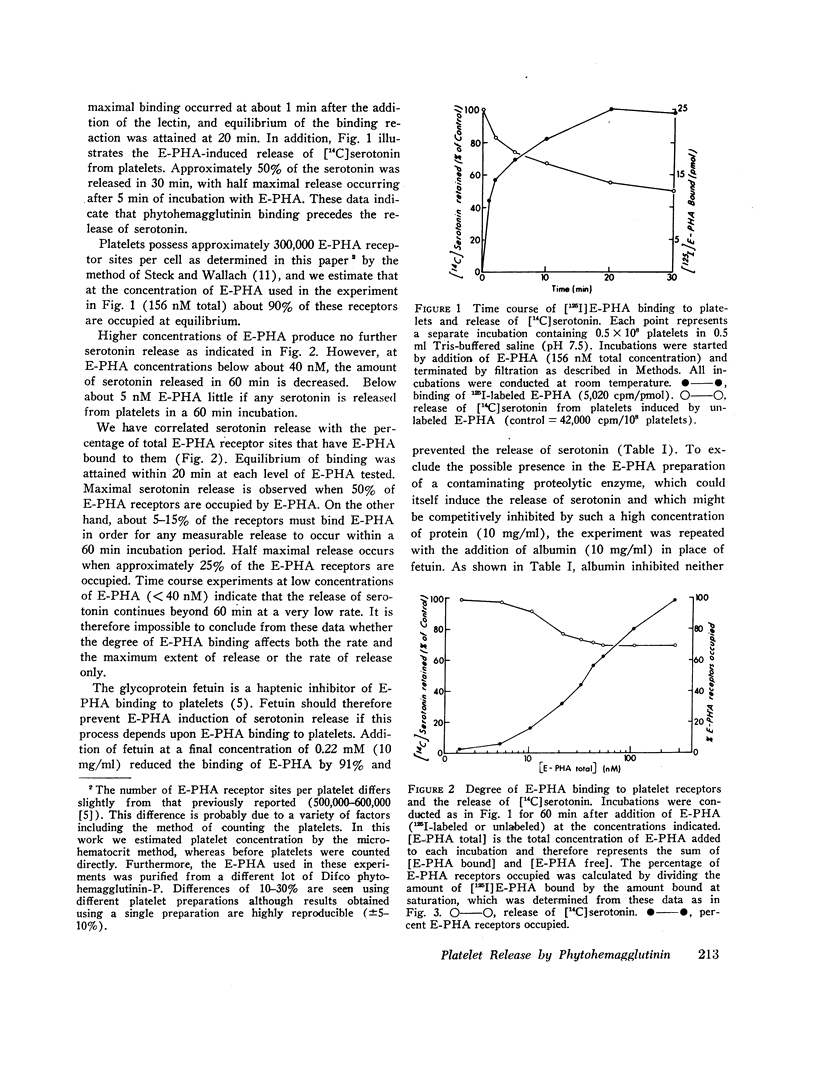
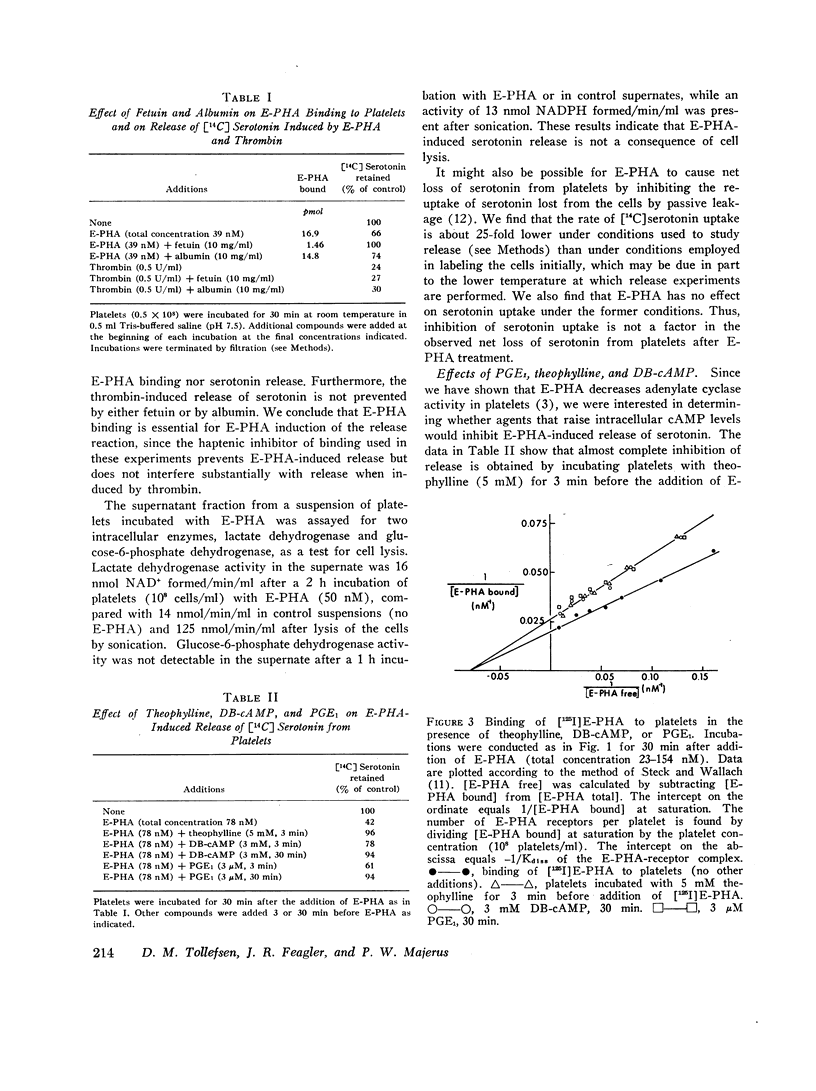
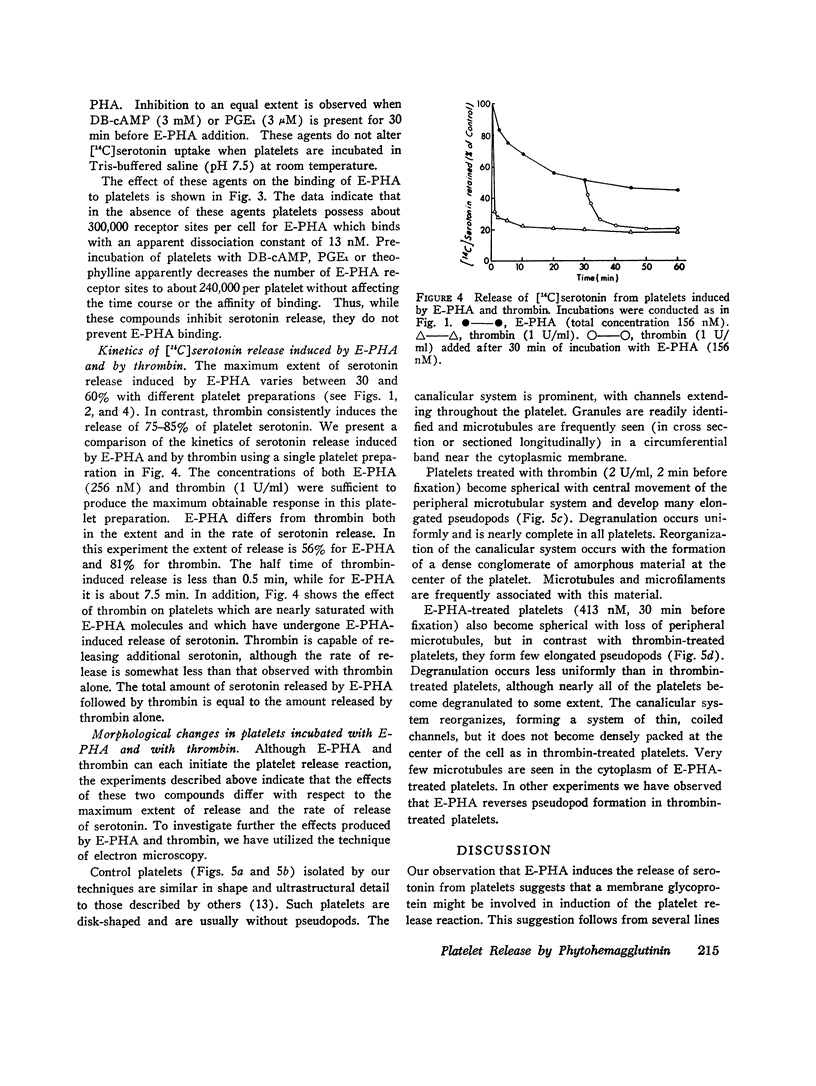
Abstract
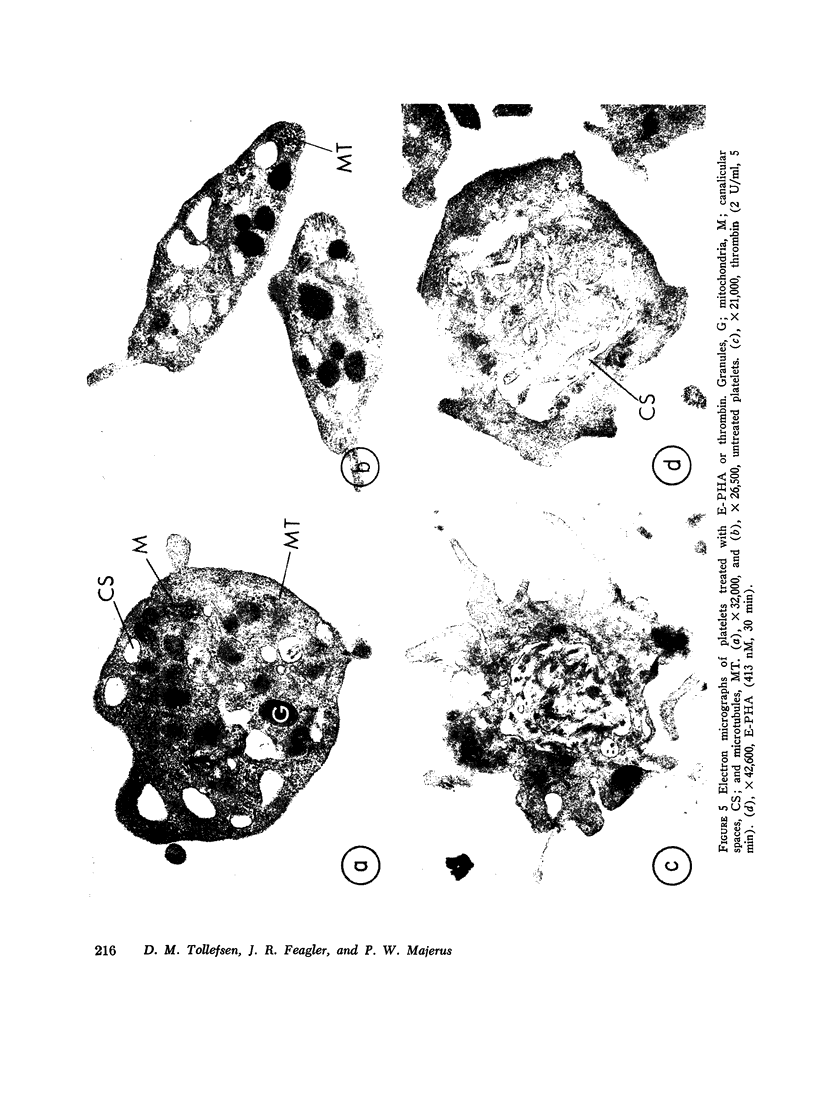
We have previously shown that the erythroagglutinating phytohemagglutinin (E-PHA) from Phaseolus vulgaris binds to the surface of intact human platelets and that adenylate cyclase activity in the particulate fraction of E-PHA-treated platelets is lower than in comparable controls. We now find that E-PHA induces release of [14C]serotonin from platelets. Release follows binding of E-PHA, and a haptenic inhibitor of E-PHA binding prevents induction of release. E-PHA does not produce platelet lysis and has little effect on [14C]serotonin uptake. Platelets possess approximately 300,000 receptor sites of E-PHA per cell, and we estimate that about 15% of these sites must be occupied by E-PHA to initiate the release reaction. Prior incubation of platelets with prostaglandin E1, theophylline, or dibutyryl cyclic AMP prevents E-PHA-induced release, although these agents have little effect on E-PHA binding to platelets. Thrombin and E-PHA produce different rates and extents of serotonin release. Thrombin (1 U/ml) causes release of 