Abstract
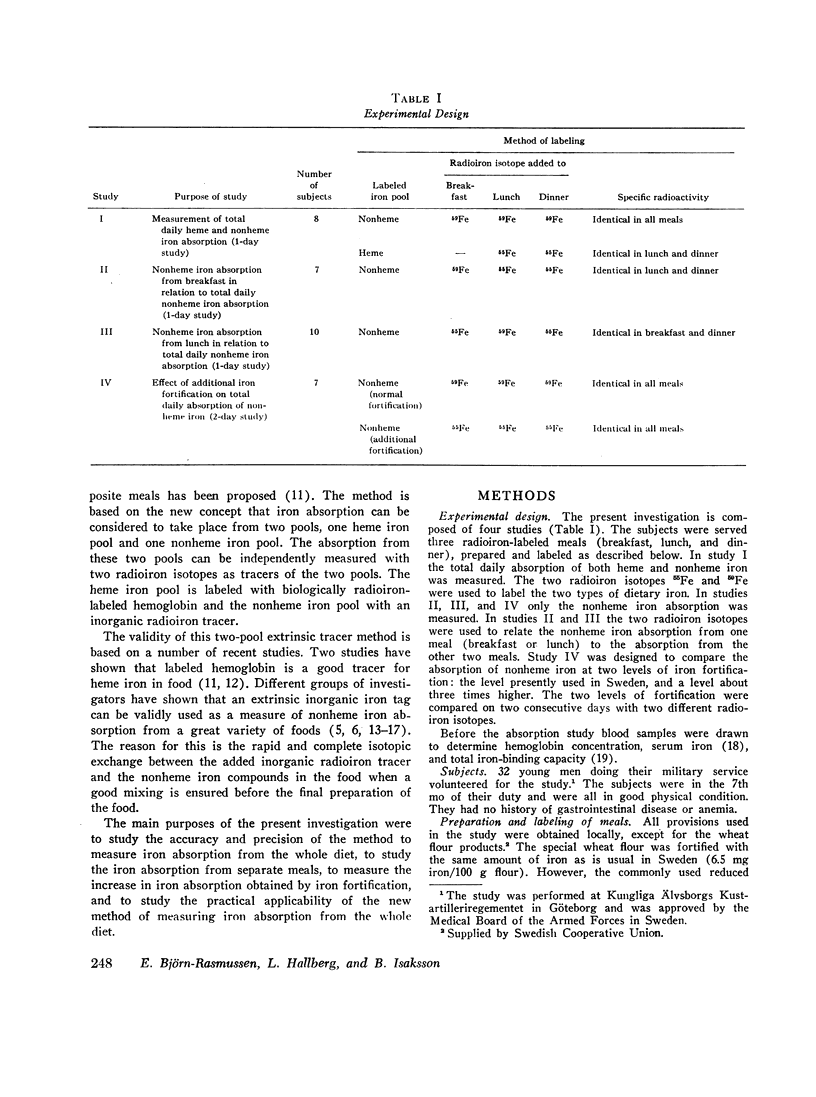
A new radioisotope method to measure iron absorption from the whole diet was used in this study. The method is based on the concept that food iron is absorbed from two pools, the heme iron pool and the nonheme iron pool, which can be especially labeled with two radioiron isotopes given as hemoglobin and as an iron salt. The purpose of this study was to test the accuracy of this two-pool extrinsic tag method.
