachidonic acid. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 1999;17:5–26. doi: 10.1007/BF02737594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Rocca B, FitzGerald GA. Cyclooxygenases and prostaglandins: shaping up the immune response. Int Immunopharmacol. 2002;2:603–630. doi: 10.1016/s1567-5769(01)00204-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Almeida PE, Silva AR, Maya-Monteiro CM, Töröcsik D, D’Avila H, Dezsö B, Magalhães KG, Castro-Faria-Neto HC, Nagy L, Bozza PT. Mycobacterium bovis bacillus Calmette-Guérin infection induces TLR2-dependent peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ expression and activation: functions in inflammation, lipid metabolism, and pathogenesis. J Immunol. 2009;183:1337–1345. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0900365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Scher JU, Pillinger MH. 15d-PGJ2: the anti-inflammatory prostaglandin? Clin Immunol. 2005;114:100–109. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2004.09.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Straus DS, Glass CK. Anti-inflammatory actions of PPAR ligands: new insights on cellular and molecular mechanisms. Trends Immunol. 2007;28:551–558. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2007.09.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Chinetti G, Fruchart JC, Staels B. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors: new targets for the pharmacological modulation of macrophage gene expression and function. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2003;14:459–468. doi: 10.1097/00041433-200310000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Peyron P, Vaubourgeix J, Poquet Y, Levillain F, Botanch C, Bardou F, Daffé M, Emile JF, Marchou B, Cardona PJ, et al. Foamy macrophages from tuberculous patients’ granulomas constitute a nutrient-rich reservoir for M. tuberculosis persistence. PLoS Pathog. 2008;4:e1000204. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Mei CL, He P, Cheng B, Liu W, Wang YF, Wan JJ. Chlamydia pneumoniae induces macrophage-derived foam cell formation via PPARα and PPARγ-dependent pathways. Cell Biol Int. 2009;33:301–308. doi: 10.1016/j.cellbi.2008.12.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Liu Y, Lu J, Shi J, Hou Y, Zhu H, Zhao S, Liu H, Ding B, Yin Y, Yi G. Increased expression of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ in the immune system of weaned pigs after Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide injection. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2008;124:82–92. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2008.02.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Potula R, Ramirez SH, Knipe B, Leibhart J, Schall K, Heilman D, Morsey B, Mercer A, Papugani A, Dou H, Persidsky Y. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ activation suppresses HIV-1 replication in an animal model of encephalitis. AIDS. 2008;22:1539–1549. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e3283081e08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Dubuquoy L, Louvet A, Hollebecque A, Mathurin P, Dharancy S. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors in HBV-related infection. PPAR Res. 2009;2009:145124. doi: 10.1155/2009/145124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Lodillinsky C, Umerez MS, Jasnis MA, Casabé A, Sandes E, Eiján AM. Bacillus Calmette-Guérin induces the expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ in bladder cancer cells. Int J Mol Med. 2006;17:269–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Fletcher HA, Keyser A, Bowmaker M, Sayles PC, Kaplan G, Hussey G, Hill AV, Hanekom WA. Transcriptional profiling of mycobacterial antigen-induced responses in infants vaccinated with BCG at birth. BMC Med Genomics. 2009;2:10. doi: 10.1186/1755-8794-2-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Lynch JP, III, Standiford TJ, Rolfe MW, Kunkel SL, Strieter RM. Neutrophilic alveolitis in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: the role of interleukin-8. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992;145:1433–1439. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/145.6.1433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Lipschik GY, Doerfler ME, Kovacs JA, Travis WD, Andrawis VA, Lawrence MG, Dichter JR, Ognibene FP, Shelhamer JH. Leukotriene B4 and interleukin-8 in human immunodeficiency virus-related pulmonary disease. Chest. 1993;104:763–769. doi: 10.1378/chest.104.3.763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Zhang M, Lin Y, Iyer DV, Gong J, Abrams JS, Barnes PF. T-cell cytokine responses in human infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1995;63:3231–3234. doi: 10.1128/iai.63.8.3231-3234.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Larsen CG, Anderson AO, Appella E, Oppenheim JJ, Matsushima K. The neutrophil-activating protein (NAP-1) is also chemotactic for T lymphocytes. Science. 1989;243:1464–1466. doi: 10.1126/science.2648569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.N’Guessan PD, Hippenstiel S, Etouem MO, Zahlten J, Beermann W, Lindner D, Opitz B, Witzenrath M, Rosseau S, Suttorp N, Schmeck B. Streptococcus pneumoniae induced p38 MAPK- and NF-κB–dependent COX-2 expression in human lung epithelium. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2006;290:L1131–L1138. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00383.2005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Yadav M, Roach SK, Schorey JS. Increased mitogen-activated protein kinase activity and TNF-α production associated with Mycobacterium smegmatis- but not Mycobacterium avium-infected macrophages requires prolonged stimulation of the calmodulin/calmodulin kinase and cyclic AMP/protein kinase A pathways. J Immunol. 2004;172:5588–5597. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.172.9.5588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Giacomini E, Iona E, Ferroni L, Miettinen M, Fattorini L, Orefici G, Julkunen I, Coccia EM. Infection of human macrophages and dendritic cells with Mycobacterium tuberculosis induces a differential cytokine gene expression that modulates T cell response. J Immunol. 2001;166:7033–7041. