Abstract
A sensitive and reproducible procedure for the detection of soluble immune complexes in sera from patients with various immunopathological disorders is reported. Radiolabeled C1q is reacted with sera containing immune complexes. Separation of free from complex bound [125I]C1q is achieved by selective precipitation with polyethylene glycol (PEG). The method is based on both the large molecular size and the C1q-binding property characterizing immune complexes. The minimal amount of aggregated immunoglobulins thus detected is about 10 μg and that of soluble human IgG-anti-IgG complexes is about 3 μg of complexed antibody. Some immune complexes formed in large antigen excess (Ag2Ab) can still be detected by this radiolabeled C1q binding assay. The specificity of the radiolabeled C1q binding test was documented by the inability of antigen-F(ab′)2 antibody complexes to lead to a precipitation of [125I]C1q in PEG.
In a second step, this radiolabeled C1q binding assay was applied to an experimental model of immune complex disease and was shown to be efficient for the detection of in vivo formed immune complexes.
Finally, the technique could be applied to the study of sera from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) or to carriers of the hepatitis B antigen (HB-Ag). Significantly increased [125I]-C1q binding values were observed in 52 sera from SLE patients when compared to values obtained with healthy blood donors (P<0.001). Particularly high values were seen in active disease, a finding which was confirmed by follow-up studies performed with four SLE patients.
No increased [125I]C1q binding was seen in 18 healthy carriers of the HB-Ag; whereas, sera from carriers with hepatitis appear to precipitate increased [125I]C1q percentages: 7/24 cases with acute transient and 4/7 cases with chronic persistent hepatitis were found to increasingly bind [125I]C1q. The results were also used for a correlative study of [125I]C1q binding to IgG levels in the sera but increased [125I]C1q binding could not be attributed to high serum IgG levels which are likely to account for gammaglobulin aggregates.
These examples suggest the utility of the radiolabeled C1q binding assay for the evaluation of immune complex diseases in human pathology.
Full text
PDF


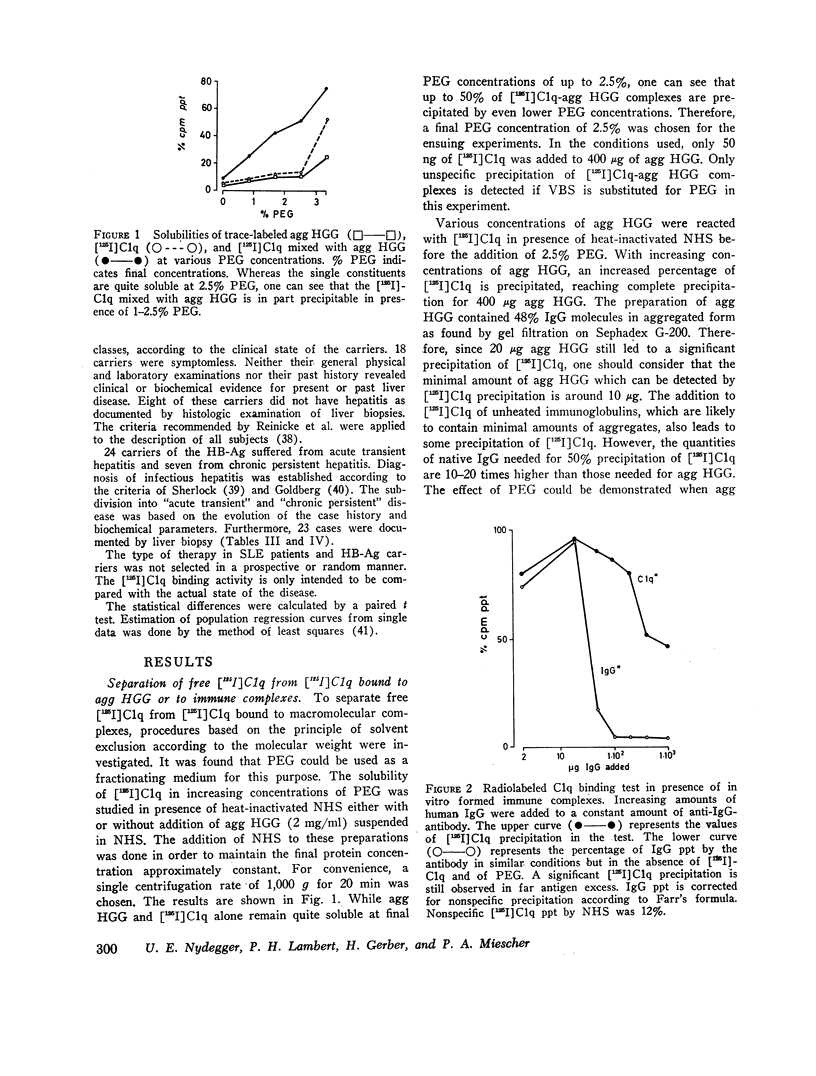
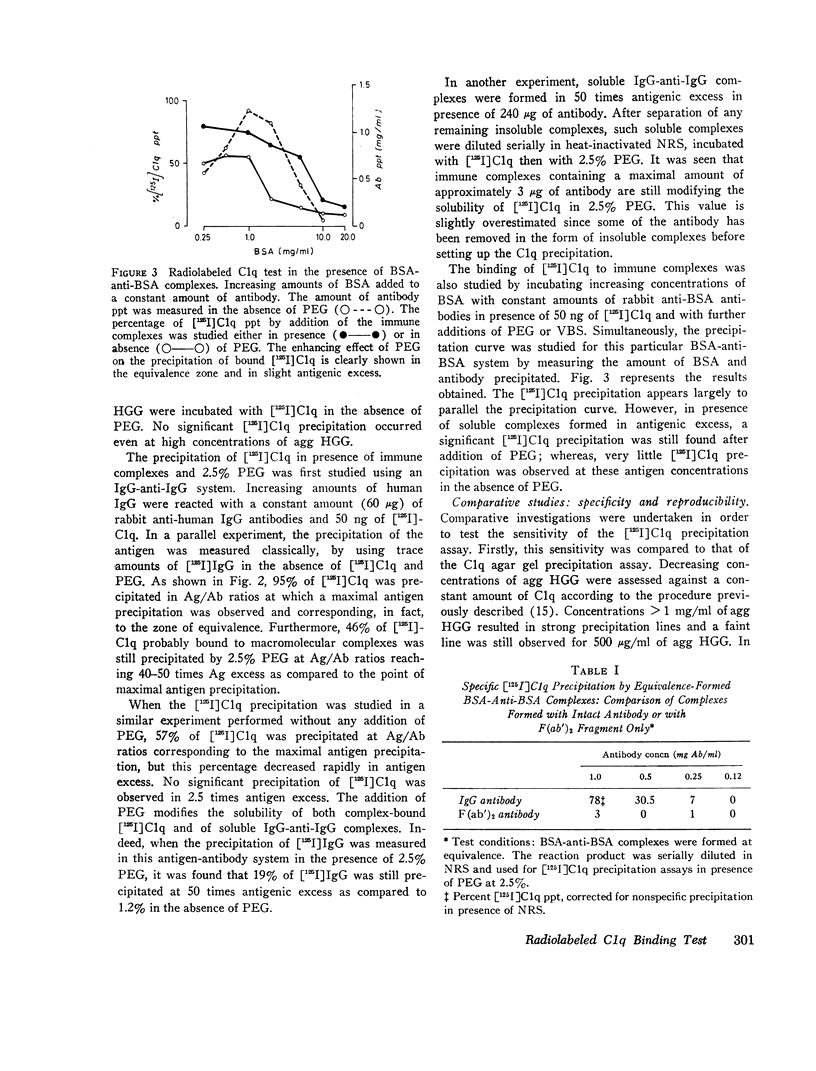
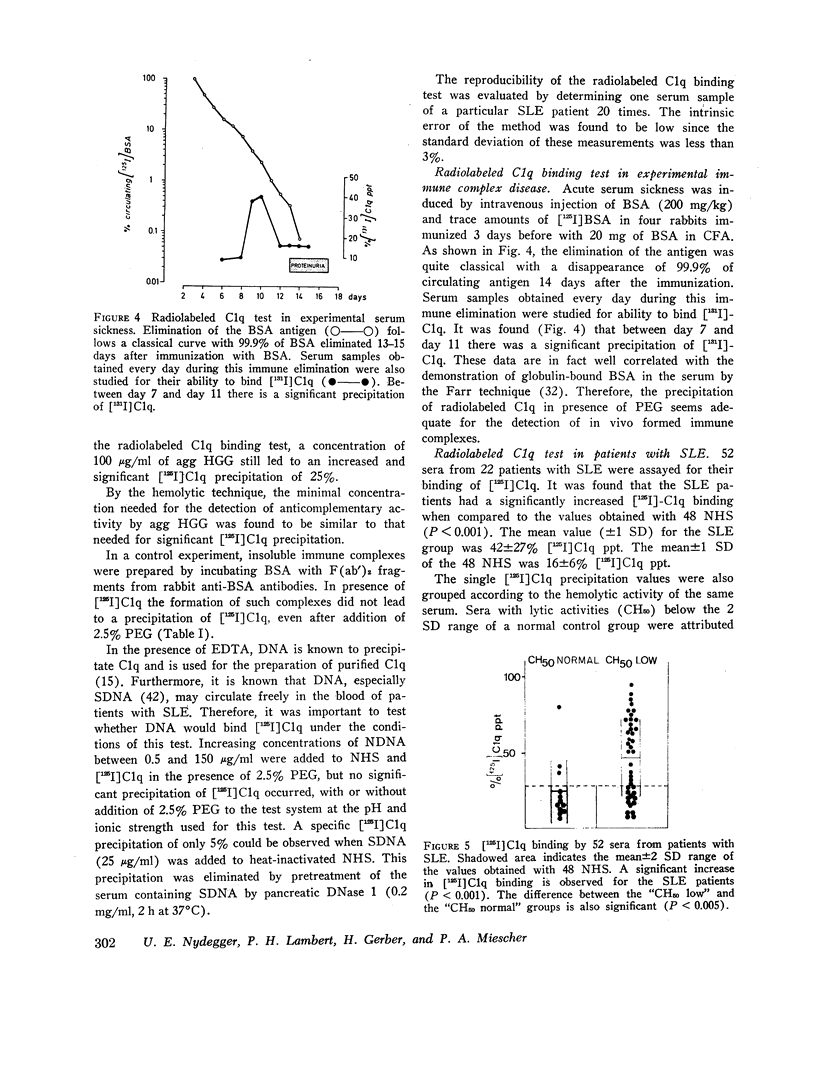






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agnello V., Koffler D., Eisenberg J. W., Winchester R. J., Kundel H. G. C1g precipitins in the sera of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and other hypocomplementemic states: characterization of high and low molecular weight types. J Exp Med. 1971 Sep 1;134(3 Pt 2):228s–241s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agnello V., Winchester R. J., Kunkel H. G. Precipitin reactions of the C1q component of complement with aggregated gamma-globulin and immune complexes in gel diffusion. Immunology. 1970 Dec;19(6):909–919. