Abstract
A radioimmunoassay for detection of anti-glomerular basement membrane (GBM) antibody was set up with a 70,000 mol wt GBM antigen, labeled with Iodine-125I and containing both types of oligosaccharidic chains present in the whole membrane.
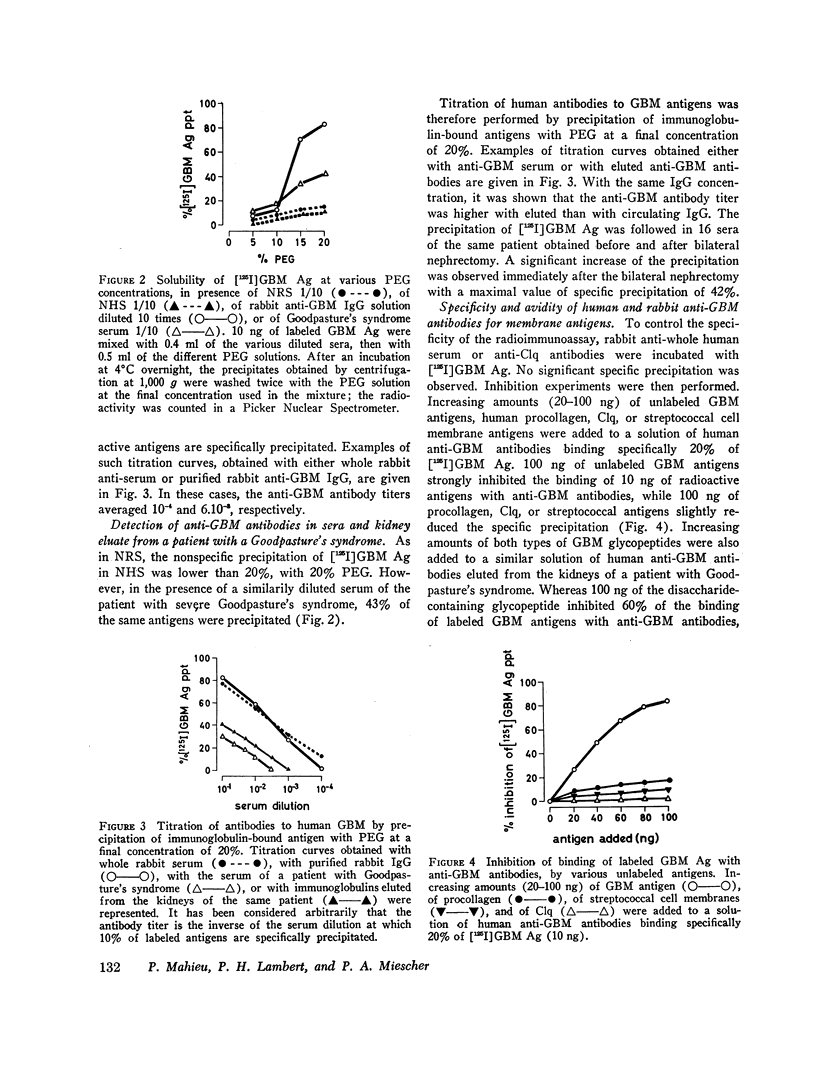
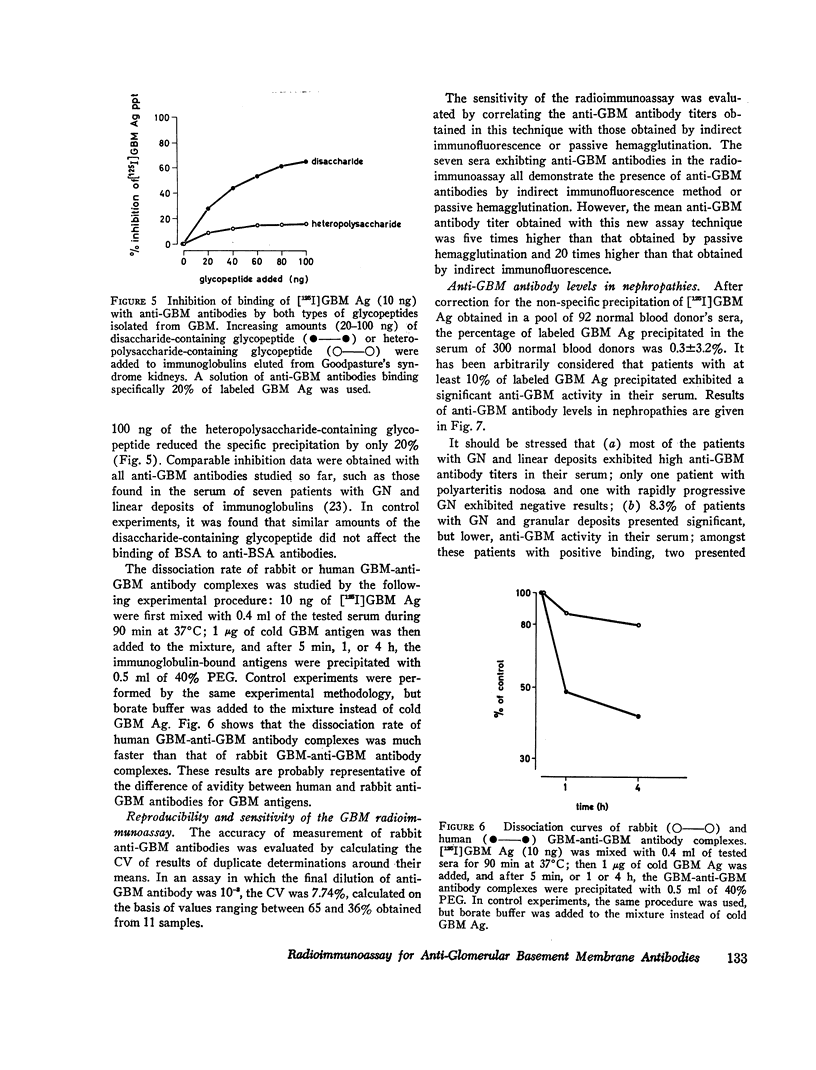
Separation of free radioactive antigens from antigens bound to immunoglobulins was obtained by precipitation with polyethylene glycol (mol wt, 6,000), at a final concentration of 20%. In the presence of normal human or rabbit sera, less than 20% of labeled antigens were precipitated. In the presence of rabbit anti-human GBM antibodies, up to 82% of GBM antigens were precipitated, while in the presence of sera or of kidney eluate from a patient with Goodpasture's syndrome, the precipitation of GBM antigens reached 43%. The avidity of rabbit anti-GBM antibodies for human GBM antigens is higher than that of human anti-GBM antibodies. In the case of Goodpasture's syndrome, the binding of anti-GBM antibodies to labeled antigens was inhibited more efficiently by the disaccharide-containing glycopeptide than by the heteropolysaccharide-containing glycopeptide purified from whole GBM.