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.166.12.7033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Yang CS, Song CH, Lee JS, Jung SB, Oh JH, Park J, Kim HJ, Park JK, Paik TH, Jo EK. Intracellular network of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, mammalian target of the rapamycin/70 kDa ribosomal S6 kinase 1, and mitogen-activated protein kinases pathways for regulating myco-bacteria-induced IL-23 expression in human macrophages. Cell Microbiol. 2006;8:1158–1171. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2006.00699.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Kramer RM, Roberts EF, Um SL, Börsch-Haubold AG, Watson SP, Fisher MJ, Jakubowski JA. p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphorylates cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2) in thrombin-stimulated platelets: evidence that proline-directed phosphorylation is not required for mobilization of arachidonic acid by cPLA2. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:27723–27729. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.44.27723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Pawliczak R, Logun C, Madara P, Lawrence M, Woszczek G, Ptasinska A, Kowalski ML, Wu T, Shelhamer JH. Cytosolic phospholipase A2 Group IVα but not secreted phospholipase A2 Group IIA, V, or X induces interleukin-8 and cyclooxygenase-2 gene and protein expression through peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors γ 1 and 2 in human lung cells. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:48550–48561. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M408926200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Schlesinger LS, Azad AK, Torrelles JB, Roberts E, Vergne I, Deretic V. Determinants of phagocytosis, phagosome biogenesis and autophagy for Mycobacterium tuberculosis. In: Kaufmann SHE, Britton WJ, editors. Handbook of Tuberculosis. Immunology and Cell Biology. Wiley-VCH Verlag; Weinheim, Germany: 2008. pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- 63.Zhang J, Tachado SD, Patel N, Zhu J, Imrich A, Manfruelli P, Cushion M, Kinane TB, Koziel H. Negative regulatory role of mannose receptors on human alveolar macrophage proinflammatory cytokine release in vitro. J Leukoc Biol. 2005;78:665–674. doi: 10.1189/jlb.1204699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Smith MR, Standiford TJ, Reddy RC. PPARs in alveolar macrophage biology. PPAR Res. 2007;2007:23812. doi: 10.1155/2007/23812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Li M, Pascual G, Glass CK. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ-dependent repression of the inducible nitric oxide synthase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 2000;20:4699–4707. doi: 10.1128/mcb.20.13.4699-4707.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Malur A, Mccoy AJ, Arce S, Barna BP, Kavuru MS, Malur AG, Thomassen MJ. Deletion of PPARγ in alveolar macrophages is associated with a Th-1 pulmonary inflammatory response. J Immunol. 2009;182:5816–5822. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0803504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Schreiber S, Blum JS, Chappel JC, Stenson WF, Stahl PD, Teitelbaum SL, Perkins SL. Prostaglandin E specifically upregulates the expression of the mannose-receptor on mouse bone marrow-derived macrophages. Cell Regul. 1990;1:403–413. doi: 10.1091/mbc.1.5.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Coste A, Dubourdeau M, Linas MD, Cassaing S, Lepert JC, Balard P, Chalmeton S, Bernad J, Orfila C, Séguéla JP, Pipy B. PPARγ promotes mannose receptor gene expression in murine macrophages and contributes to the induction of this receptor by IL-13. Immunity. 2003;19:329–339. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(03)00229-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Kerrigan AM, Brown GD. C-type lectins and phagocytosis. Immunobiology. 2009;214:562–575. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2008.11.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Bernardo J, Billingslea AM, Blumenthal RL, Seetoo KF, Simons ER, Fenton MJ. Differential responses of human mononuclear phagocytes to mycobacterial lipoarabinomannans: role of CD14 and the mannose receptor. Infect Immun. 1998;66:28–35. doi: 10.1128/iai.66.1.28-35.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.van de Veerdonk FL, Marijnissen RJ, Kullberg BJ, Koenen HJ, Cheng SC, Joosten I, van den Berg WB, Williams DL, van der Meer JW, Joosten LA, Netea MG. The macrophage mannose receptor induces IL-17 in response to Candida albicans. Cell Host Microbe. 2009;5:329–340. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2009.02.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Yamashita M, Shinohara T, Tsuji S, Myrvik QN, Nishiyama A, Henriksen RA, Shibata Y. Catalytically inactive cyclooxygenase 2 and absence of prostaglandin E2 biosynthesis in murine peritoneal macrophages following in vivo phagocytosis of heat-killed Mycobacterium bovis bacillus Calmette-Guérin. J Immunol. 2007;179:7072–7078. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.10.7072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Snijdewint FG, Kaliński P, Wierenga EA, Bos JD, Kapsenberg ML. Prostaglandin E2 differentially modulates cytokine secretion profiles of human T helper lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1993;150:5321–5329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Akasaki Y, Liu G, Chung NH, Ehtesham M, Black KL, Yu JS. Induction of a CD4+ T regulatory type 1 response by cyclooxygenase-2–overexpressing glioma. J Immunol. 2004;173:4352–4359. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.173.7.4352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Powlesland AS, Ward EM, Sadhu SK, Guo Y, Taylor ME, Drickamer K. Widely divergent biochemical properties of the complete set of mouse DC-SIGN–related proteins. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:20440–20449. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M601925200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Serhan CN. Lipoxins and novel aspirin-triggered 15-epilipoxins (ATL): a jungle of cell-cell interactions or a therapeutic opportunity? Prostaglandins. 1997;53:107–137. doi: 10.1016/s0090-6980(97)00001-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Lee CH, Evans RM. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ in macrophage lipid homeostasis. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2002;13:331–335. doi: 10.1016/s1043-2760(02)00668-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]