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almeida J. D., Waterson A. P. Immune complexes in hepatitis. Lancet. 1969 Nov 8;2(7628):983–986. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)90540-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alper C. A., Rosen F. S. Alper CA, Rosen FS: Studies of the in vivo behavior of human C'3 in normal subjects and patients. J Clin Invest. 1967 Dec;46(12):2021–2034. doi: 10.1172/JCI105691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brzosko W. J., Madaliński K., Krawczyński K., Nowoslawski A. Duality of hepatitis B antigen and its antibody. I. Immunofluorescence studies. J Infect Dis. 1973 Apr;127(4):424–428. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.4.424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creighton W. D., Lambert P. H., Miescher P. A. Detection of antibodies and soluble antigen-antibody complexes by precipitation with polyethylene glycol. J Immunol. 1973 Oct;111(4):1219–1227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON F. J., FELDMAN J. D., VAZQUEZ J. J. Experimental glomerulonephritis. The pathogenesis of a laboratory model resembling the spectrum of human glomerulonephritis. J Exp Med. 1961 May 1;113:899–920. doi: 10.1084/jem.113.5.899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON F. J. THE ROLE OF ANTIGEN-ANTIBODY COMPLEXES IN DISEASE. Harvey Lect. 1963;58:21–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDELMAN G. M., KUNKEL H. G., FRANKLIN E. C. Interaction of the rheumatoid factor with antigen-antibody complexes and aggregated gamma globulin. J Exp Med. 1958 Jul 1;108(1):105–120. doi: 10.1084/jem.108.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARR R. S. A quantitative immunochemical measure of the primary interaction between I BSA and antibody. J Infect Dis. 1958 Nov-Dec;103(3):239–262. doi: 10.1093/infdis/103.3.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREEDMAN P., MARKOWITZ A. S. Gamma globulin and complement in the diseased kidney. J Clin Invest. 1962 Feb;41:328–334. doi: 10.1172/JCI104486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gocke D. J., Hsu K., Morgan C., Bombardieri S., Lockshin M., Christian C. L. Vasculitis in association with Australia antigen. J Exp Med. 1971 Sep 1;134(3 Pt 2):330s–336s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg D. M. Diagnosis of infectious hepatitis in general practice. Lancet. 1971 Mar 27;1(7700):641–643. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91567-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrington J. C., Fenton J. W., 2nd, Pert J. H. Polymer-induced precipitation of antigen-antibody complexes: "precipiplex" reactions. Immunochemistry. 1971 May;8(5):413–421. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90504-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellsing K. Immune reactions in polysaccharide media. Investigation on complex-formation between some polysaccharides, albumin and immunoglobulin G. Biochem J. 1969 May;112(4):483–487. doi: 10.1042/bj1120483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heusser C., Boesman M., Nordin J. H., Isliker H. Effect of chemical and enzymatic radioiodination on in vitro human Clq activities. J Immunol. 