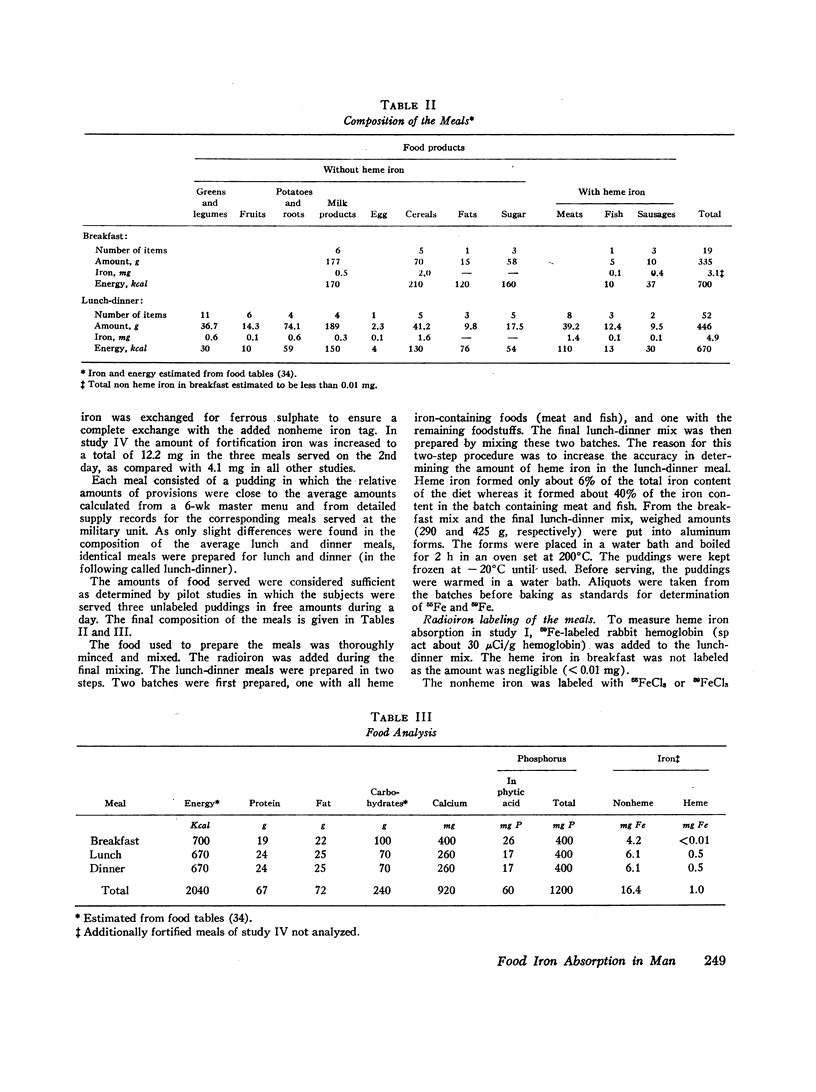
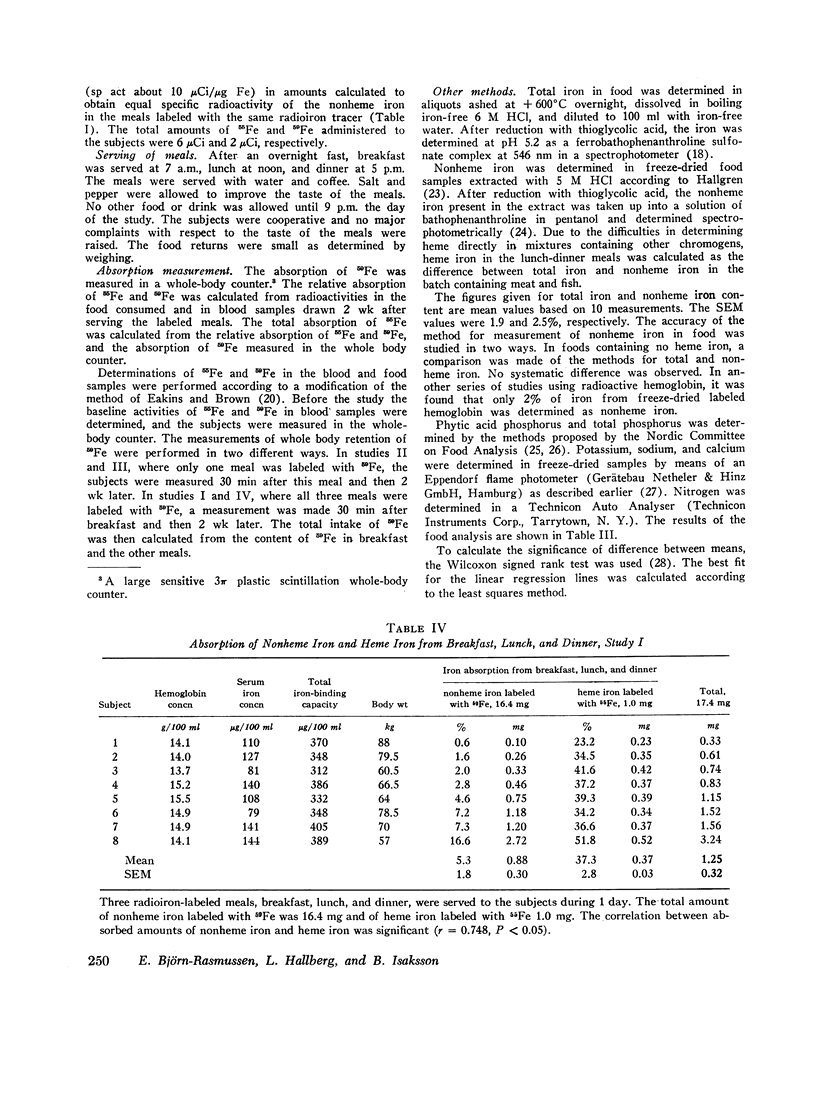
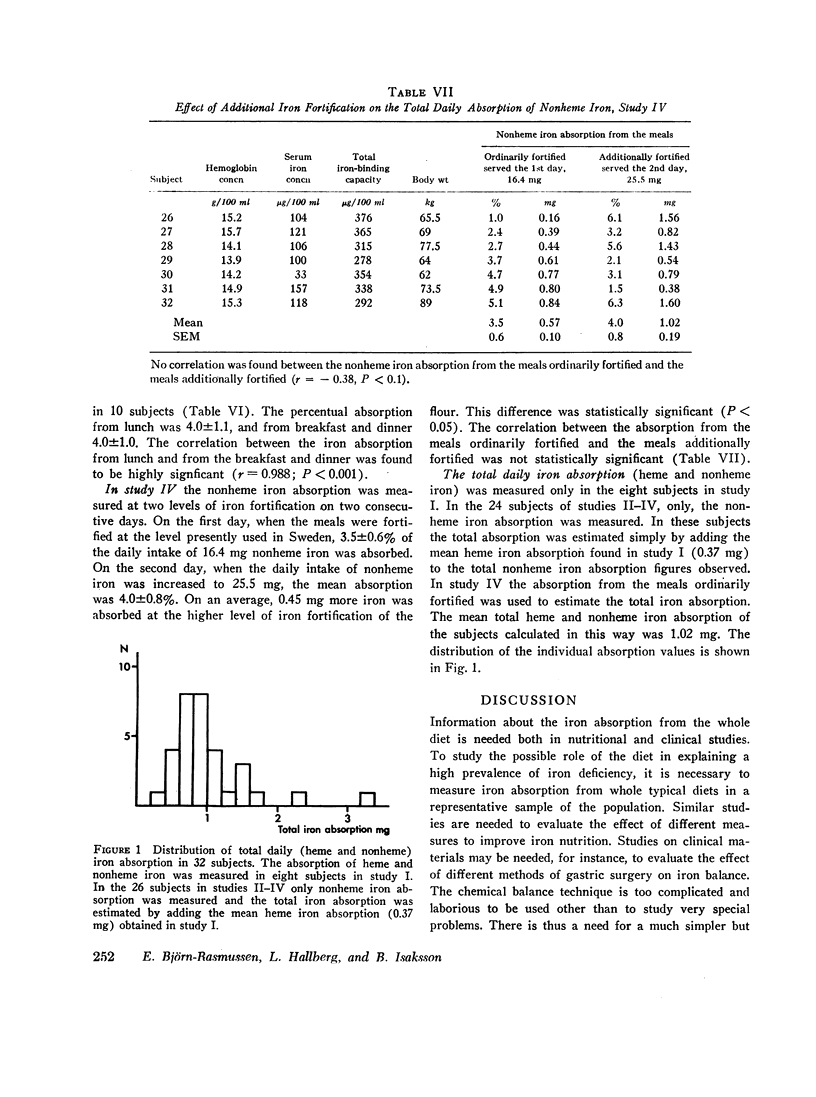
The meals served were composed as an average of 6 wk consumption in the present material of 32 young enlisted men. The mean and total heme and nonheme iron absorption in all the 32 young men was 1.01±0.11. This figure agrees well with the mean daily losses expected for this group of subjects (1.0 mg). The conclusion can therefore be made that there are no major systematic errors of the present method to measure the total iron absorption from a mixed diet.
