Abstract
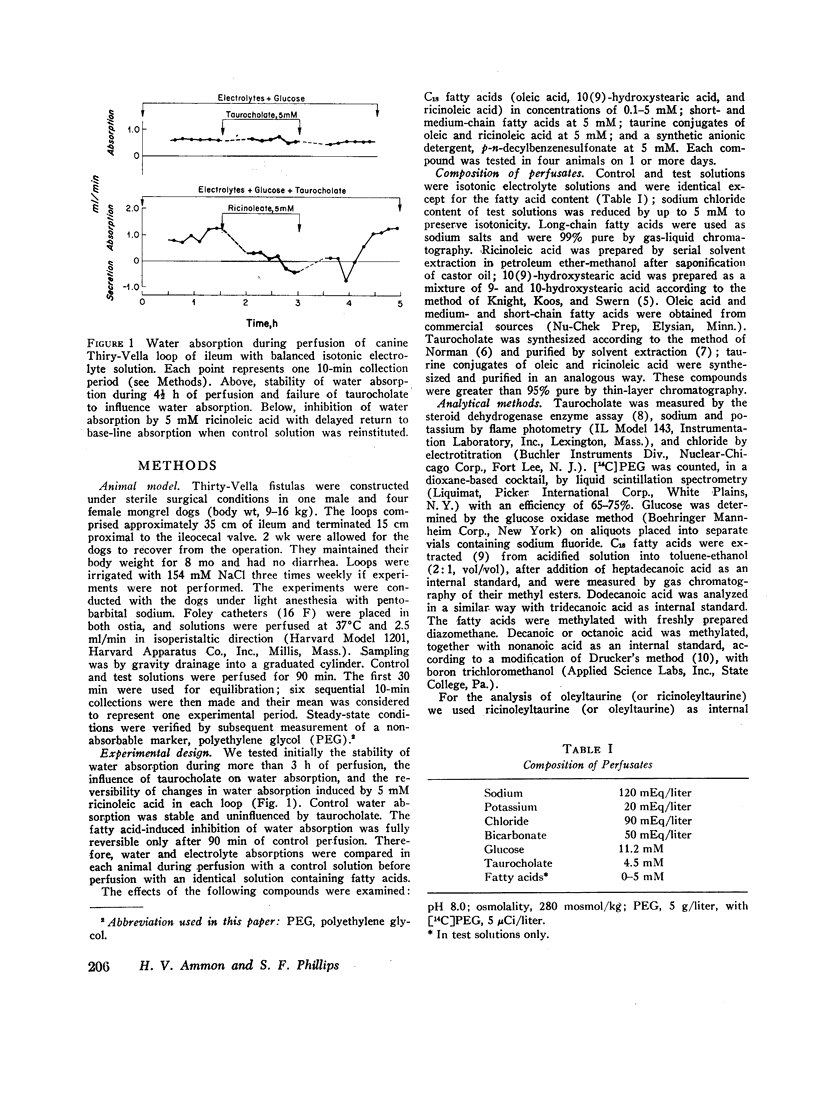
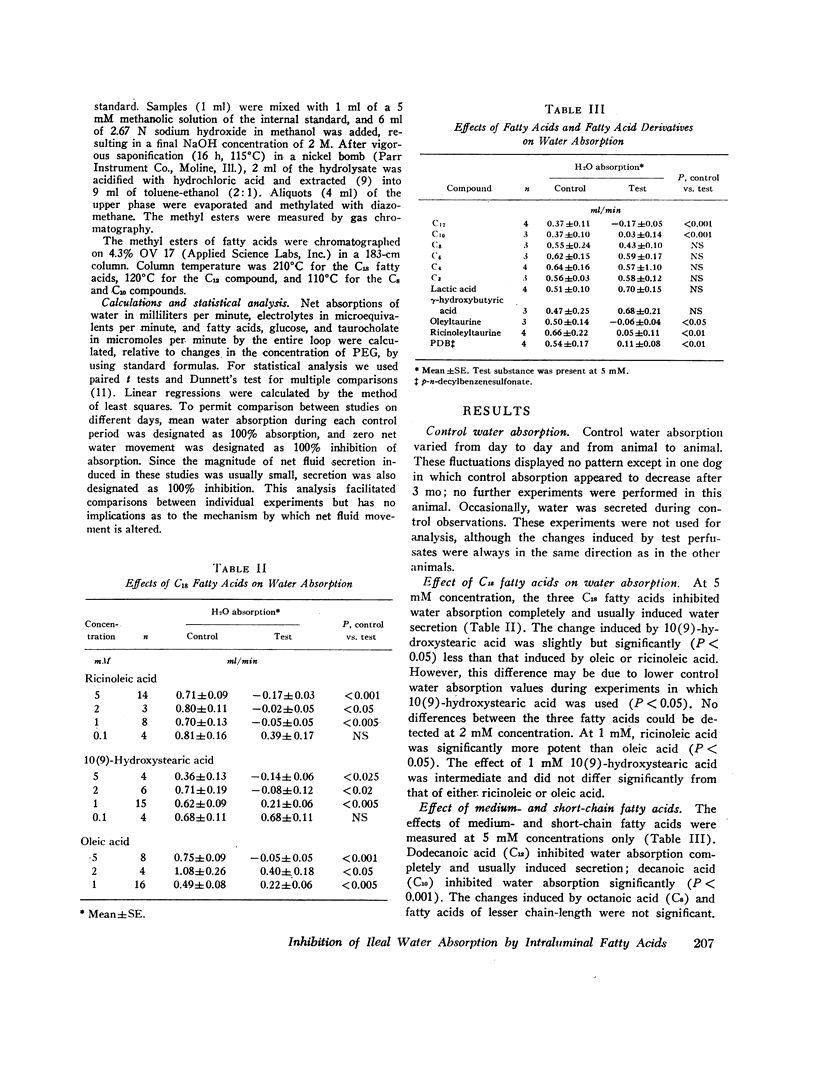
The influence of fatty acids on ileal absorption of water, electrolytes, glucose, and taurocholate was examined in Thirty-Vella fistulas in five mongrel dogs. Fatty acid absorption also was measured. Segments of terminal ileum were perfused at steady state with isotonic electrolyte solutions containing 11.2 mM glucose, 4.5 mM taurocholate, and 0.1-5.0 mM fatty acid. Three C18 fatty acids, oleic acid, 10(9)-hydroxystearic acid, and ricinoleic acid, completely inhibited water absorption at 5 mM. Sodium, chloride, and potassium absorptions were inhibited in parallel with absorption of water. Differences between the potencies of C18 fatty acids were apparent when lesser concentrations were perfused. Dodecanoic and decanoic acids were as effective as C18 fatty acids at 5 mM but octanoic and hexanoic acids were ineffective. The polar group of C18 fatty acids was modified by conjugating oleic and ricinoleic acids with taurine. When these compounds and a substituted C18 fatty acid, p-n-decylbenzenesulfonate, were perfused, water absorption was also inhibited. Short-chain fatty acids (C3 and C4) and their hydroxylated derivatives were ineffective at 5 mM. When water absorption was inhibited, absorption of glucose and taurocholate was decreased. We speculate that the phenomenon of inhibition of water and electrolyte absorption by fatty acids may be relevant to steatorrhea and diarrhea in man.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bright-Asare P., Binder H. J. Stimulation of colonic secretion of water and electrolytes by hydroxy fatty acids. Gastroenterology. 1973 Jan;64(1):81–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christopher N. L., Bayless T. M. Role of the small bowel and colon in lactose-induced diarrhea. Gastroenterology. 1971 May;60(5):845–852. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M., Morgan R. G., Hofmann A. F. One-step quantitative extraction of medium-chain and long-chain fatty acids from aqueous samples. J Lipid Res. 1969 Sep;10(5):614–616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWSON A. M., HOLDSWORTH C. D., WEBB J. ABSORPTION OF SHORT CHAIN FATTY ACIDS IN MAN. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Oct;117:97–100. doi: 10.3181/00379727-117-29505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond J. M., Wright E. M. Biological membranes: the physical basis of ion and nonelectrolyte selectivity. Annu Rev Physiol. 