75-85% of platelet [14C]-serotonin, with half-maximal release occurring less than 0.5 min after thrombin addition. E-PHA, however, induces release of only 30-60% of platelet serotonin at a 10-fold slower rate. In addition, utilizing electron microscopy, we have observed striking differences in the morphological changes that occur in platelets exposed to E-PHA as compared with thrombin. Thus, the platelet release reaction may be triggered in part by binding of E-PHA to the cell surface, but this reaction only partially resembles that produced by thrombin.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baenziger N. L., Brodie G. N., Majerus P. W. A thrombin-sensitive protein of human platelet membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jan;68(1):240–243. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.1.240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baenziger N. L., Brodie G. N., Majerus P. W. Isolation and properties of a thrombin-sensitive protein of human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 10;247(9):2723–2731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodie G. N., Baenziger N. L., Chase L. R., Majerus P. W. The effects of thrombin on adenyl cyclase activity and a membrane protein from human platelets. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jan;51(1):81–88. doi: 10.1172/JCI106800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld R., Kornfeld S. The structure of a phytohemagglutinin receptor site from human erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1970 May 25;245(10):2536–2545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld S., Rogers J., Gregory W. The nature of the cell surface receptor site for Lens culinaris phytohemagglutinin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Nov;246(21):6581–6586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majerus P. W., Brodie G. N. The binding of phytohemagglutinins to human platelet plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jul 10;247(13):4253–4257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majerus P. W., Smith M. B., Clamon G. H. Lipid metabolism in human platelets. I. Evidence for a complete fatty acid synthesizing system. J Clin Invest. 1969 Jan;48(1):156–164. doi: 10.1172/JCI105964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuda M., Nemerson Y. Transport of serotonin by blood platelets: a pump-leak system. Am J Physiol. 1971 Jan;220(1):283–288. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.1.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STECK T. L., HOELZLWALLACH D. F. THE BINDING OF KIDNEY-BEAN PHYTOHEMAGGLUTININ BY EHRLICH ASCITES CARCINOMA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Mar 8;97:510–522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WROBLEWSKI F., LADUE J. S. Lactic dehydrogenase activity in blood. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1955 Oct;90(1):210–213. doi: 10.3181/00379727-90-21985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber T., Nordman C. T., Gräsbeck R. Separation of lymphocyte-stimulating and agglutinating activities in phytohaemagglutinin (PHA) from Phaseolus vulgaris. Scand J Haematol. 1967;4(1):77–80. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1967.tb01601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe S. M., Shulman N. R. Inhibition of platelet energy production and release reaction by PGE1, theophylline and cAMP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Oct 9;41(1):128–134. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90478-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]