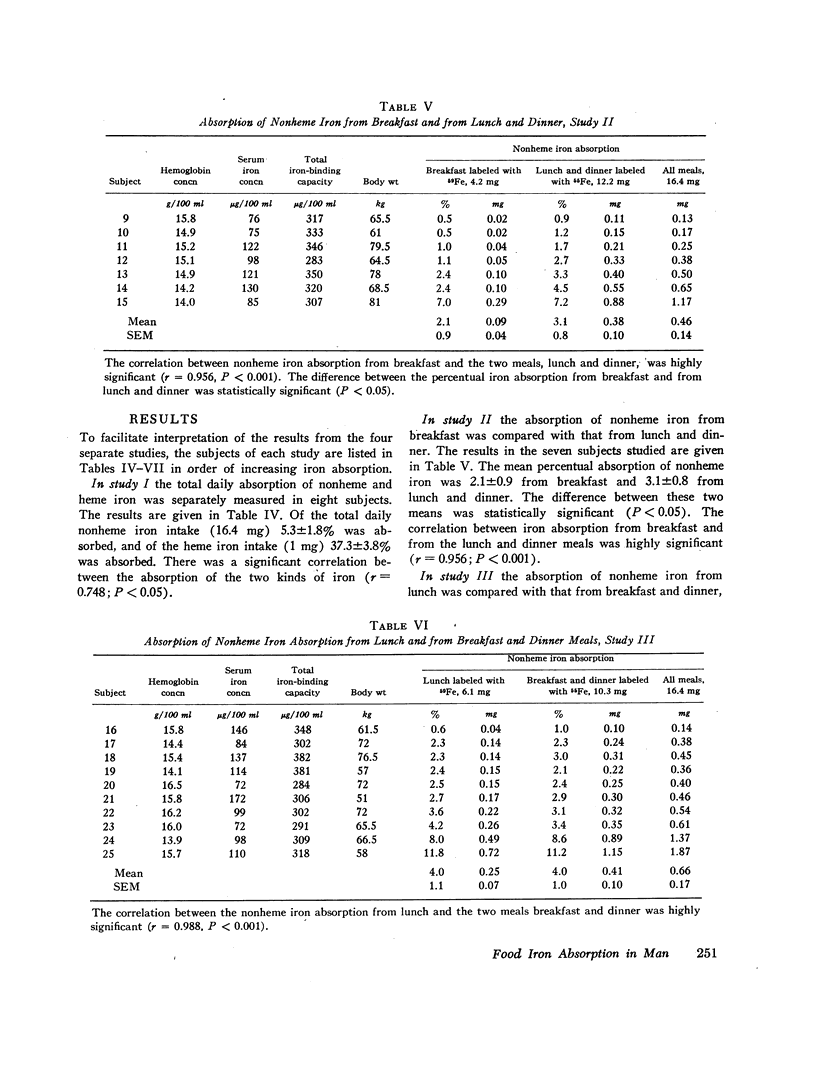
In one series a comparison was made of the absorption of heme and nonheme iron from the meals. A significant correlation between the absorption of the two kinds of iron was found. However, a much greater fraction of the heme iron was absorbed (37%) than of the nonheme iron (5%).
