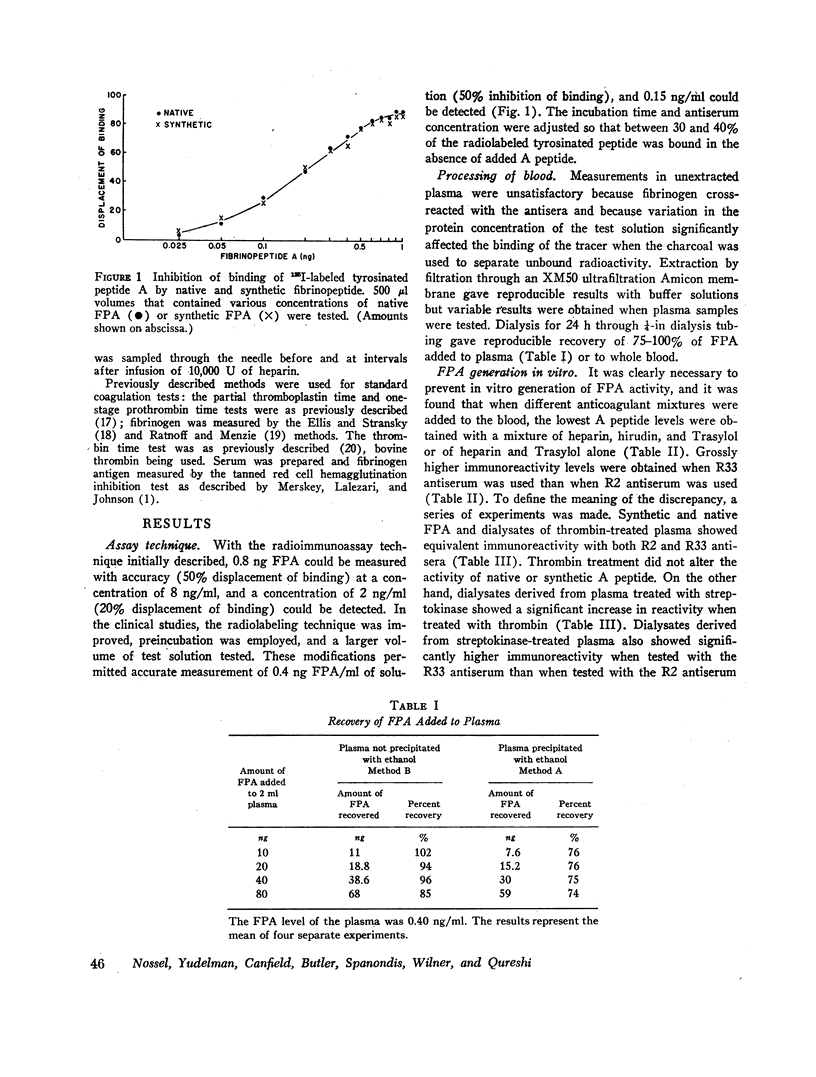
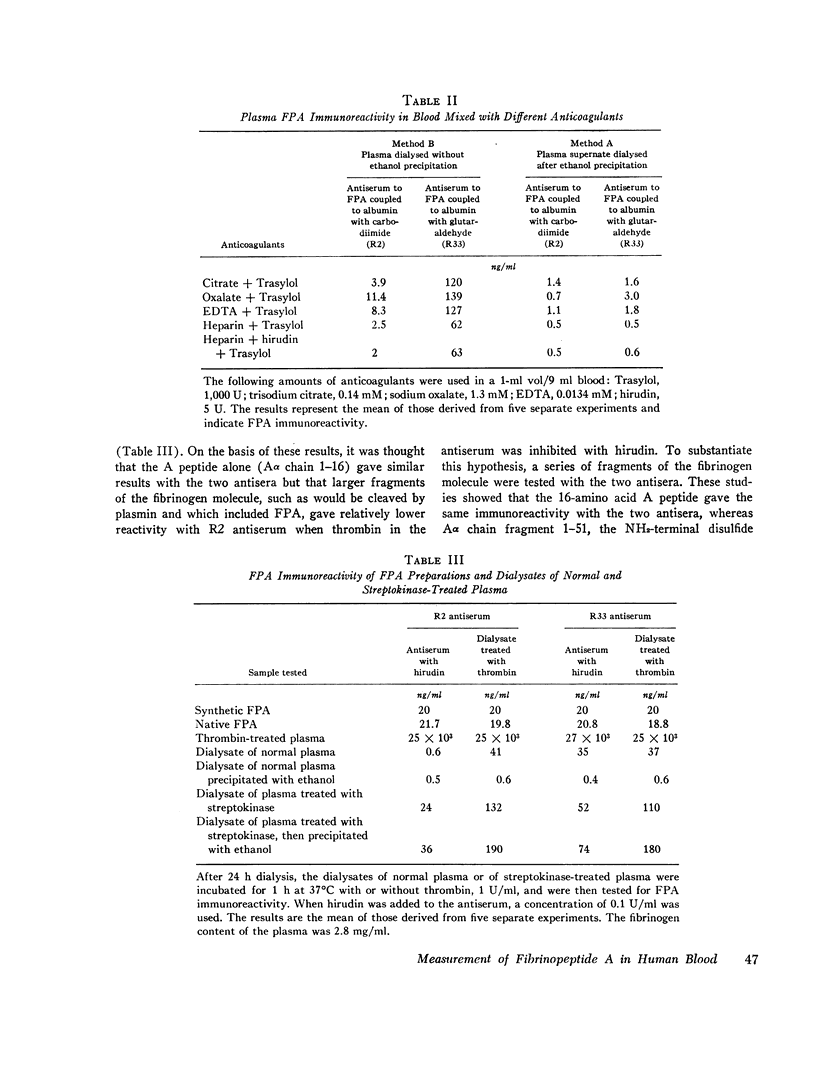
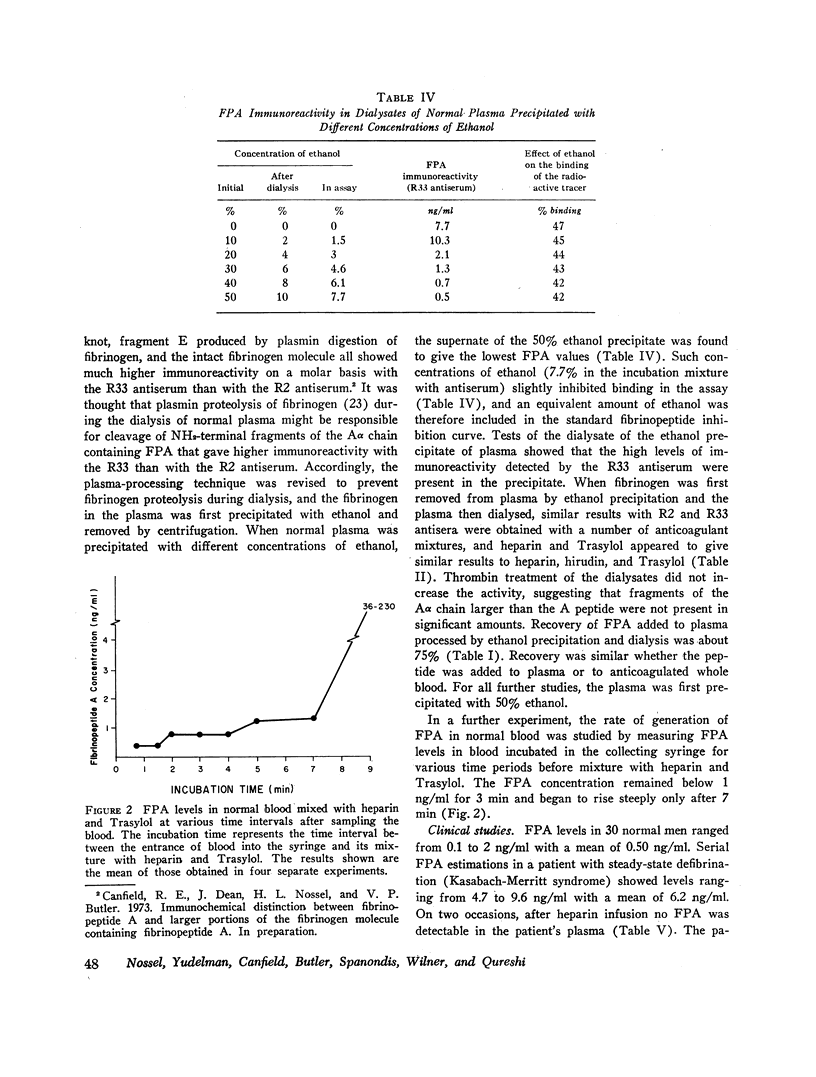
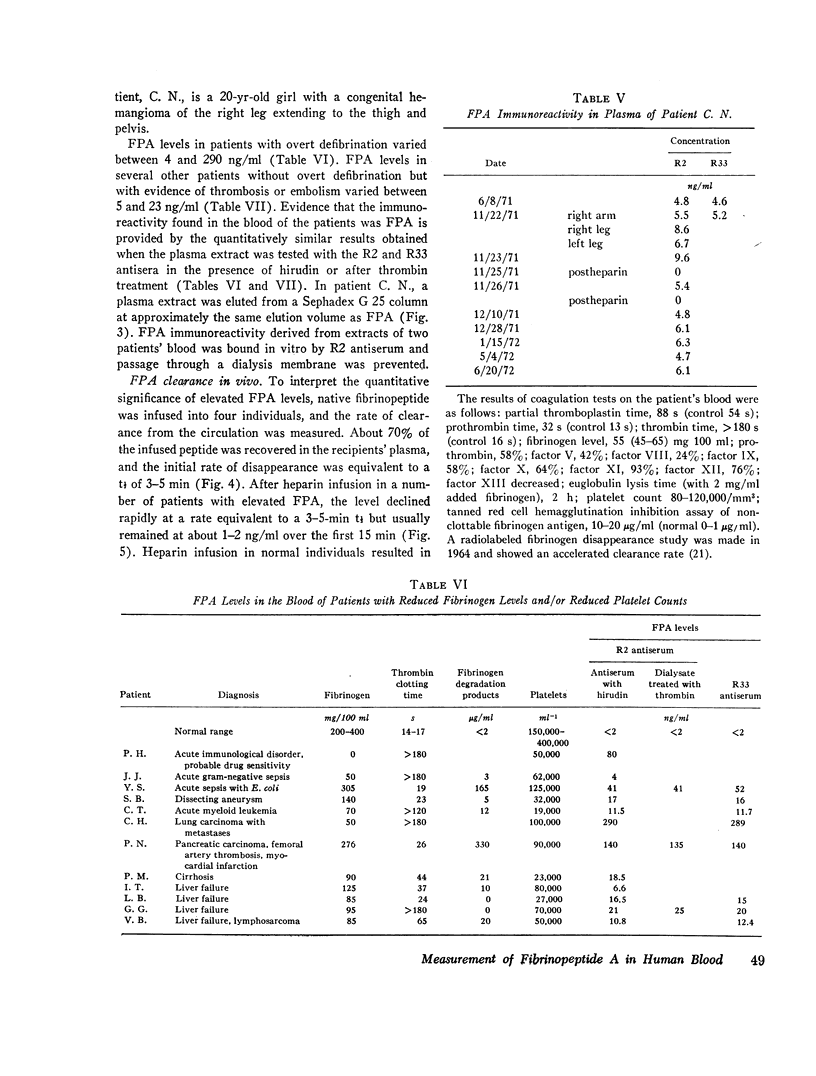
Abstract
Since thrombin cleaves fibrinopeptides A (FPA) and B from the NH2-terminal end of the fibrinogen molecule, measurement of fibrinopeptide levels in plasma may provide a direct index of thrombin action. Recently a radioimmunoassay for FPA has been developed, and in the present paper, we describe the application of this assay to the measurement of FPA levels in clinical blood samples. Since fibrinogen cross-reacts with antibodies to FPA, dialysis was used to extract the peptide from plasma. In vitro generation of FPA was prevented by removing the fibrinogen from the plasma by precipitation with ethanol before dialysis. The processing technique permitted recovery of 75% of FPA added to blood in vitro. Evidence that the immunoreactivity measured in plasma is due to FPA was provided by the results of experiments in which two antisera to FPA with different specificities showed comparable results and addition of thrombin caused no change in immunoreactivity. In contrast, extracts of streptokinasetreated plasma showed a five-fold increase in activity when treated with thrombin and markedly different immunoreactivity with the two antisera.