1969;31:581–646. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.31.030169.003053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberger N. J., Rodgers J. B., Isselbacher K. J. Absorption of medium and long chain triglycerides: factors influencing their hydrolysis and transport. J Clin Invest. 1966 Feb;45(2):217–227. doi: 10.1172/JCI105334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFMANN A. F. THE FUNCTION OF BILE SALTS IN FAT ABSORPTION. THE SOLVENT PROPERTIES OF DILUTE MICELLAR SOLUTIONS OF CONJUGATED BILE SALTS. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:57–68. doi: 10.1042/bj0890057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IWATA T., YAMASAKI K. ENZYMATIC DETERMINATION AND THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY OF BILE ACIDS IN BLOOD. J Biochem. 1964 Nov;56:424–431. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JAMES A. T., WEBB J. P., KELLOCK T. D. The occurrence of unusual fatty acids in faecal lipids from human beings with normal and abnormal fat absorption. Biochem J. 1961 Feb;78:333–339. doi: 10.1042/bj0780333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekjian H. S., Phillips S. F., Hofmann A. F. Colonic secretion of water and electrolytes induced by bile acids: perfusion studies in man. J Clin Invest. 1971 Aug;50(8):1569–1577. doi: 10.1172/JCI106644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips S. F. Diarrhea: a current view of the pathophysiology. Gastroenterology. 1972 Sep;63(6):495–518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein R., Howard A. V., Wrong O. M. In vivo dialysis of faeces as a method of stool analysis. IV. The organic anion component. Clin Sci. 1969 Oct;37(2):549–564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. J. Identification of some enteric bacteria which convert oleic acid to hydroxystearic acid in vitro. Gastroenterology. 1972 Mar;62(3):430–435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingate D. L., Phillips S. F., Hofmann A. F. Effect of glycine-conjugated bile acids with and without lecithin on water and glucose absorption in perfused human jejunum. J Clin Invest. 1973 May;52(5):1230–1236. doi: 10.1172/JCI107290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurier R. B., Patterson J. F., Levitanr Relationship between net water absorption and hexanoic acid absorption from the intact human jejunum. Am J Dig Dis. 1968 Feb;13(2):109–112. doi: 10.1007/BF02232952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]