1973 Mar;110(3):820–828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KISTLER P., NITSCHMANN H. Large scale production of human plasma fractions. Eight years experience with the alcohol fractionation procedure of Nitschmann, Kistler and Lergier. Vox Sang. 1962 Jul-Aug;7:414–424. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1962.tb03274.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNKEL H. G., MULLER-EBERHARD H. J., FUDENBERG H. H., TOMASI T. B. Gamma globulin complexes in rheumatoid arthritis and certain other conditions. J Clin Invest. 1961 Jan;40:117–129. doi: 10.1172/JCI104224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koffler D., Agnello V., Winchester R., Kunkel H. G. The occurrence of single-stranded DNA in the serum of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and other diseases. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jan;52(1):198–204. doi: 10.1172/JCI107165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koffler D., Schur P. H., Kunkel H. G. Immunological studies concerning the nephritis of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Exp Med. 1967 Oct 1;126(4):607–624. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.4.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert P. H., Bricteux N., Salmon J., Miescher P. A. Dynamics of immune complex nephritis during antibody excess. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1973;45(1):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000231026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert P. H., Tribollet E., Knoepfel M., Madalinski K., Miescher P. A. PEG test: a new radioimmunoassay for the detection of hepatitis B antigen. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1974 Jan 26;104(4):128–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MULLER-EBERHARD H. J., KUNKEL H. G. Isolation of a thermolabile serum protein which precipitates gamma-globulin aggregates and participates in immune hemolysis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1961 Feb;106:291–295. doi: 10.3181/00379727-106-26313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michael A. F., Jr, Drummond K. N., Good R. A., Vernier R. L. Acute poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis: immune deposit disease. J Clin Invest. 1966 Feb;45(2):237–248. doi: 10.1172/JCI105336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowbray J. F., Hoffbrand A. V., Holborow E. J., Seah P. P., Fry L. Circulating immune complexes in dermatitis herpetiformis. Lancet. 1973 Feb 24;1(7800):400–402. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)90253-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notkins A. L., Mahar S., Scheele C., Goffman J. Infectious virus-antibody complex in the blood of chronically infected mice. J Exp Med. 1966 Jul 1;124(1):81–97. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.1.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nydegger U. E., Achermann L. M., Lambert P. H., Miescher P. A. A simple automated method for complement estimation in a continuous flow system. J Immunol. 1972 Oct;109(4):910–913. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B., Dixon F. J. Immune complex disease in chronic viral infections. J Exp Med. 1971 Sep 1;134(3 Pt 2):32s–40s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POLSON A., POTGIETER G. M., LARGIER J. F., MEARS G. E., JOUBERT F. J. THE FRACTIONATION OF PROTEIN MIXTURES BY LINEAR POLYMERS OF HIGH MOLECULAR WEIGHT. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Mar 16;82:463–475. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(64)90438-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paronetto F., Koffler D. Immunofluorescent localization of immunoglobulins, complement, and fibrinogen in human diseases. I. Systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1965 Oct;44(10):1657–1664. doi: 10.1172/JCI105272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinicke V., Dybkjaer E., Poulsen H., Banke O., Lylloff K., Nordenfelt E. A study of Australia-antigen-positive blood donors and their recipients, with special reference to liver histology. N Engl J Med. 1972 Apr 20;286(16):867–870. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197204202861604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
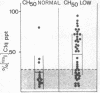
- Rojas-Espinosa O., Mendez-Navarrete I., Estrada-Parra S. Presence of C1q-reactive immune complexes in patients with leprosy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Oct;12(2):215–223. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman N. R., Barker L. F. Virus-like antigen, antibody, and antigen-antibody complexes in hepatitis measured by complement fixation. Science. 1969 Jul 18;165(3890):304–306. doi: 10.1126/science.165.3890.304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiry L., Clinet G., Toussaint C., Vereerstraeten P. The use of complement fixation tests to detect Australia antigen-antibody complexes and antibodies to a Tween antigen. Vox Sang. 1973;24(Suppl):36–43. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1973.tb03511.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winchester R. J., Kunkel H. G., Agnello V. Occurrence of -globulin complexes in serum and joint fluid of rheumatoid arthritis patients: use of monoclonal rheumatoid factors as reagents for their demonstration. J Exp Med. 1971 Sep 1;134(3 Pt 2):286s–295s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wold R. T., Young F. E., Tan E. M., Farr R. S. Deoxyribonucleic acid antibody: a method to detect its primary interaction with deoxyribonucleic acid. Science. 1968 Aug 23;161(3843):806–807. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3843.806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]