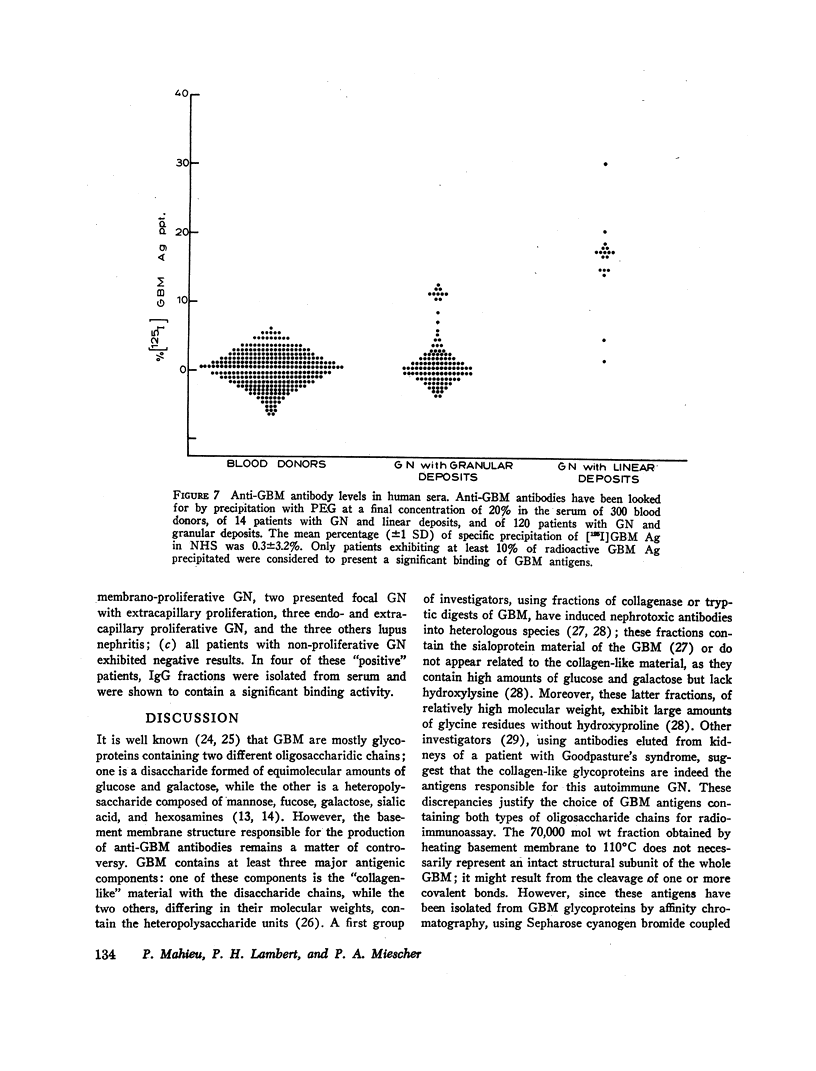
Anti-GBM antibodies were searched for in the serum of 300 normal blood donors, of 120 patients with glomerulonephritis (GN) and granular deposits, and of 14 patients with GN and linear deposits of immunoglobulins. After correction for the “nonspecific” precipitation, the average percentage (±1 SD) of labeled antigens precipitated in the serum of normal blood donors was 0.3±3.2%; 12 patients with GN and linear deposits exhibited high circulating anti-GBM antibody titers, while 8% of the patients with GN and granular deposits presented significant, albeit lower, anti-GBM activity in their sera.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Creighton W. D., Lambert P. H., Miescher P. A. Detection of antibodies and soluble antigen-antibody complexes by precipitation with polyethylene glycol. J Immunol. 1973 Oct;111(4):1219–1227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunker A. K., Rueckert R. R. Observations on molecular weight determinations on polyacrylamide gel. J Biol Chem. 1969 Sep 25;244(18):5074–5080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgington T. S., Glassock R. J., Dixon F. J. Autologous immune-complex pathogenesis of experimental allergic glomerulonephritis. Science. 1967 Mar 17;155(3768):1432–1434. doi: 10.1126/science.155.3768.1432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARR R. S. A quantitative immunochemical measure of the primary interaction between I BSA and antibody. J Infect Dis. 1958 Nov-Dec;103(3):239–262. doi: 10.1093/infdis/103.3.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo G. R. Elution studies in kidneys with linear deposition of immunoglobulin in glomeruli. Am J Pathol. 1970 Dec;61(3):377–394. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRAKOWER C. A., GREENSPON S. A. Localization of the nephrotoxic antigen within the isolated renal glomerulus. AMA Arch Pathol. 1951 Jun;51(6):629–639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
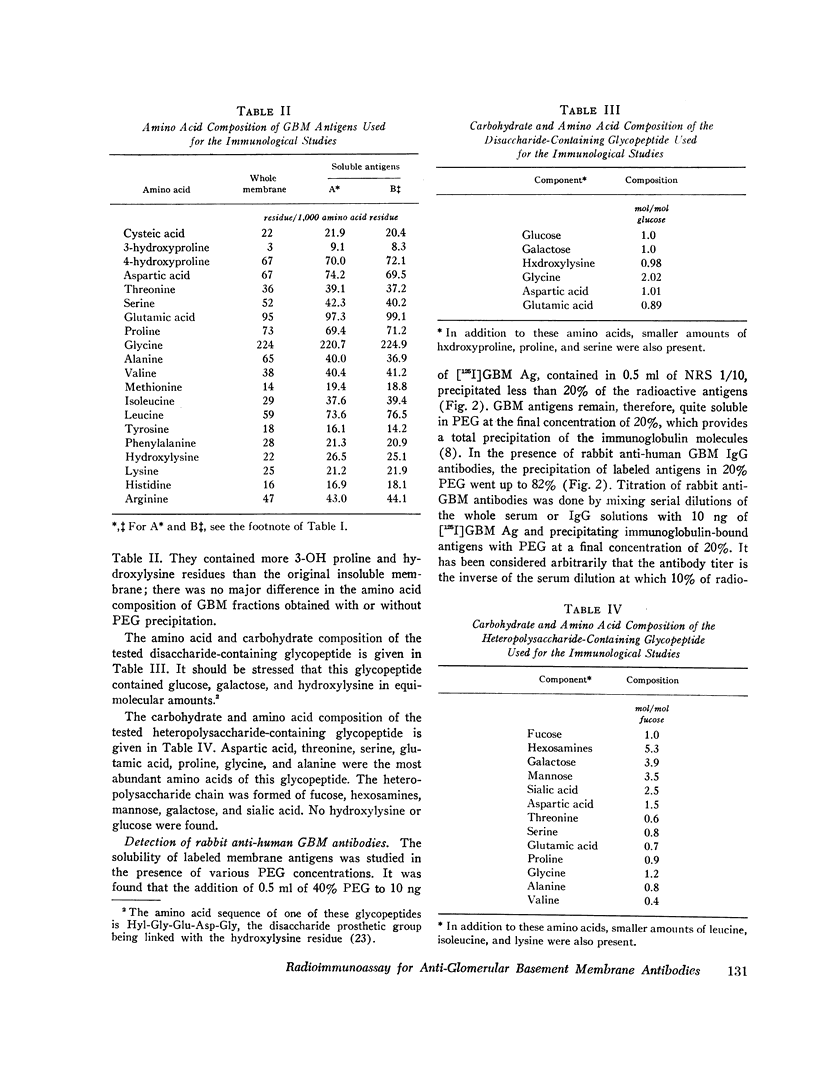
- Kefalides N. A., Winzler R. J. The chemistry of glomerular basement membrane and its relation to collagen. Biochemistry. 1966 Feb;5(2):702–713. doi: 10.1021/bi00866a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert P. H., Dixon F. J. Pathogenesis of the glomerulonephritis of NZB/W mice. J Exp Med. 1968 Mar 1;127(3):507–522. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.3.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner R. A., Glassock R. J., Dixon F. J. The role of anti-glomerular basement membrane antibody in the pathogenesis of human glomerulonephritis. J Exp Med. 1967 Dec 1;126(6):989–1004. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.6.989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARKOWITZ A. S., LANGE C. F., Jr STREPTOCOCCAL RELATED GLOMERULONEPHRITIS. I. ISOLATION, IMMUNOCHEMISTRY AND COMPARATIVE CHEMISTRY OF SOLUBLE FRACTIONS FROM TYPE 12 NEPHRITOGENIC STREPTOCOCCI AND HUMAN GLOMERULI. J Immunol. 1964 Apr;92:565–575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOORE S., STEIN W. H. A modified ninhydrin reagent for the photometric determination of amino acids and related compounds. J Biol Chem. 1954 Dec;211(2):907–913. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahieu P. M., Lambert P. H., Maghuin-Rogister G. R. Primary structure of a small glycopeptide isolated from human glomerular basement membrane and carrying a major antigenic site. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Dec 17;40(2):599–606. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03232.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahieu P. M., Winand R. J. Carbohydrate and amino-acid composition of human glomerular-basement-membrane fractions purified by affinity chromatography. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Aug 1;37(1):157–163. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02970.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahieu P., Dardenne M., Bach J. F. Detection of humoral and cell-mediated immunity to kidney basement membranes in human renal diseases. Am J Med. 1972 Aug;53(2):185–192. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(72)90128-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahieu P., Winand R. J. Chemical structure of tubular and glomerular basement membranes of human kidney. Isolation and characterization of the carbohydrate units. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Sep;15(3):520–524. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb01035.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahieu P., Winand R. J. Chemical structure of tubular and glomerular basement membranes of human kidney. Isolation, purification, carbohydrate and amino acid composition. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Feb;12(3):410–418. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00867.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCluskey R. T. The value of immunofluorescence in the study of human renal disease. J Exp Med. 1971 Sep 1;134(3 Pt 2):242s–255s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh R. M., Griswold W. Antigen identification in Goodpasture's syndrome. Arch Pathol. 1971 Nov;92(5):329–333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPhaul J. J., Jr, Dixon F. J. Basement membrane antigens in serum and urine. Transplant Proc. 1969 Dec;1(4):964–967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPhaul J. J., Jr, Dixon F. J. Characterization of human anti-glomerular basement membrane antibodies eluted from glomerulonephritic kidneys. J Clin Invest. 