The absorption both from breakfast and lunch was in two series found to give a good prediction of the total daily nonheme iron absorption. One series was designed to compare the effect of two levels of iron fortification. There was a significant increase in iron absorption when the level of iron fortification of the meals was increased.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Björn-Rasmussen E., Hallberg L., Walker R. B. Food iron absorption in man. I. Isotopic exchange between food iron and inorganic iron salt added to food: studies on maize, wheat, and eggs. Am J Clin Nutr. 1972 Mar;25(3):317–323. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/25.3.317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook J. D., Layrisse M., Finch C. A. The measurement of iron absorption. Blood. 1969 Mar;33(3):421–429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook J. D., Layrisse M., Martinez-Torres C., Walker R., Monsen E., Finch C. A. Food iron absorption measured by an extrinsic tag. J Clin Invest. 1972 Apr;51(4):805–815. doi: 10.1172/JCI106875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eakins J. D., Brown D. A. An improved method for the simultaneous determination of iron-55 and iron-59 in blood by liquid scintillation counting. Int J Appl Radiat Isot. 1966 Jul;17(7):391–397. doi: 10.1016/0020-708x(66)90065-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green R., Charlton R., Seftel H., Bothwell T., Mayet F., Adams B., Finch C., Layrisse M. Body iron excretion in man: a collaborative study. Am J Med. 1968 Sep;45(3):336–353. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(68)90069-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallberg L., Björn-Rasmussen E. Determination of iron absorption from whole diet. A new two-pool model using two radioiron isotopes given as haem and non-haem iron. Scand J Haematol. 1972;9(3):193–197. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1972.tb00930.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallberg L., Sölvell L. Absorption of hemoglobin iron in man. Acta Med Scand. 1967 Mar;181(3):335–354. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1967.tb15161.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert V., Gottlieb C. W., Lau K. S., Fisher M., Gevirtz N. R., Wasserman L. R. Coated charcoal assay of unsaturated iron-binding capacity. J Lab Clin Med. 1966 May;67(5):855–862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaksson B., Sjögren B. On the concept "constant diet" in metabolic balance studies. Nutr Dieta Eur Rev Nutr Diet. 1965;7(3):175–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOSEPHS H. W. Absorption of iron as a problem in human physiology; a critical review. Blood. 1958 Jan;13(1):1–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layrisse M., Martinez-Torres C., Cook J. D., Walker R., Finch C. A. Iron fortification of food: its measurement by the extrinsic tag method. Blood. 1973 Mar;41(3):333–352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layrisse M., Martínez-Torres C. Model for measuring dietary absorption of heme iron: test with a complete meal. Am J Clin Nutr. 1972 Apr;25(4):401–411. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/25.4.401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layrisse M., Martínez-Torres C., Roche M. Effect of interaction of various foods on iron absorption. Am J Clin Nutr. 1968 Oct;21(10):1175–1183. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/21.10.1175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOORE C. V., DUBACH R. Observations on the absorption of iron from foods tagged with radioiron. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1951;64:245–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Torres C., Layrisse M. Effect of amino acids on iron absorption from a staple vegetable food. Blood. 1970 May;35(5):669–682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Torres C., Layrisse M. Iron absorption from veal muscle. Am J Clin Nutr. 1971 May;24(5):531–540. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/24.5.531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHARPE L. M., PEACOCK W. C., COOKE R., HARRIS R. S. The effect of phytate and other food factors on iron absorption. J Nutr. 1950 Jul;41(3):433–446. doi: 10.1093/jn/41.3.433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sayers M. H., Lynch S. R., Jacobs P., Charlton R. W., Bothwell T. H., Walker R. B., Mayet F. The effects of ascorbic acid supplementation on the absorption of iron in maize, wheat and soya. Br J Haematol. 1973 Feb;24(2):209–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1973.tb05741.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sköldborn H., Arvidsson B., Andersson M. A new whole body monitoring laboratory. Acta Radiol Suppl. 1972;313:233–241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TURNBULL A., CLETON F., FINCH C. A. Iron absorption. IV. The absorption of hemoglobin iron. J Clin Invest. 1962 Oct;41:1897–1907. doi: 10.1172/JCI104646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



