Abstract
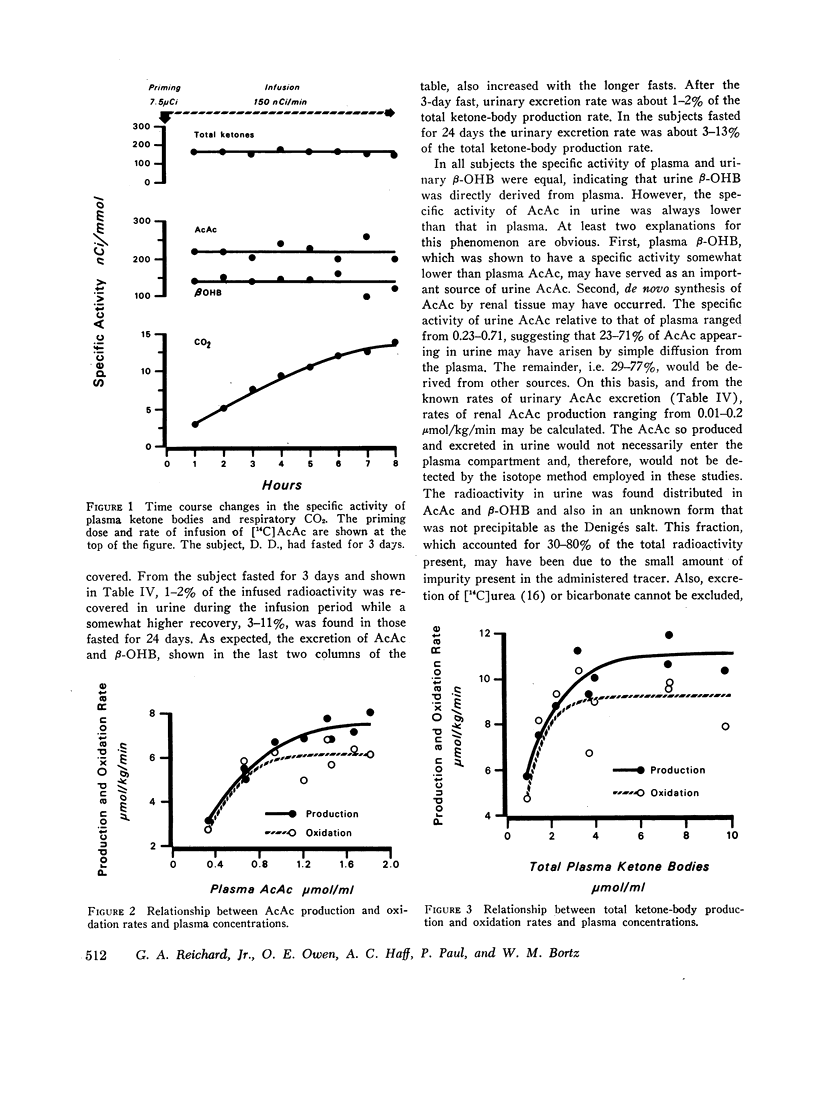
Rates of plasma acetoacetate and total ketone-body production and oxidation to CO2 were determined by an isotope tracer technique in eight obese subjects undergoing progressive starvation. After a brief fast and under conditions of mild ketonemia and minimal ketonuria, rates of acetoacetate and total ketone-body production and oxidation were directly related to the increasing plasma concentration. After a longer fast and with severer ketonemia, acetoacetate and total ketone-body production and oxidation rates were higher but became constant and unrelated to the plasma concentrations. The maximum rates of total ketone-body production and oxidation were about 150 g/24 h and 129 g/24 h, respectively. Although an increased ketone-body production was the primary factor responsible for the hyperketonemia, an imbalance between production and removal of the ketone bodies cannot be excluded. Such an imbalance could account, at least in part, for the developing hyperketonemia and for the lack of relationship between production rates and plasma concentrations.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERGMAN E. N., KON K. ACETOACETATE TURNOVER AND OXIDATION RATES IN OVINE PREGNANCY KETOSIS. Am J Physiol. 1964 Feb;206:449–452. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.206.2.449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERGMAN E. N., KON K., KATZ M. L. QUANTITATIVE MEASUREMENTS OF ACETOACETATE METABOLISM AND OXIDATION IN SHEEP. Am J Physiol. 1963 Oct;205:658–662. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1963.205.4.658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balasse E. O., Havel R. J. Evidence for an effect of inulin on the peripheral utilization of ketone bodies in dogs. J Clin Invest. 1971 Apr;50(4):801–813. doi: 10.1172/JCI106551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates M. W., Krebs H. A., Williamson D. H. Turnover rates of ketone bodies in normal, starved and alloxan-diabetic rats. Biochem J. 1968 Dec;110(4):655–661. doi: 10.1042/bj1100655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bondy P. K., Bloom W. L., Whitner V. S., Farrar B. W. STUDIES OF THE ROLE OF THE LIVER IN HUMAN CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM BY THE VENOUS CATHETER TECHNIC. II. PATIENTS WITH DIABETIC KETOSIS, BEFORE AND AFTER THE ADMINISTRATION OF INSULIN. J Clin Invest. 1949 Sep;28(5 Pt 2):1126–1133. doi: 10.1172/JCI102146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bortz W. M., Paul P., Haff A. C., Holmes W. L. Glycerol turnover and oxidation in man. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jun;51(6):1537–1546. doi: 10.1172/JCI106950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOLE V. P., MEINERTZ H. Microdetermination of long-chain fatty acids in plasma and tissues. J Biol Chem. 1960 Sep;235:2595–2599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flatt J. P. On the maximal possible rate of ketogenesis. Diabetes. 1972 Jan;21(1):50–53. doi: 10.2337/diab.21.1.50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenfeldt L., Wahren J. Human forearm muscle metabolism during exercise. 3. Uptake, release and oxidation of beta-hydroxybutyrate and observations on the beta-hydroxybutyrate/acetoacetate ratio. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1968;21(4):314–320. doi: 10.3109/00365516809076999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson R. W., Ziporin Z. Z. Factors influencing the utilization of ketone bodies by mouse adipose tissue. J Lipid Res. 1966 Jan;7(1):56–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz M. L., Bergman E. N. Hepatic and portal metabolism of glucose, free fatty acids, and ketone bodies in the sheep. Am J Physiol. 1969 Apr;216(4):953–960. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.216.4.953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGarry J. D., Foster D. W. Regulation of ketogenesis and clinical aspects of the ketotic state. Metabolism. 1972 May;21(5):471–489. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(72)90059-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGarry J. D., Guest M. J., Foster D. W. Ketone body metabolism in the ketosis of starvation and alloxan diabetes. J Biol Chem. 1970 Sep 10;245(17):4382–4390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen O. E., Felig P., Morgan A. P., Wahren J., Cahill G. F., Jr Liver and kidney metabolism during prolonged starvation. J Clin Invest. 1969 Mar;48(3):574–583. doi: 10.1172/JCI106016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen O. E., Morgan A. P., Kemp H. G., Sullivan J. M., Herrera M. G., Cahill G. F., Jr Brain metabolism during fasting. J Clin Invest. 1967 Oct;46(10):1589–1595. doi: 10.1172/JCI105650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen O. E., Reichard G. A., Jr Human forearm metabolism during progressive starvation. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jul;50(7):1536–1545. doi: 10.1172/JCI106639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul P., Bortz W. M. Turnover and oxidation of plasma glucose in lean and obese humans. Metabolism. 1969 Jul;18(7):570–584. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(69)90091-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitts R. F., Ayer J. L., Schiess W. A., Miner P. THE RENAL REGULATION OF ACID-BASE BALANCE IN MAN. III. THE REABSORPTION AND EXCRETION OF BICARBONATE. J Clin Invest. 1949 Jan;28(1):35–44. doi: 10.1172/JCI102050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEELE R., ALTSZULER N., WALL J. S., DUNN A., DE BODO R. C. Influence of adrenalectomy on glucose turnover and conversion to CO2: studies with C14 glucose in the dog. Am J Physiol. 1959 Feb;196(2):221–230. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1959.196.2.221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söling H. D., Zahlten R., Reimold W. V., Willms B. Utilization of ketone bodies by adipose tissue and its regulation by carbohydrate metabolism. Horm Metab Res. 1970 Mar;2(2):56–63. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1095108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMSON D. H., MELLANBY J., KREBS H. A. Enzymic determination of D(-)-beta-hydroxybutyric acid and acetoacetic acid in blood. Biochem J. 1962 Jan;82:90–96. doi: 10.1042/bj0820090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidemann M. J., Krebs H. A. The fuel of respiration of rat kidney cortex. Biochem J. 1969 Apr;112(2):149–166. doi: 10.1042/bj1120149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