1970 Feb;49(2):308–317. doi: 10.1172/JCI106240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPhaul J. J., Jr, Dixon F. J. The presence of anti-glomerular basement membrane antibodies in peripheral blood. J Immunol. 1969 Dec;103(6):1168–1175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohos S. C., Skoza L. Glomerular sialoprotein. Science. 1969 Jun 27;164(3887):1519–1521. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3887.1519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocklin R. E., Lewis E. J., David J. R. In vitro evidence for cellular hypersensitivity to glomerular-basement-membrane antigens in human glomerulonephritis. N Engl J Med. 1970 Sep 3;283(10):497–501. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197009032831001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbard D., Rayford P. L., Cooper J. A., Ross G. T. Statistical quality control of radioimmunoassays. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1968 Oct;28(10):1412–1418. doi: 10.1210/jcem-28-10-1412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOBER H. A., PETERSON E. A. Protein chromatography on ion exchange cellulose. Fed Proc. 1958 Dec;17(4):1116–1126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEBLAY R. W. Glomerulonephritis induced in sheep by injections of heterologous glomerular basement membrane and Freund's complete adjuvant. J Exp Med. 1962 Aug 1;116:253–272. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.2.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata S., Miyakawa Y., Naruse T., Nagasawa T., Takuma T. A glycoprotein that induces nephrotoxic antibody: its isolation and purification from rat glomerular basement membrane. J Immunol. 1969 Mar;102(3):593–601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiro R. G. Studies on the renal glomerular basement membrane. Nature of the carbohydrate units and their attachment to the peptide portion. J Biol Chem. 1967 Apr 25;242(8):1923–1932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiro R. G. Studies on the renal glomerular basement membrane. Preparation and chemical composition. J Biol Chem. 1967 Apr 25;242(8):1915–1922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R., Dixon F. J. Experimental glomerulonephritis: immunological events and pathogenetic mechanisms. Adv Immunol. 1967;6:1–90. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60521-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonemasu K., Stroud R. M. Clq: rapid purification method for preparation of monospecific antisera and for biochemical studies. J Immunol. 1971 Feb;106(2):304–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]