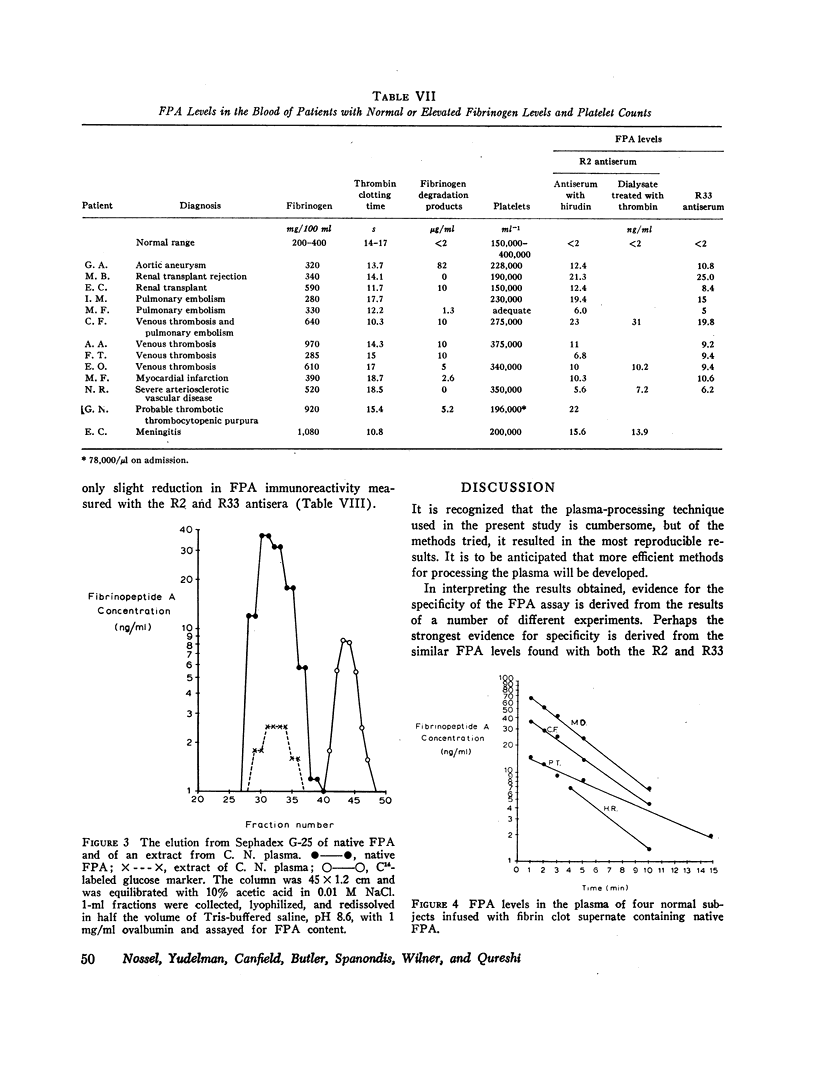
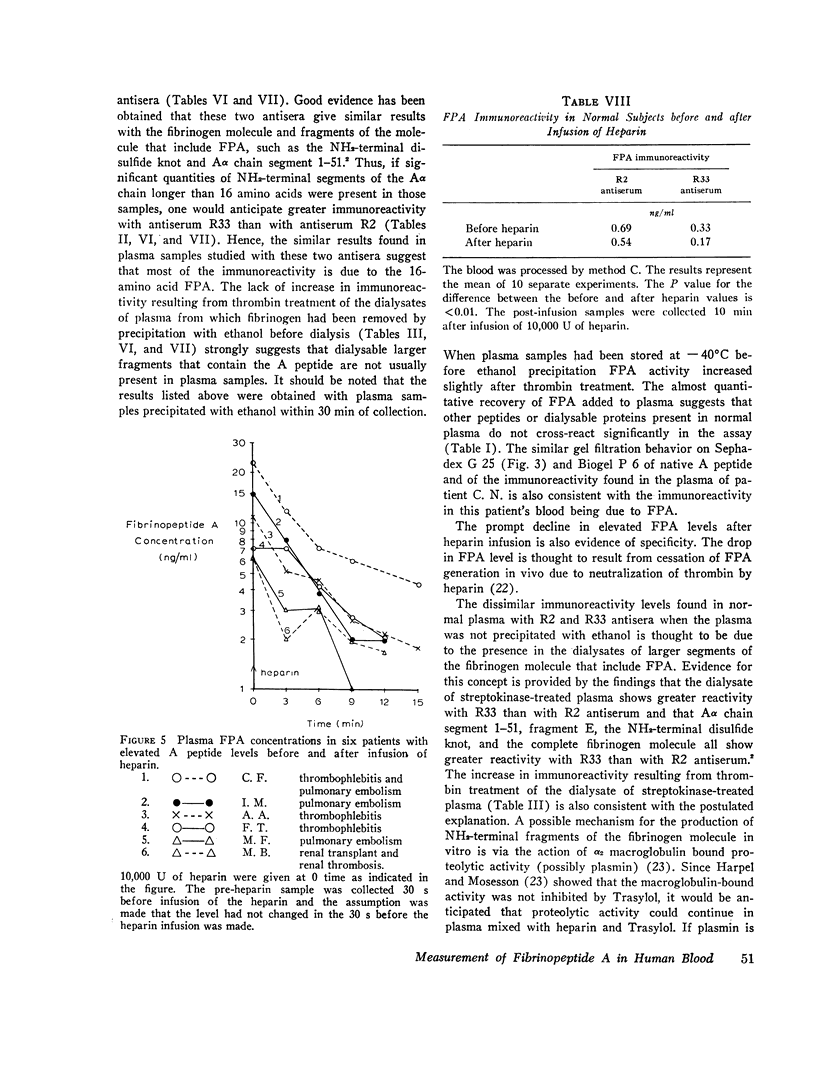
Plasma FPA levels in 30 normal men were below 2 ng/ml, with a mean of 0.5 ng/ml. FPA levels in 12 patients with reduced fibrinogen levels or reduced platelet counts or both ranged between 4 and 289 ng/ml. FPA levels in 13 patients with normal or elevated fibrinogen levels, including 6 patients with clinical evidence of venous thrombosis or pulmonary embolism or both, ranged between 5 and 23 ng/ml. FPA and fibrinogen degradation product levels did not correlate, and in several patients, elevated FPA levels were found in the presence of normal fibrinogen degradation product levels. After infusion of FPA-containing solutions in four normal individuals, FPA showed a disappearance rate from the plasma consistent with a t½ of 3—5 min. Heparin infusions in six patients with venous thrombosis or pulmonary embolism or both and elevated FPA levels were followed by a prompt decline in FPA level at a mean rate equivalent to a 3—5 min t½.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASTRUP T. The haemostatic balance. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1958 Sep 1;2(3-4):347–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blombäck B., Blombäck M., Edman P., Hessel B. Human fibrinopeptides. Isolation, characterization and structure. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 28;115(2):371–396. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90437-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLIS B. C., STRANSKY A. A quick and accurate method for the determination of fibronogen in plasma. J Lab Clin Med. 1961 Sep;58:477–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher A. P., Alkjaersig N., O'Brien J., Tulevski V. G. Blood hypercoagulability and thrombosis. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1970;83:159–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODFRIEND T. L., LEVINE L., FASMAN G. D. ANTIBODIES TO BRADYKININ AND ANGIOTENSIN: A USE OF CARBODIIMIDES IN IMMUNOLOGY. Science. 1964 Jun 12;144(3624):1344–1346. doi: 10.1126/science.144.3624.1344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodfriend T. L., Ball D. L. Radioimmunoassay of bradykinin: chemical modification to enable use of radioactive iodine. J Lab Clin Med. 1969 Mar;73(3):501–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HJORT P. F., HASSELBACK R. A critical review of the evidence for a continous hemostasis in vivo. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1961 Dec 15;6:580–612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpel P. C., Mosesson M. W. Degradation of human fibrinogen by plasms alpha2-macroglobulin-enzyme complexes. J Clin Invest. 1973 Sep;52(9):2175–2184. doi: 10.1172/JCI107402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillman R. S., Phillips L. L. Clotting-fibrinolysis in a cavernous hemangioma. Am J Dis Child. 1967 Jun;113(6):649–653. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1967.02090210063003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwanaga S., Wallén P., Gröndahl N. J., Henschen A., Blombäck B. On the primary structure of human fibrinogen. Isolation and characterization of N-terminal fragments from plasmic digests. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Mar;8(2):189–199. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00514.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kisker C. T., Rush R. Detection of intravascular coagulation. J Clin Invest. 1971 Nov;50(11):2235–2241. doi: 10.1172/JCI106720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER K. D., COPELAND W. H. HUMAN THROMBIN: ISOLATION AND STABILITY. Exp Mol Pathol. 1965 Aug;26:431–437. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(65)90051-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrifield R. B. Solid-phase peptide synthesis. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1969;32:221–296. doi: 10.1002/9780470122778.ch6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merskey C., Lalezari P., Johnson A. J. A rapid, simple, sensitive method for measuring fibrinolytic split products in human serum. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Jul;131(3):871–875. doi: 10.3181/00379727-131-33998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niemetz J., Nossel H. L. Activated coagulation factors: in-vivo and in-vitro studies. Br J Haematol. 1969 Apr;16(4):337–351. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1969.tb00411.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niewiarowski S., Gurewich V. Laboratory identification of intravascular coagulation. The serial dilution protamine sulfate test for the detection of fibrin monomer and fibrin degradation products. J Lab Clin Med. 1971 Apr;77(4):665–676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossel H. L., Younger L. R., Wilner G. D., Procupez T., Canfield R. E., Butler V. P., Jr Radioimmunoassay of human fibrinopeptide A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Oct;68(10):2350–2353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.10.2350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RATNOFF O. D., MENZIE C. A new method for the determination of fibrinogen in small samples of plasma. J Lab Clin Med. 1951 Feb;37(2):316–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda Y. Studies of the metabolism and distribution of fibrinogen in healthy men with autologous 125-I-labeled fibrinogen. J Clin Invest. 1966 Jan;45(1):103–111. doi: 10.1172/JCI105314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiger-Nilsson A. C. Studies on tissue thromboplastin, thrombin and fibrinopeptides in intravascular coagulation. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1968;319:1–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



